Watch the history of biopower plants in the United States
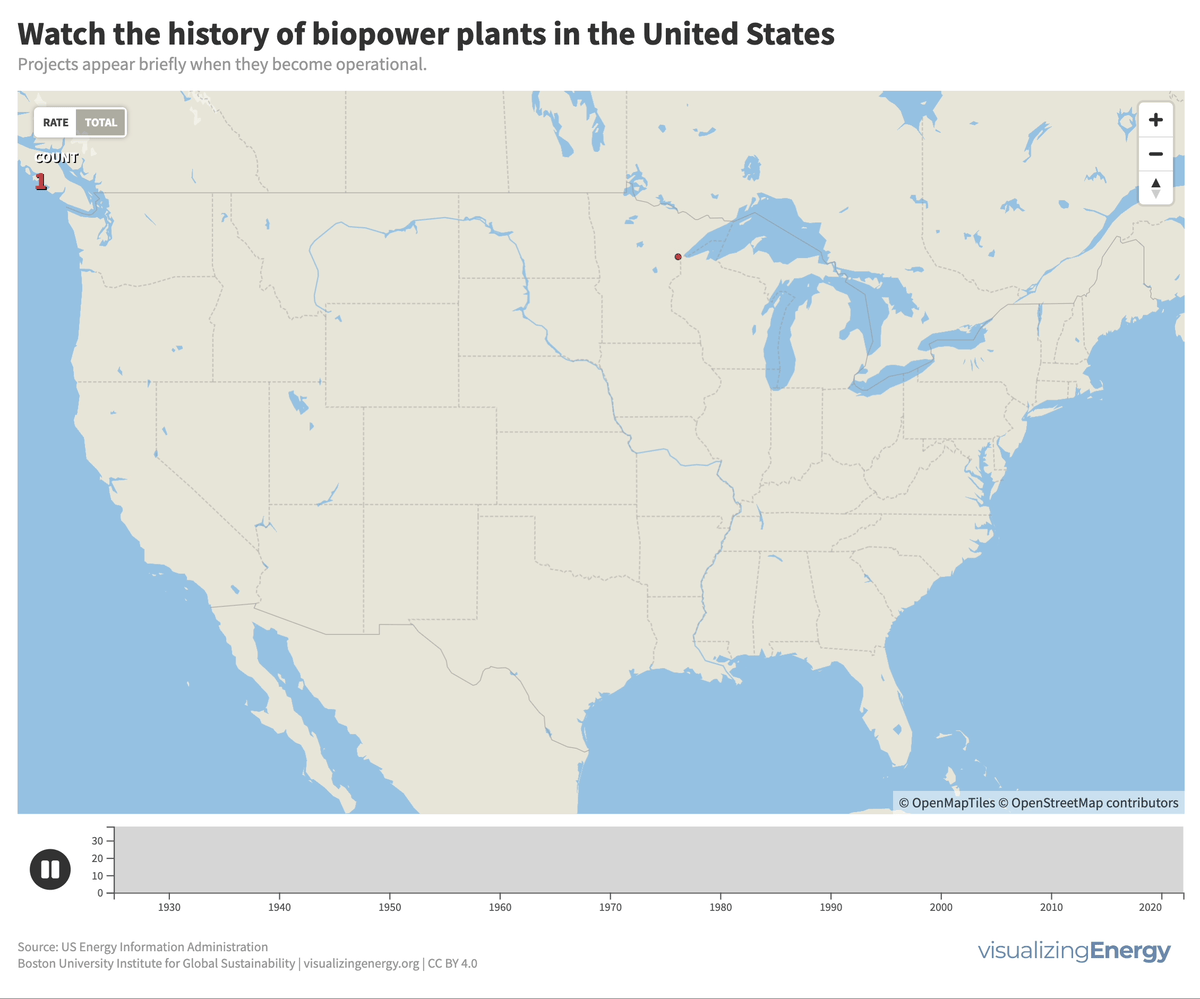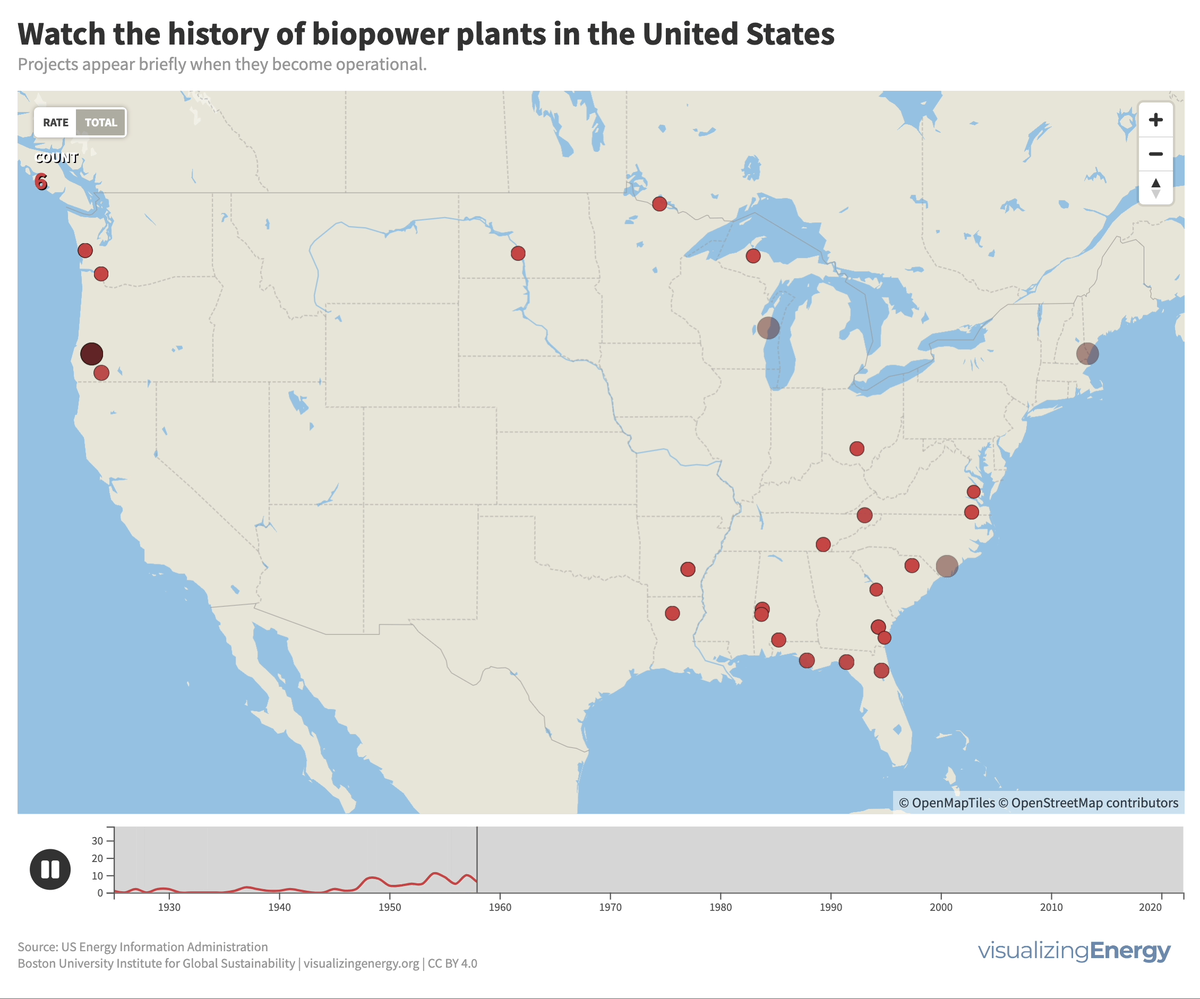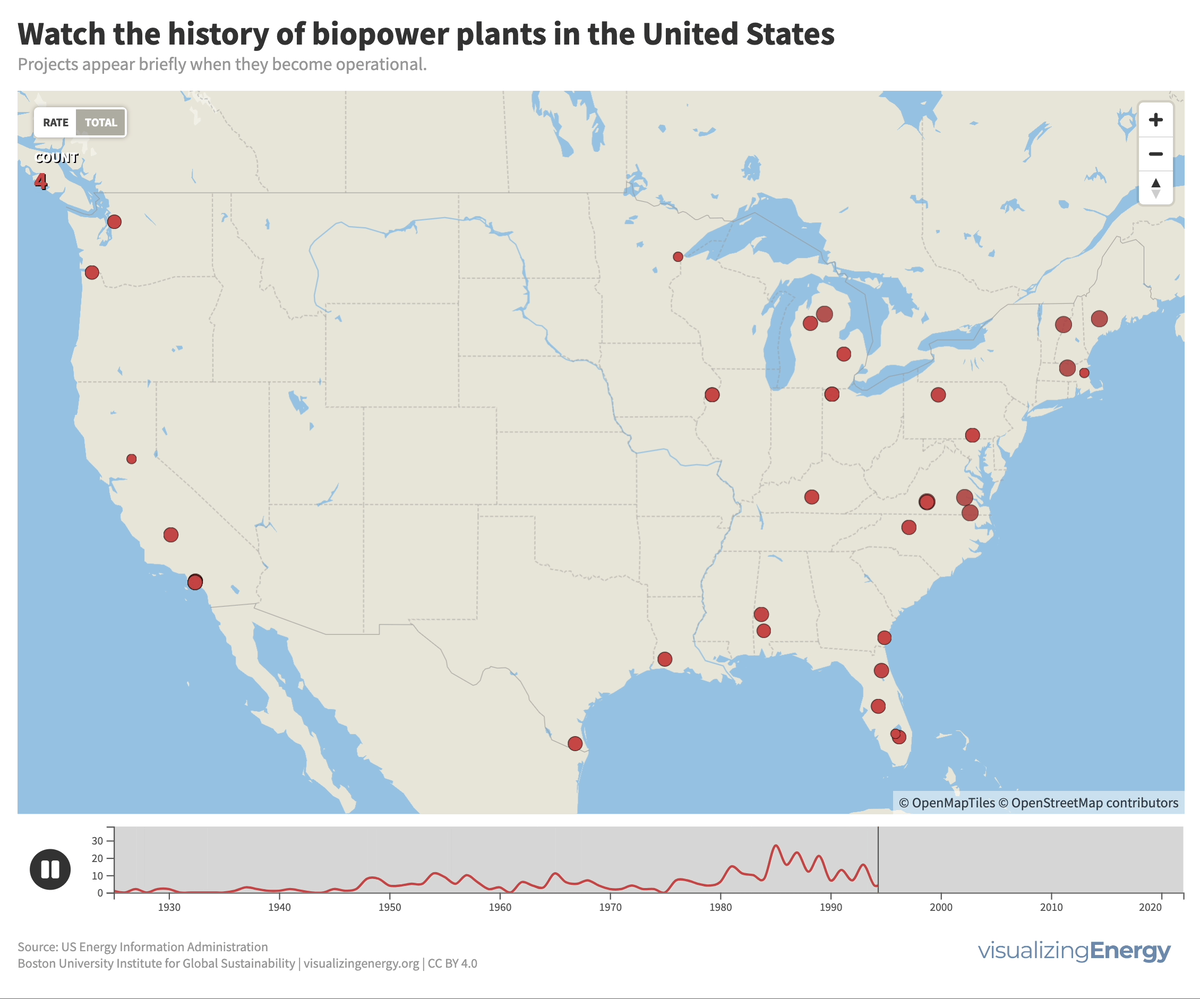