Where are people dying due to indoor air pollution from cooking fuels?
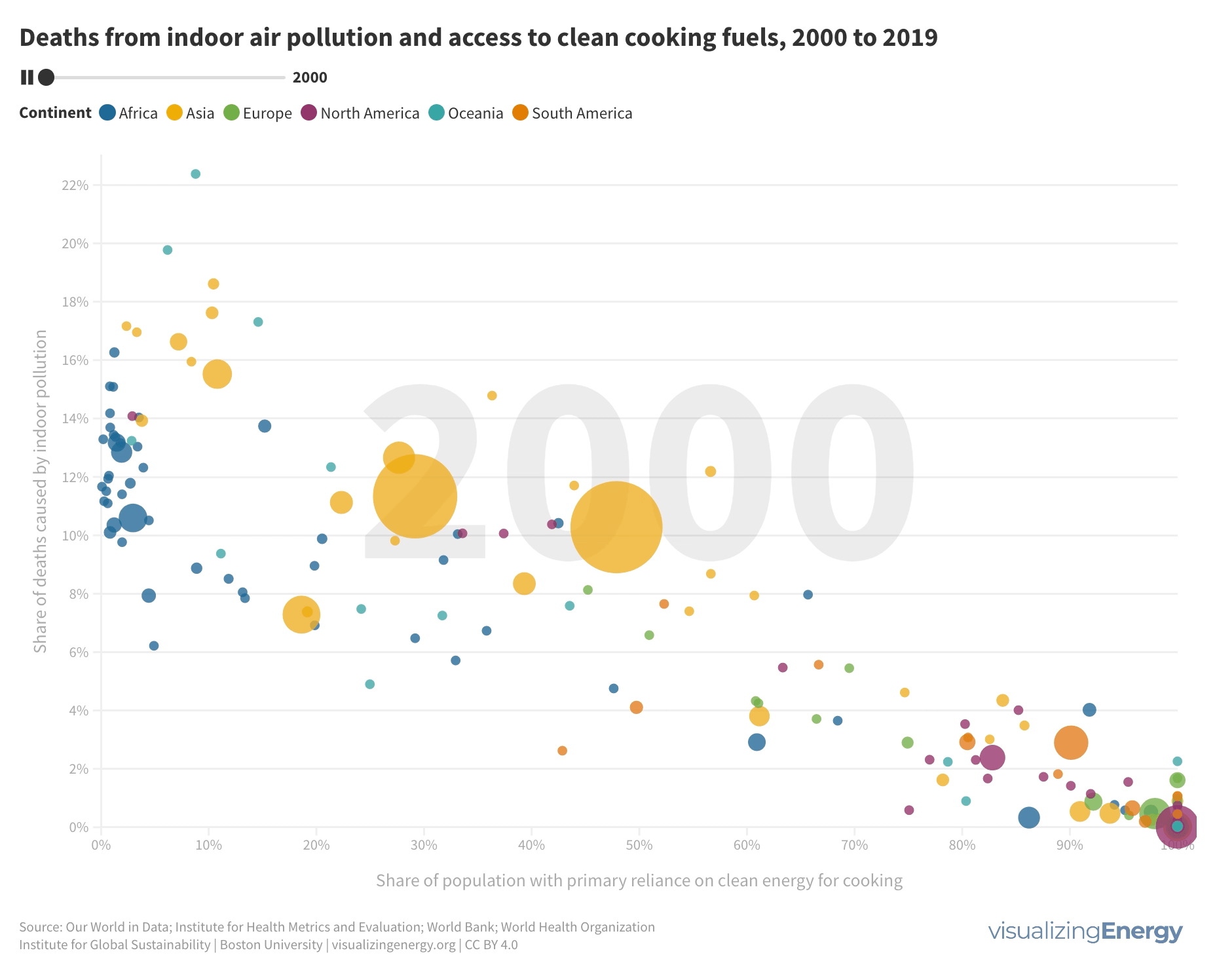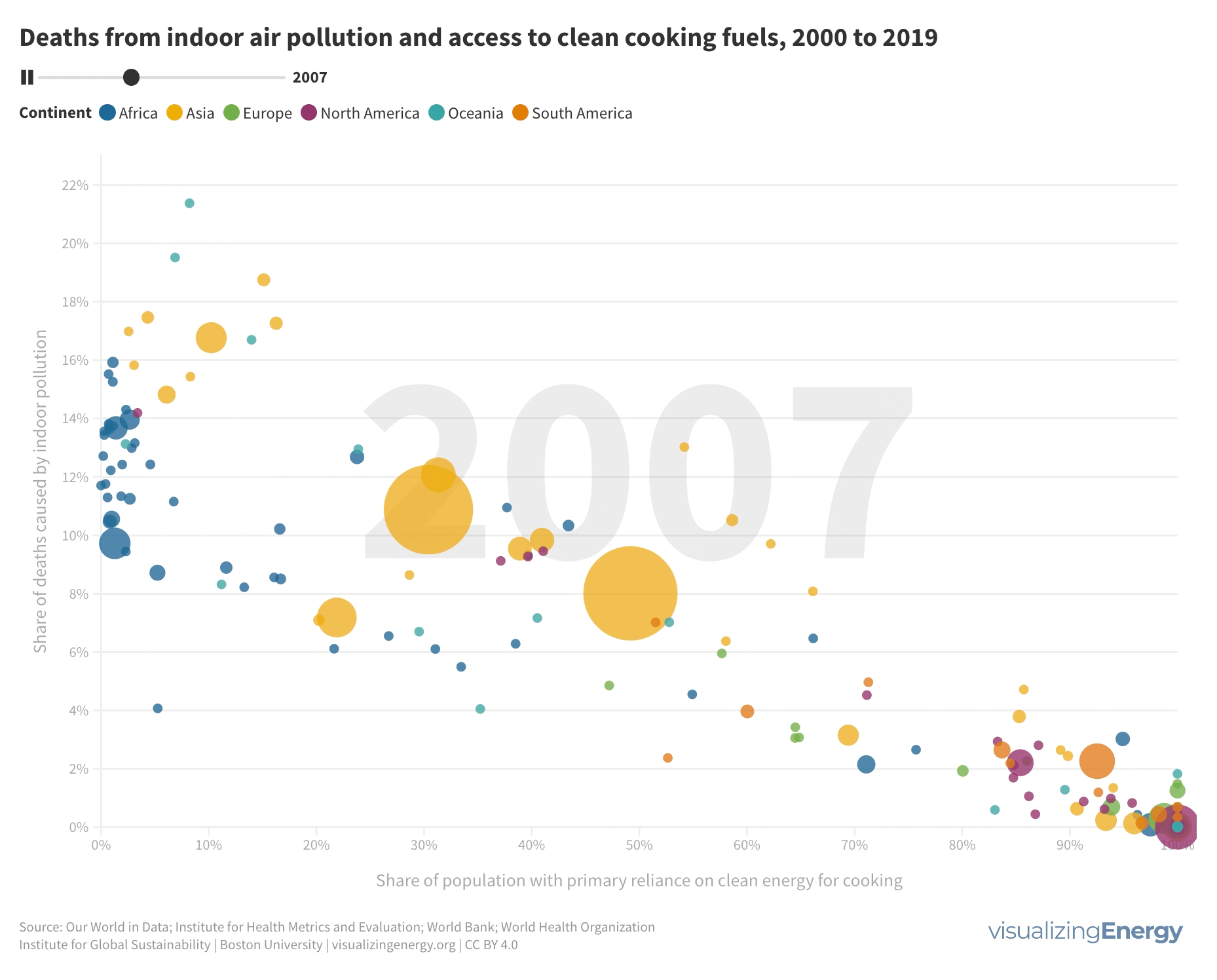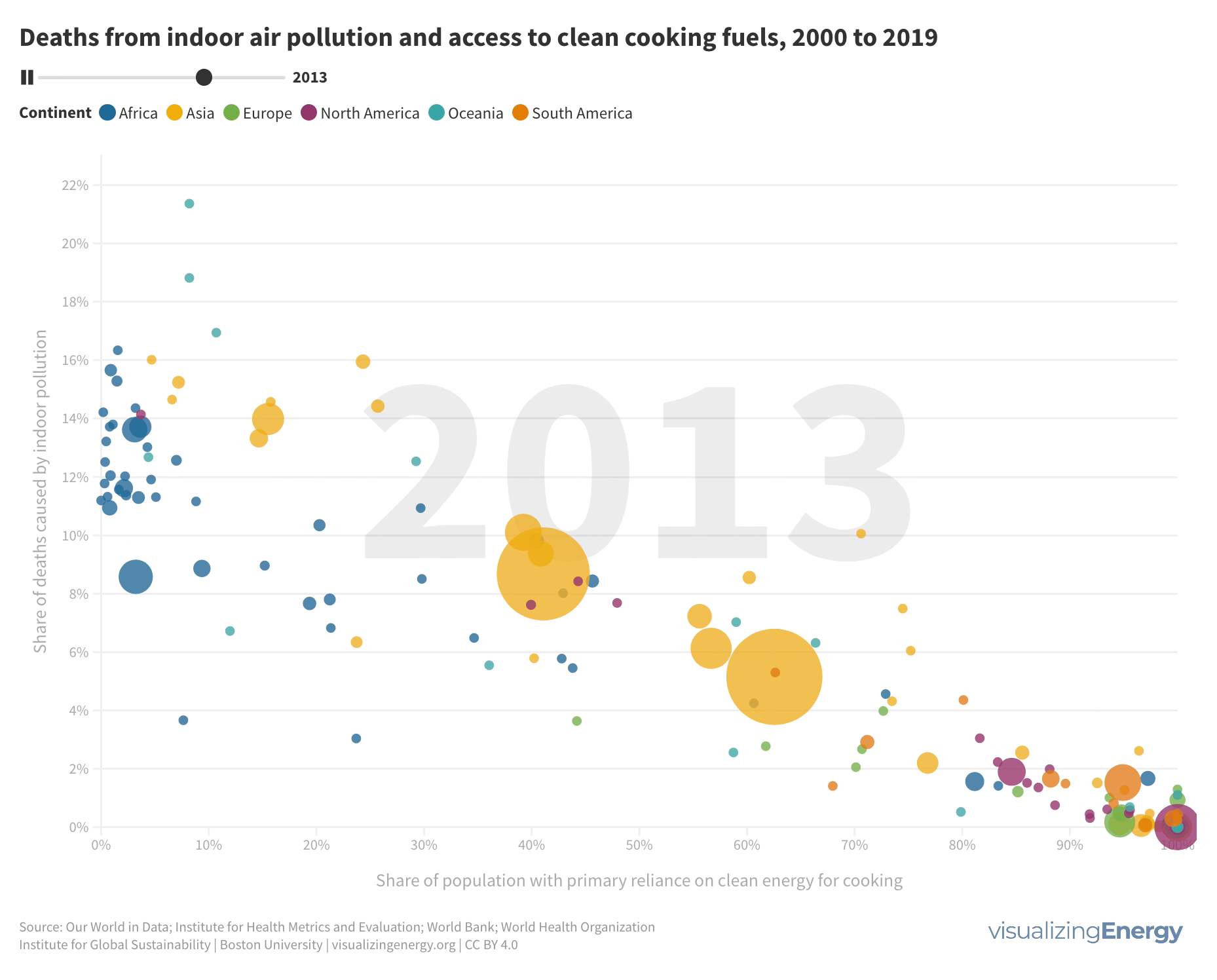