Watch the history of solar power in the United States
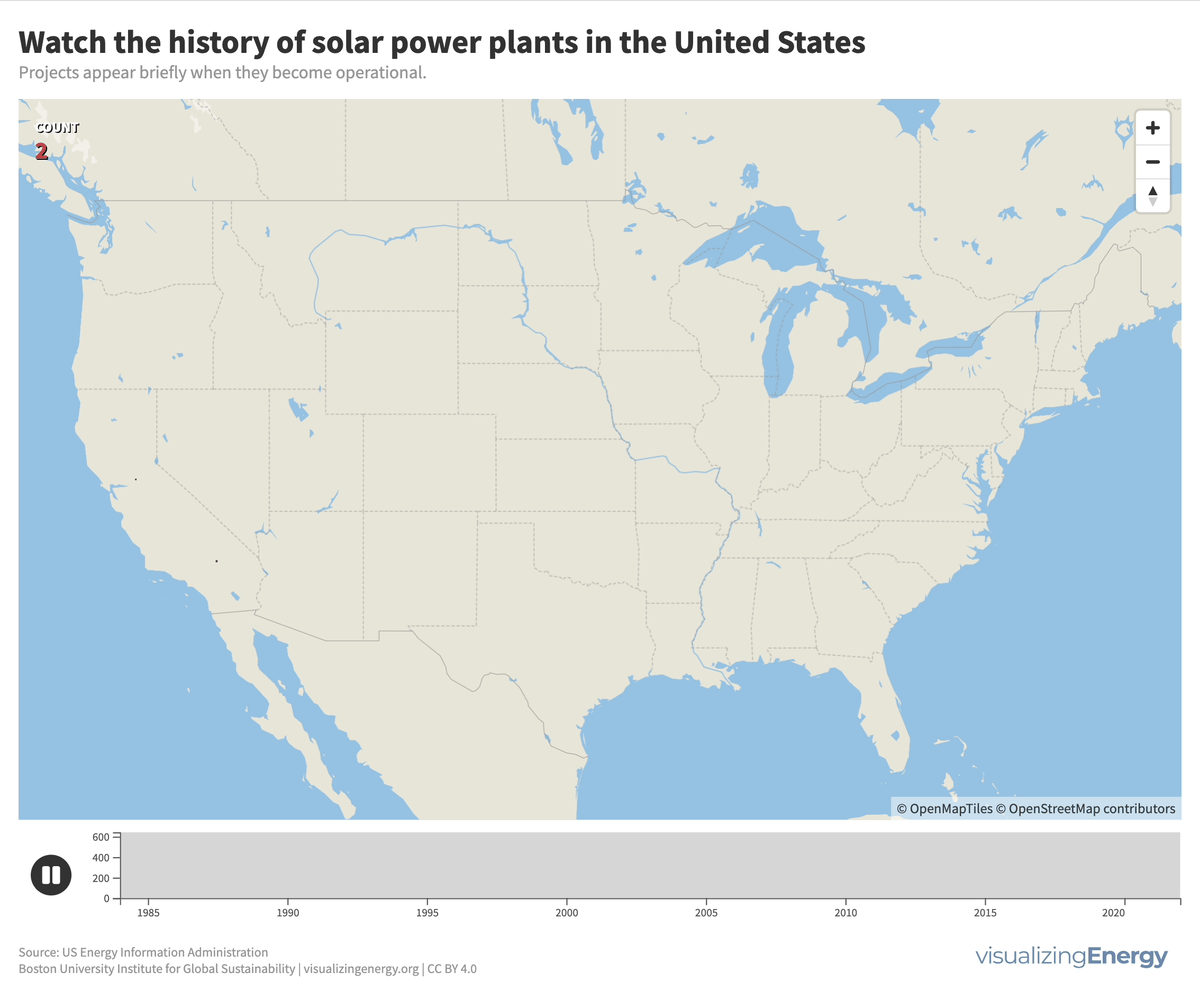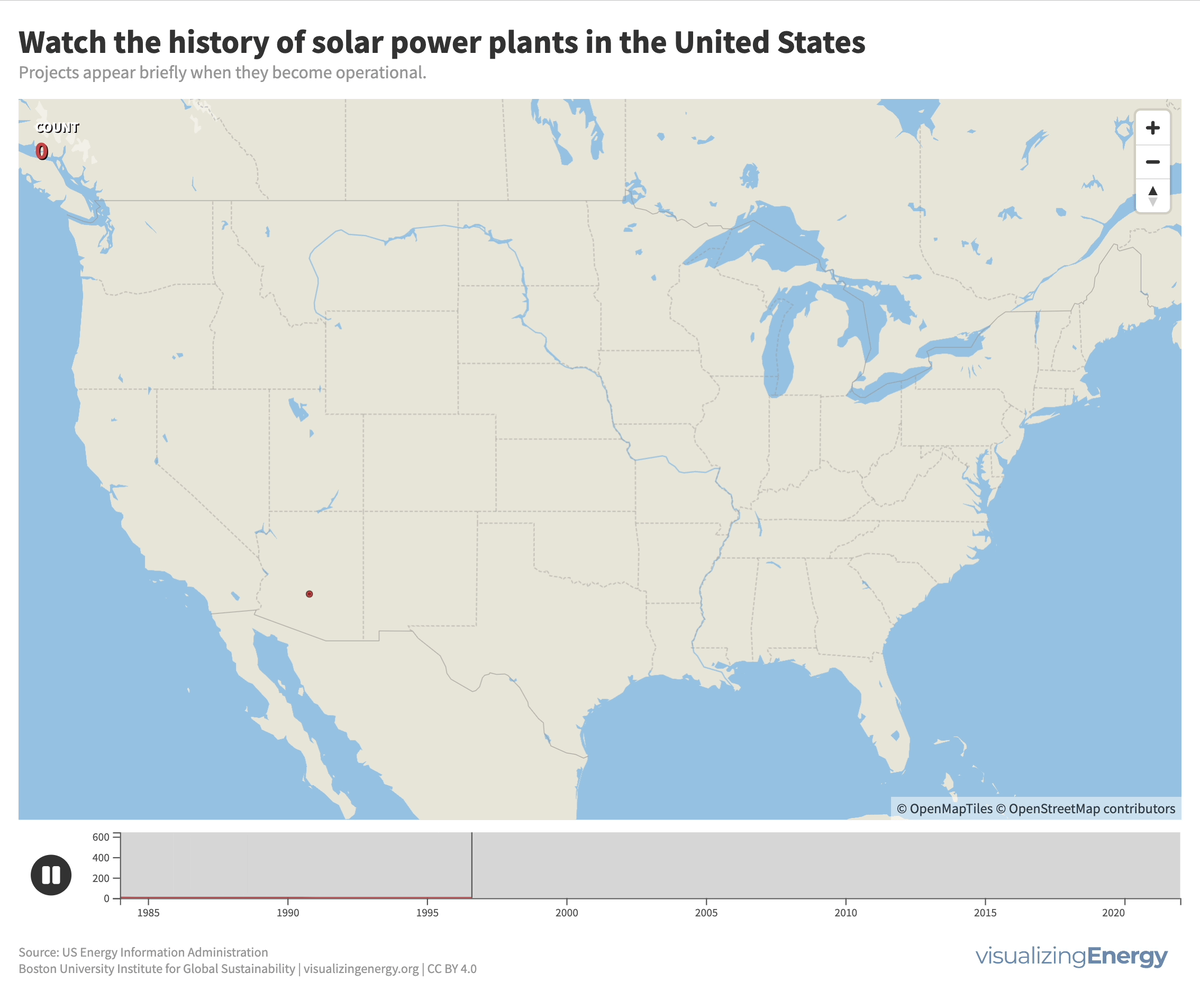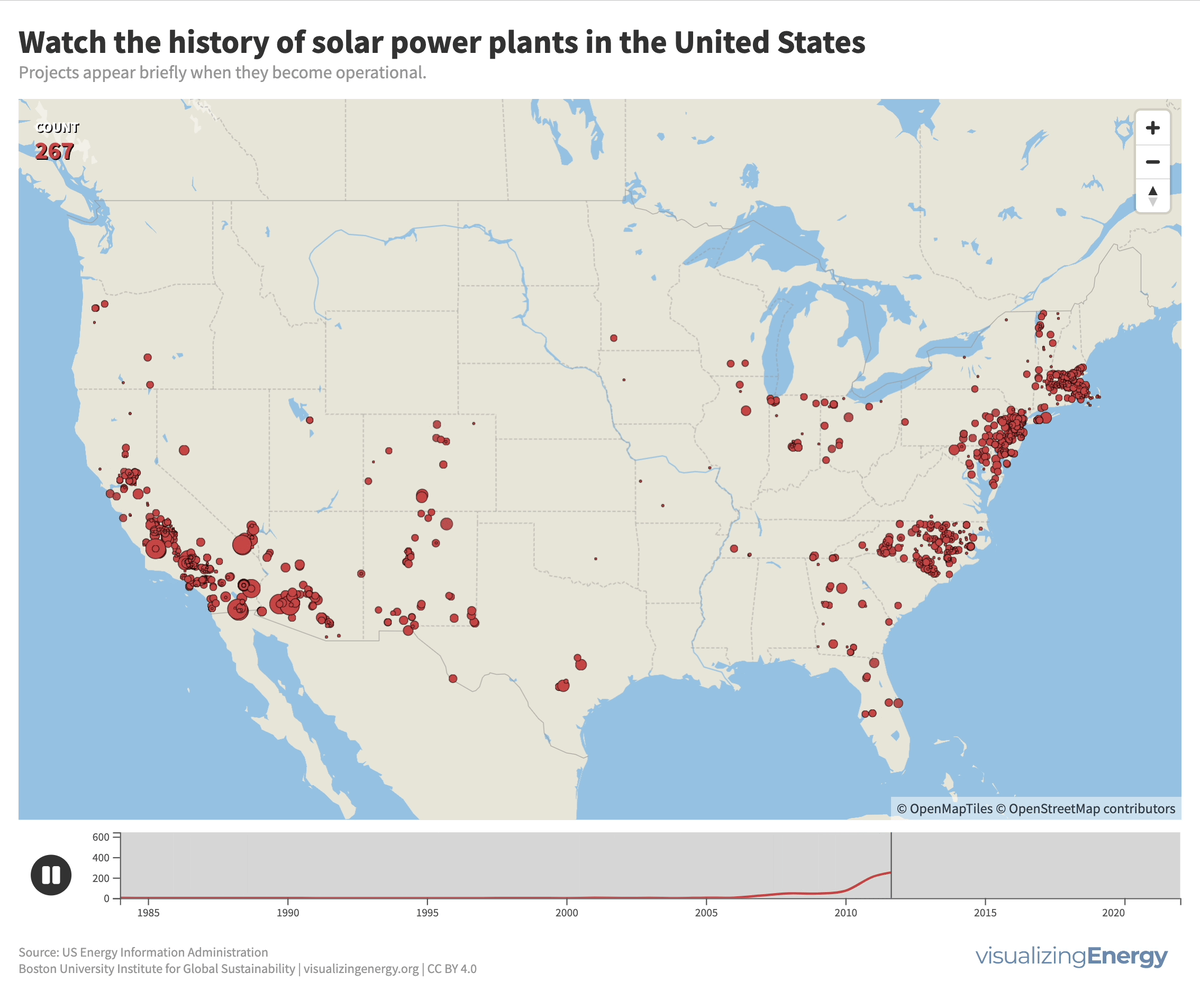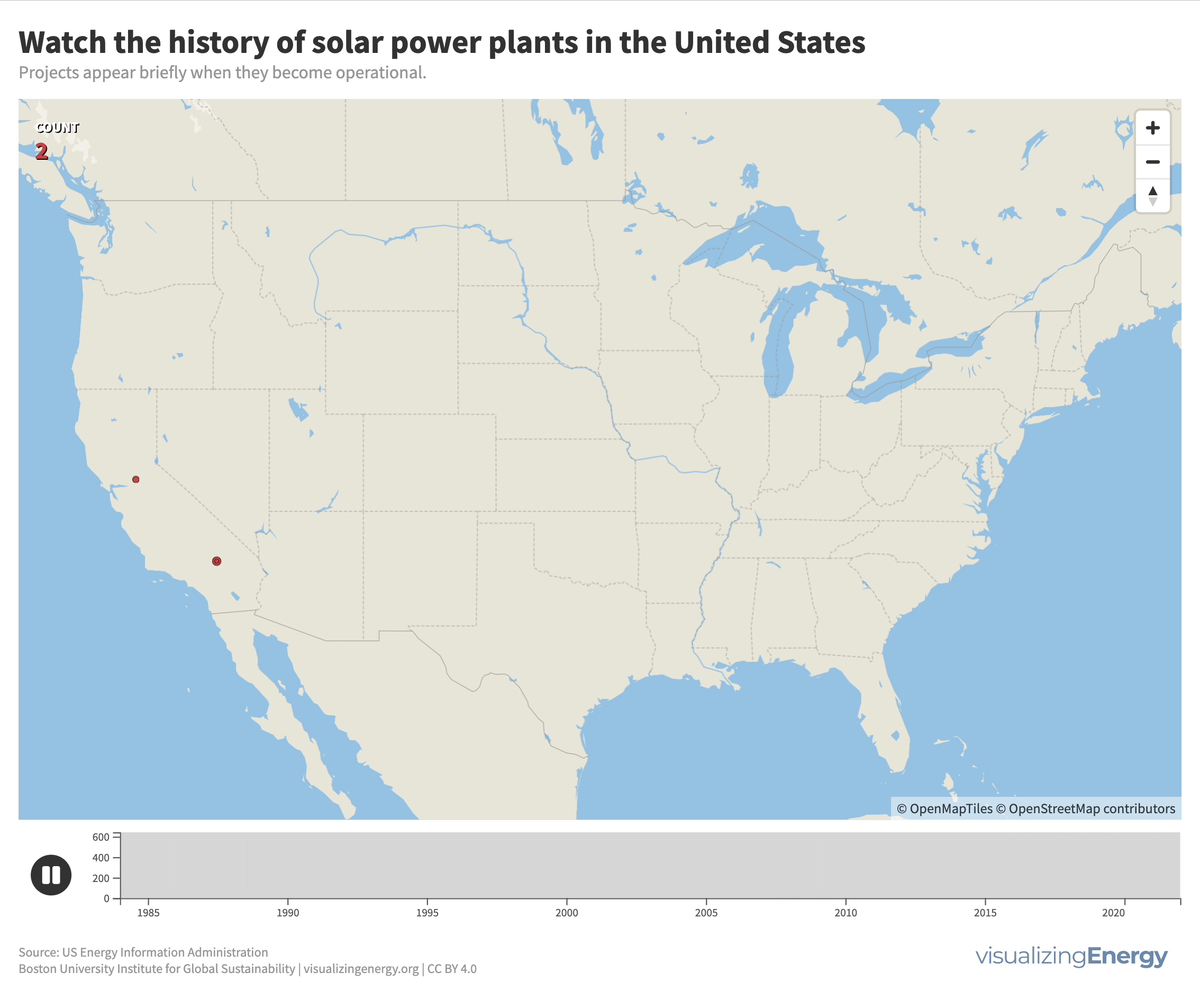
In 2022, the United States saw a significant rise in solar power generation, with 5730 utility-scale solar PV plants and 13 solar thermal plants producing 146 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity, equal to 3.4% of total utility-scale generation. This growth traces back to the 2000s, marked by falling solar system costs, enhanced efficiency, and government incentives like the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009.
