World electricity generation since 1900
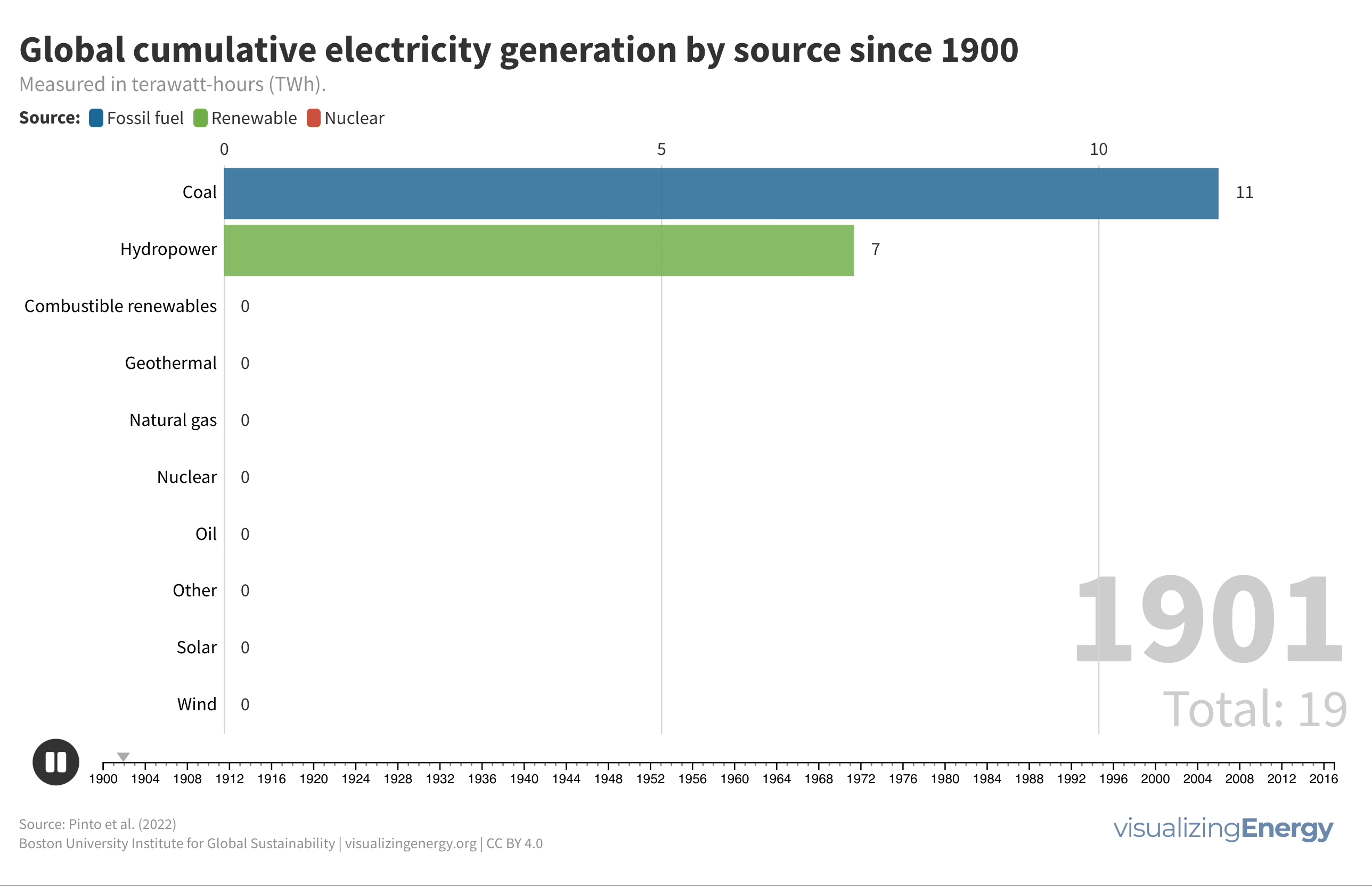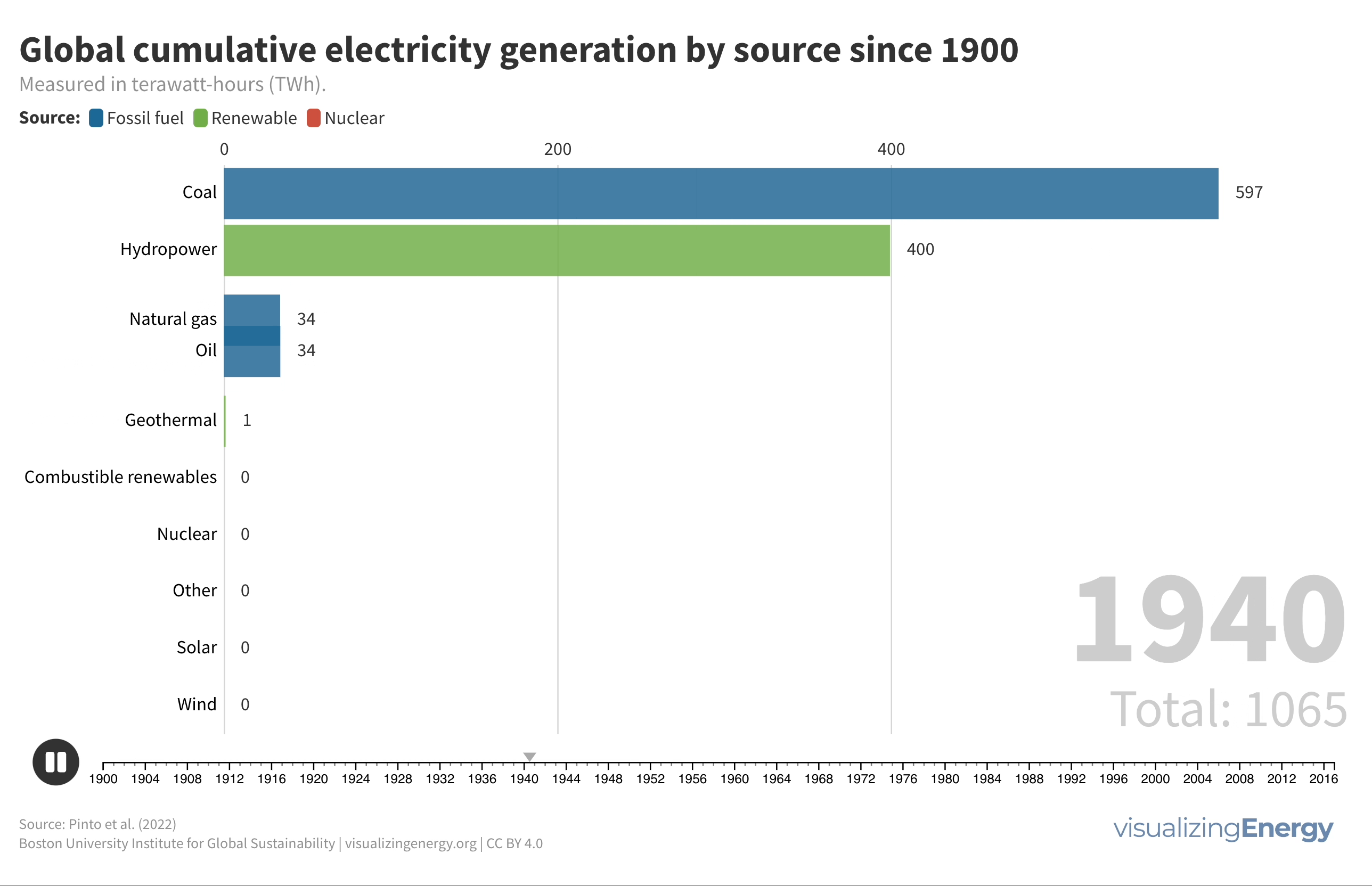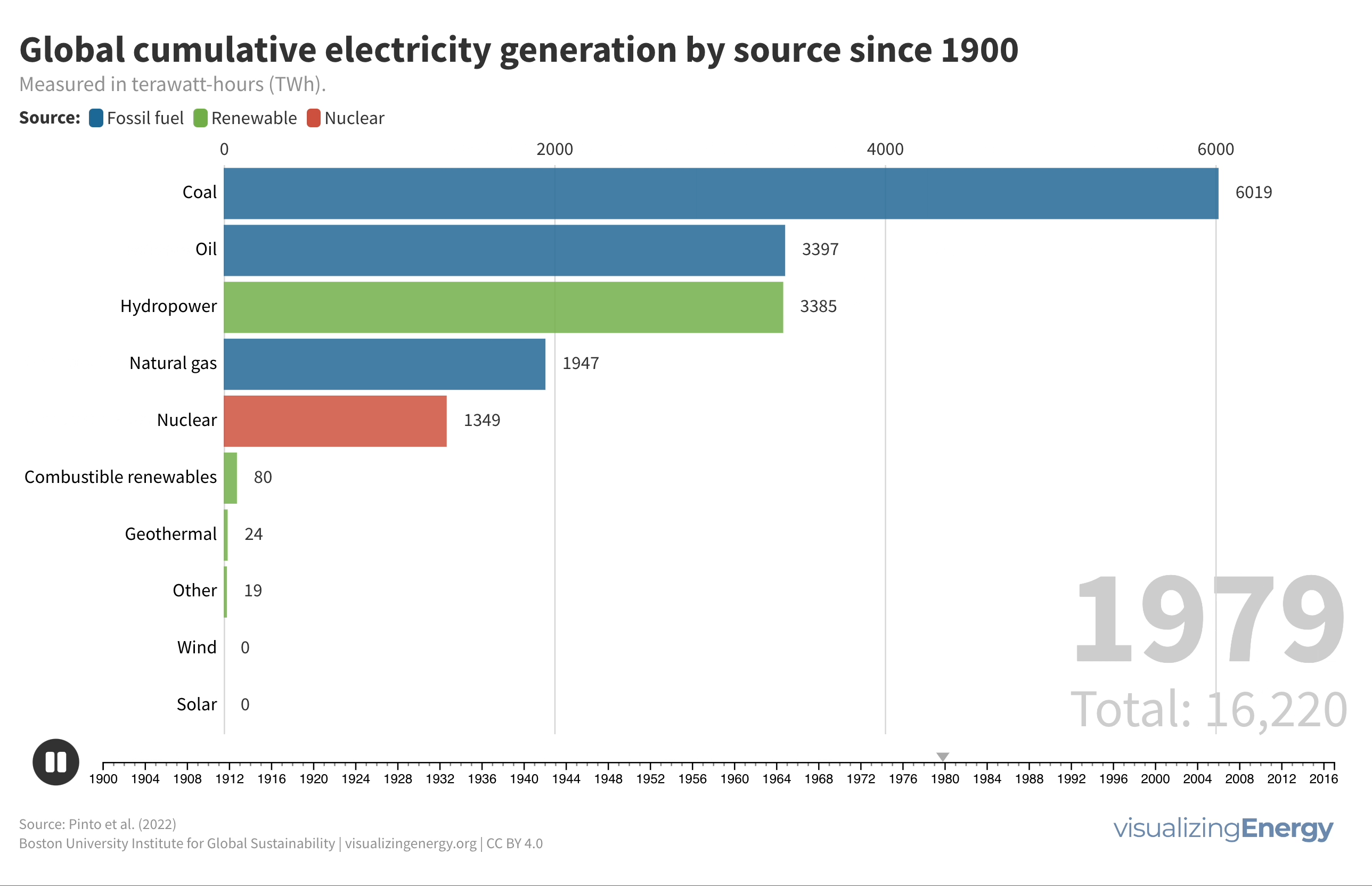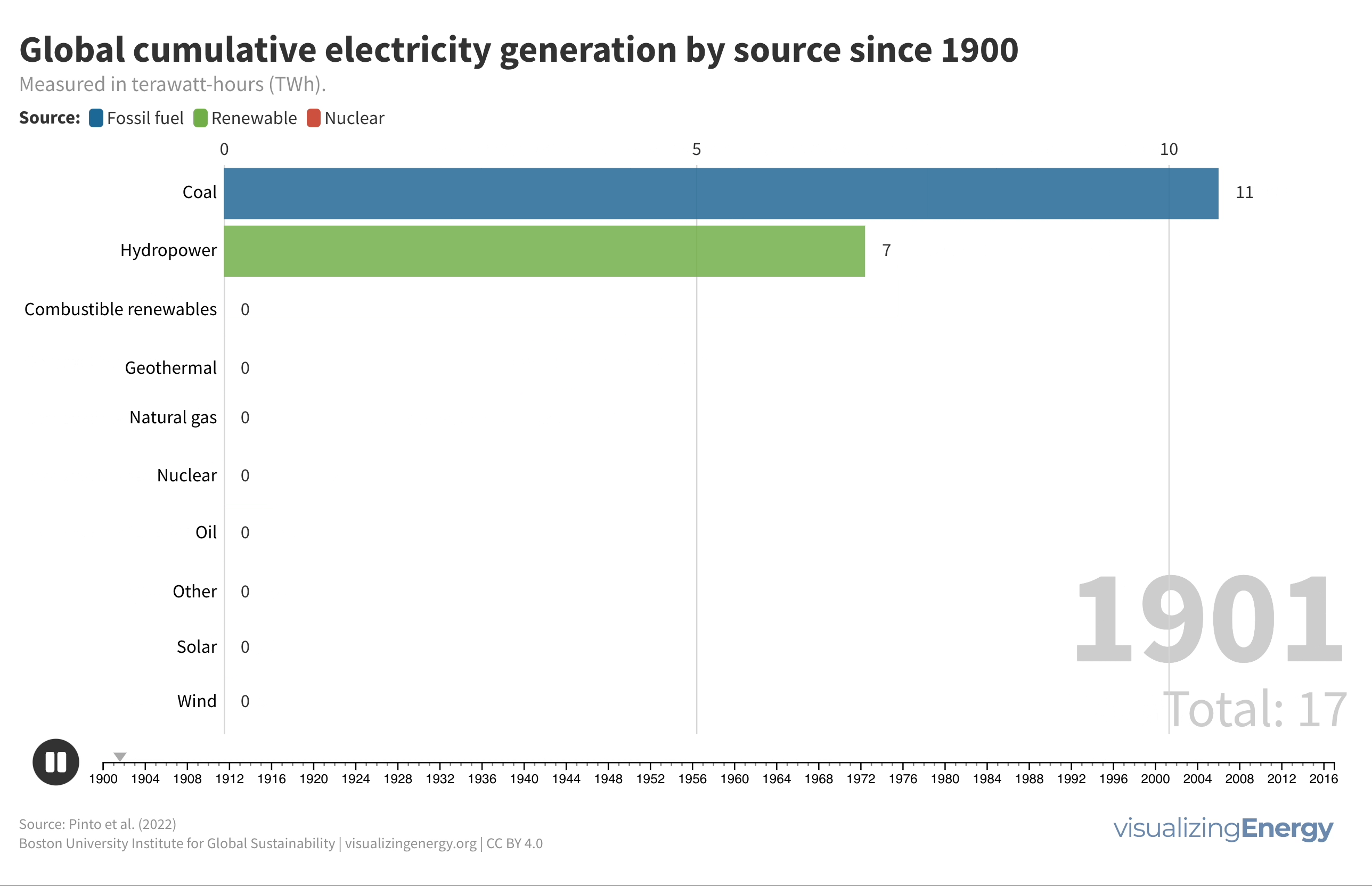
From 1900 to 2022, global electricity generation grew remarkably from 66.4 TWh to 29,165 TWh. Fossil fuels maintained a stable share of around 60% throughout this period, while renewables like