Fuel energy density: What is it and why is it important?
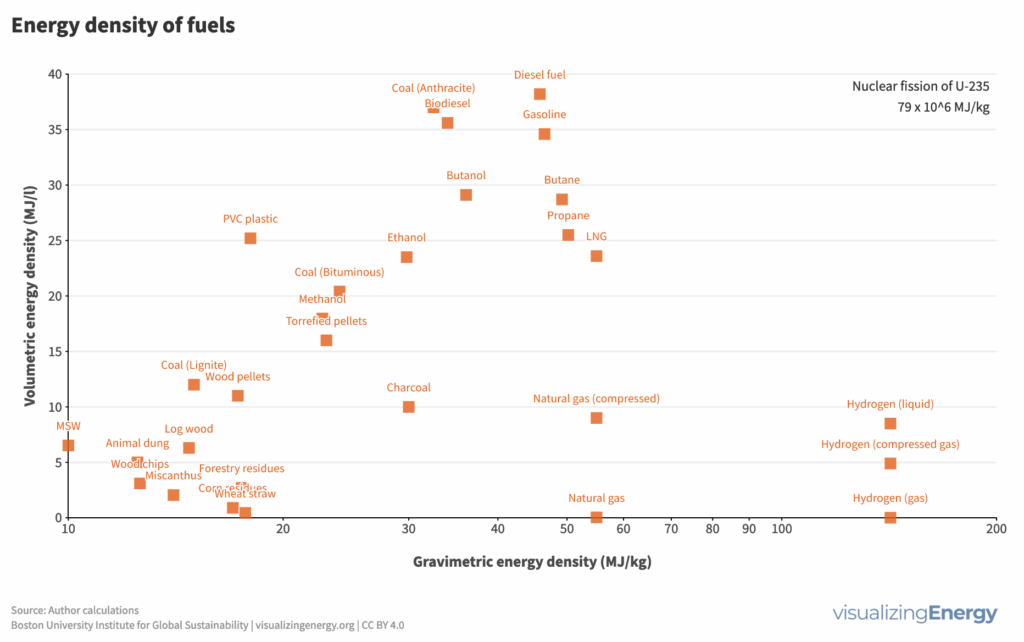
Fuels like wood, diesel, and natural gas have shaped human energy history, driven by technological, economic, and environmental forces. Liquid fuels from oil, with their high mass and volumetric energy density, led to their supremacy in transportation. Shifts in fuel types also influence the devices that convert them into energy services.
Government expenditures on environmental protection
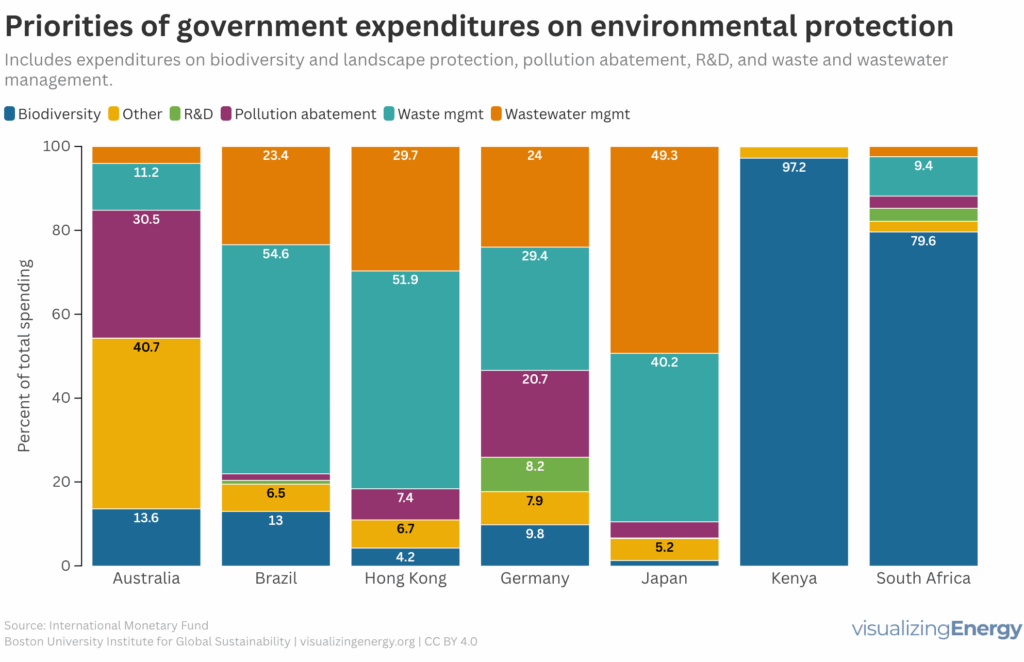
National governments began spending on environmental protection in the late 19th century, escalating after World War II due to pollution concerns. Key legislation emerged worldwide, including Japan’s 1967 law and the U.S. Endangered Species Act. In 2023, EU spending on environmental protection totaled €142 billion, highlighting diverse national priorities in tackling environmental issues.