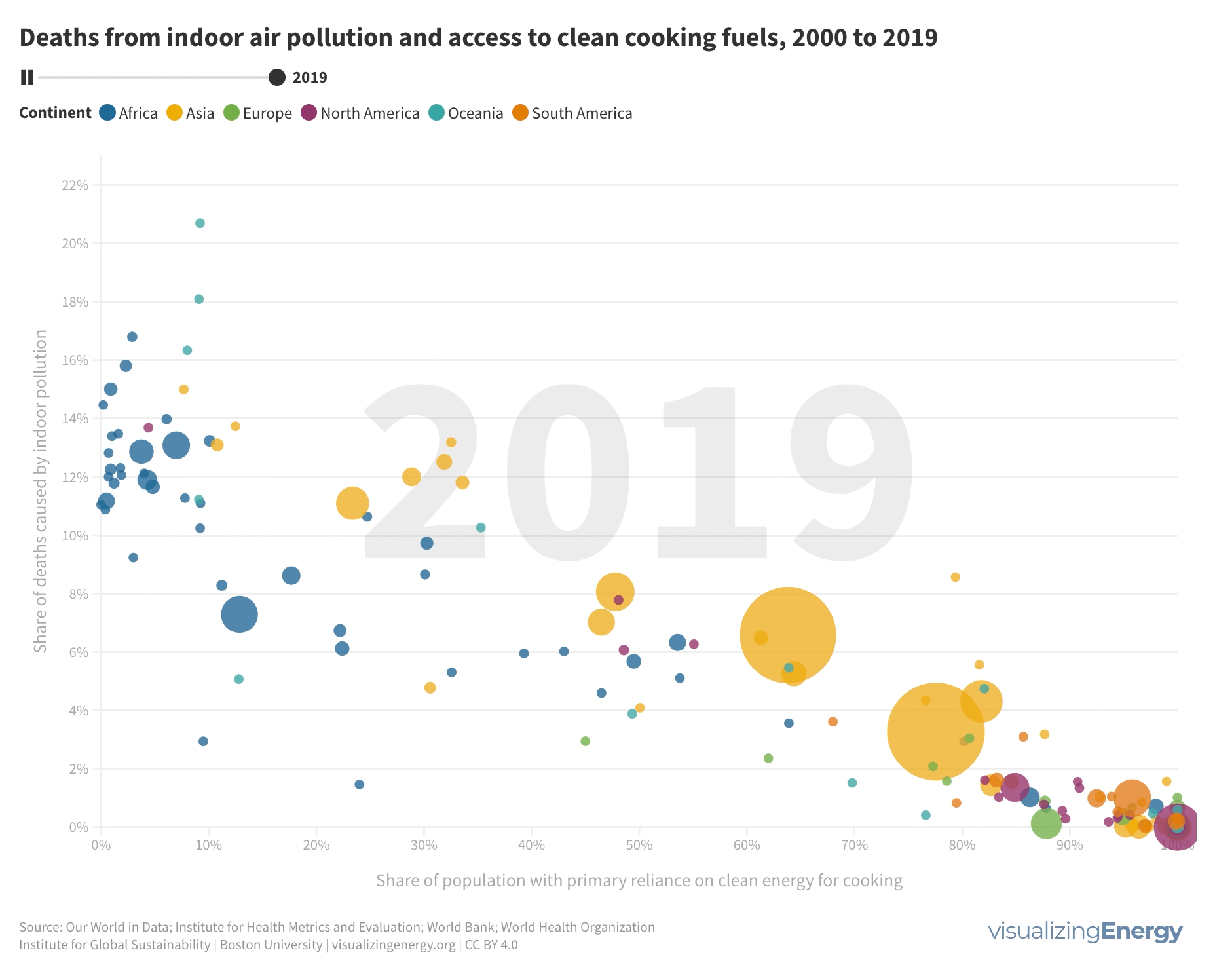
Millions of people die each year due to indoor air pollution caused by the combustion of solid fuels and kerosene in inefficient stoves. Heart disease, stroke, COPD, lung cancer, and other illnesses are major contributors to these deaths. Access to clean cooking fuels is closely linked to lower death rates, with countries having universal access showing the lowest rates.
Will the Inflation Reduction Act enable the United States to meet its climate targets?
