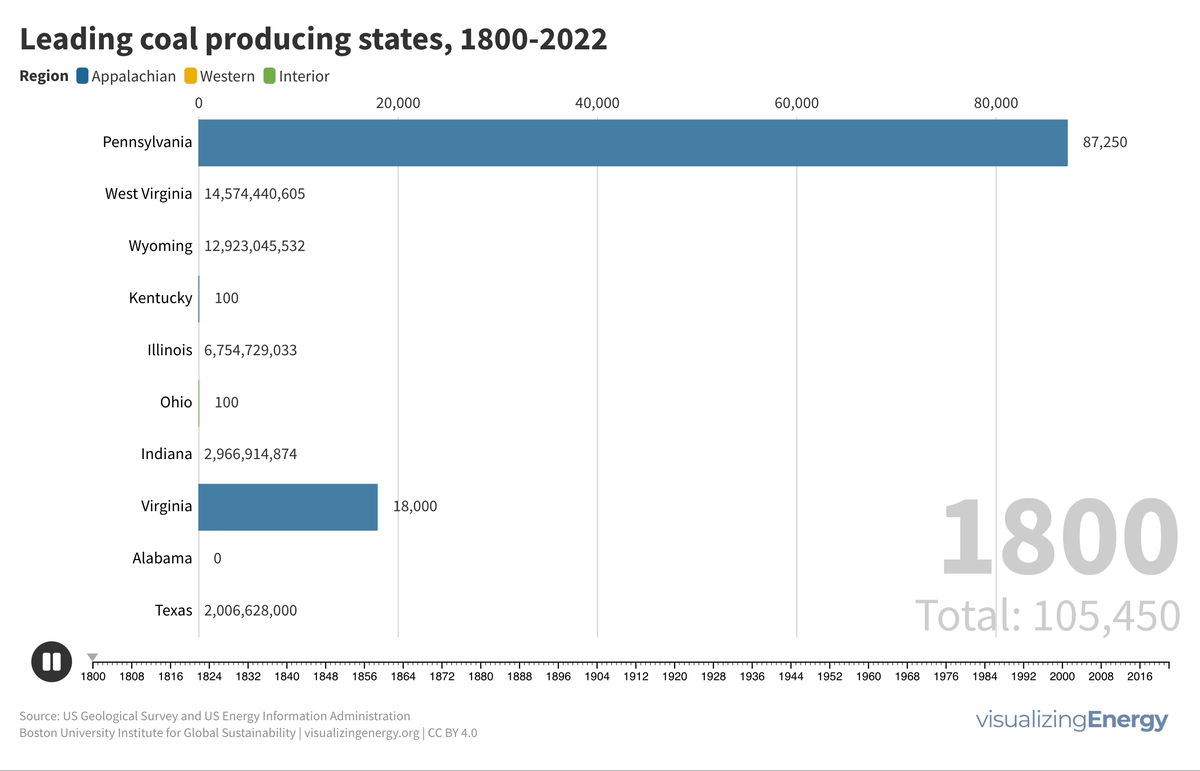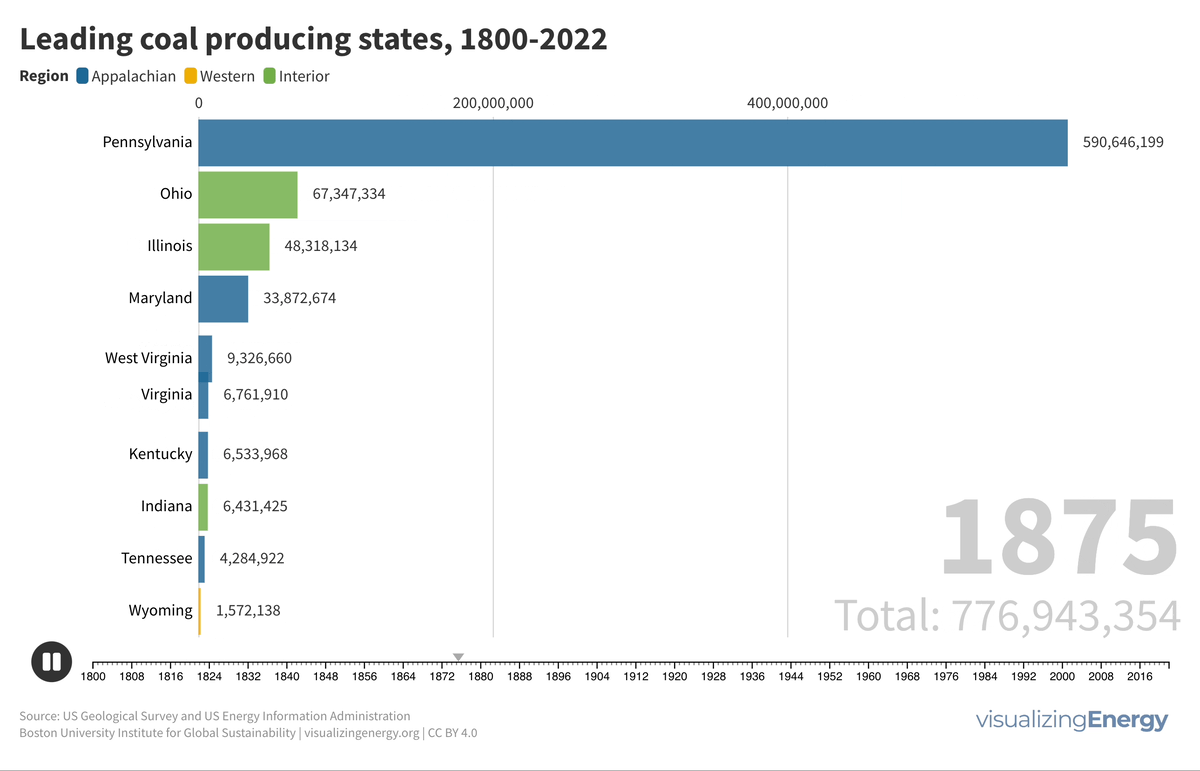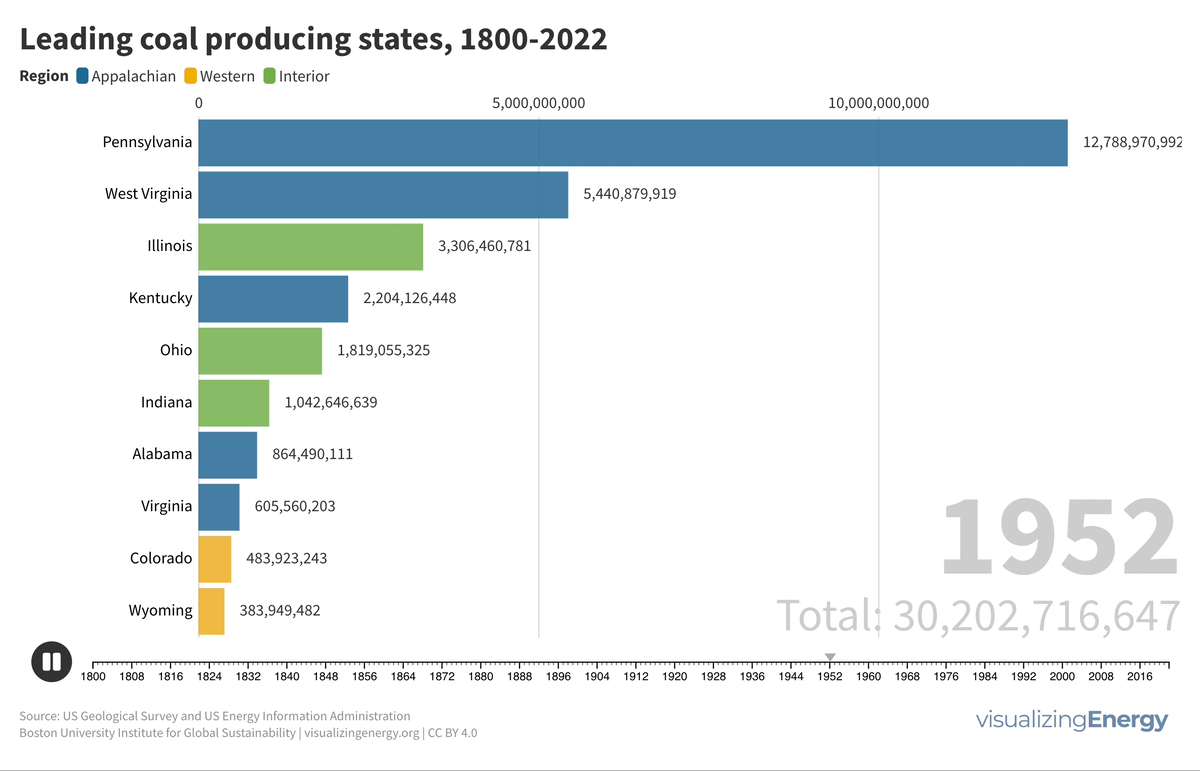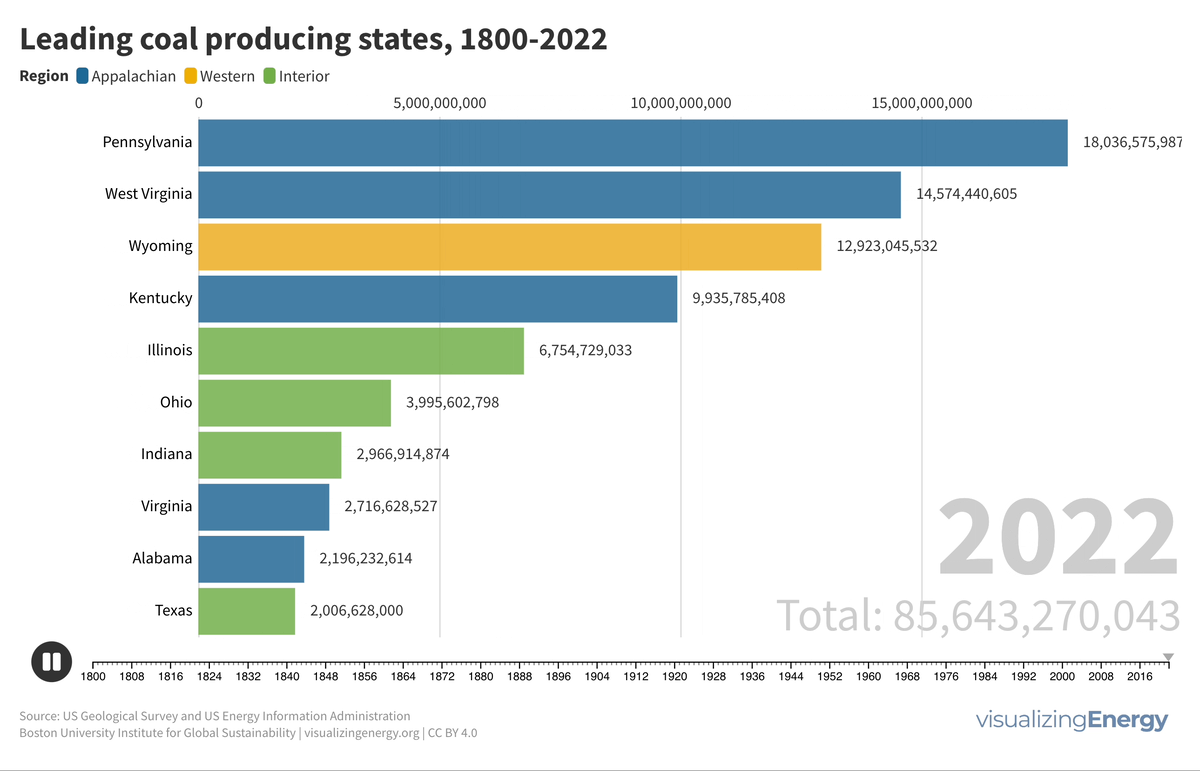