wind and solar saw rapid growth from the 2000s. The 1960s saw a rise in oil power plants, but energy price shocks in the 1970s shifted focus to natural gas and nuclear generation, with significant investments in gas power plants from the 2000s onward.
Power plant efficiency since 1900
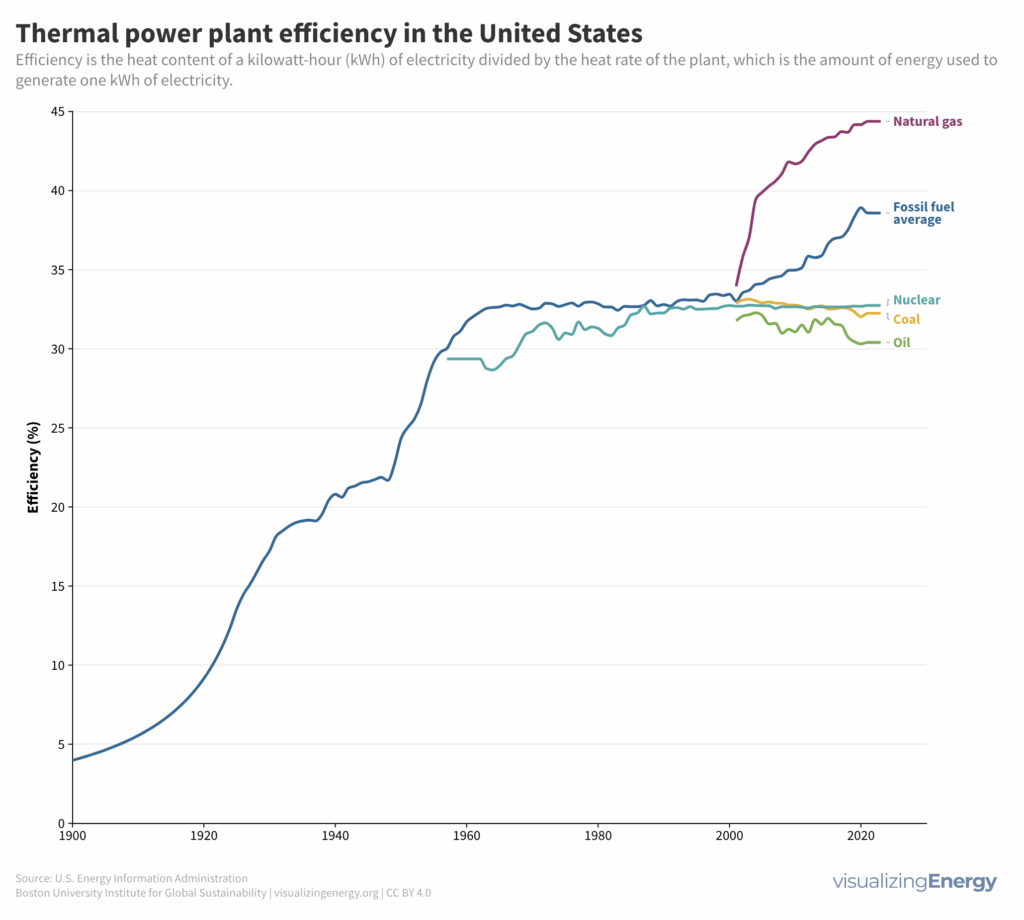
The efficiency of a thermal power plant is the ratio of the electricity output to the energy input, taking into account the heat losses. Over the years, the average efficiency of thermal power plants using fossil fuels in the United States has significantly increased, from 4% in 1900 to 43% in 2023. This improvement is attributed to reducing heat loss in the three main energy conversion processes: fuel combustion, steam generation, and electricity generation.