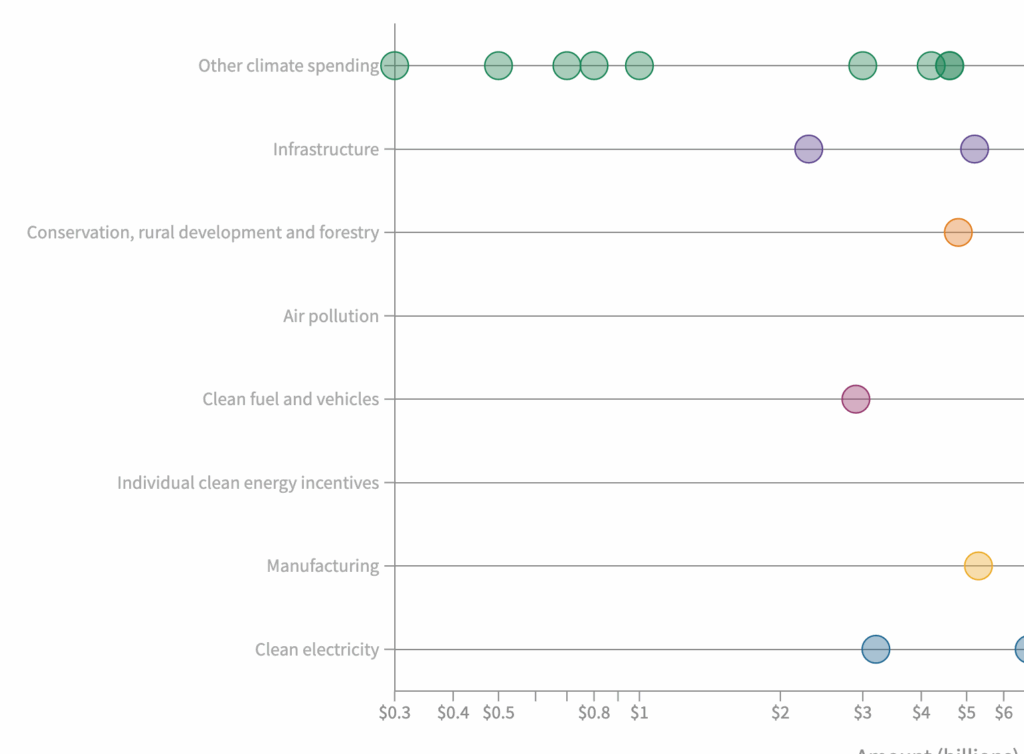
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) is the largest-ever federal program focused on energy and the environment, allocating $369 billion over a decade. With a laser focus on climate change, the IRA aims to cut greenhouse gas emissions, promote clean energy, and enhance climate resilience. Its provisions have the potential to create jobs, lower electricity costs, and significantly contribute to meeting the US climate targets.
Is Boston on track to be carbon-neutral by 2050?
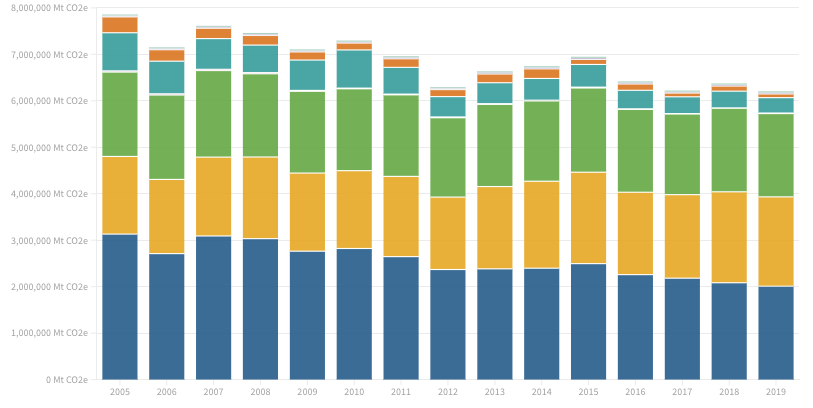
Boston strives for carbon neutrality by 2050, but faces hurdles with its reliance on fossil fuels. Buildings contribute most to emissions, driven by electricity and natural gas. Decarbonizing the grid and eliminating natural gas are vital for success. While progress has been made, meeting targets remains uncertain. Priorities include electrifying buildings, local energy planning, coastal resilience, and climate justice.