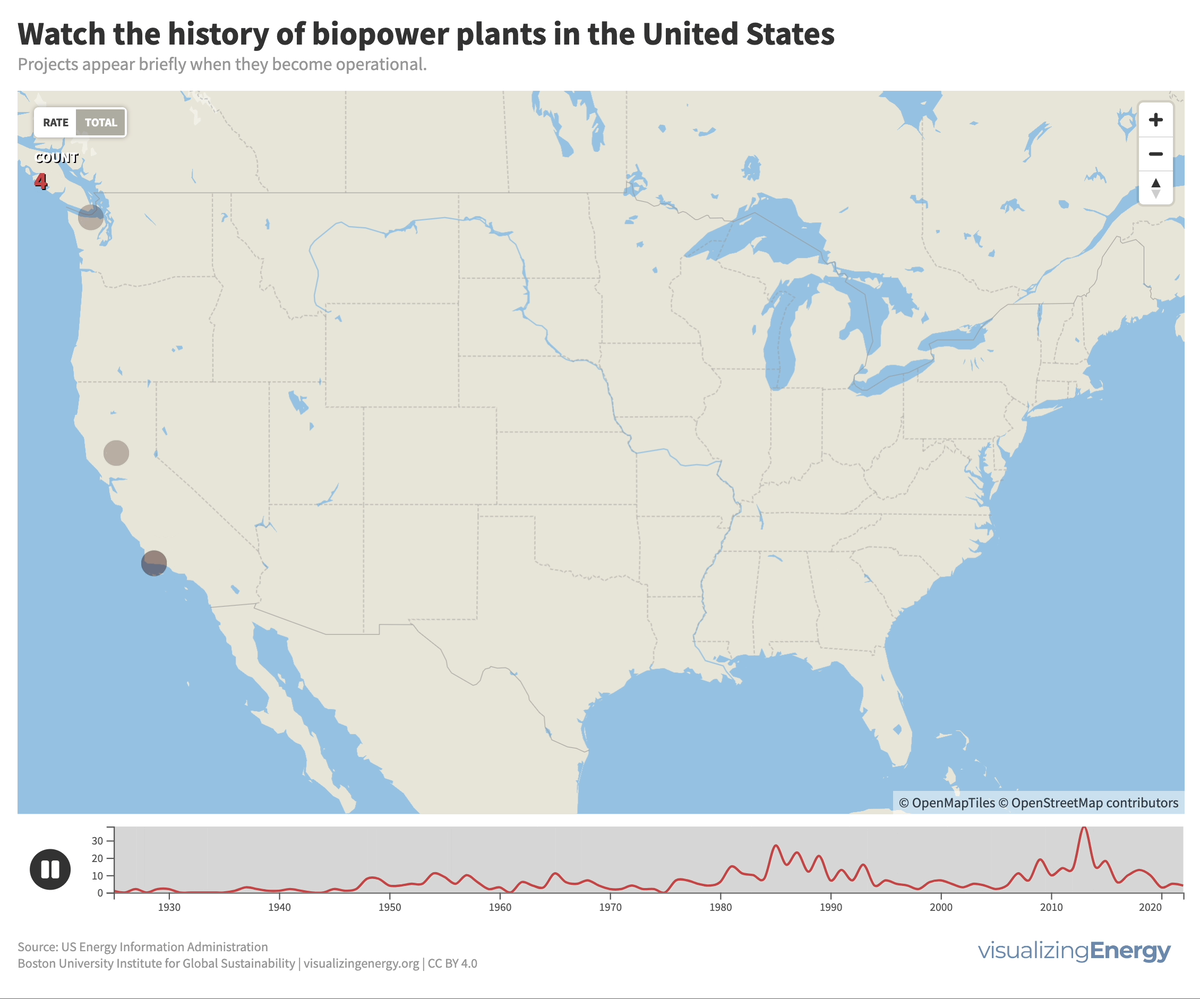
Biomass generates electricity, or biopower, from sources like wood, agricultural residues, and urban waste. In the US, it accounts for 1.2% of electricity.