Is the reserve-to-production ratio for fossil fuels a meaningful indicator?
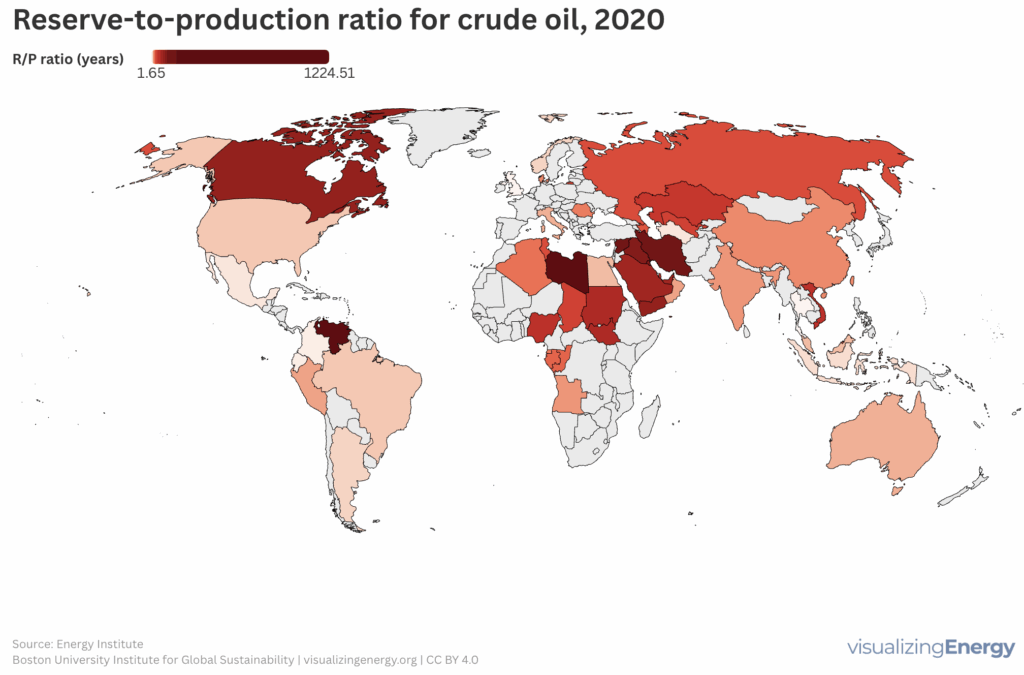
The reserve-to-production (R/P) ratio calculates the lifespan of fossil fuel reserves based on production rates. In the U.S., regulatory frameworks affect reserve reporting, with oil R/P ratios declining from over 40:1 in the early 20th century to about 10:1 today. State-owned enterprises often inflate reserves, complicating future availability assessments.
What happens to low level nuclear waste in the United States?
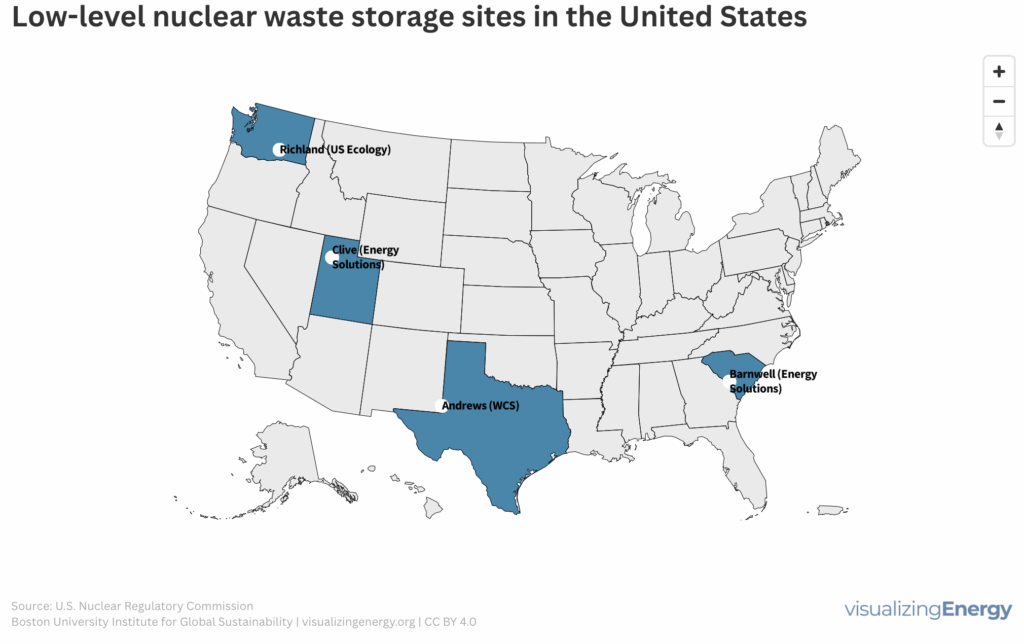
Low-level radioactive waste (LLW) is produced by various commercial operations and the U.S. Department of Energy. It includes contaminated materials like clothes, tools, and medical supplies. LLW is typically stored on-site until it decays or is shipped to disposal sites, regulated under the Low-Level Radioactive Waste Policy Act of 1980.