Who has a high energy burden in the United States?
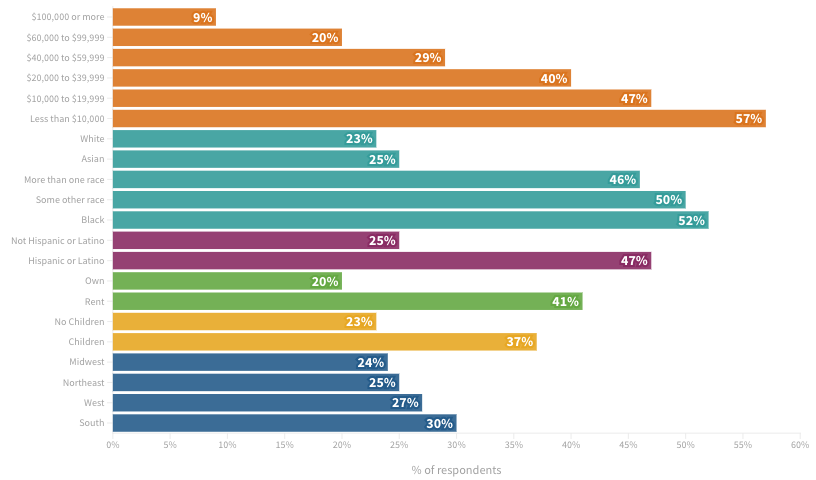
Many US households, particularly low-income, minority, and renting households, face a high energy burden, spending a significant portion of their income on fuel and electricity. In 2020, 27% of households reported difficulty paying energy bills. Federal programs provide some relief, but addressing the underlying causes of social inequity is crucial for long-term energy security.
Does more energy use raise incomes?
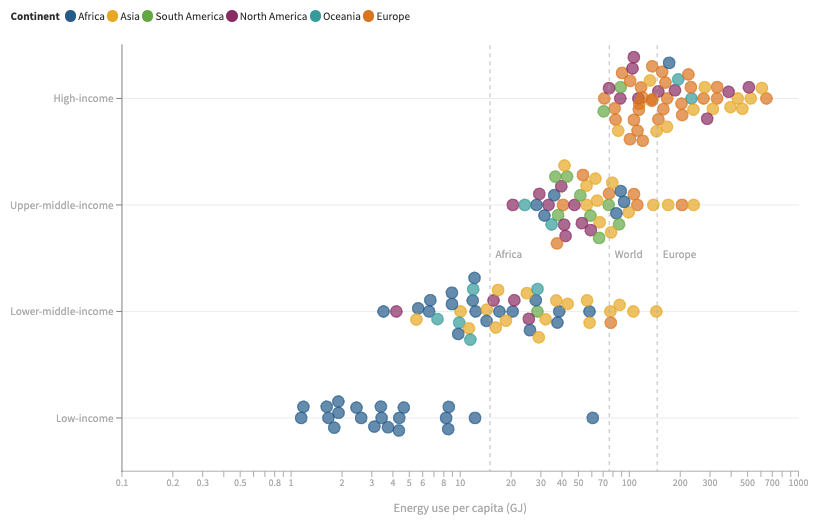
While moving up the income ladder is generally accompanied by increased energy use, there are significant variations within income groups. Factors such as the economy’s structure, geography, climate, lifestyle, public policy, and consumer attitudes also influence how effectively energy use translates into income.
Can global poverty be eliminated with more energy use?