Two centuries of declining prices for personal transportation in the United Kingdom
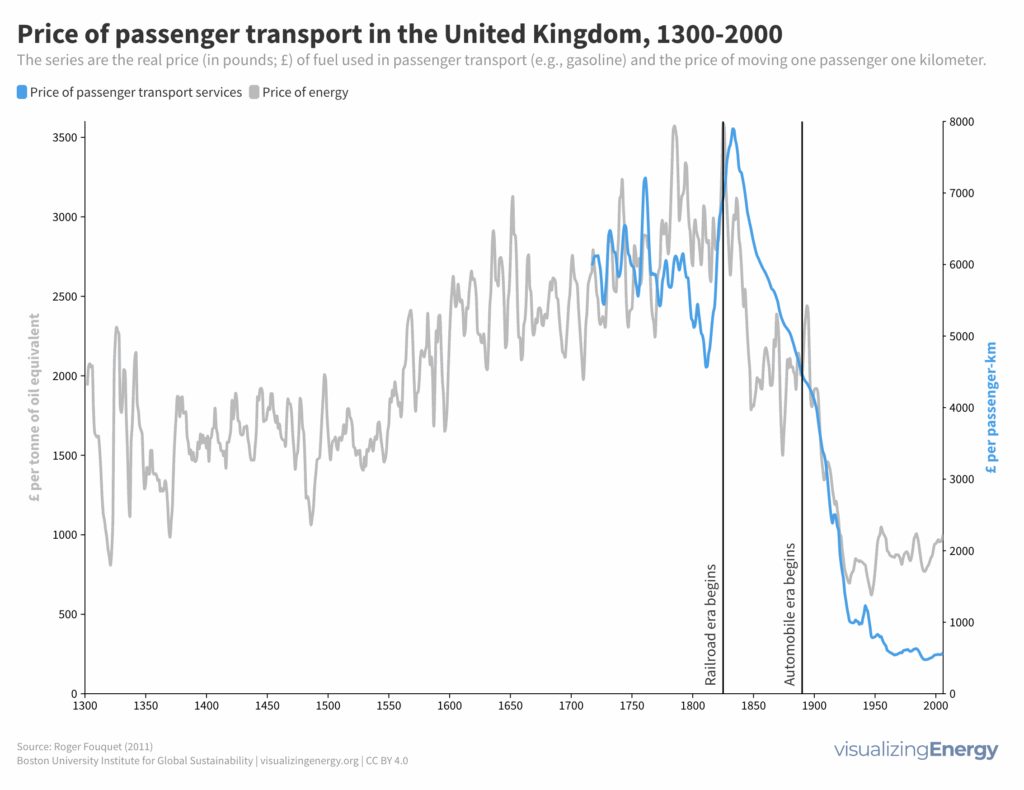
Access to personal mobility has played a crucial role in people’s life satisfaction, with personal vehicles revolutionizing daily life since the early 1900s. The number of global car registrations has dramatically increased over the years, reaching 1.1 billion in 2019. The energy historian Roger Fouquet explored the impact of personal transportation services in the United Kingdom from the 14th to the 20th century, revealing