Biomass generates electricity, or biopower, from sources like wood, agricultural residues, and urban waste. In the US, it accounts for 1.2% of electricity.
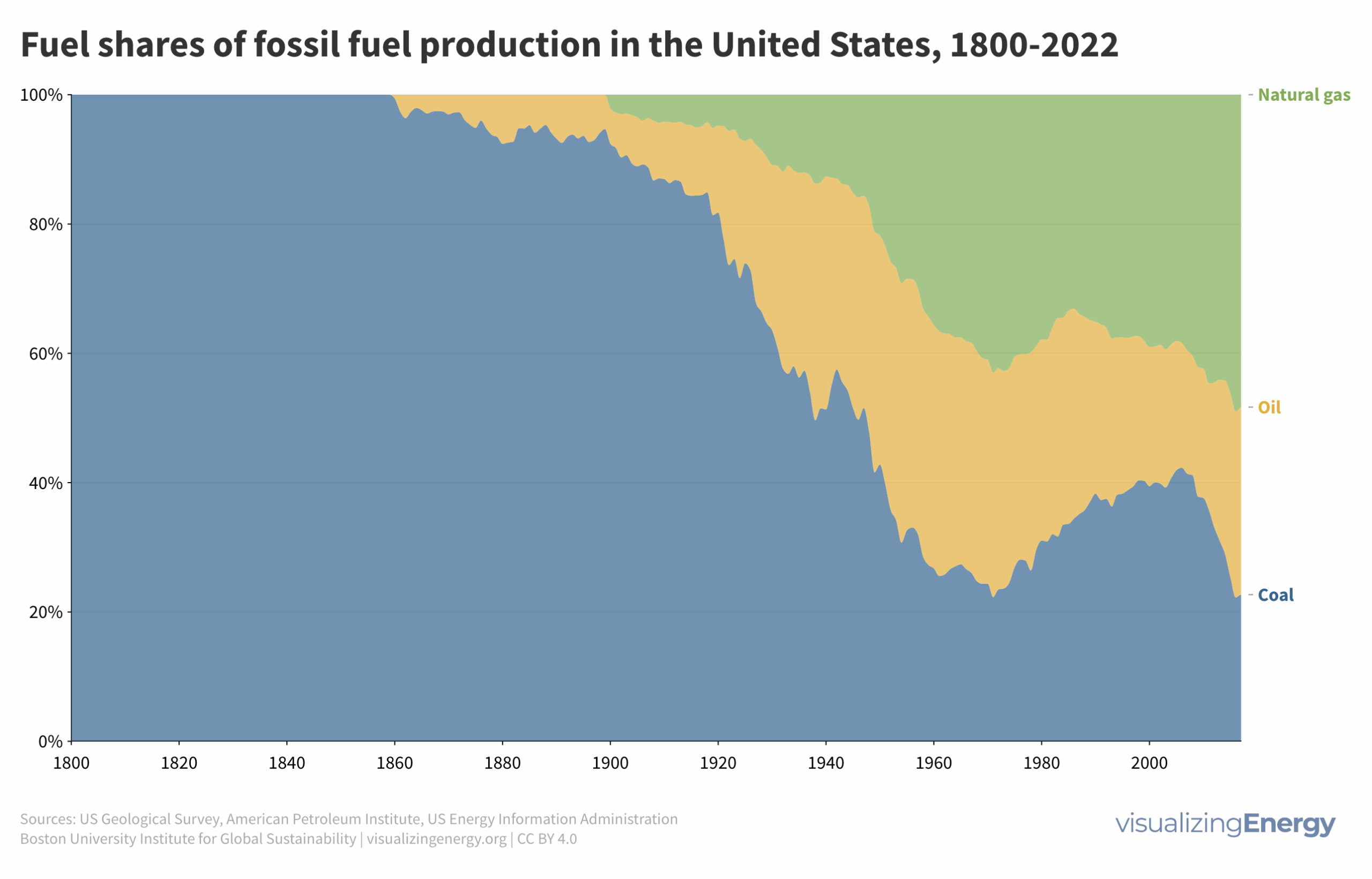
Coal, oil, and natural gas have played major roles in U.S. industrialization and energy. Coal dominated in the 20th century, but oil and natural gas gained prominence after World War II. Fracking revitalized oil and gas production, leading to major shifts in fossil fuel production and investment trends.
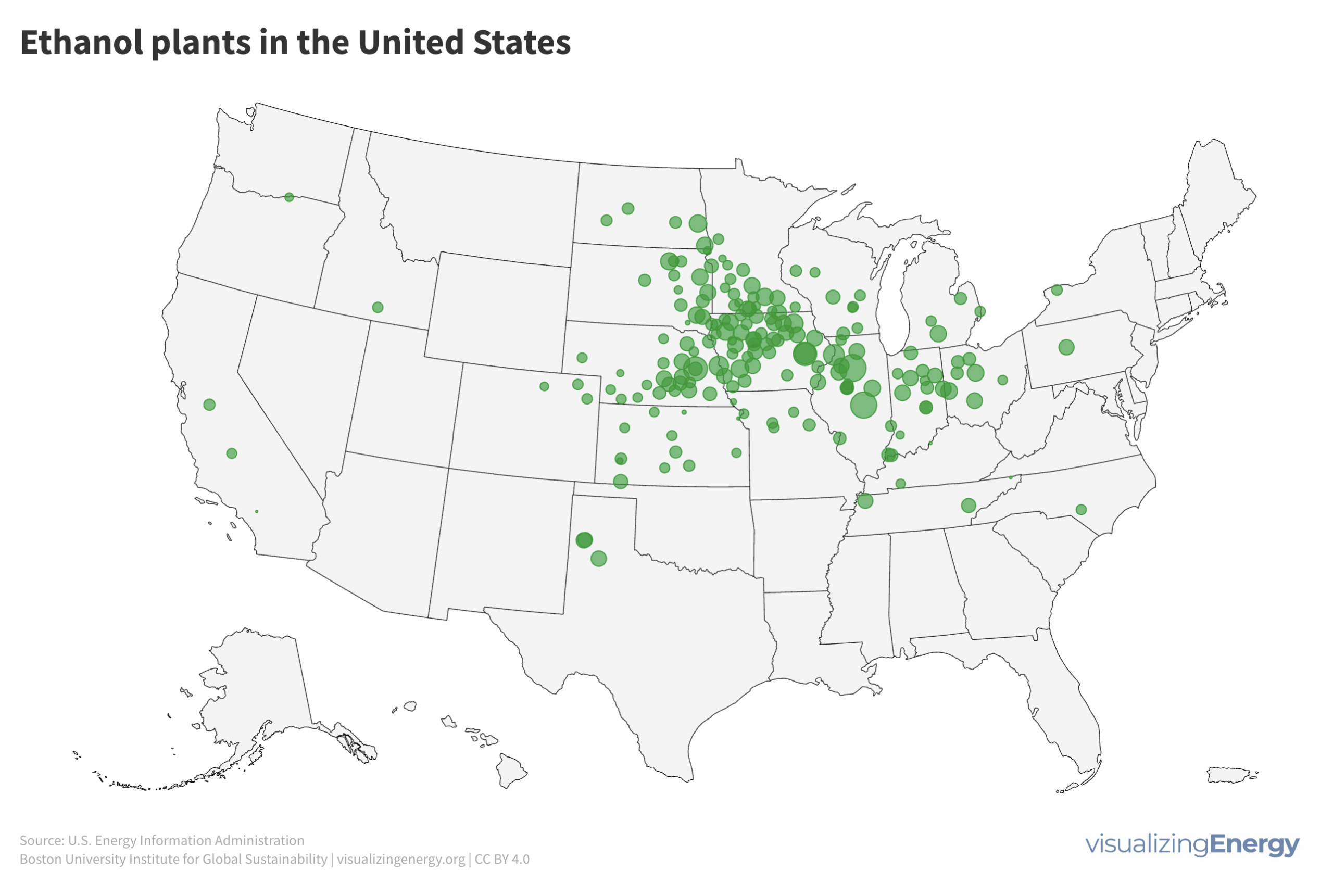
In the United States, ethanol is mainly produced in the Midwest from corn, with Iowa, Nebraska, and Illinois leading in capacity. Ethanol is used as a fuel additive, with E85 being a high-level ethanol-gasoline blend used in flex-fuel vehicles. Biodiesel, made from vegetable oils and animal fats, is mainly produced in states with these feedstocks. Renewable diesel, chemically identical to petroleum diesel, is primarily used in California to meet emissions regulations.