Sankey diagrams for national energy systems
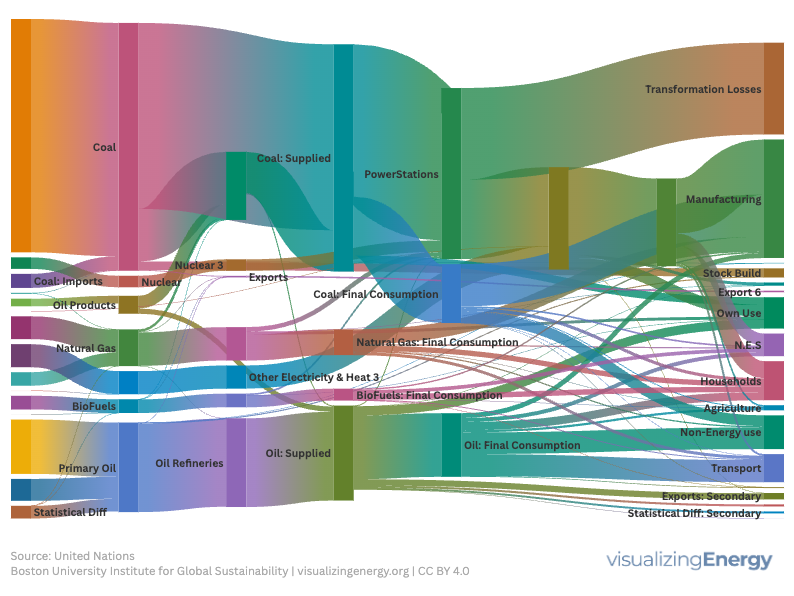
In 1898, H. Riall Sankey developed a diagram illustrating steam engine efficiency, leading to the widespread use of Sankey diagrams for visualizing energy flows in various systems. They effectively display energy extraction, transformation, consumption, and losses while mapping the roles of primary and secondary energy sources across different usage sectors.