the economic, social, and environmental changes brought about by the expansion of personal travel.
How the price of lighting decreased 12,000-fold in the United Kingdom
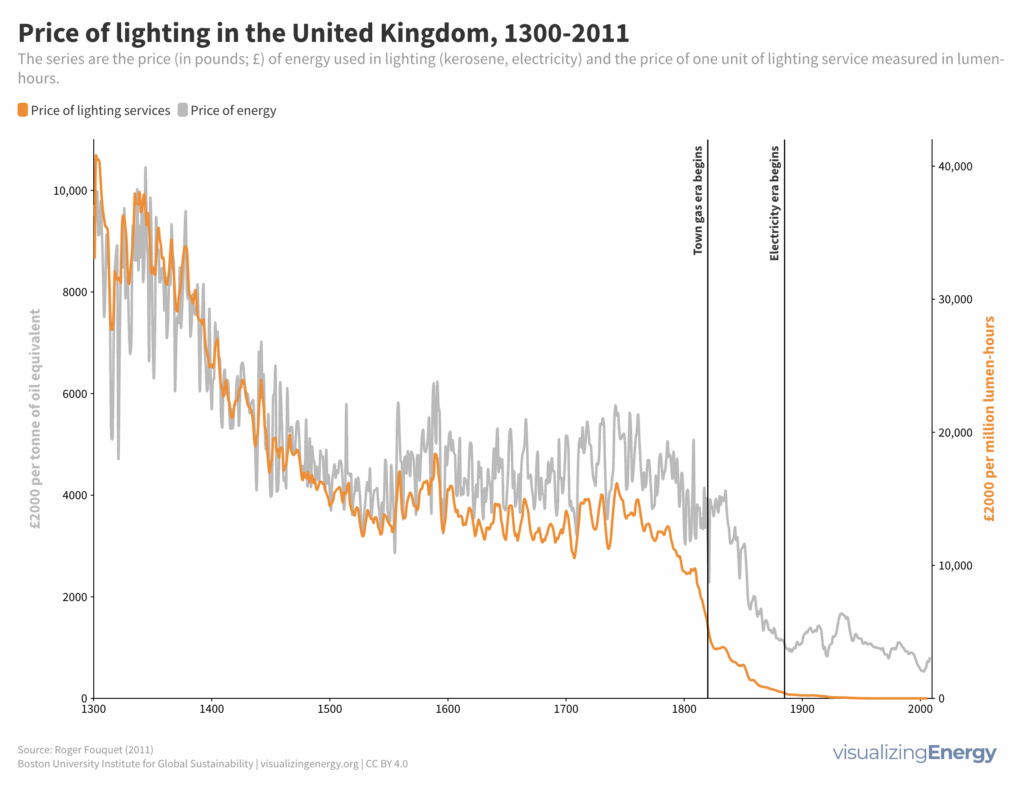
The transition from traditional lighting methods to modern illumination in the United Kingdom has had significant social, economic, and environmental consequences. Historically, lighting services relied on candles made from animal fat, but the 19th century saw the introduction of new fuels such as town gas, kerosene, and eventually electricity.