Is wind energy a major threat to birds?
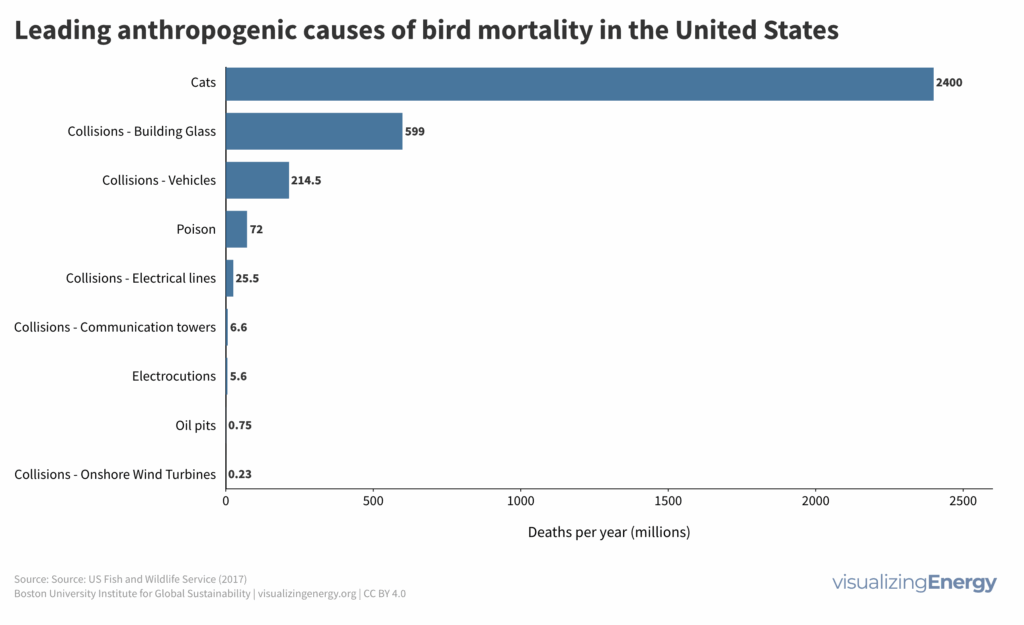
Concerns about wind turbines causing bird deaths are often exaggerated. Data shows that bird fatalities from wind turbines are relatively low compared to other causes like domestic cats and building collisions. When assessing the relative impact on bird mortality, wind energy appears less harmful than many other forms of electricity generation.
How did people benefit from energy transitions in the United Kingdom?