What makes a cooking fuel “clean?”
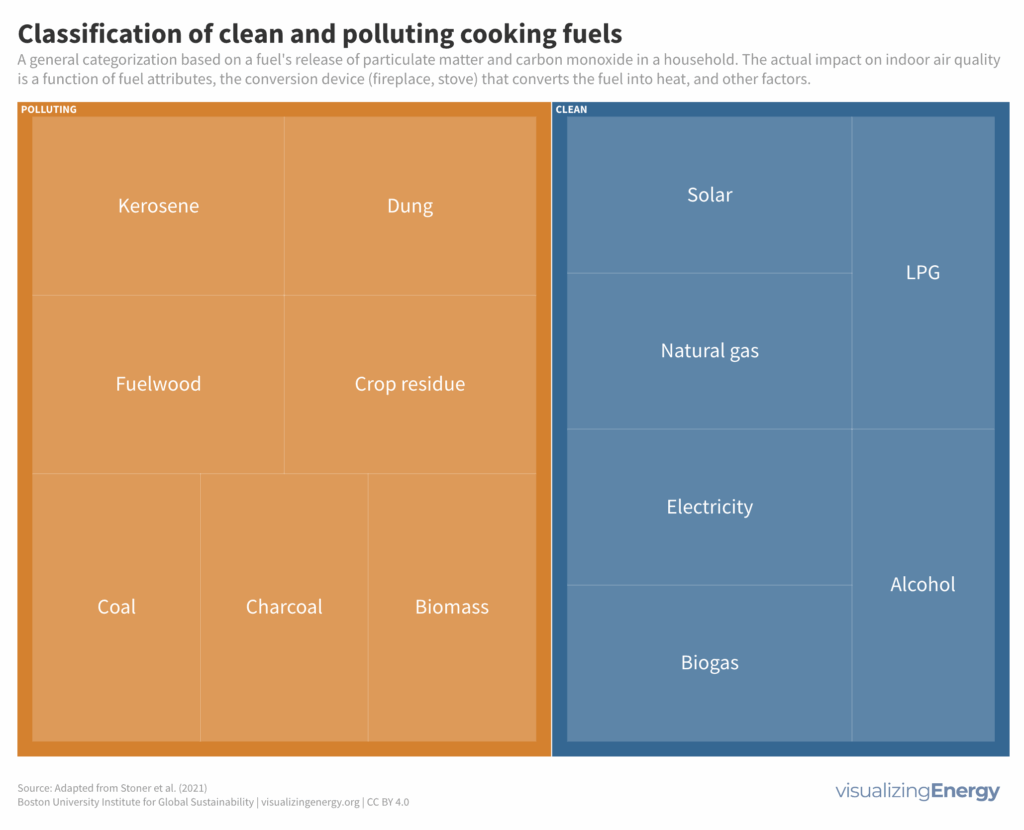
The United Nations established 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to address poverty, health, education, inequality, economic growth, climate change, and environmental conservation. SDG 7 focuses on providing affordable, sustainable, and clean energy for all. The World Health Organization sets