Does more energy use lead to greater life satisfaction?
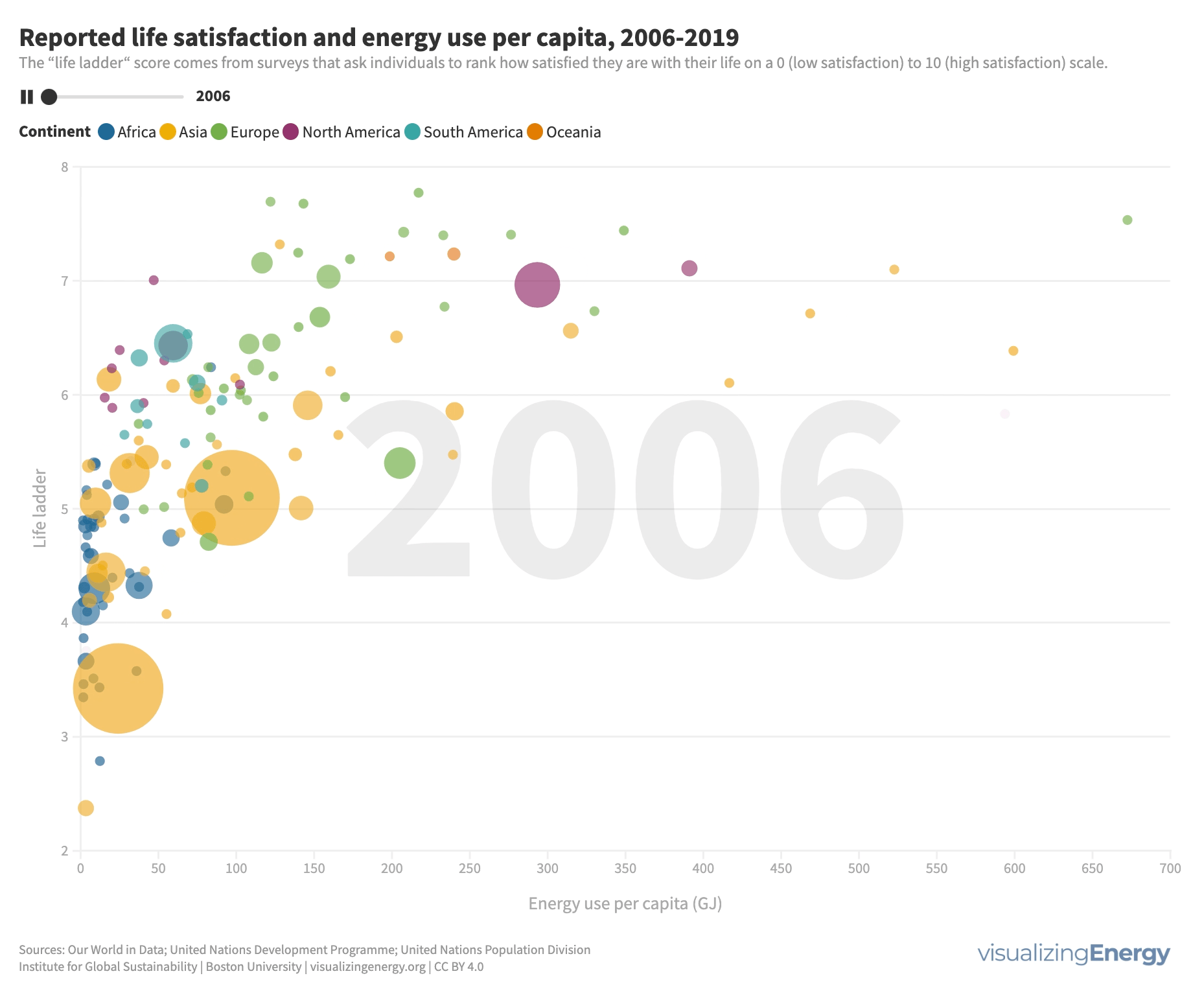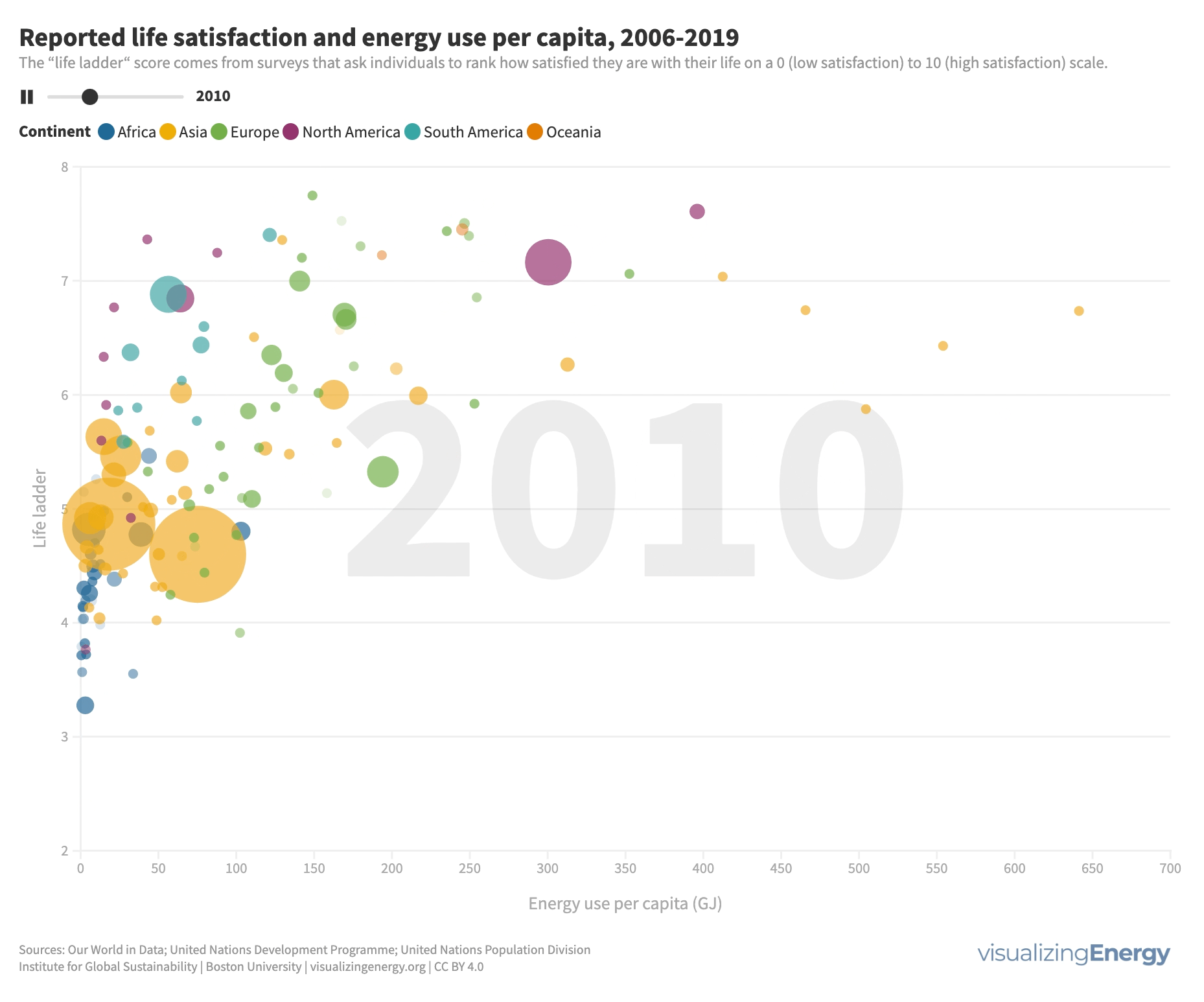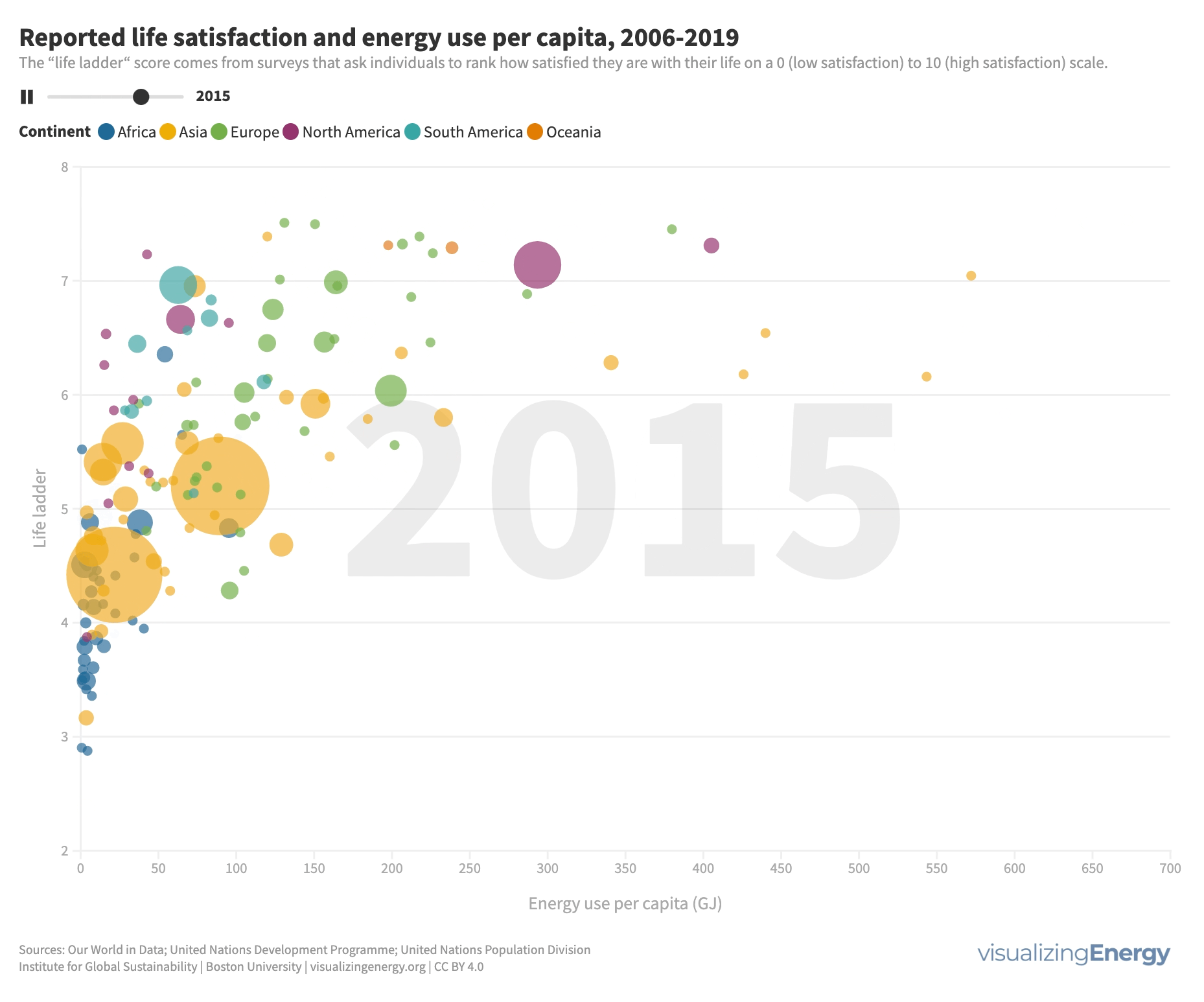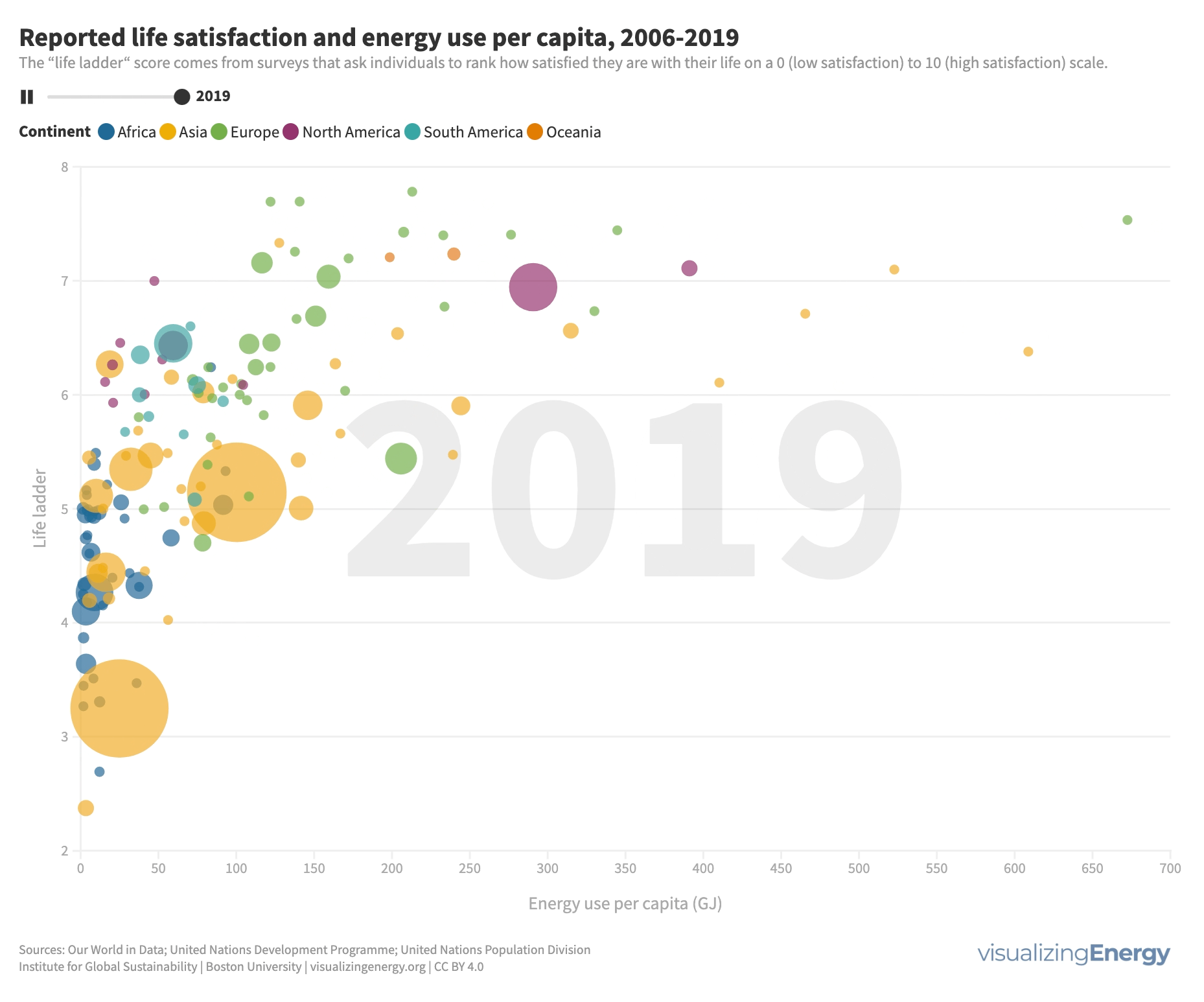
While higher incomes generally lead to greater life satisfaction, it’s not a guarantee. People in countries with high life satisfaction tend to use more energy, which can enhance comfort and mobility. Modest increases in energy use can significantly improve life satisfaction, but there are diminishing returns at higher levels.