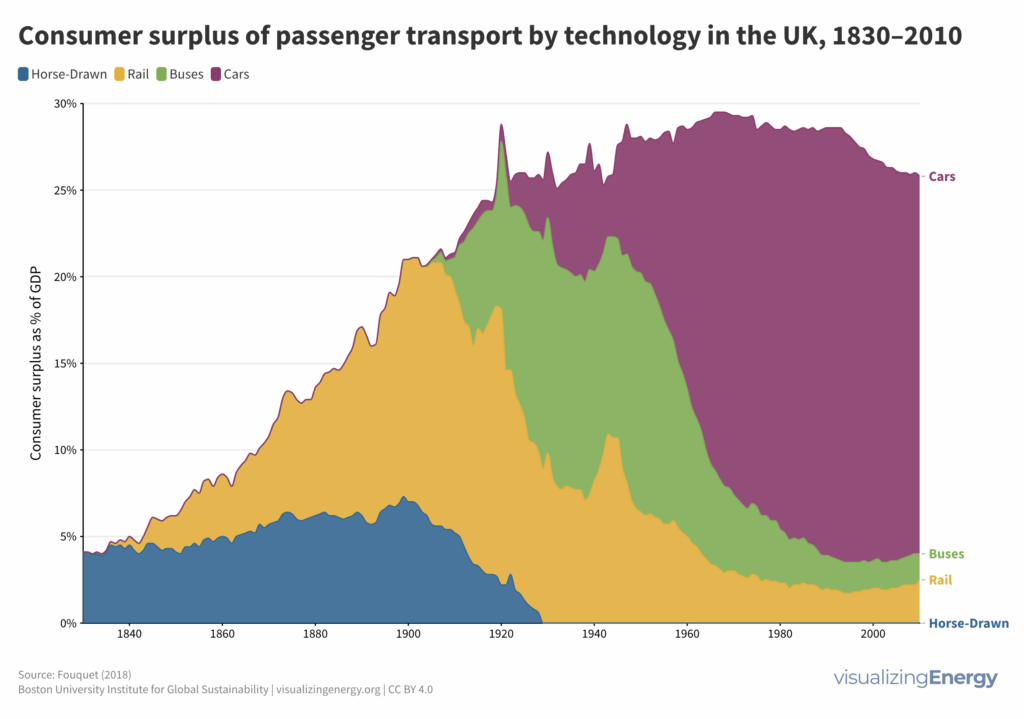
Historic energy transitions, primarily driven by fossil fuels, significantly improved human well-being, measured through consumer surplus. In the UK, transitions from stagecoaches to railways to cars, and from candles to gaslight to electric lighting, substantially increased consumer surplus. However, these benefits diminish as societies reach high well-being levels.
Watch the history of oil power plants in the United States