benchmarks for “clean” cooking, favoring efficient and low-emission technologies while discouraging the use of polluting fuels.
Gender mainstreaming in clean energy: informal urban settlements in sub-Saharan Africa

Approximately 2.3 billion people globally lack access to clean cooking, posing health risks, especially for women and children in low- and middle-income countries. Gender mainstreaming is crucial for achieving universal clean energy access. However, integration into energy projects in informal urban areas remains fragmented, necessitating better support and capacity building.
Watch the history of nuclear power in the U.S.
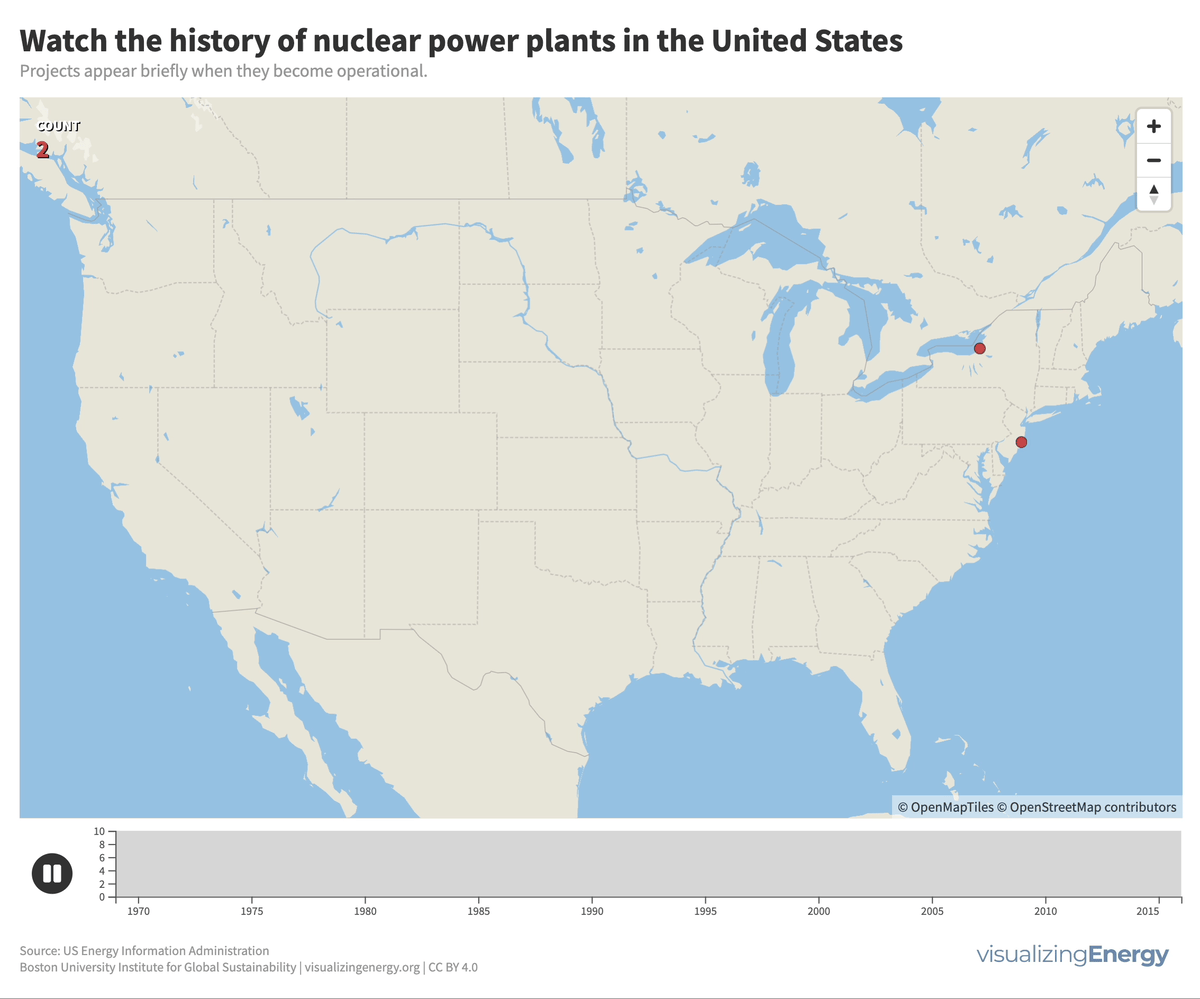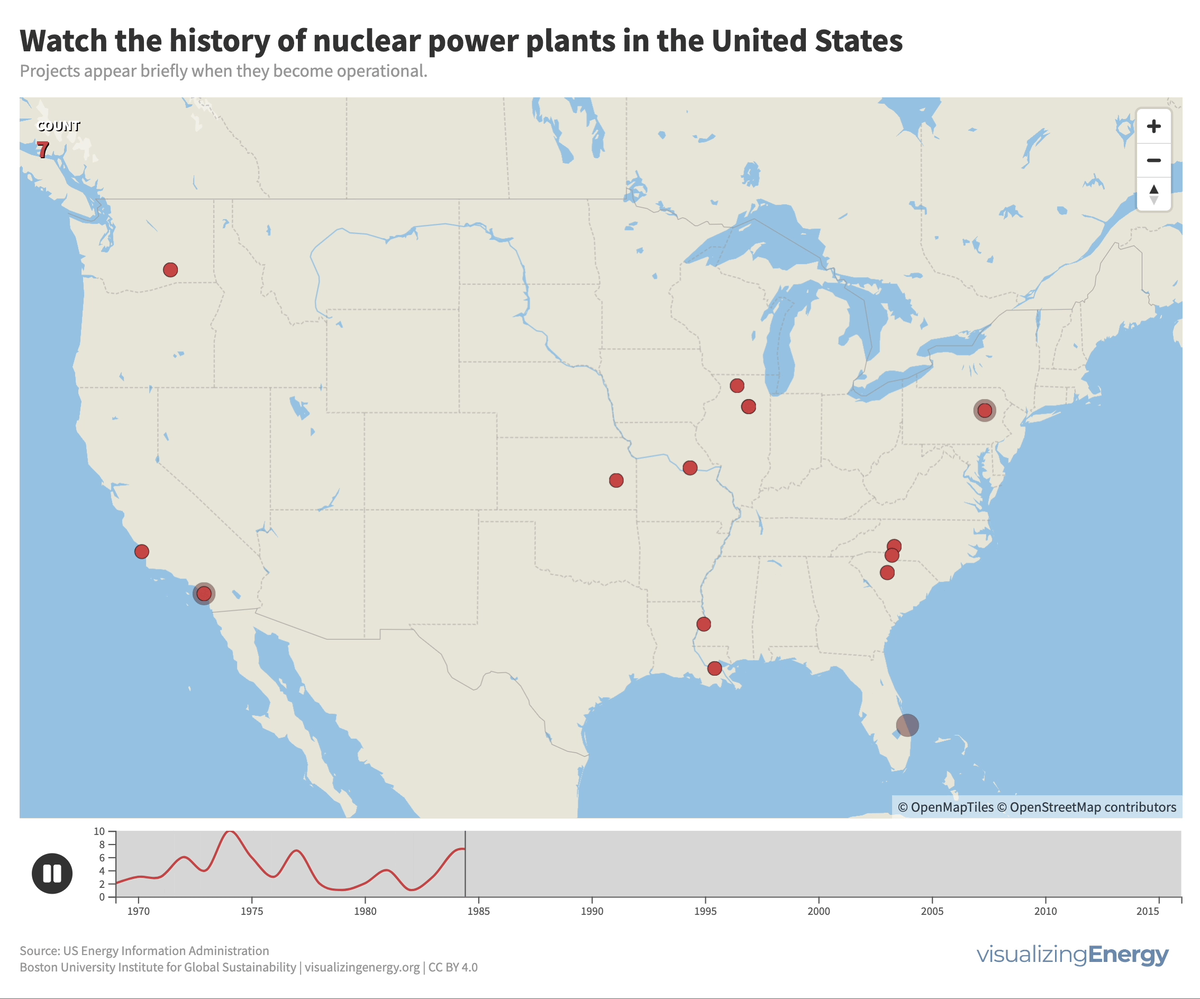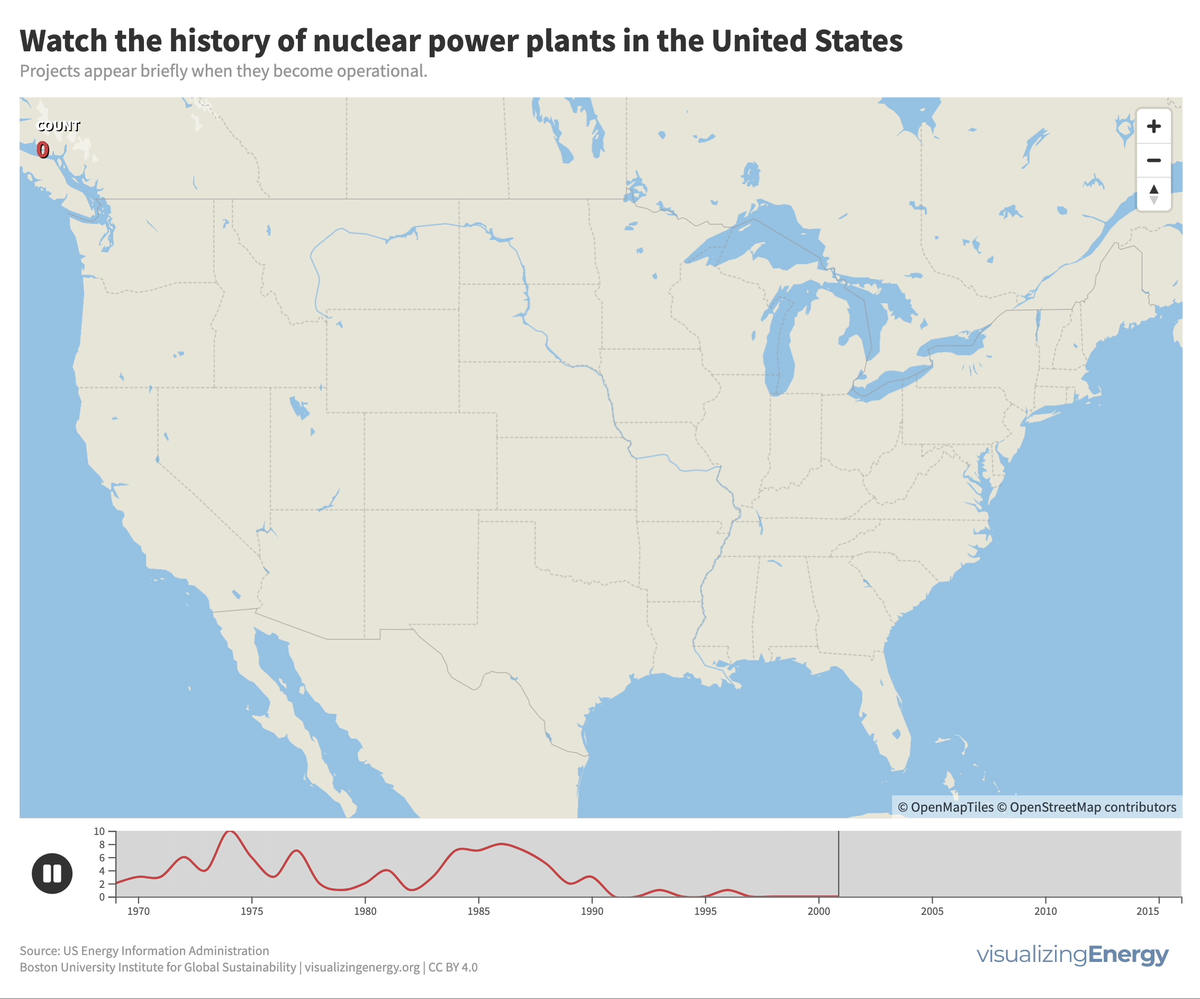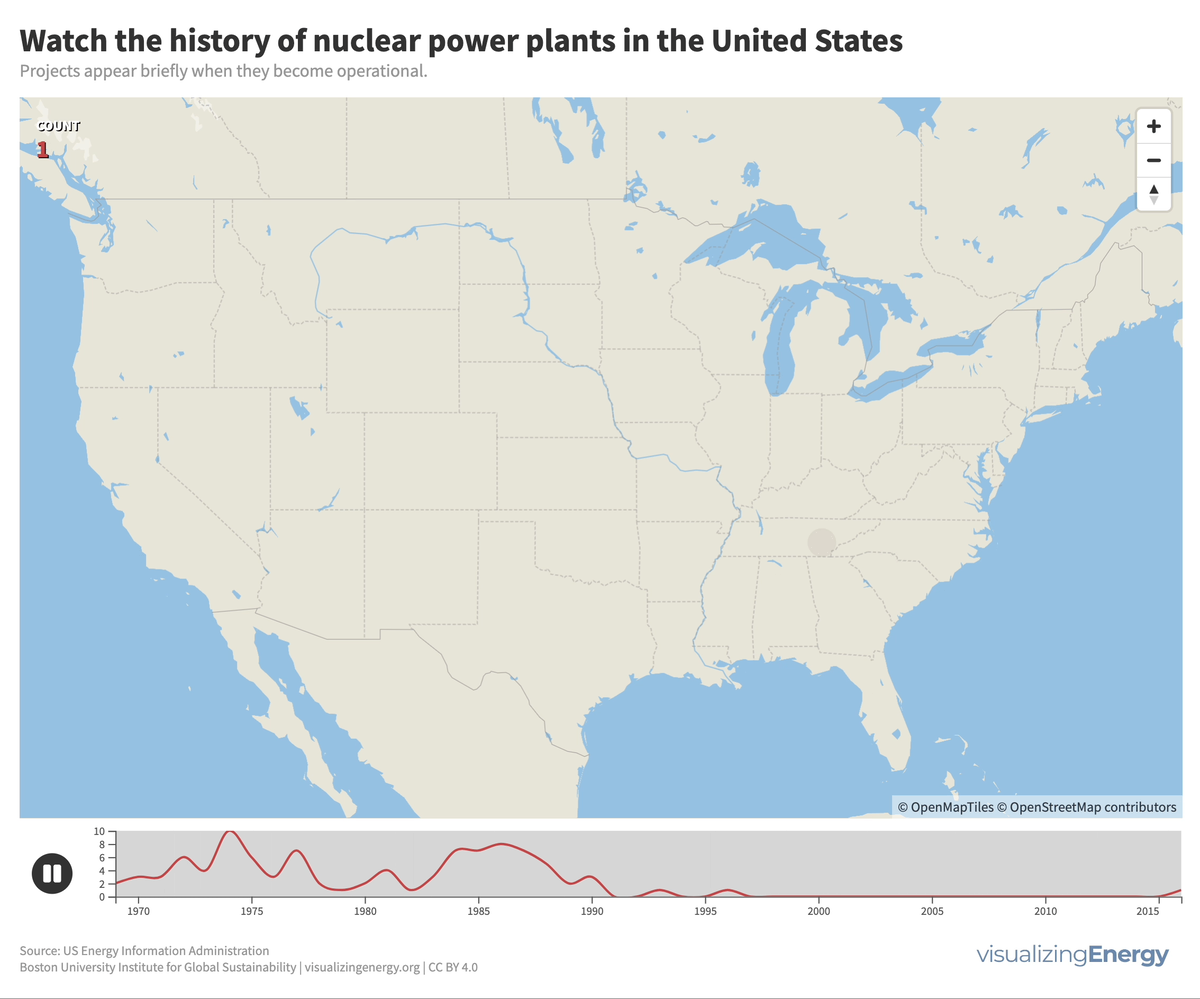
In 2022, the U.S. had 92 nuclear power plants generating 18% of total electricity. The industry, once a major player, declined due to high costs, long construction timelines, decreased demand, accidents, regulations, and market deregulation. There’s renewed interest in nuclear power to combat climate change, with the first new plant in 30 years, though debates continue on cost, safety, and alternative energy sources.
Is wind energy a major threat to birds?