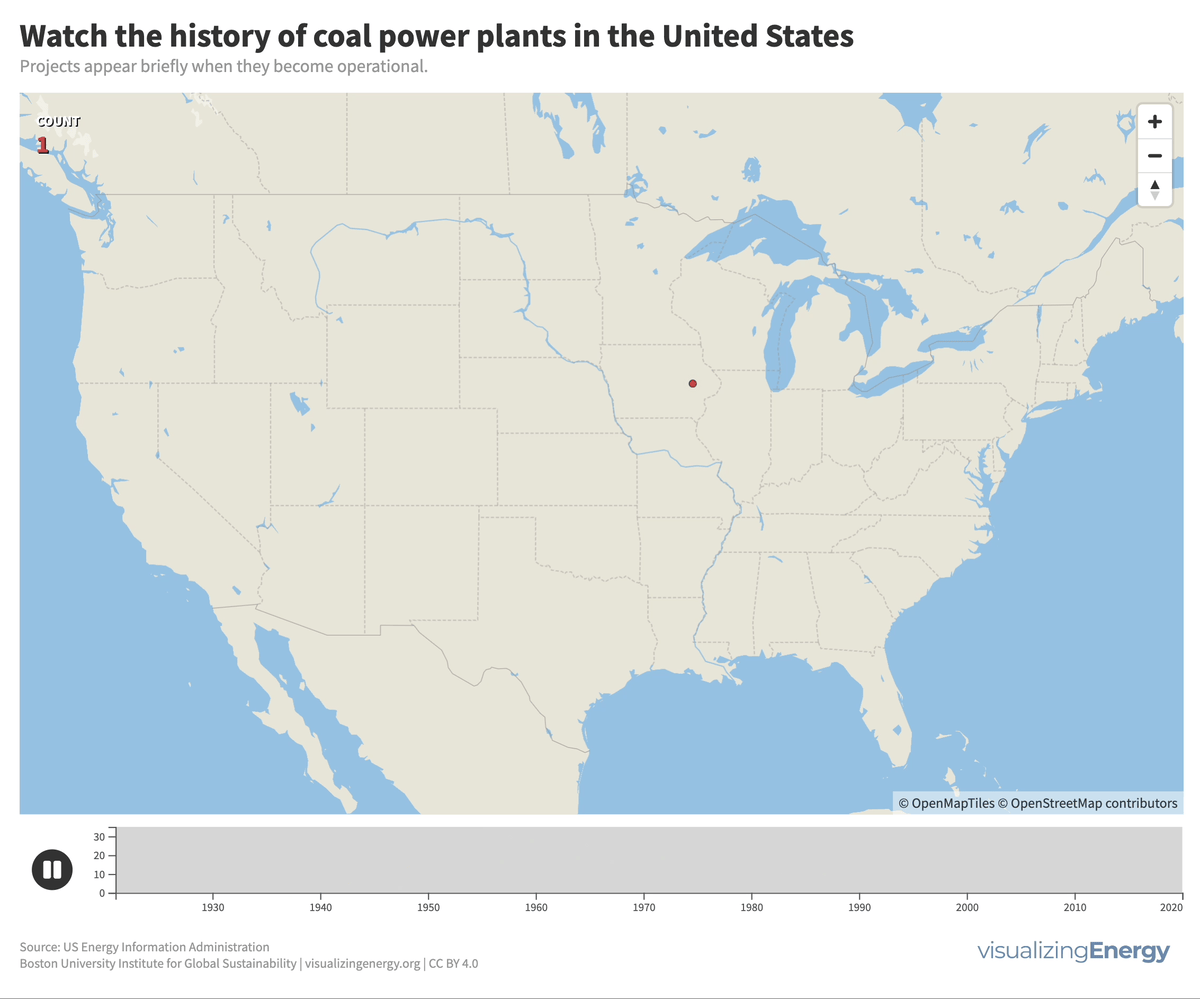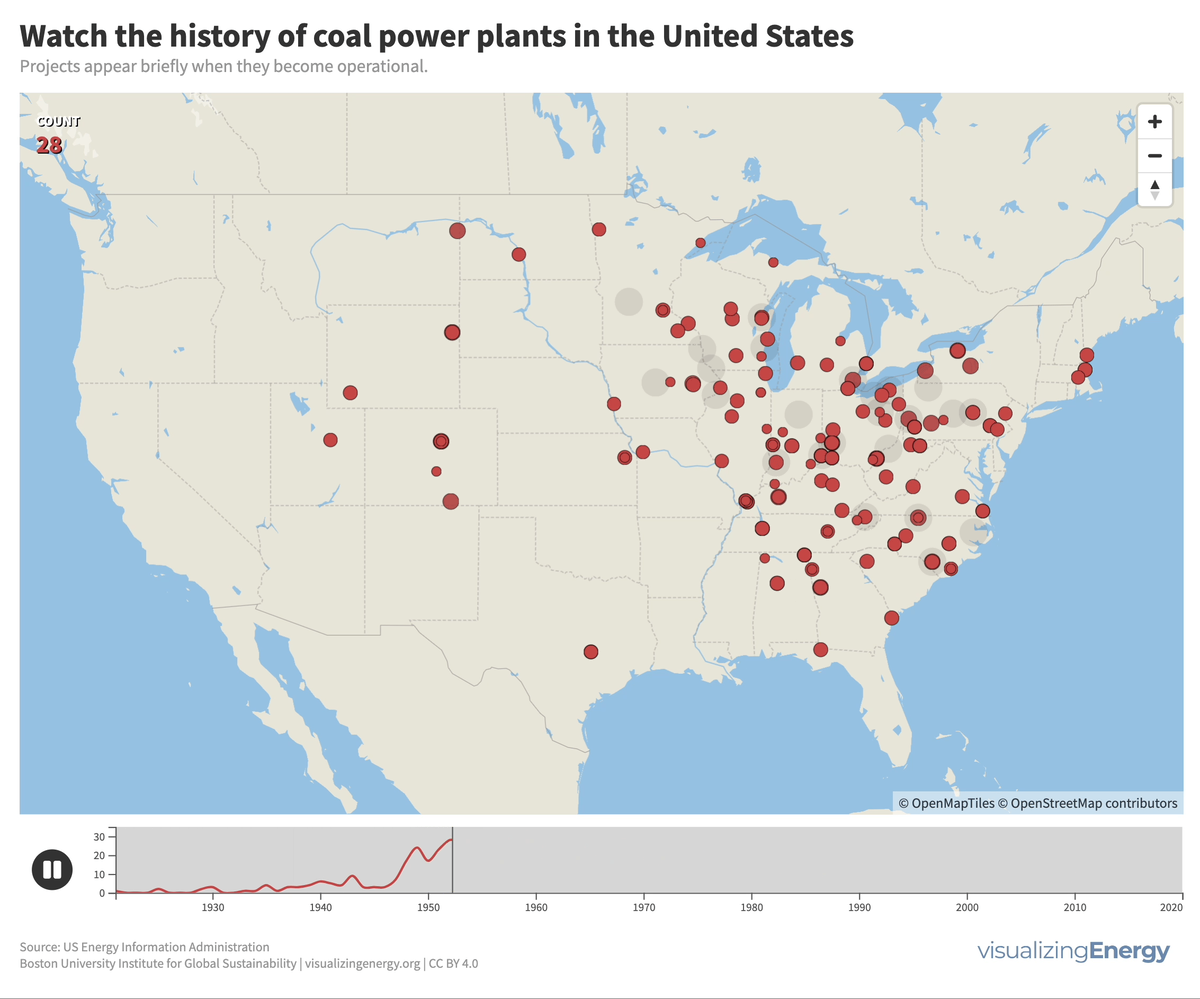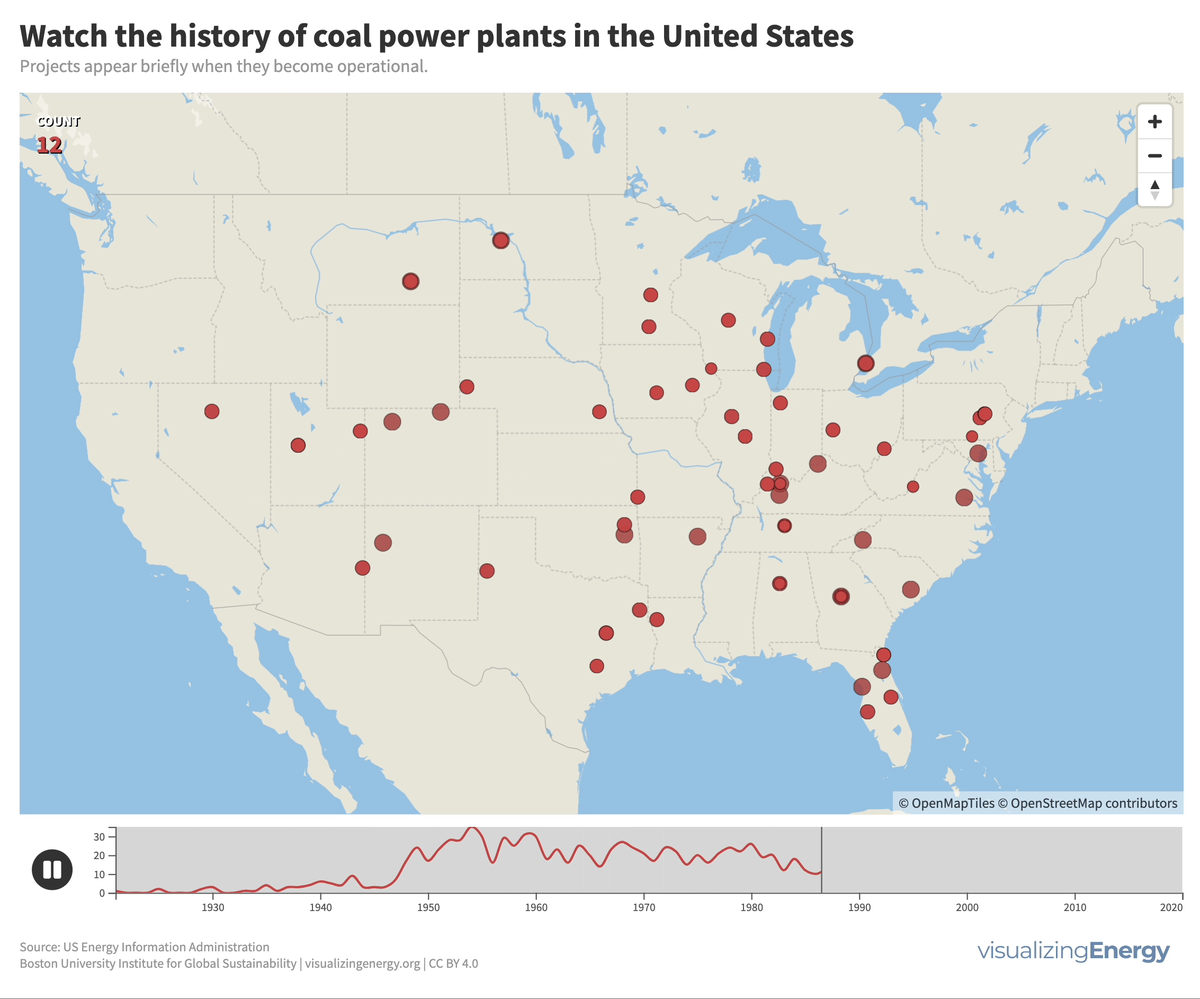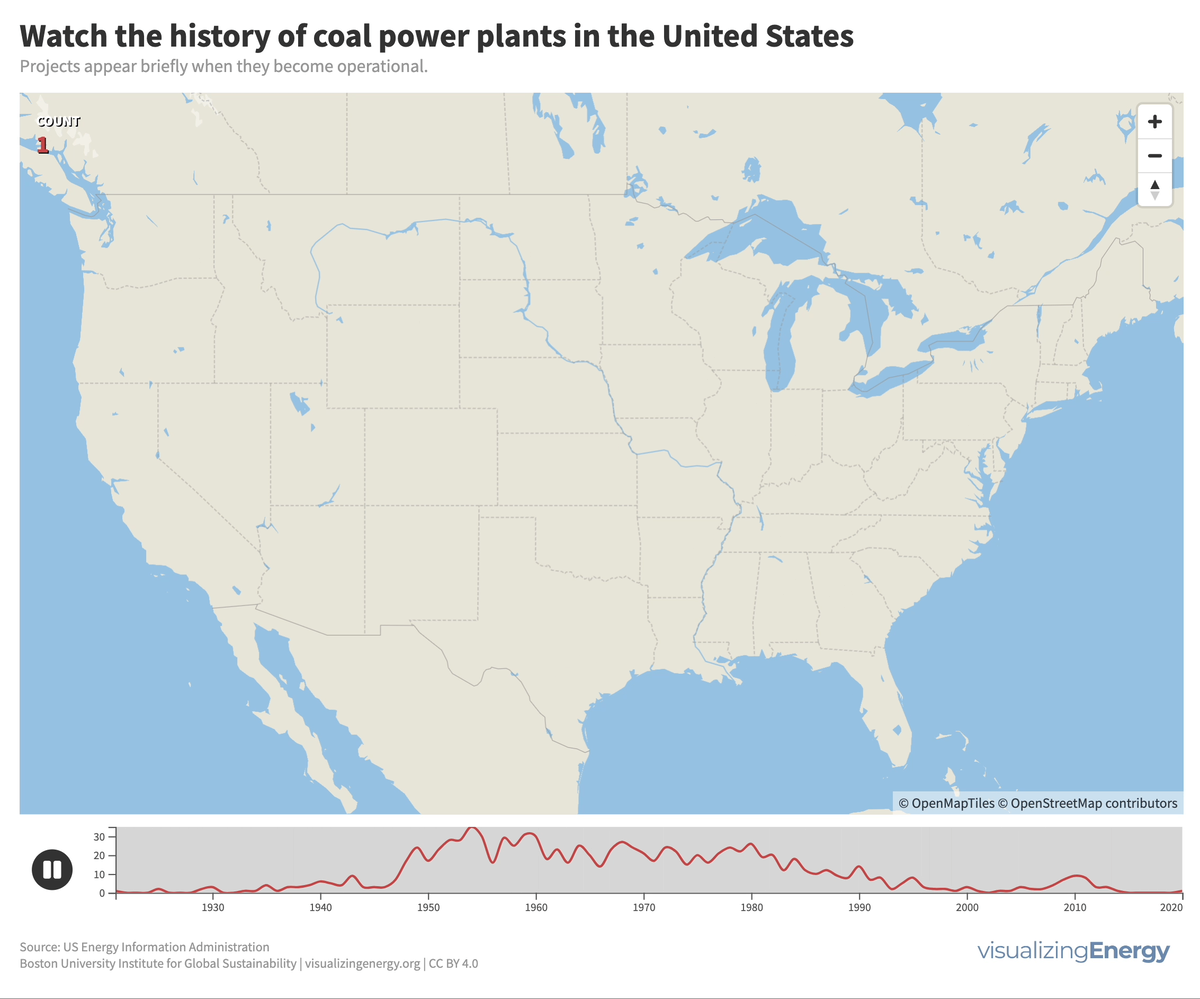
Coal played a significant role in the US, generating half of the nation’s electricity in 1920 and maintaining that