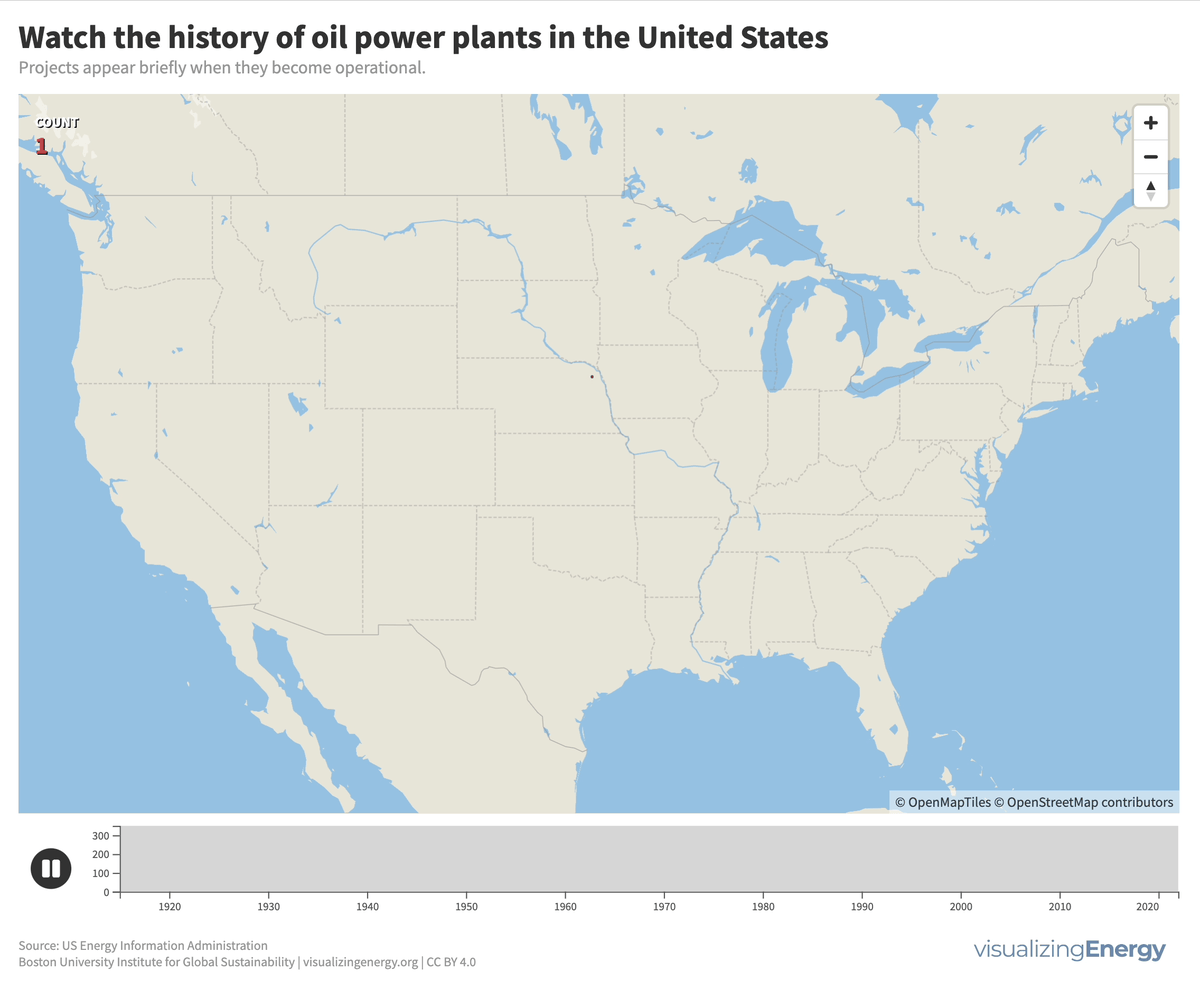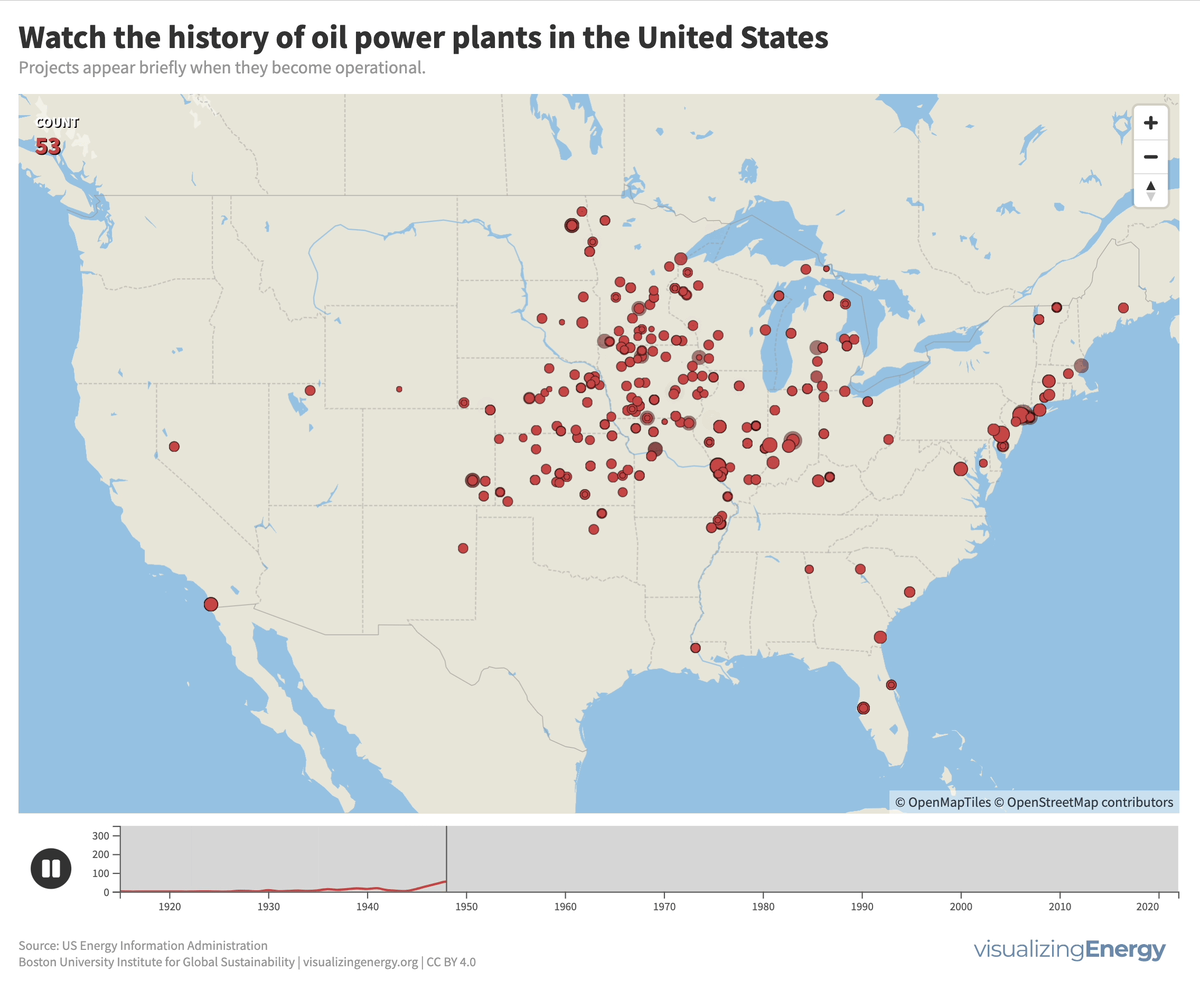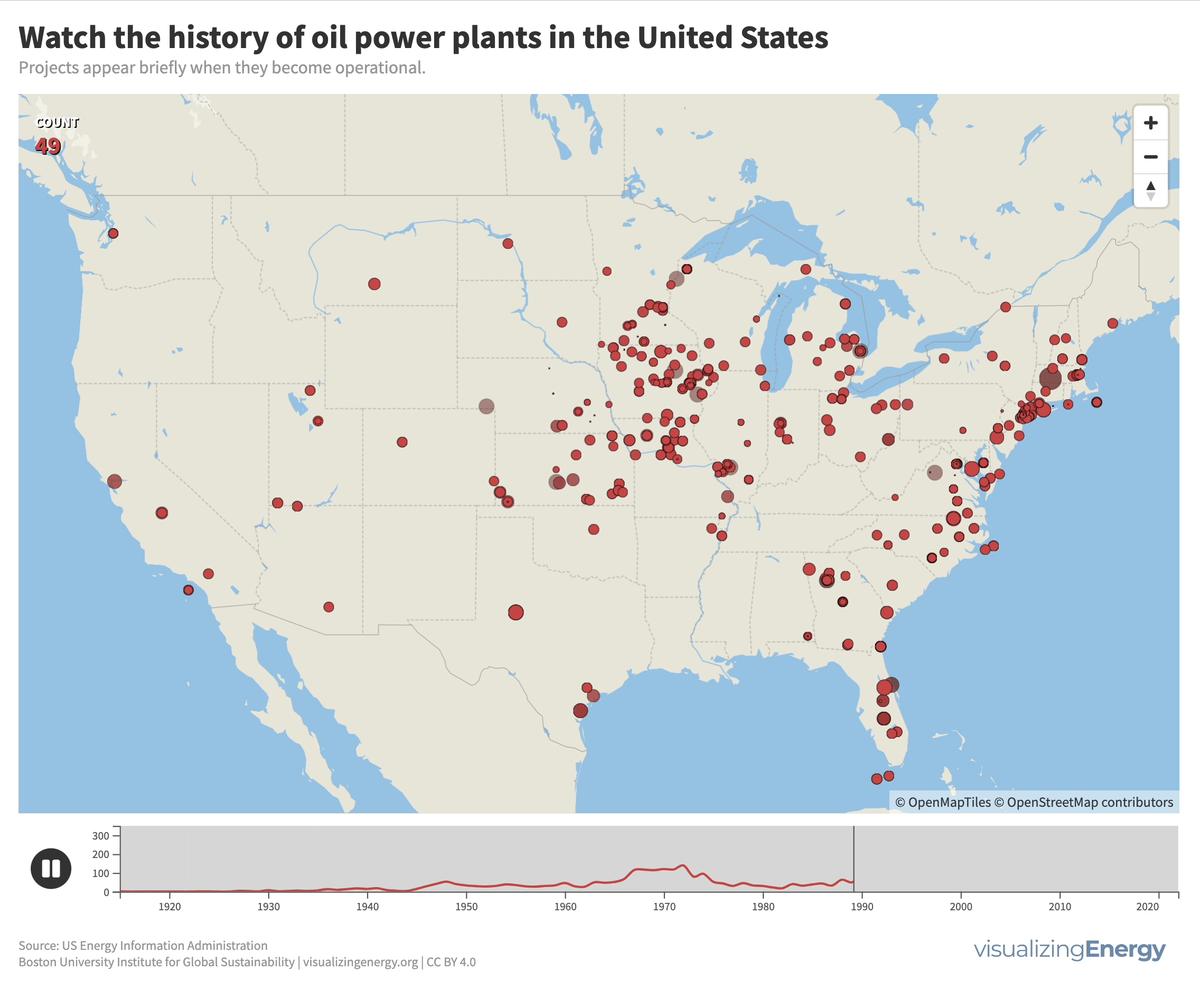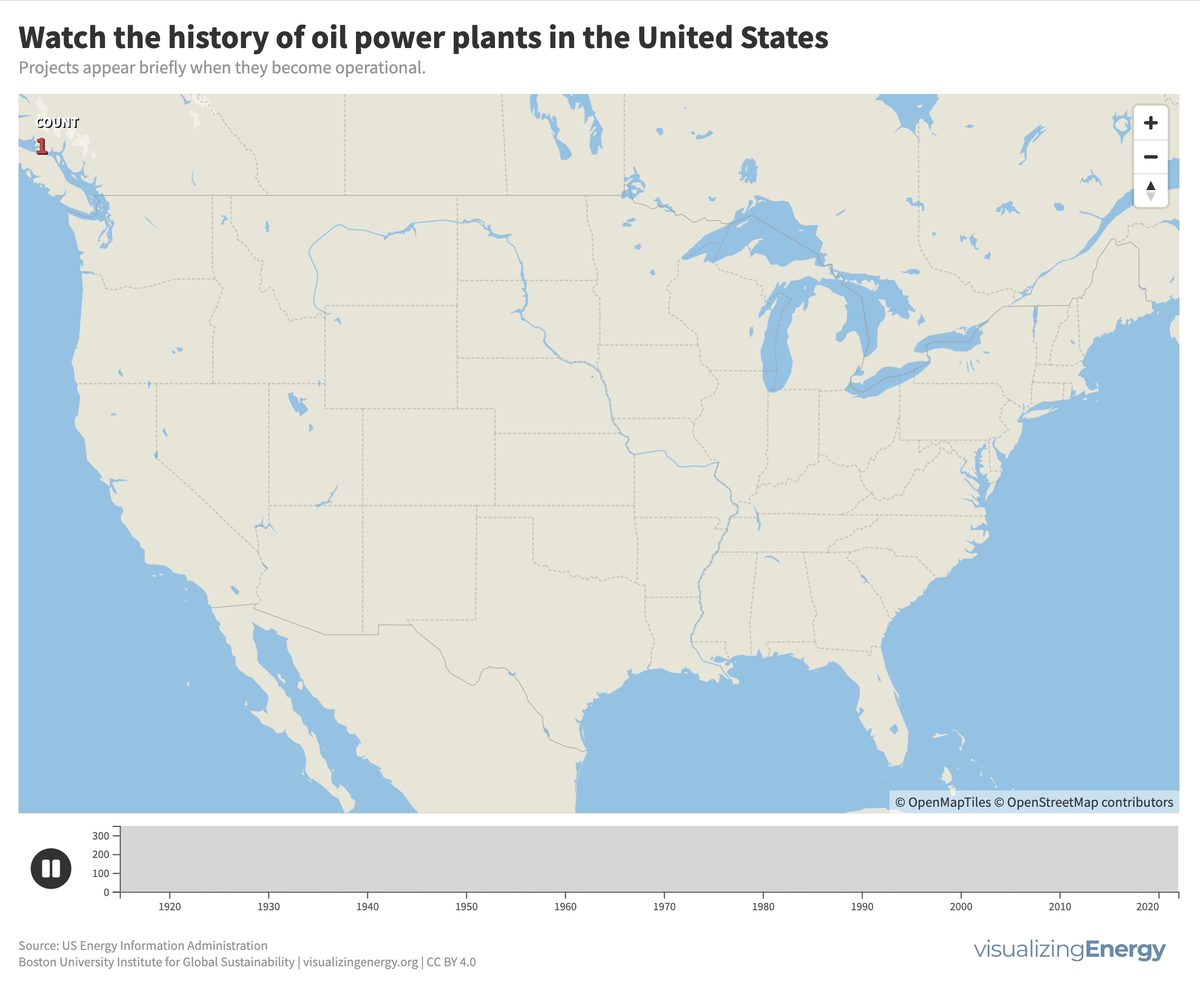
In 2022, the US had about 4,000 petroleum-burning generators, providing only 0.6% of the nation’s electricity due to lower efficiency and higher costs than alternatives. These smaller generators are mainly used for peak power and emergency backup, with policies since 1978 discouraging their use to reduce oil dependence for national security.