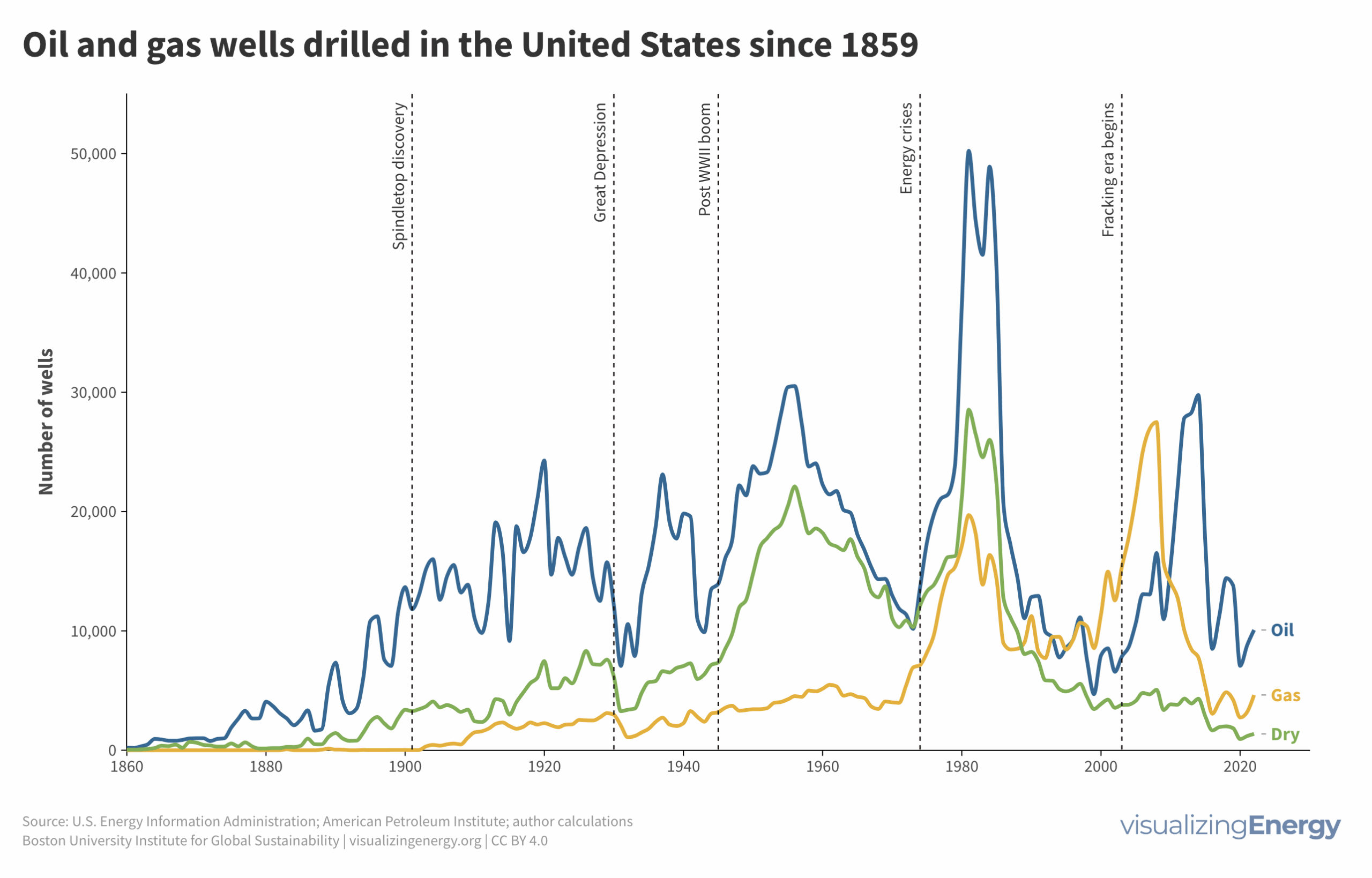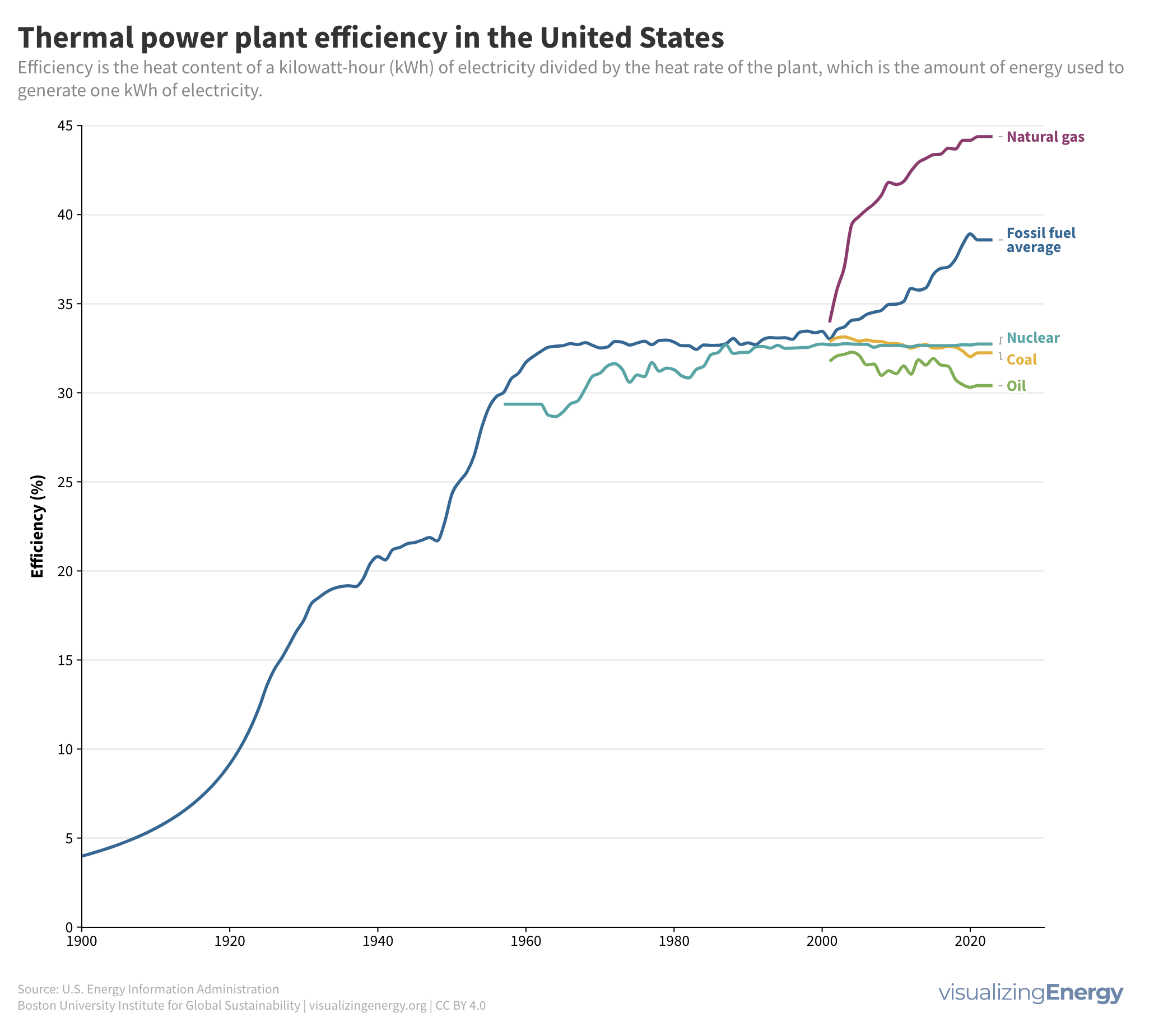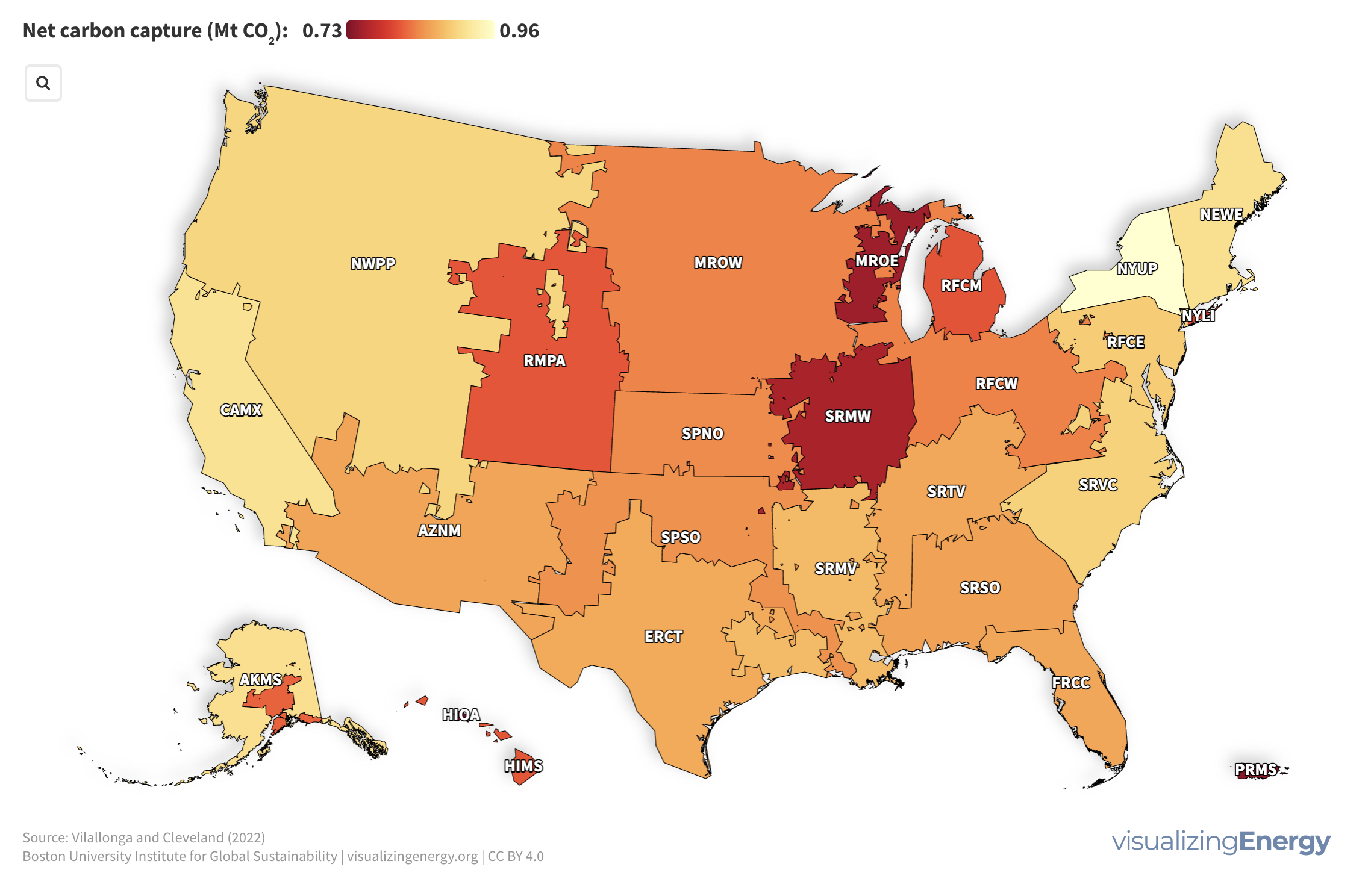