Maximum efficiencies of engines and turbines, 1700-2000
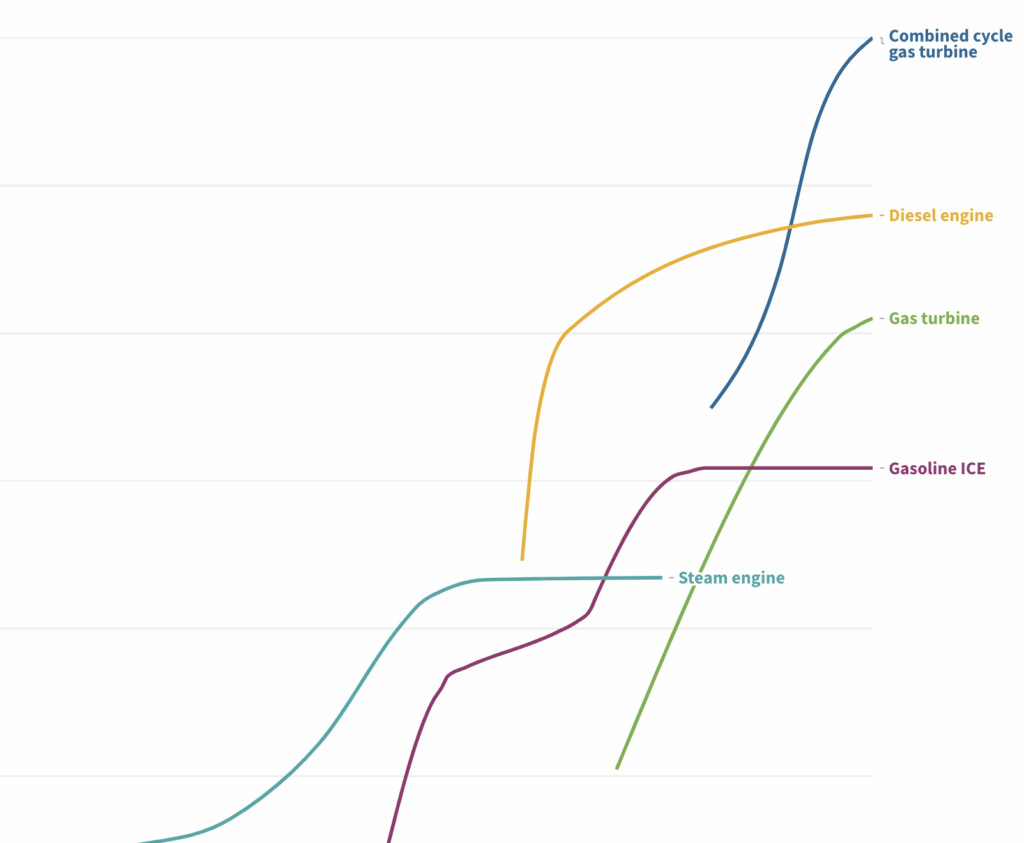
Throughout human history, the development of new machines to replace and enhance human and animal labor has played a major role in the energy sector. Key advancements include combustion engines and turbines, which convert fuels like gasoline and natural gas into useful work.
Health impacts from oil and gas production in the United States
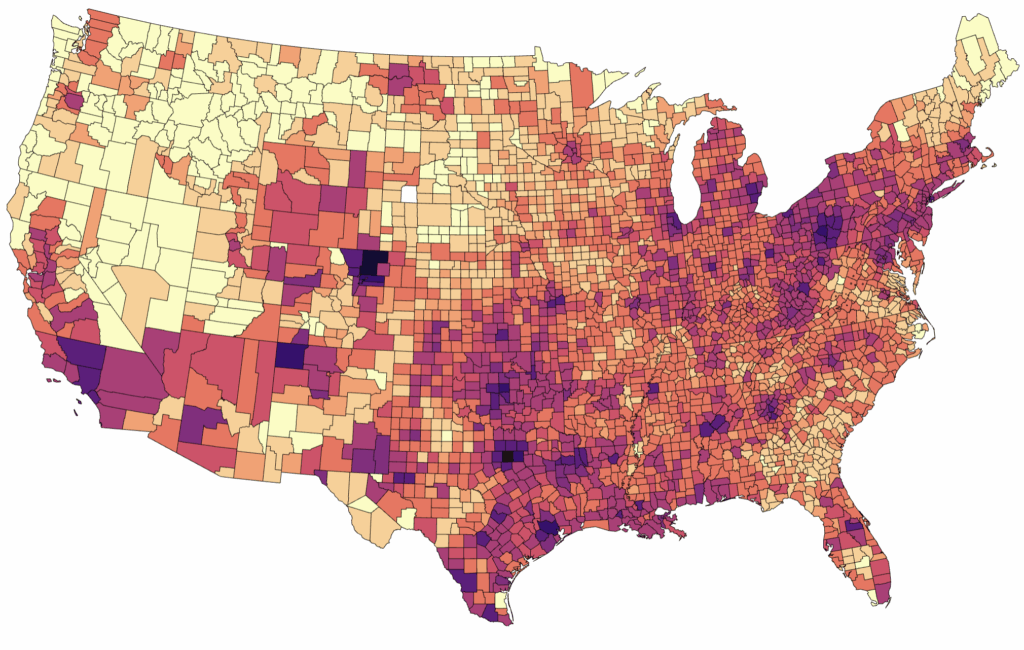
Oil and gas activities contribute to significant air pollution, resulting in adverse health effects and economic costs. Emissions from drilling, production, and transportation release pollutants that are linked to asthma, heart attacks, and premature deaths, especially impacting vulnerable populations. Addressing these emissions is crucial for protecting public health, mitigating economic burdens, and implementing comprehensive policies to reduce air pollution from the oil and gas industry.
How the power of machines transformed the world
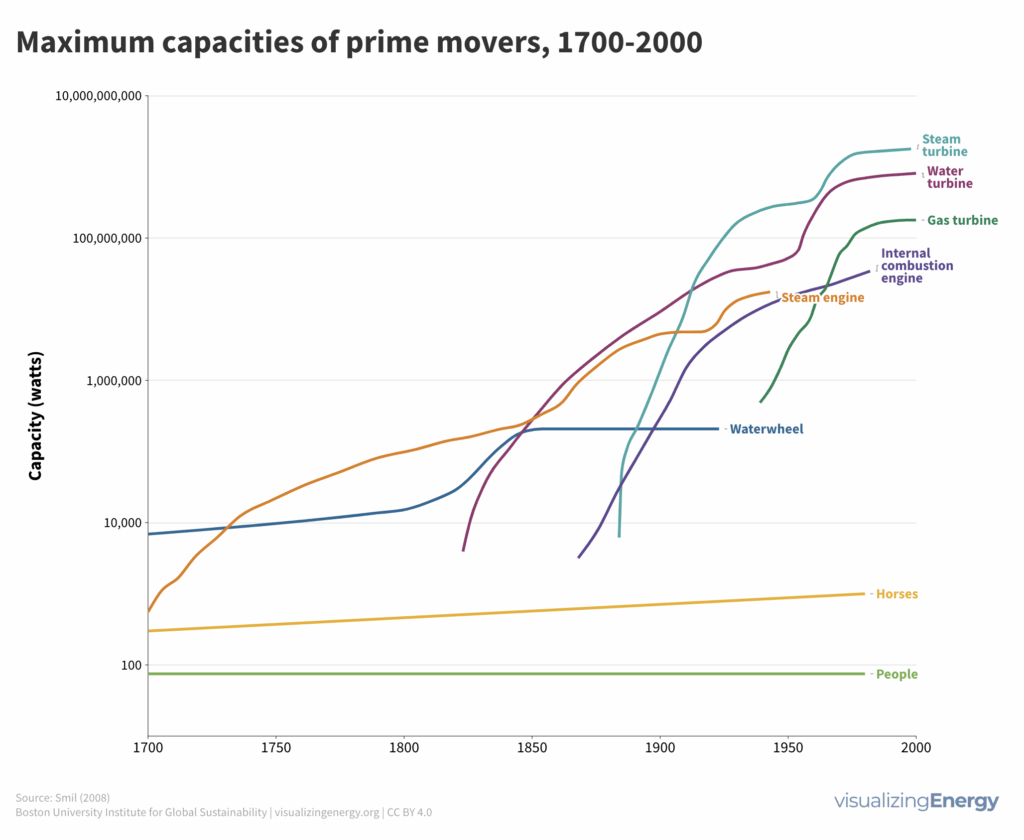
Throughout history, humans relied on their own muscles and later utilized draft animals and machines to perform physical tasks. The transformative impact of waterwheels, windmills, and the steam engine marked significant milestones in human energy history. Now, the transition to clean energy is crucial to mitigate the environmental impact and shape a sustainable future.