The history of coal production in the United States
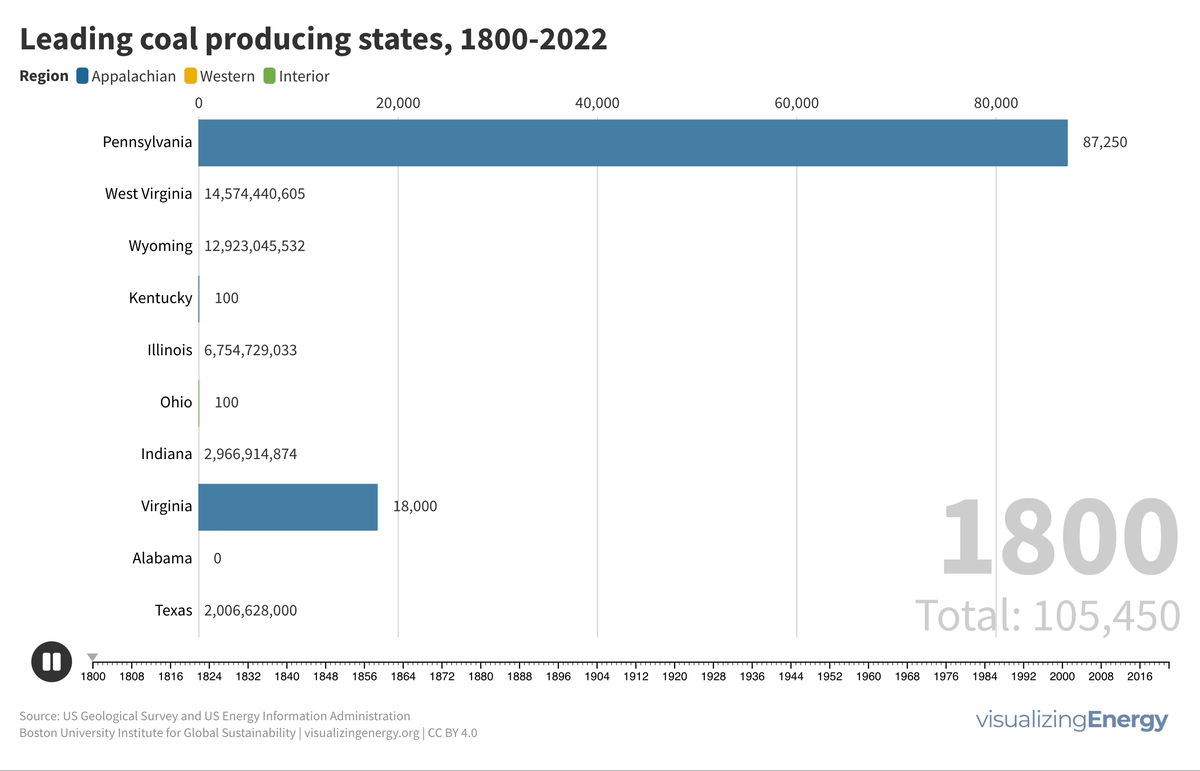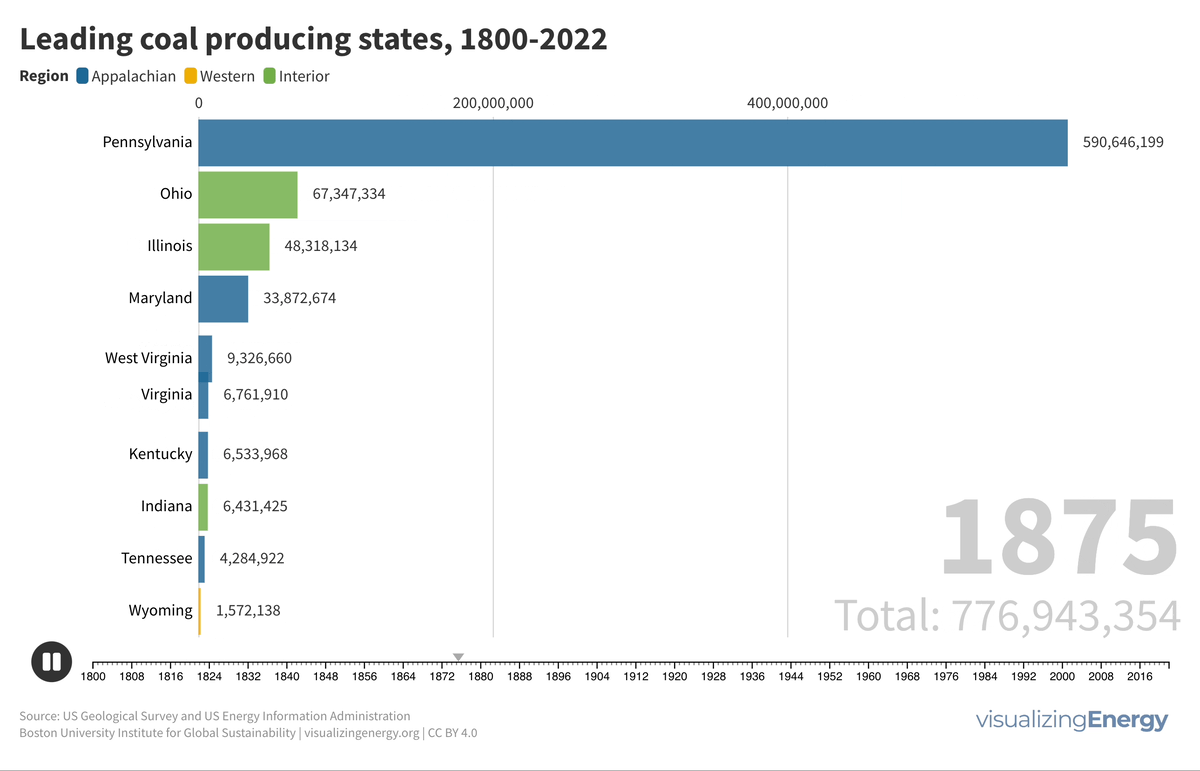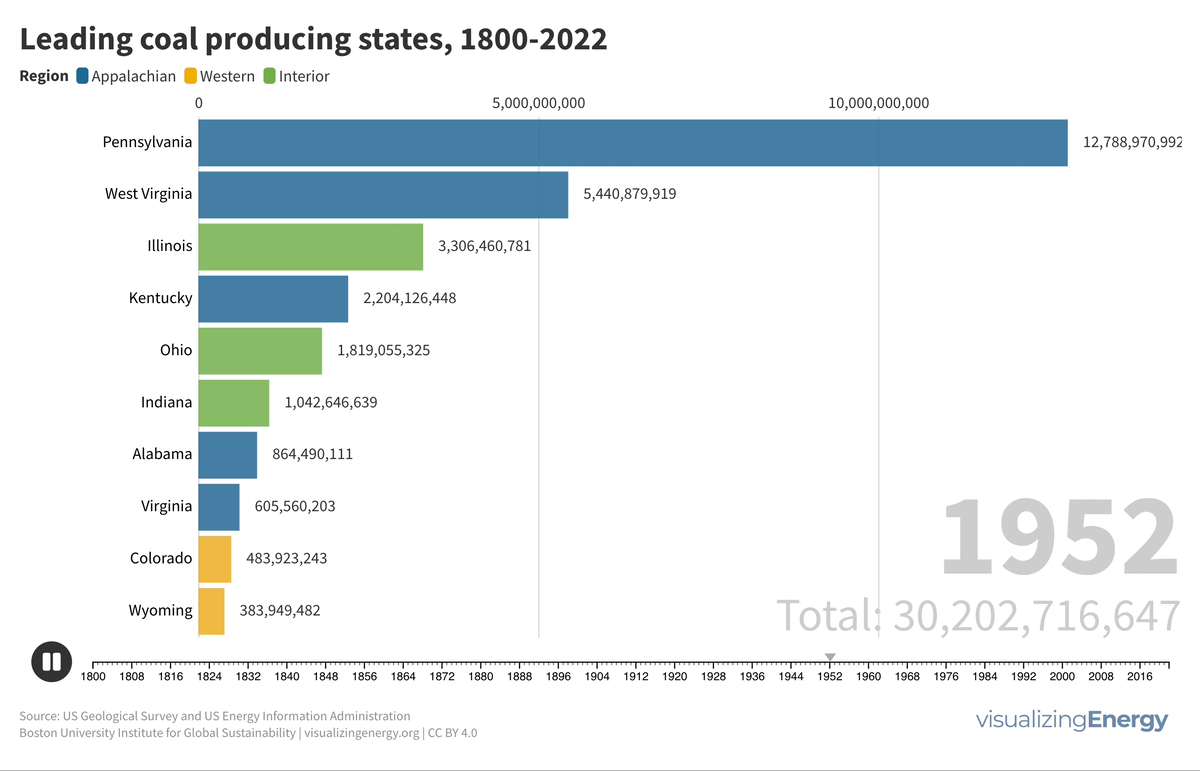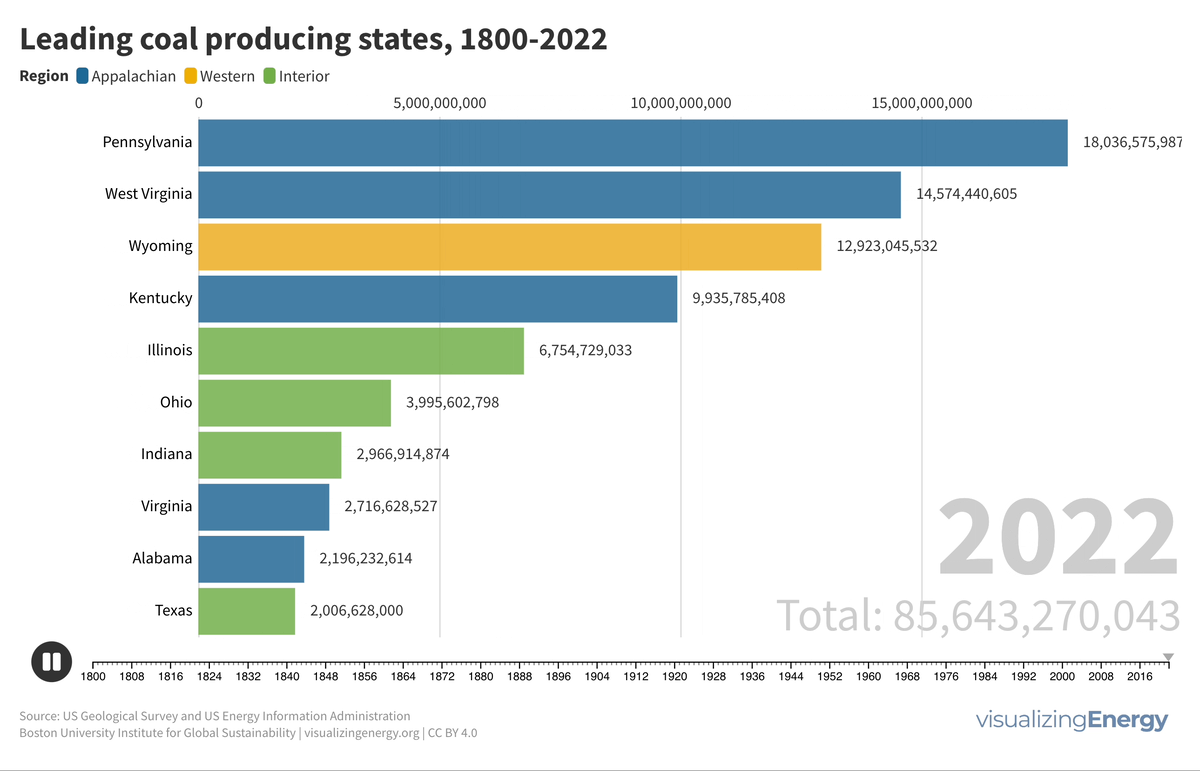
Coal has played a pivotal role in the United States’ industrial history, fueling steel production, electricity generation, and economic growth in the early 20th century. However, this legacy also comes with significant environmental and health issues, including miner health problems, landscape degradation, abandoned mines, and pollution.