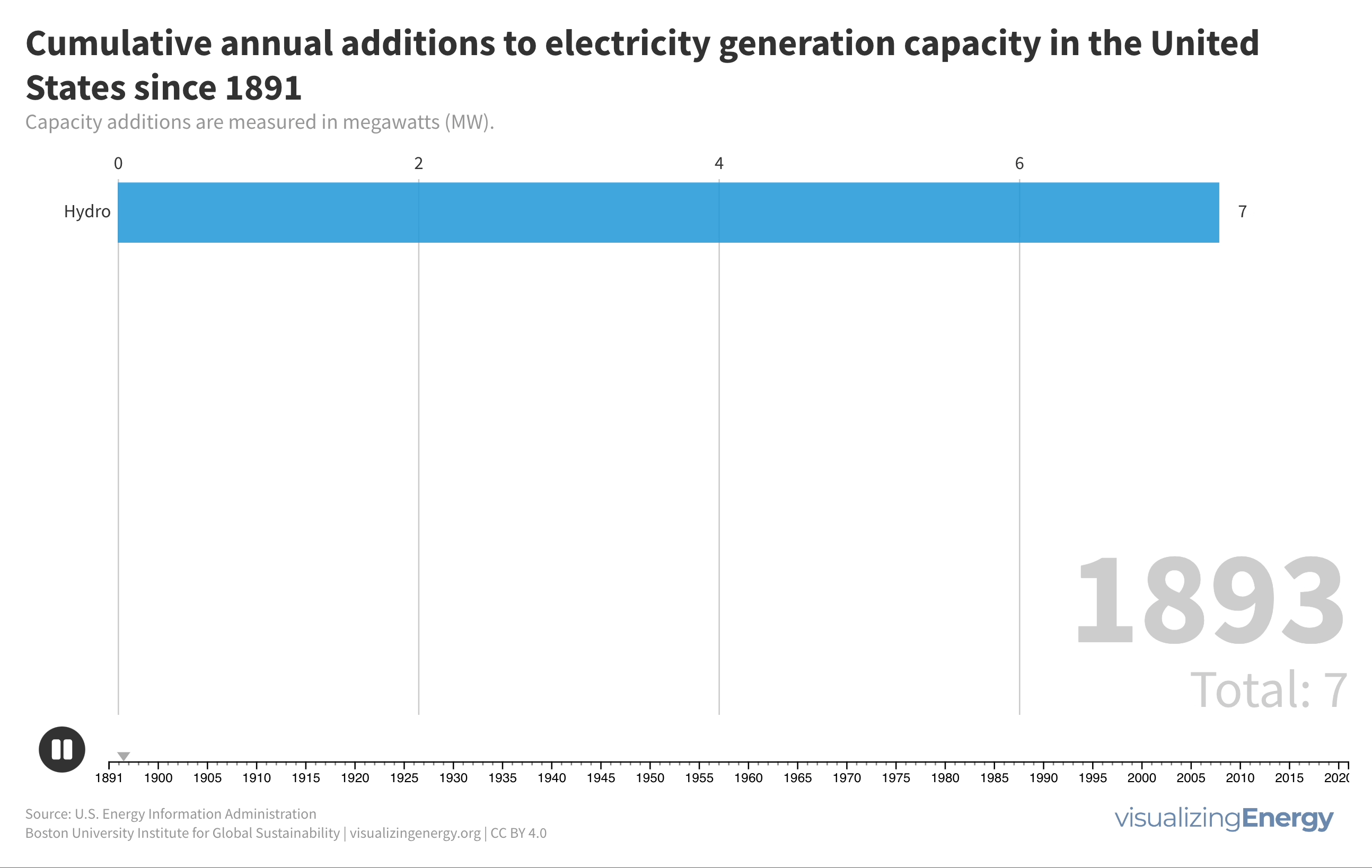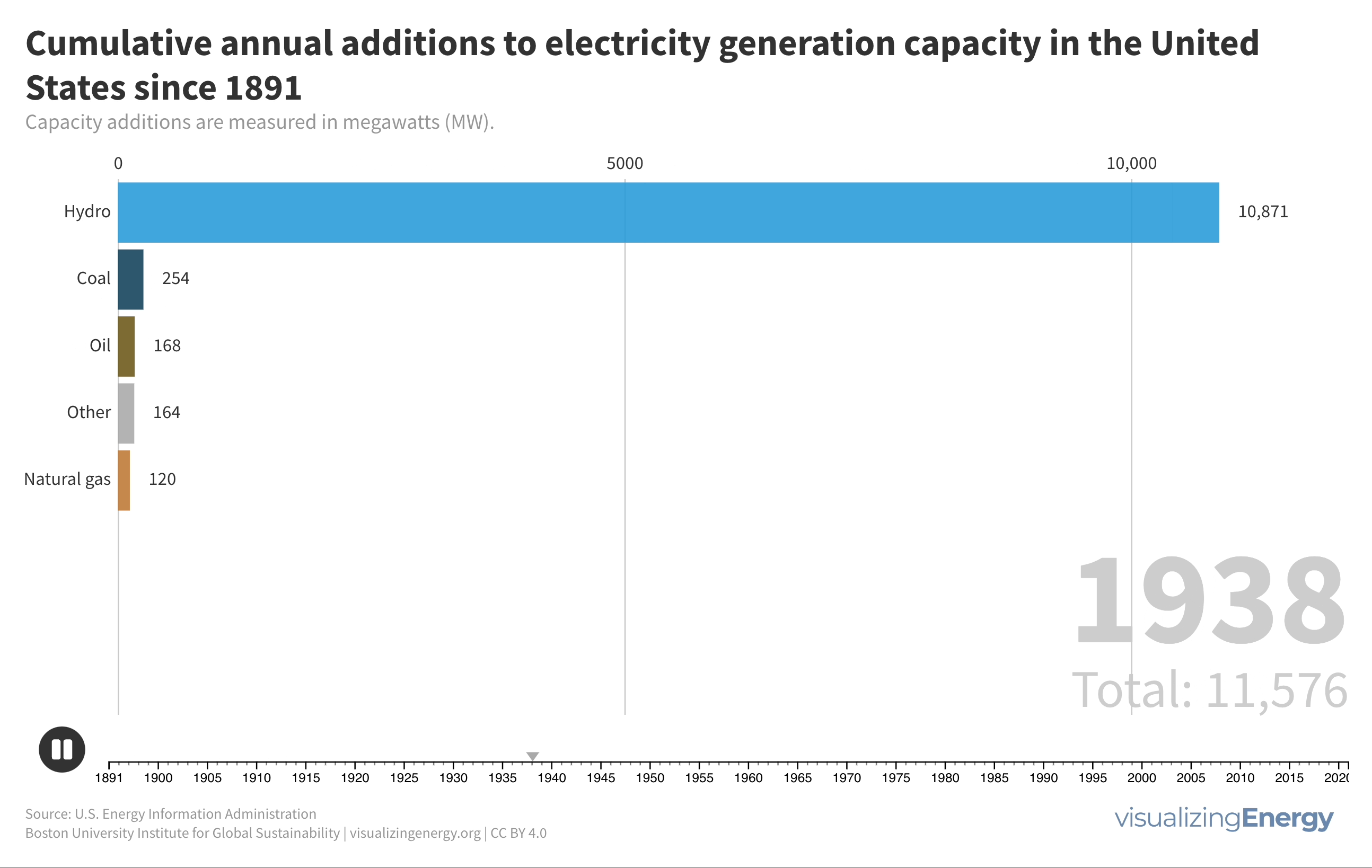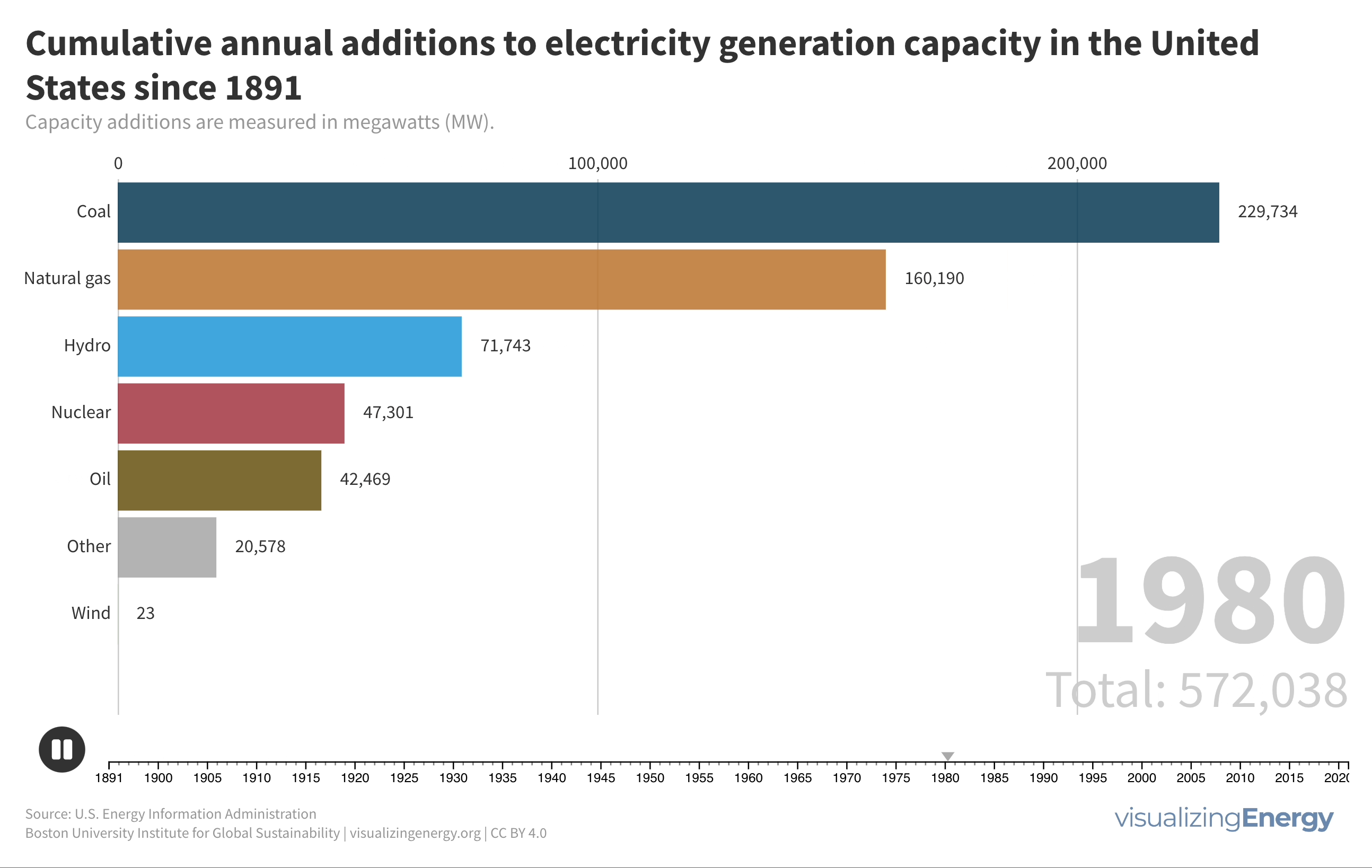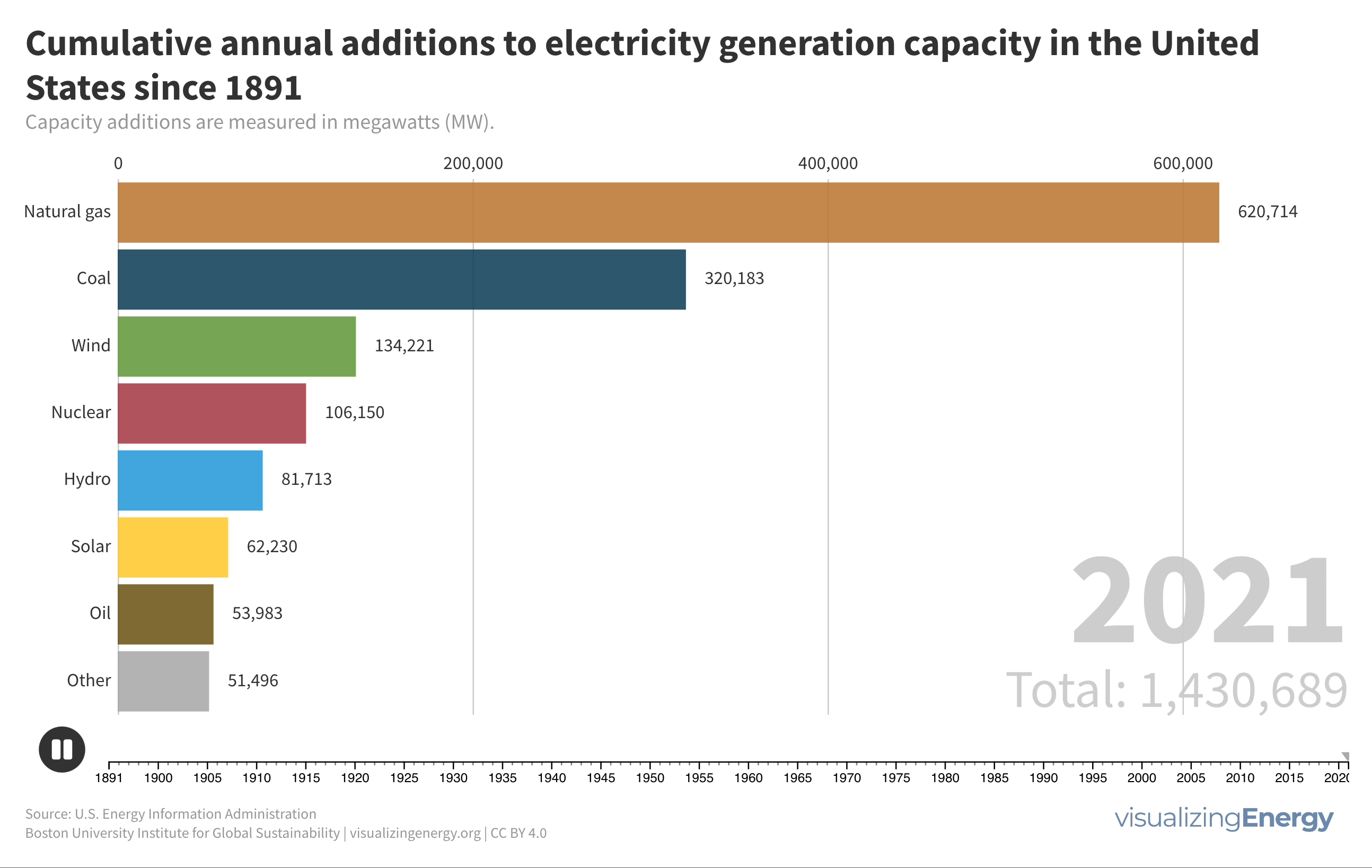