Non-energy uses of fossil fuels
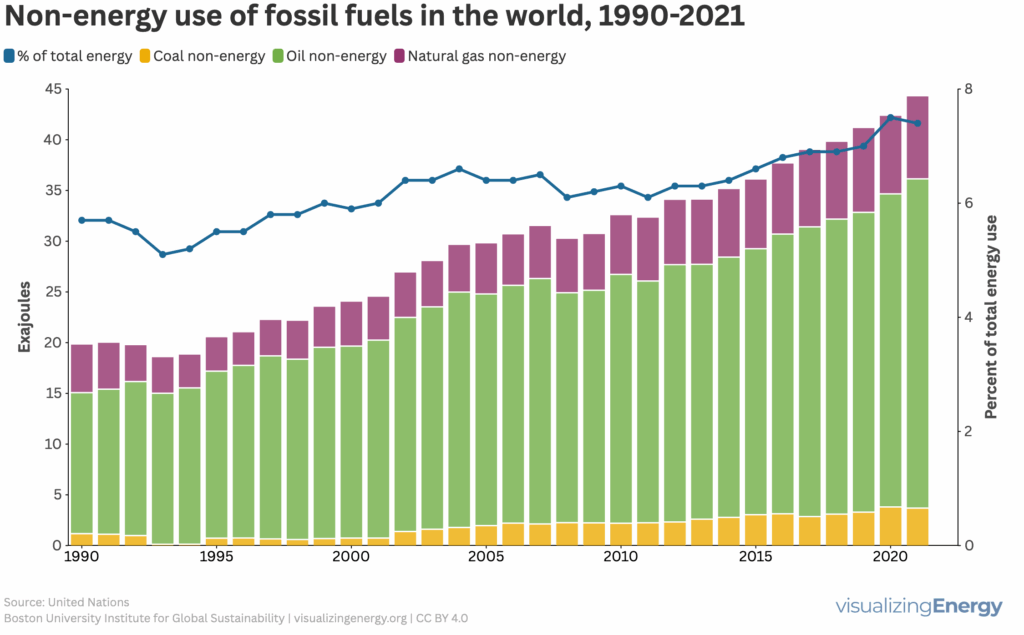
Fossil fuels are most thought of in terms of the energy services they provide: petroleum-derived fuels in transportation, natural gas for heating, and coal for electricity generation. But fossil fuels are consumed—but not combusted—when used as construction materials, chemical feedstocks, and many other non-energy products. About eight percent of fossil fuels used worldwide are for […]
The price of power in the United Kingdom, 1300-2000
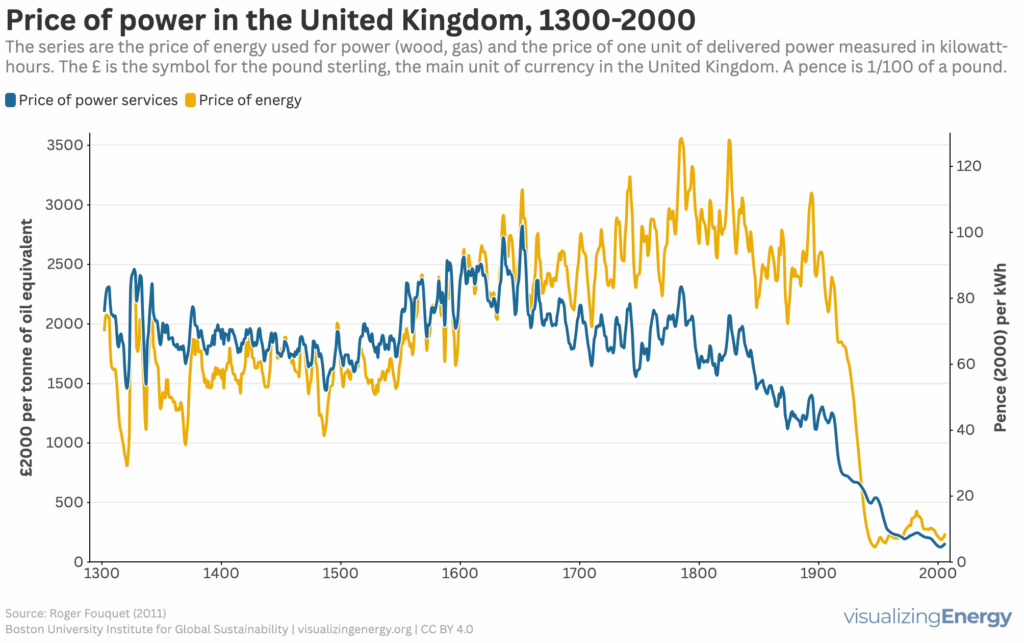
One outstanding feature of historical energy transitions was the change in the cost, power, and efficiency of the energy converters that humans used to perform useful work. These included animate energy converters such as people and draft animals, and inanimate energy converters such as water wheels, windmills, sailing ships, steam engines, internal combustion engines, and […]
Global anthropogenic carbon monoxide emissions, 1750-2022