Where are new hydropower plants being built?
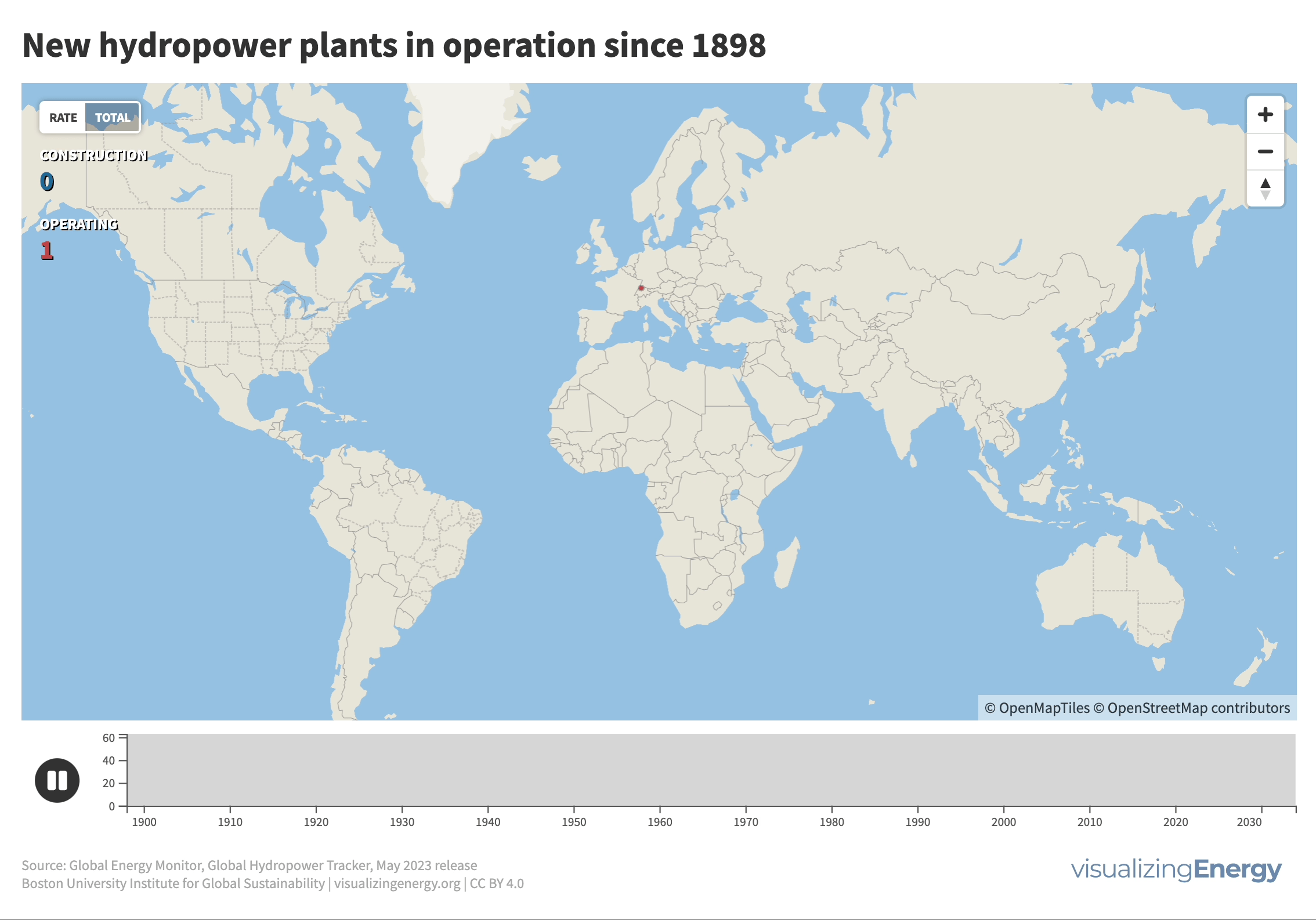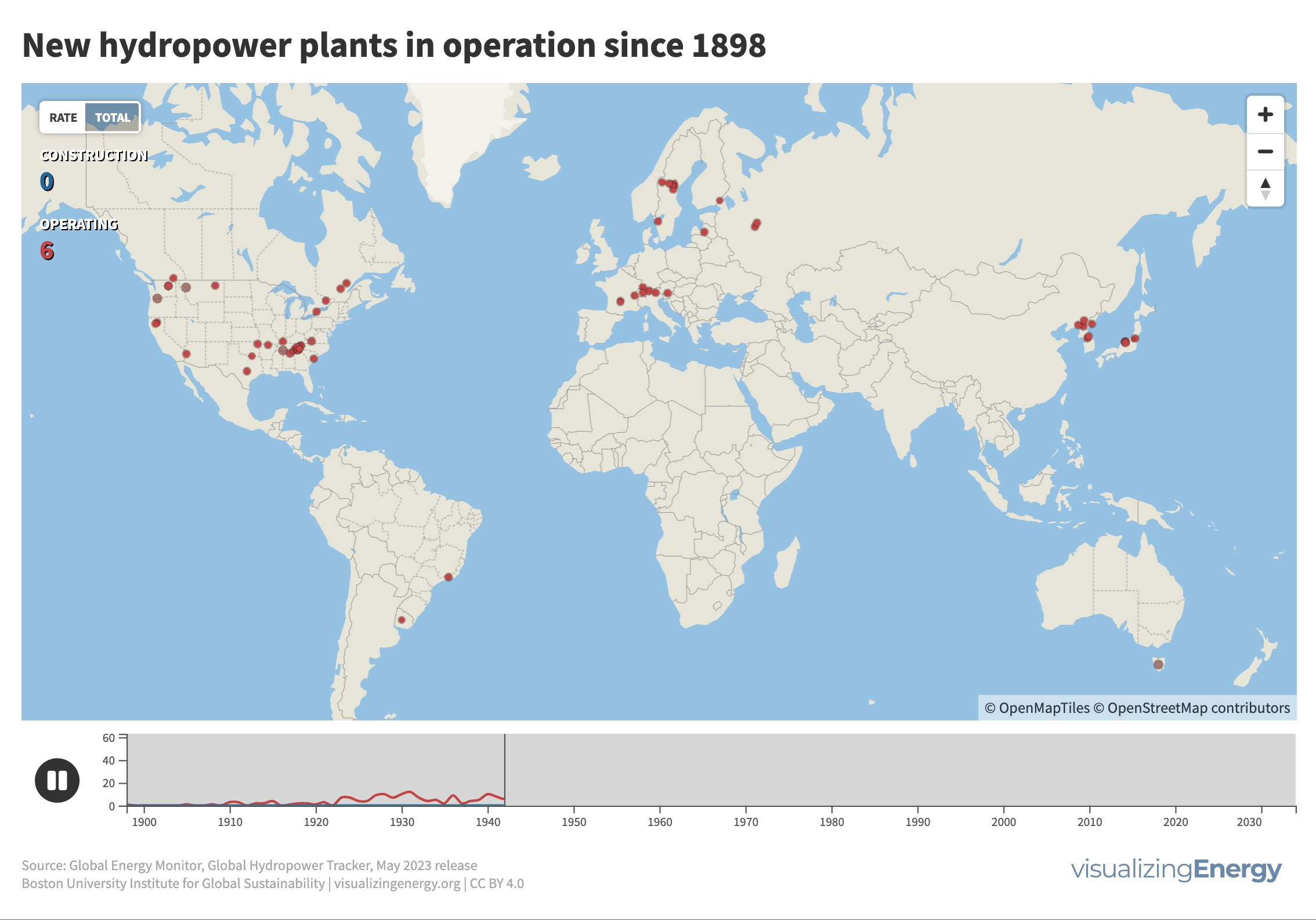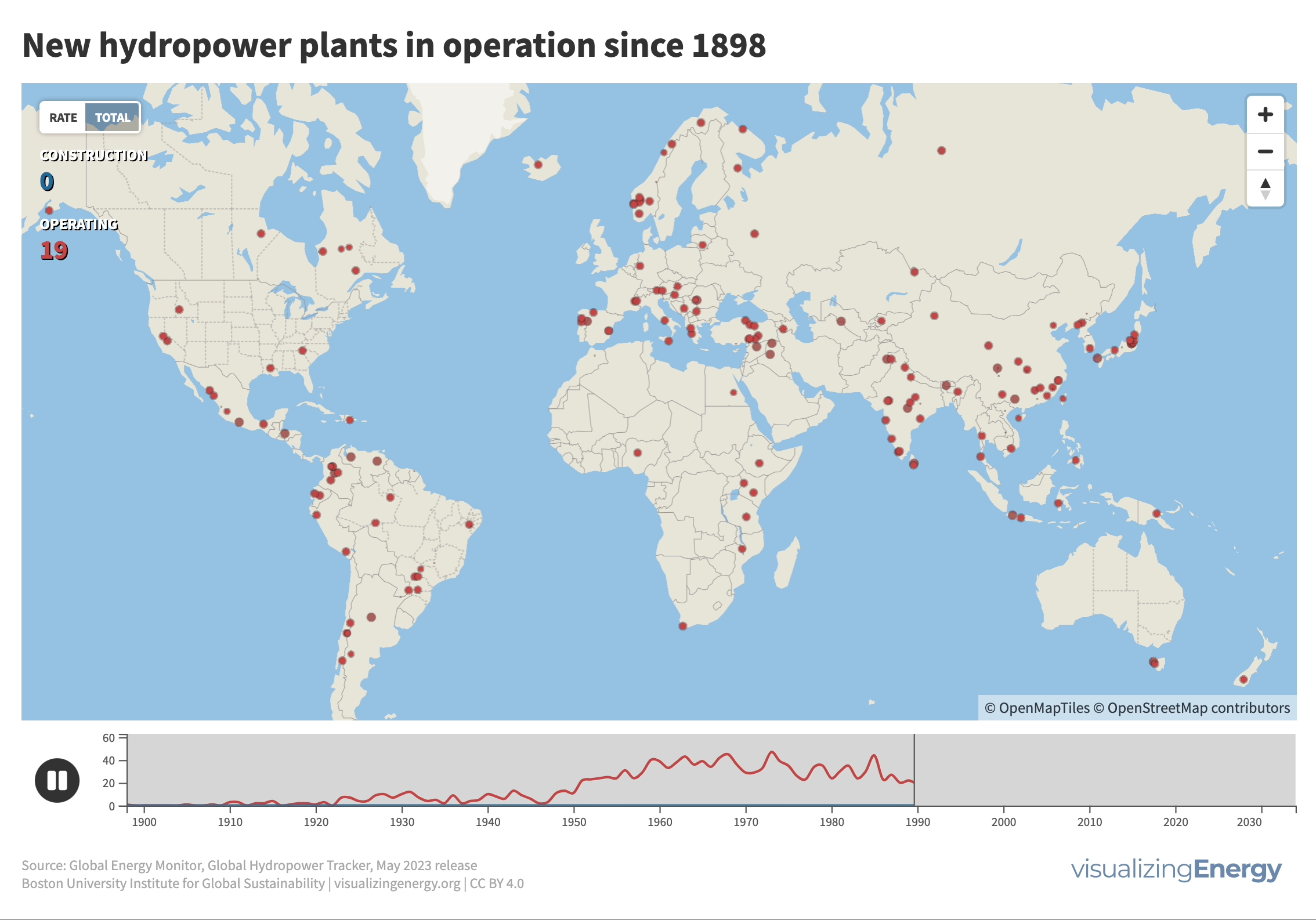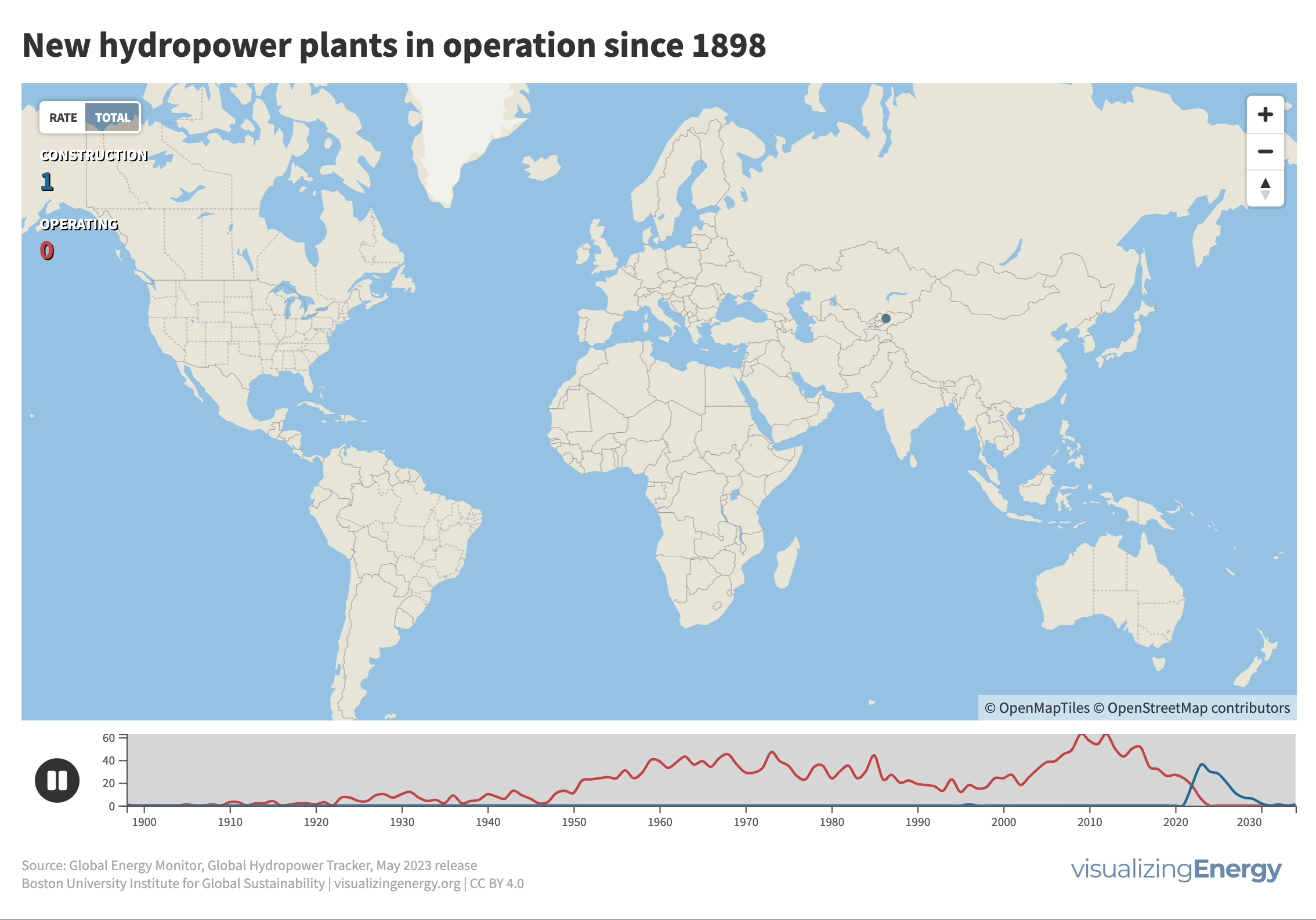
Hydropower’s history traces back to 1882 when the first facility began supplying electricity in Wisconsin. Its adoption surged across North America, Europe, and beyond, with China notably driving expansion in recent decades. Hydropower now contributes 17% of global electricity, surpassing nuclear, wind, solar, bioenergy, and geothermal combined.