Who are the major LNG importers and exporters?
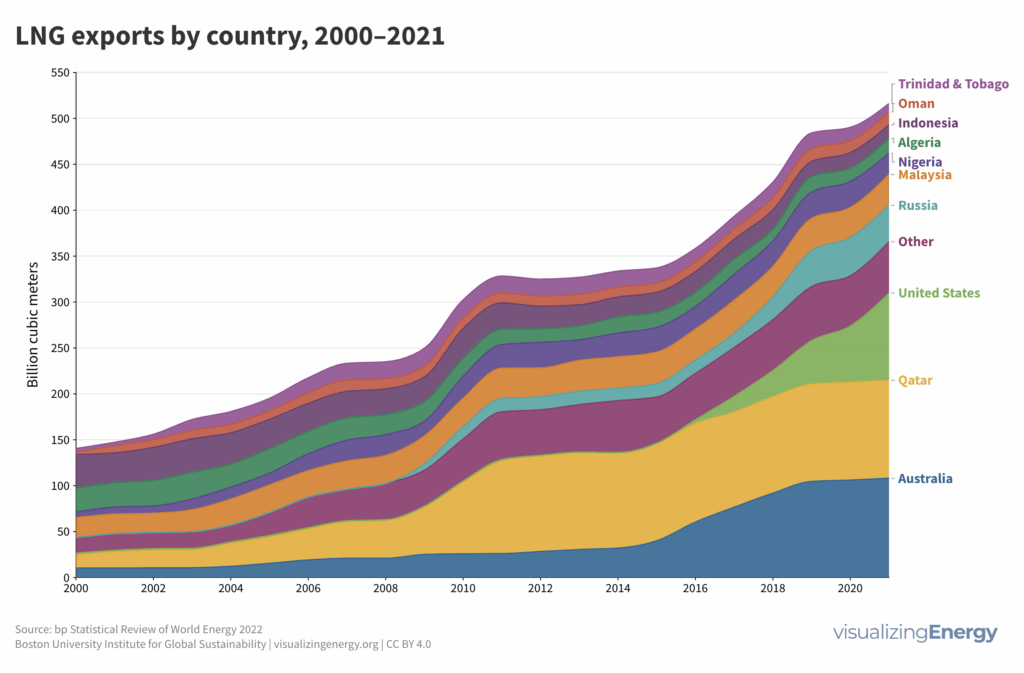
Global natural gas consumption has risen 70% from 2000 to 2022, fueled by economic growth and coal-to-gas transition. Hydraulic fracturing in the US has played a major role. Liquefied natural gas (LNG) enables long-distance shipping, but presents climate and energy justice challenges.
Bitcoin’s energy and carbon footprint
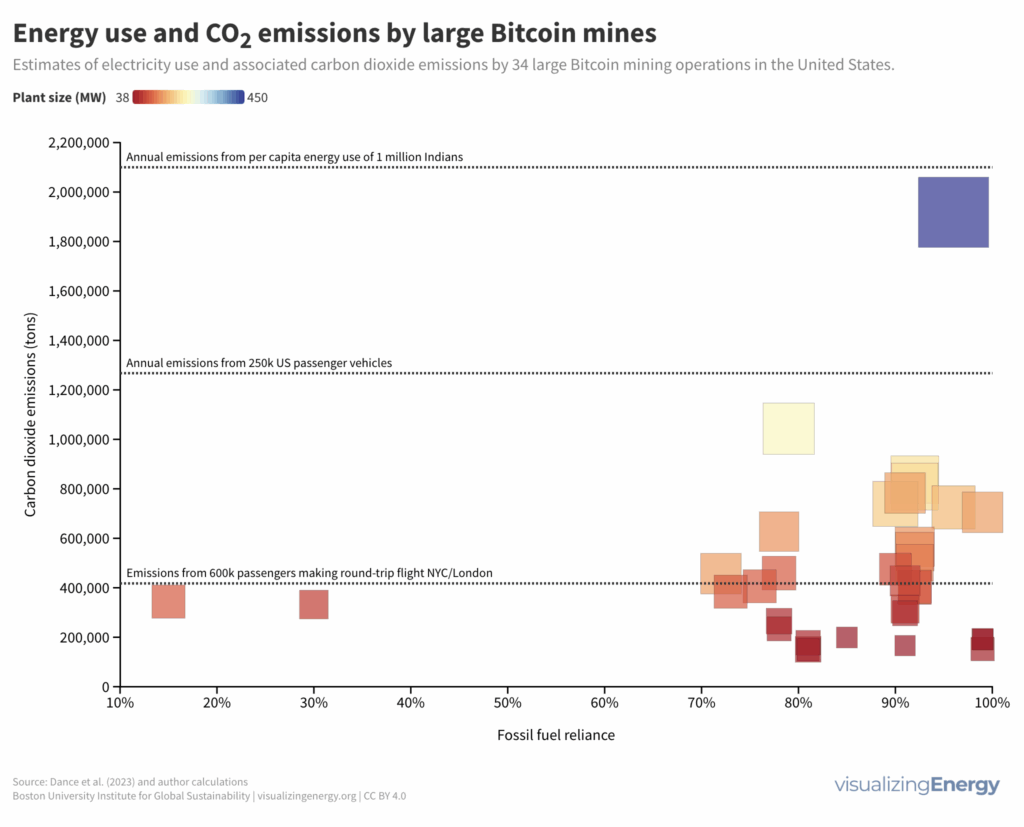
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin rely on blockchain technology and crypto mining, which consume massive amounts of electricity and have significant carbon footprints. The lack of transparency and regulation in the industry raises concerns about the economic, social, and environmental costs associated with crypto mines.