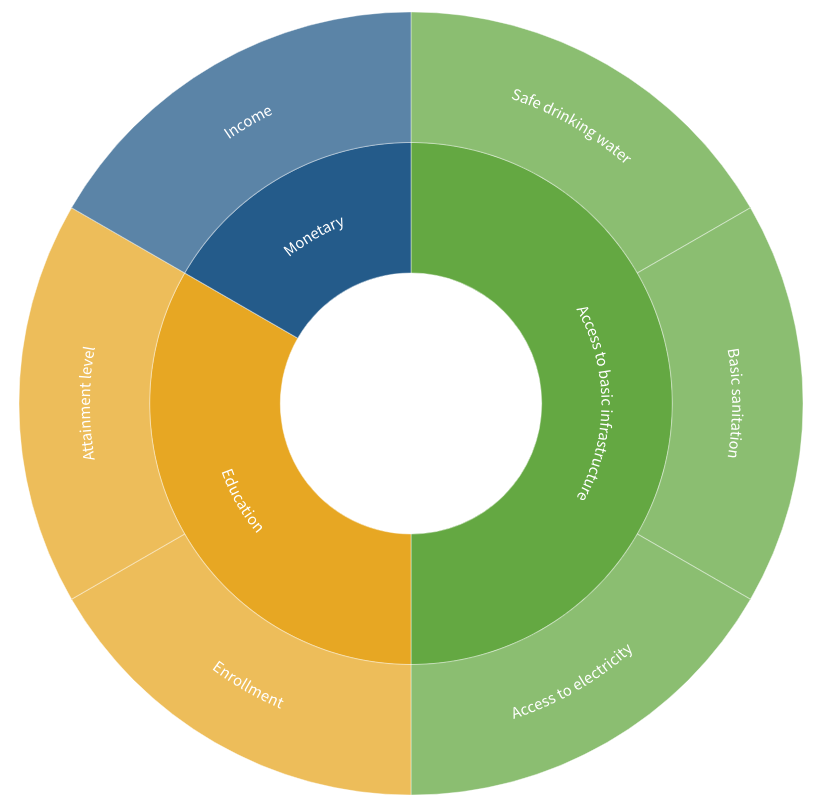
Increased energy use per capita is linked to decreased poverty rates. Modest energy increases can lead to significant poverty reduction, but the relationship is not always linear. Factors like governance and social policies also influence poverty levels. Beyond a certain threshold, further energy increases have diminishing returns.
Is the United States government doing enough to reduce energy poverty?
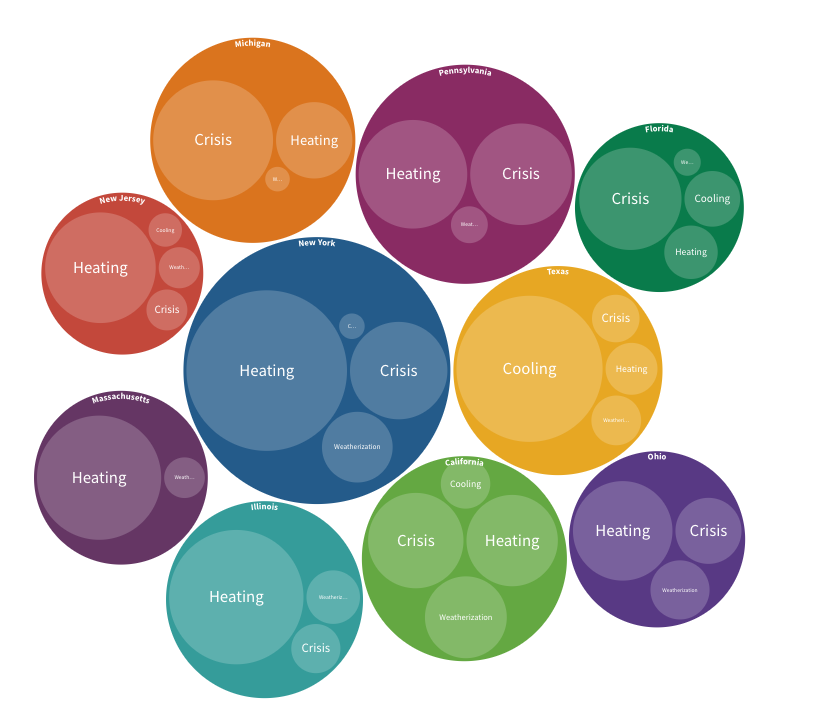
Energy poverty is a significant concern in the United States, with over one in four households experiencing insecurity. Government programs like LIHEAP and WAP aim to address this issue, but funding levels often fall short of the need. A more comprehensive approach is necessary, considering the impact on well-being and addressing racial and socioeconomic disparities.