share for decades. However, aging coal plants are being retired due to competition from efficient natural gas and renewable energy sources, as well as state climate policies. This shift reflects growing concerns about cost and carbon emissions.
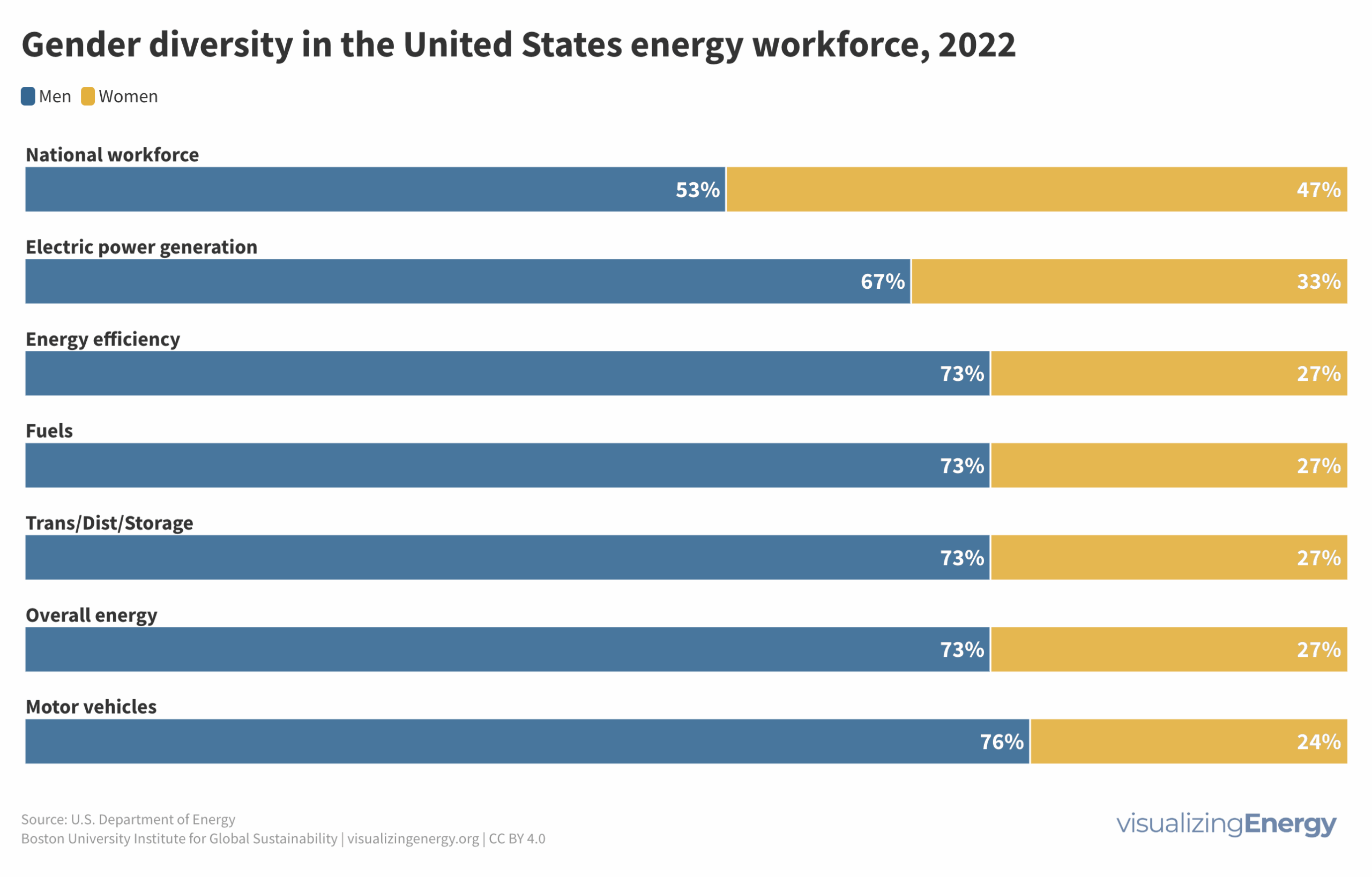
Gender equity is vital for economic stability. In the U.S. energy industry, women hold 27% of jobs, despite recent growth. Challenges persist globally in solar, wind, and hydropower industries, emphasizing the need for ongoing efforts to address gender disparities.