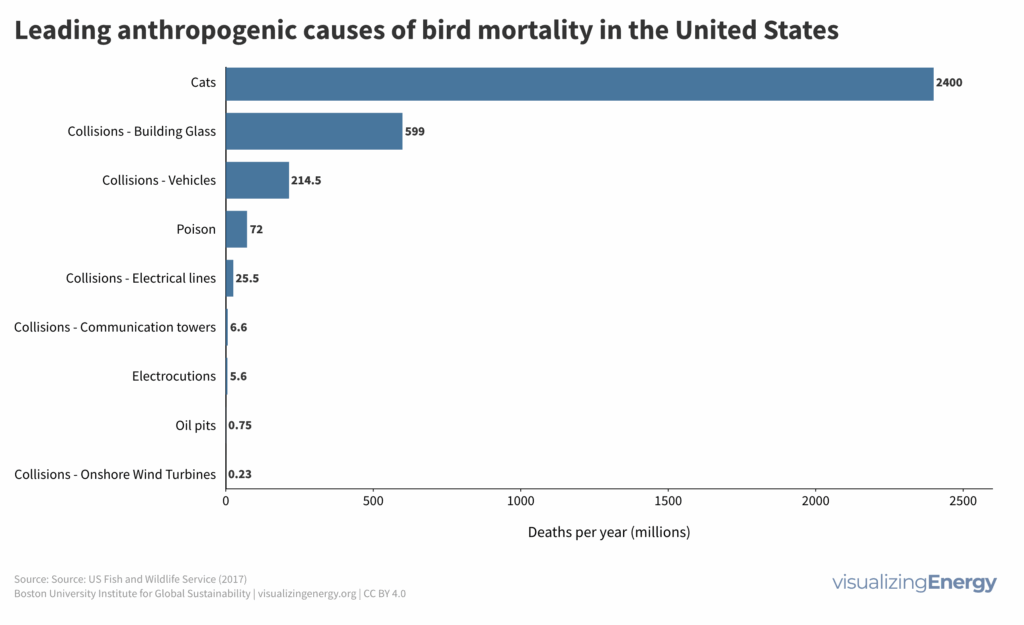
Concerns about wind turbines causing bird deaths are often exaggerated. Data shows that bird fatalities from wind turbines are relatively low compared to other causes like domestic cats and building collisions. When assessing the relative impact on bird mortality, wind energy appears less harmful than many other forms of electricity generation.
Four million wells and counting: the history of oil and gas drilling in the U.S.
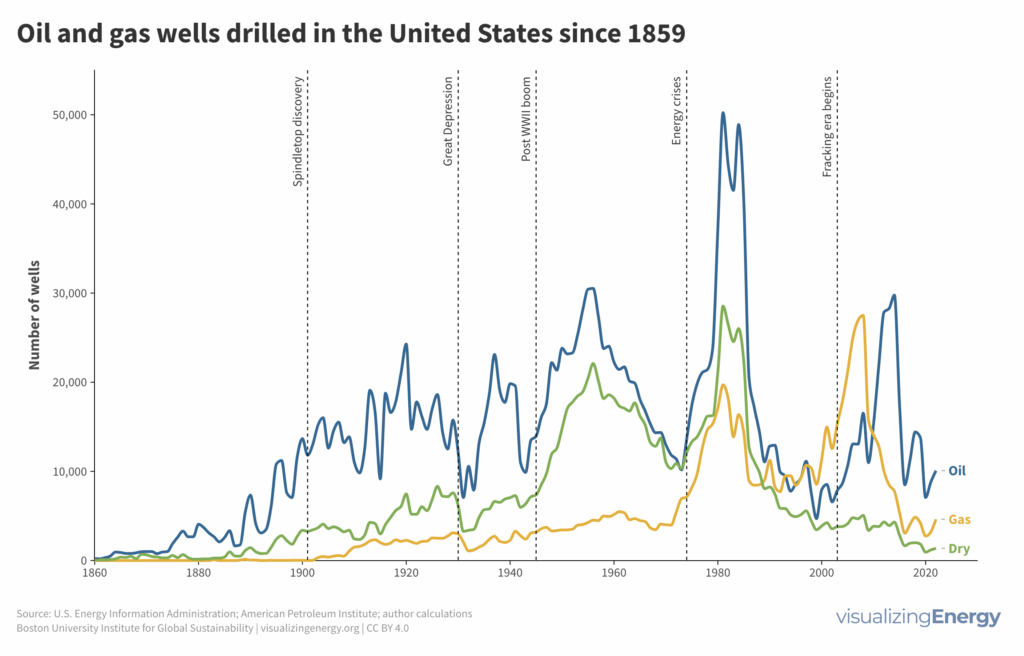
Since the first successful oil well in 1859, the U.S. has drilled millions of wells for oil and gas. Drilling surged with demand, technology, and geopolitics, with notable periods like the post-WWII boom and the fracking-driven increase in natural gas wells. This progress has brought economic benefits and energy shifts, yet also raised environmental and social concerns.