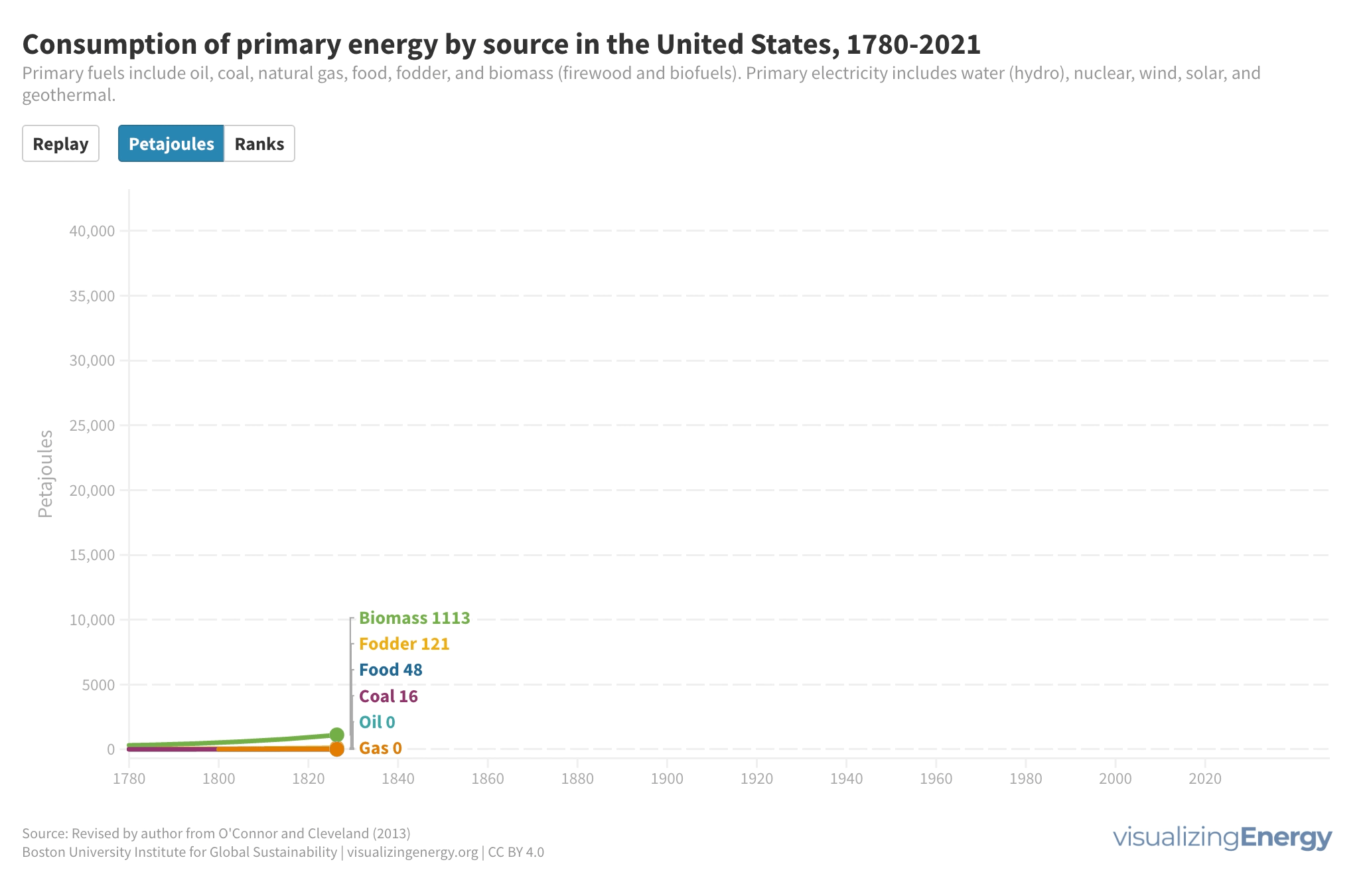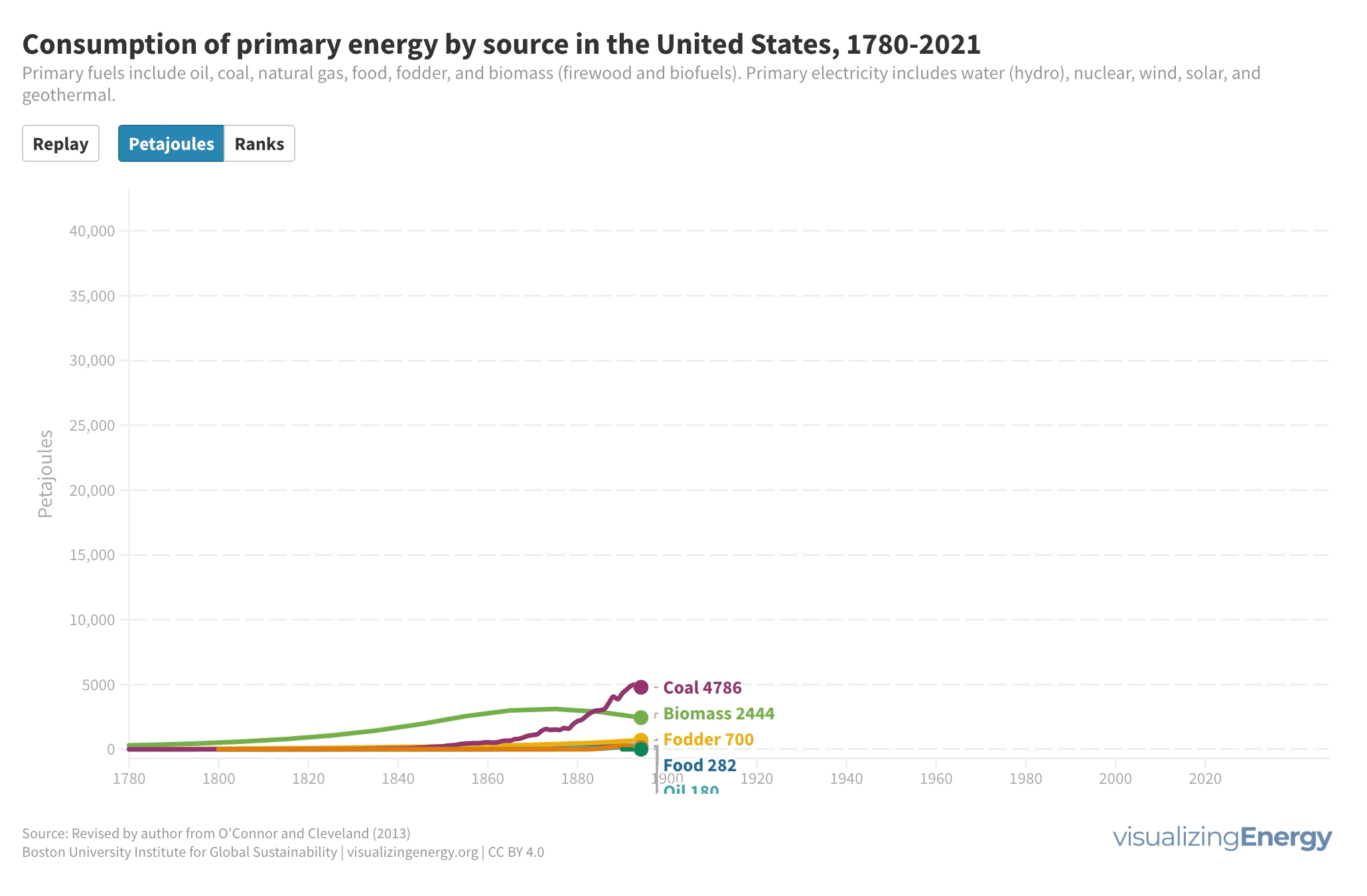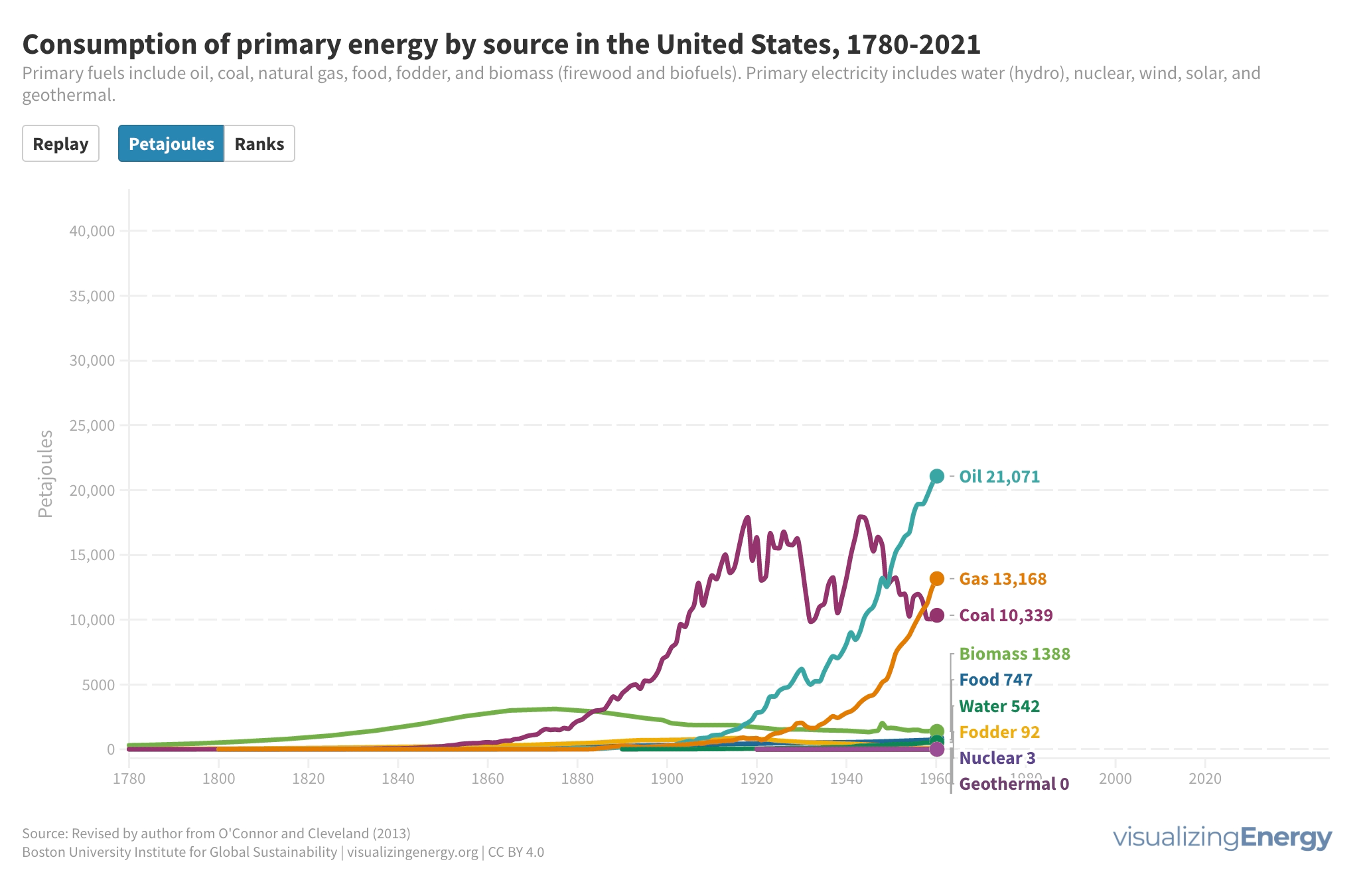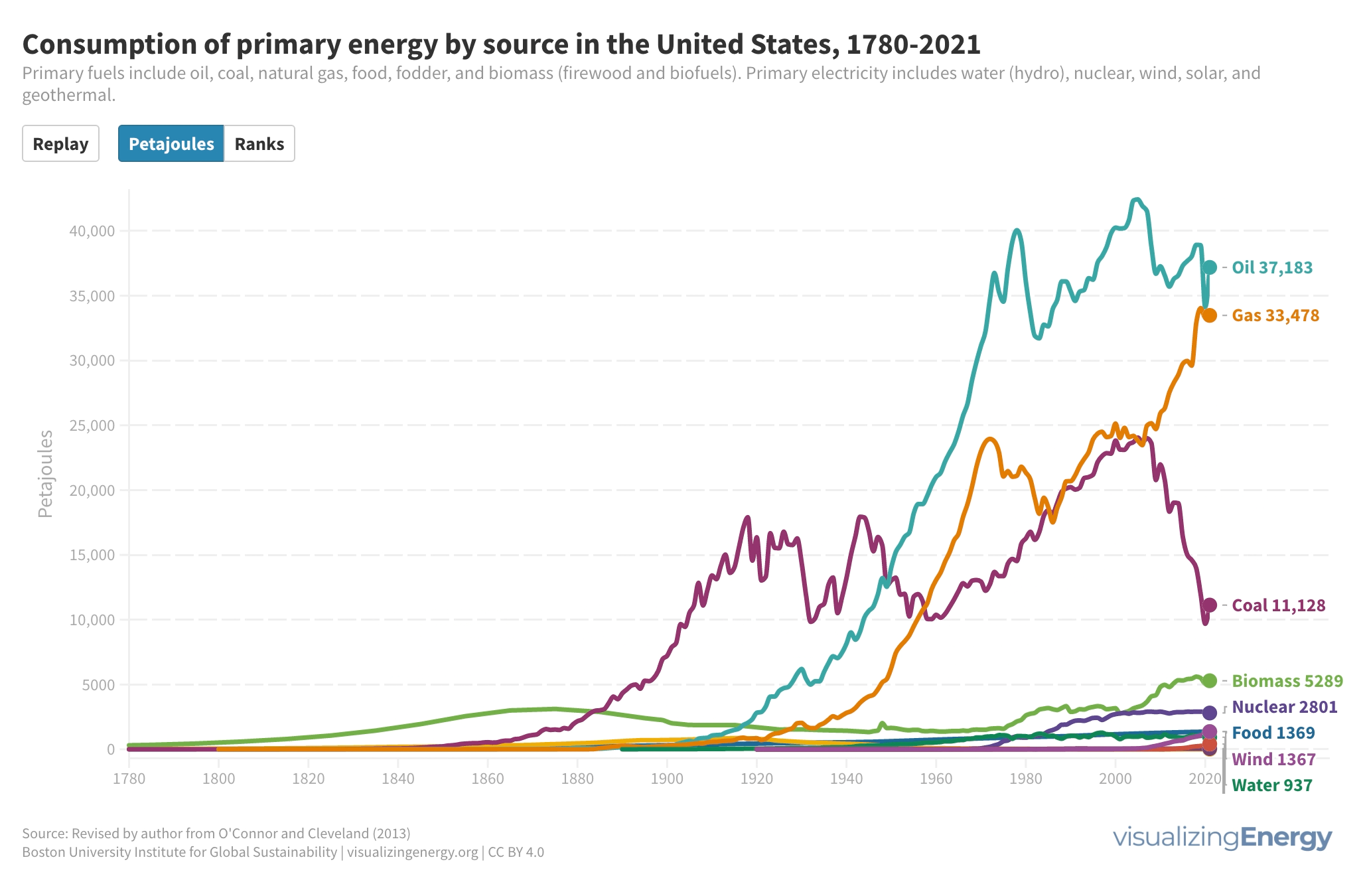