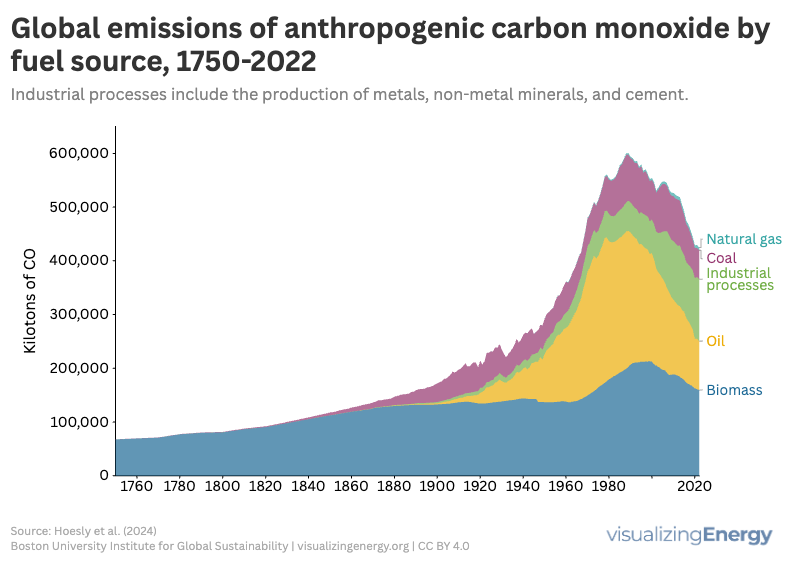
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a toxic, colorless gas from incomplete combustion of fuels, leading to potential health hazards like headaches and confusion. Residential sources produce significant CO emissions, impacting 2.4 billion people reliant on biomass. Globally, emissions peaked in 1989, but have since declined due to regulations and technological advancements in combustion efficiency.
Global anthropogenic nitrogen dioxide emissions, 1750-2022
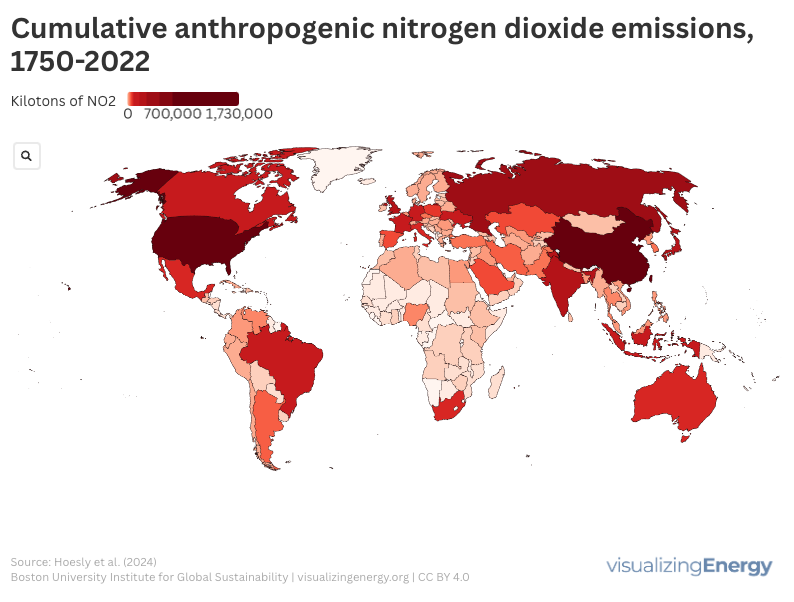
NOx, comprising nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide, significantly impacts air pollution and health, causing respiratory issues and contributing to harmful pollutants. Mainly emitted from transportation and industrial activities, NOx levels vary globally. Efforts to reduce emissions include regulatory policies and technology advancements, along with a shift towards cleaner energy sources.