Power plant efficiency since 1900
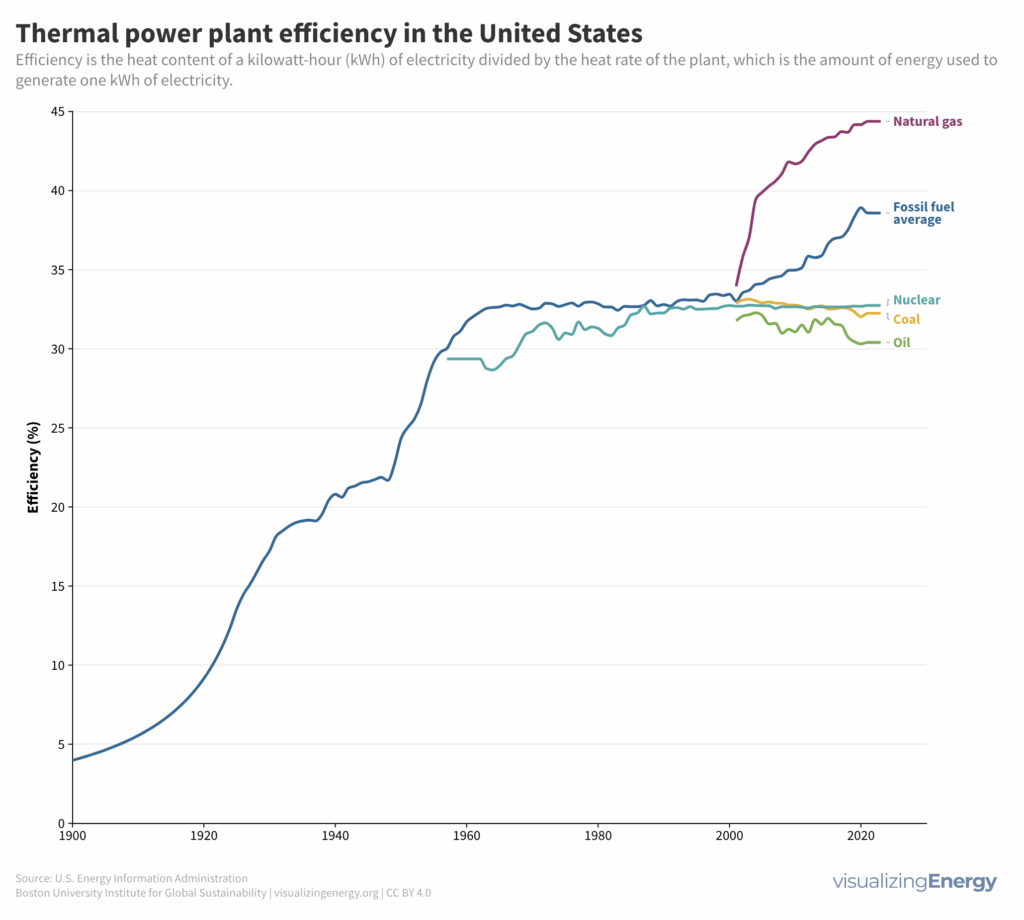
The efficiency of a thermal power plant is the ratio of the electricity output to the energy input, taking into account the heat losses. Over the years, the average efficiency of thermal power plants using fossil fuels in the United States has significantly increased, from 4% in 1900 to 43% in 2023. This improvement is attributed to reducing heat loss in the three main energy conversion processes: fuel combustion, steam generation, and electricity generation.