Watch the history of oil power plants in the United States
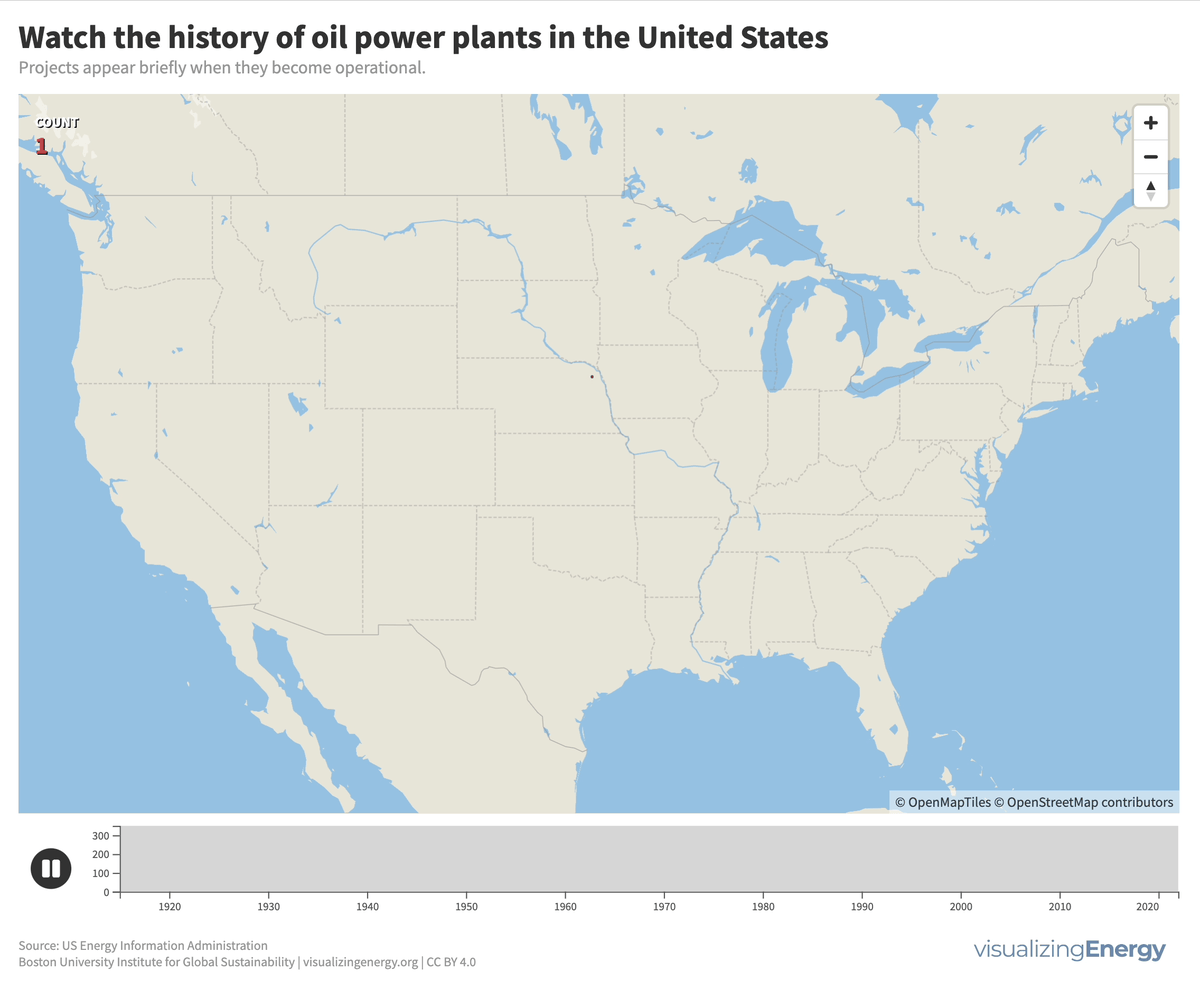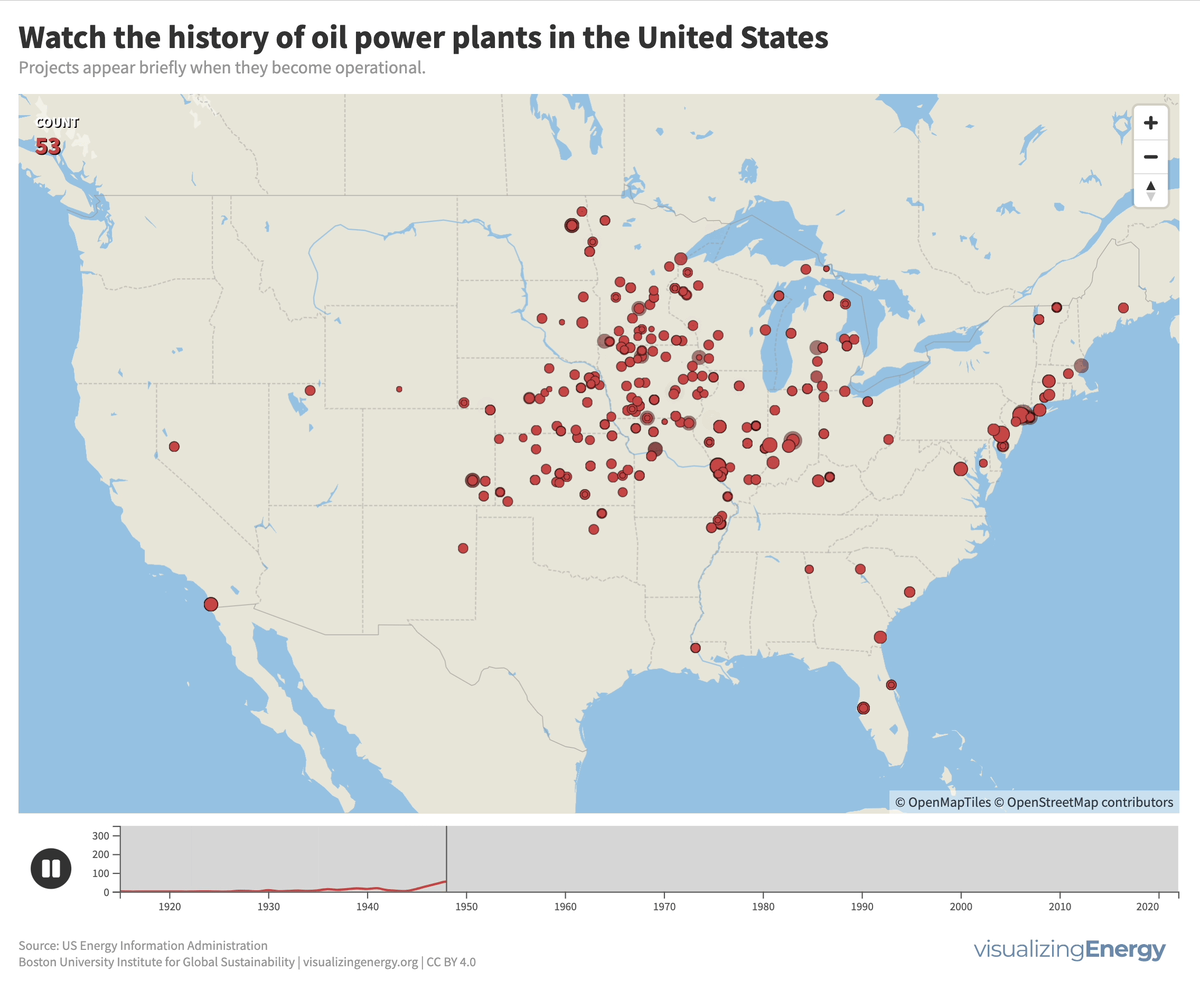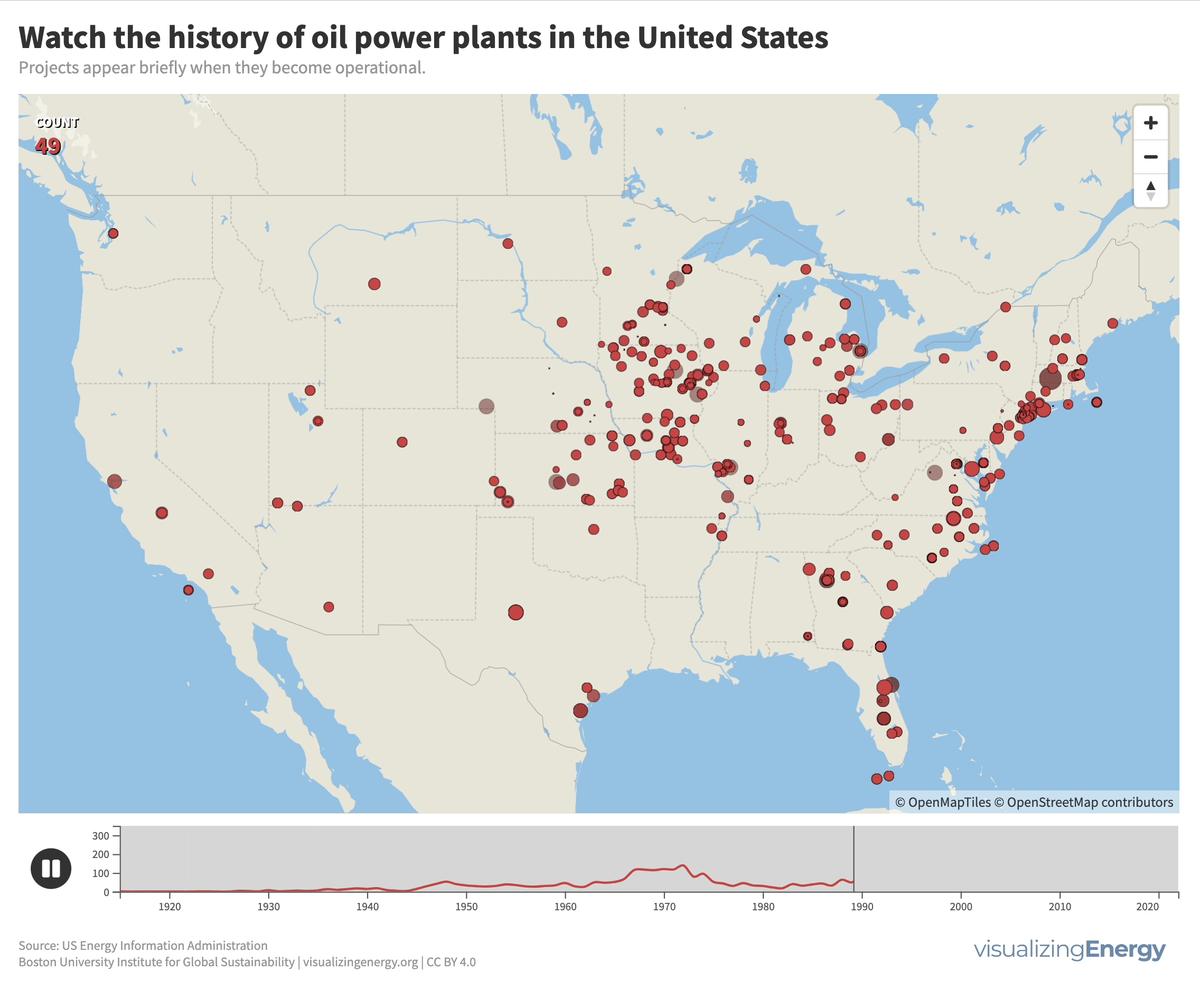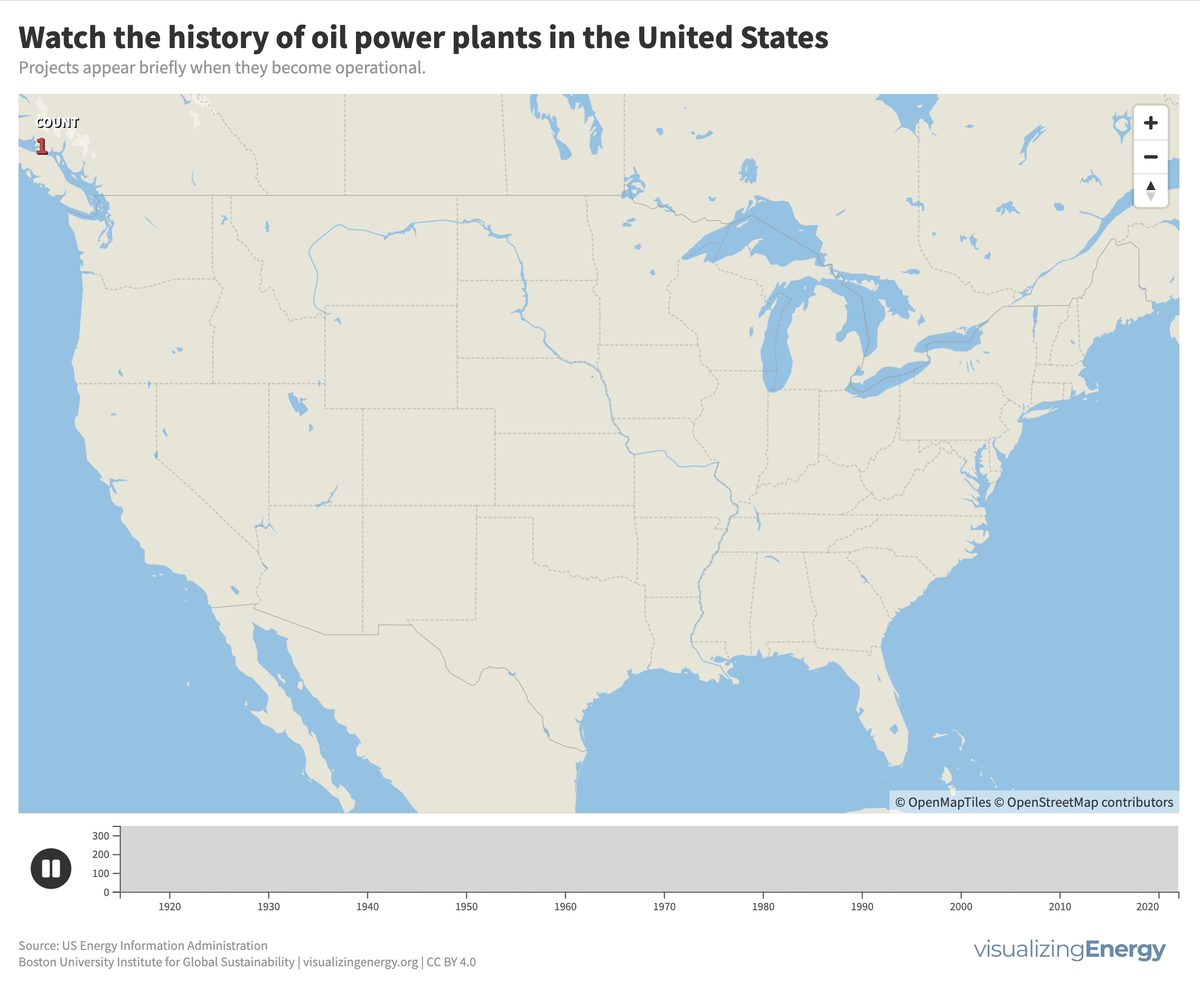
In 2022, the US had about 4,000 petroleum-burning generators, providing only 0.6% of the nation’s electricity due to lower efficiency and higher costs than alternatives. These smaller generators are mainly used for peak power and emergency backup, with policies since 1978 discouraging their use to reduce oil dependence for national security.