What are “orphaned” oil and gas wells and why should we care about them?
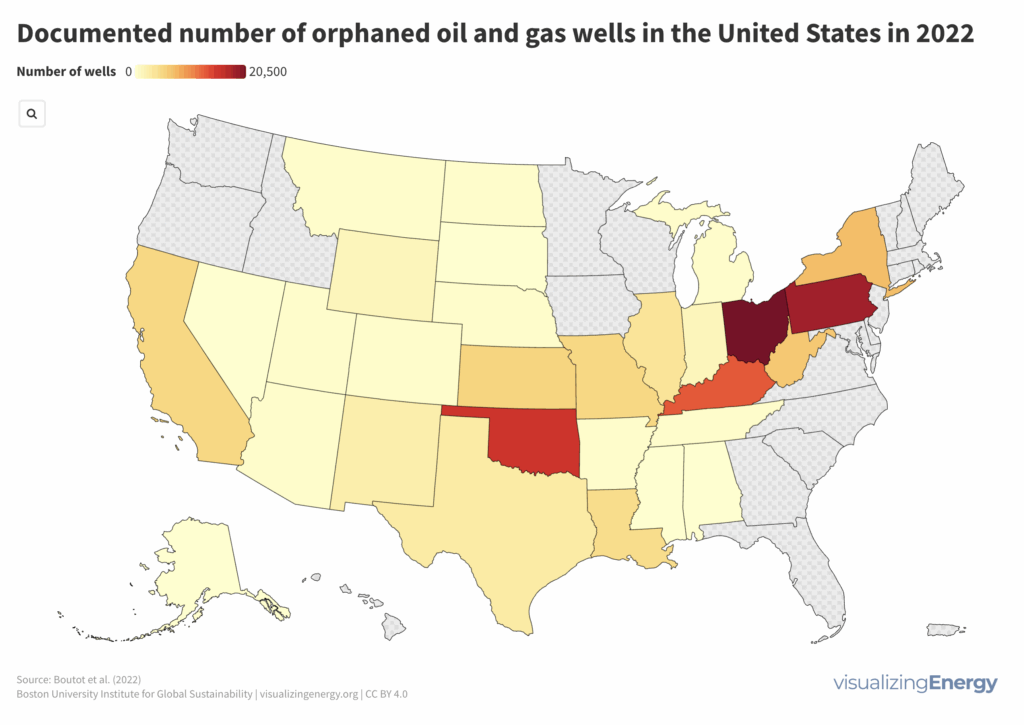
Of the millions of wells drilled, approximately 3.5 million are now abandoned, with some being properly plugged and others left unplugged. Unplugged wells can emit greenhouse gases, contaminate surrounding environments, and pose safety hazards. Orphaned wells, which lack a responsible operator, become the financial responsibility of the government and taxpayers.
Health impacts from oil and gas production in the United States
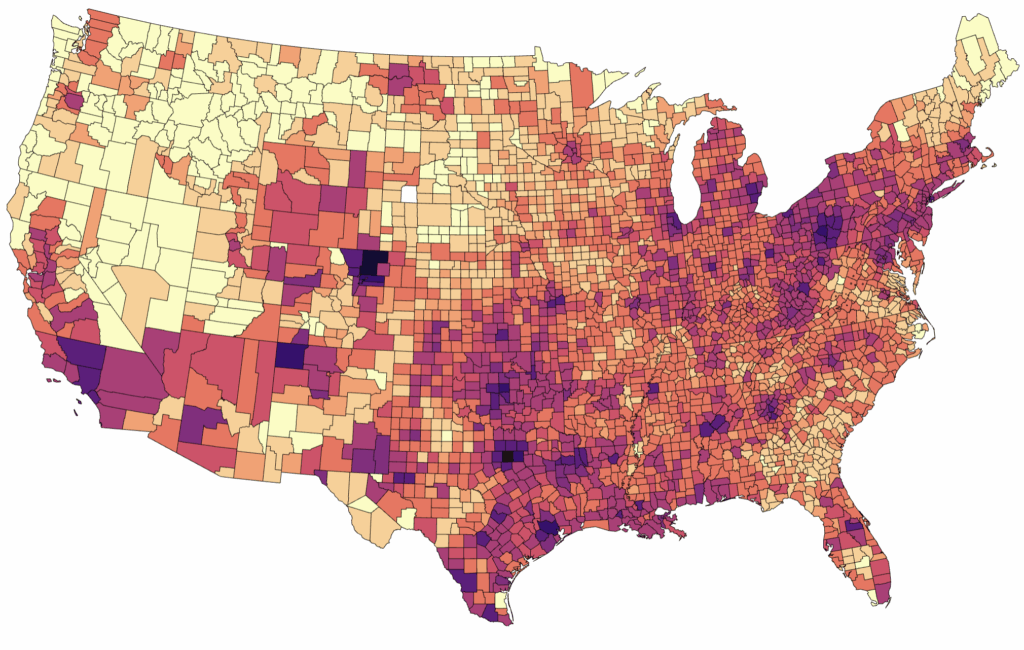
Oil and gas activities contribute to significant air pollution, resulting in adverse health effects and economic costs. Emissions from drilling, production, and transportation release pollutants that are linked to asthma, heart attacks, and premature deaths, especially impacting vulnerable populations. Addressing these emissions is crucial for protecting public health, mitigating economic burdens, and implementing comprehensive policies to reduce air pollution from the oil and gas industry.
Who are the major LNG importers and exporters?
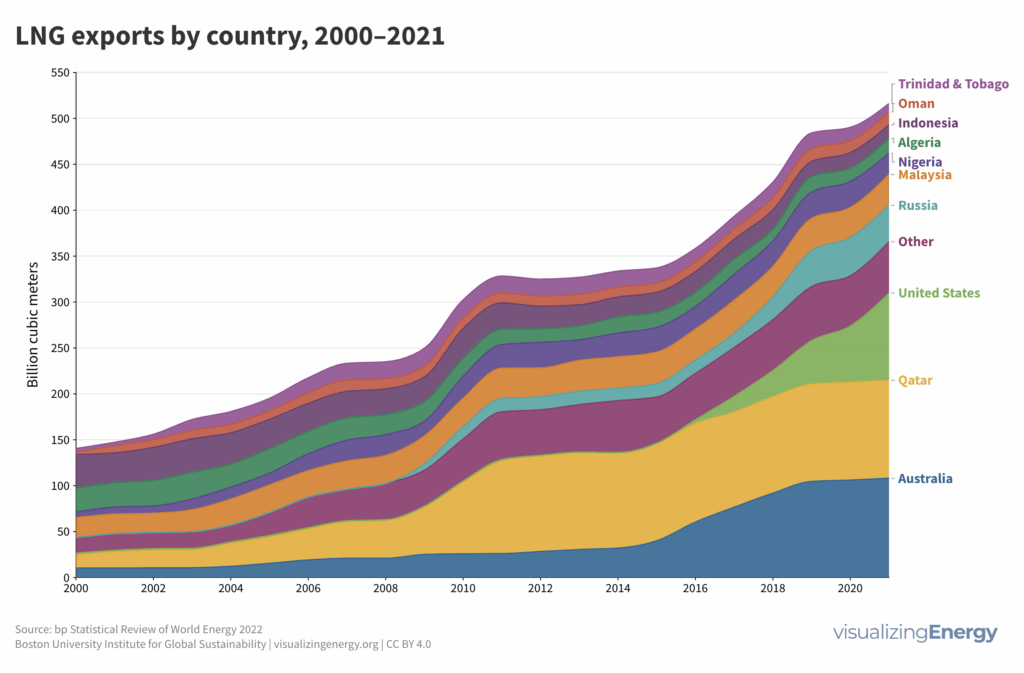
Global natural gas consumption has risen 70% from 2000 to 2022, fueled by economic growth and coal-to-gas transition. Hydraulic fracturing in the US has played a major role. Liquefied natural gas (LNG) enables long-distance shipping, but presents climate and energy justice challenges.