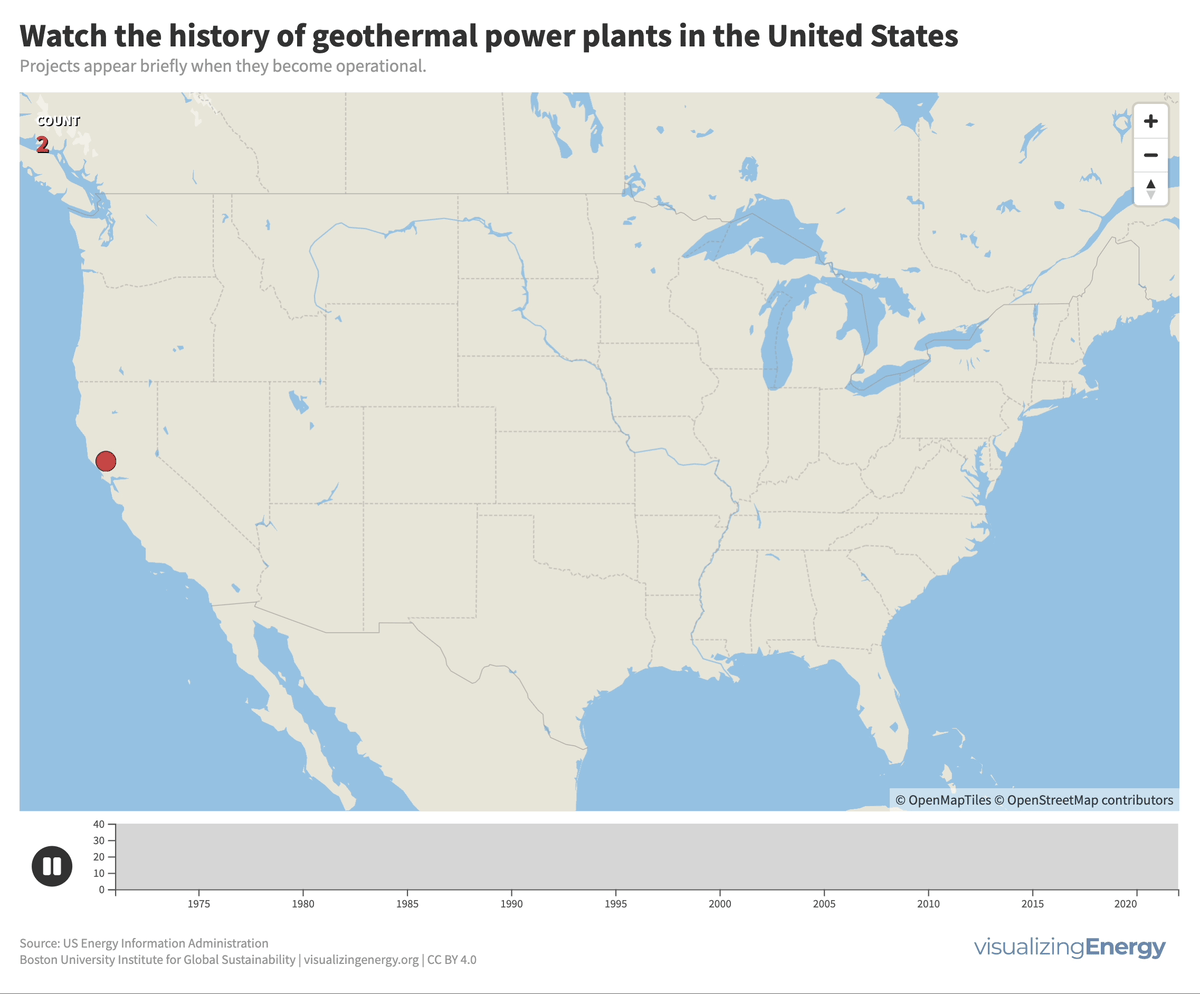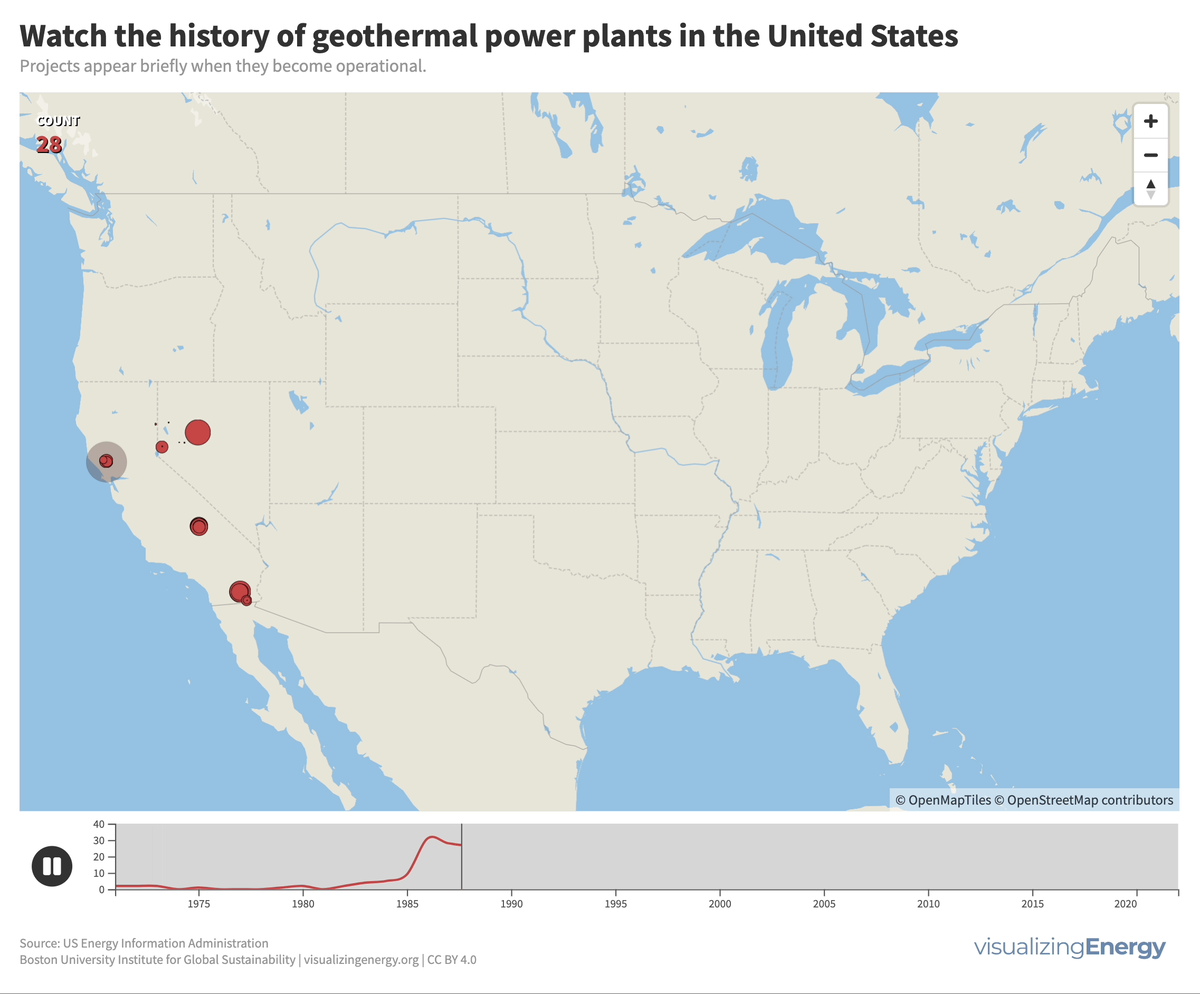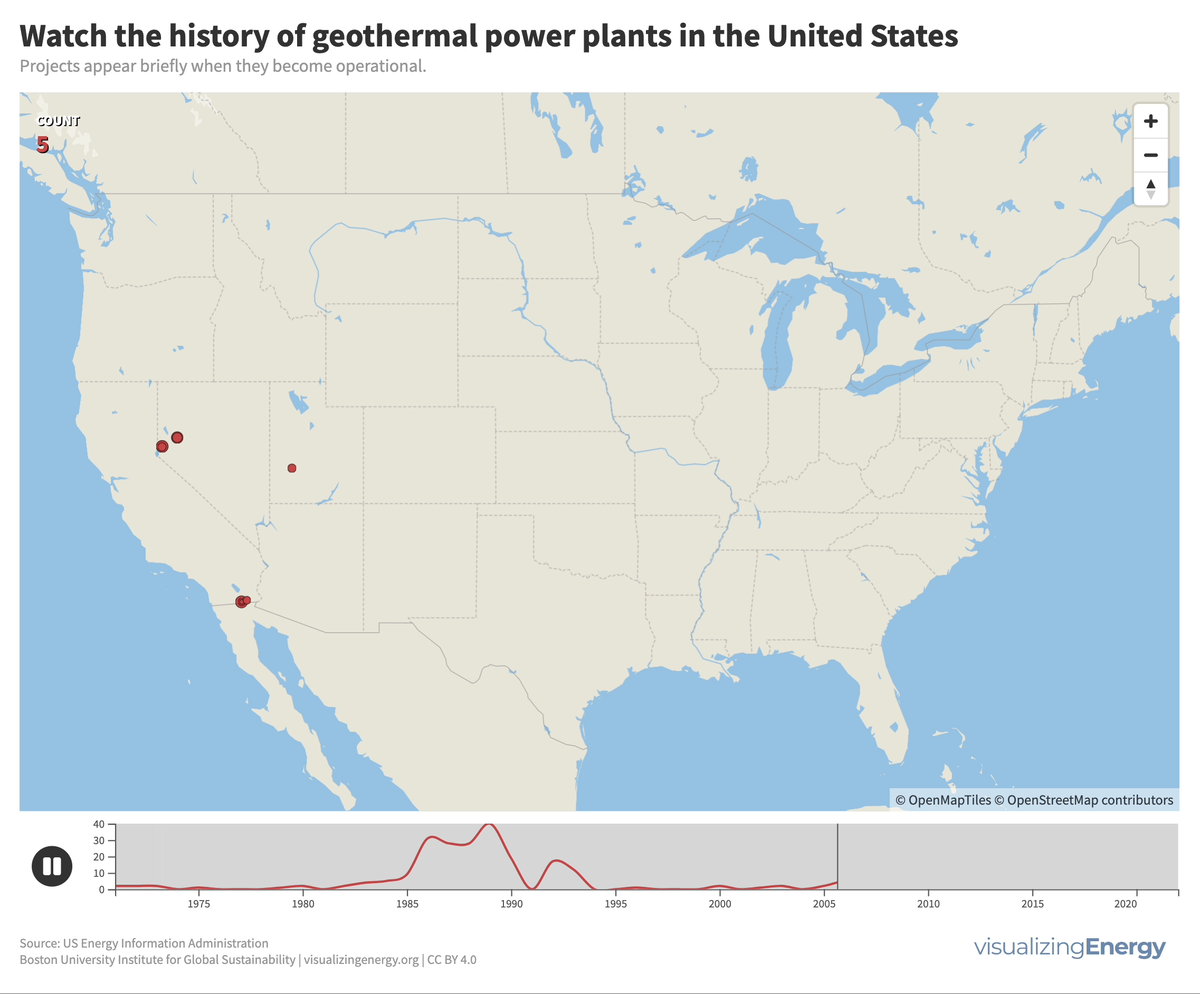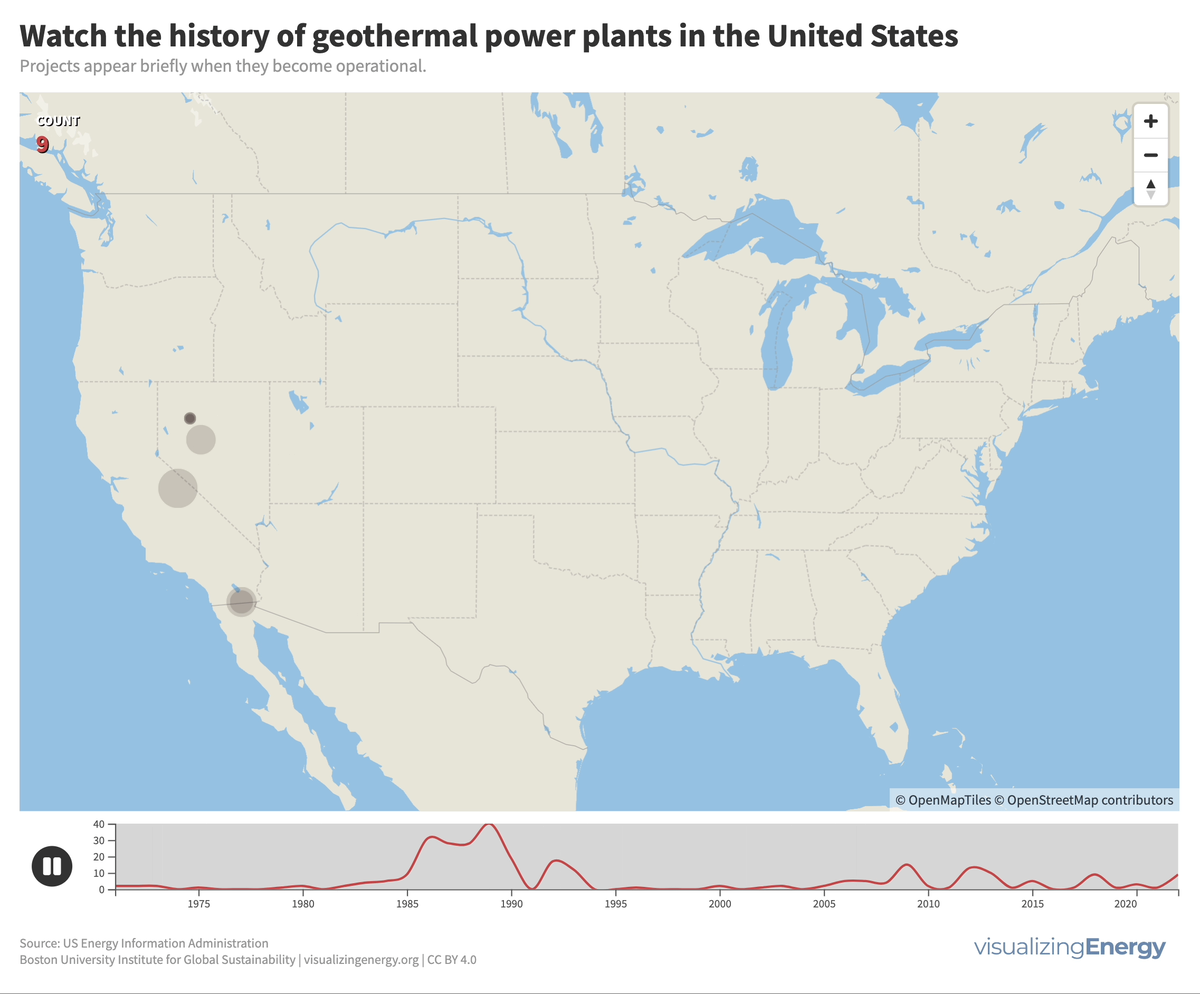
In the United States, geothermal power plants are predominantly located in six western states due to significant tectonic activity. In 2022, California housed 72% of this capacity, generating 6% of its electricity from geothermal power. The Geysers project in northern California is the world’s largest geothermal array.
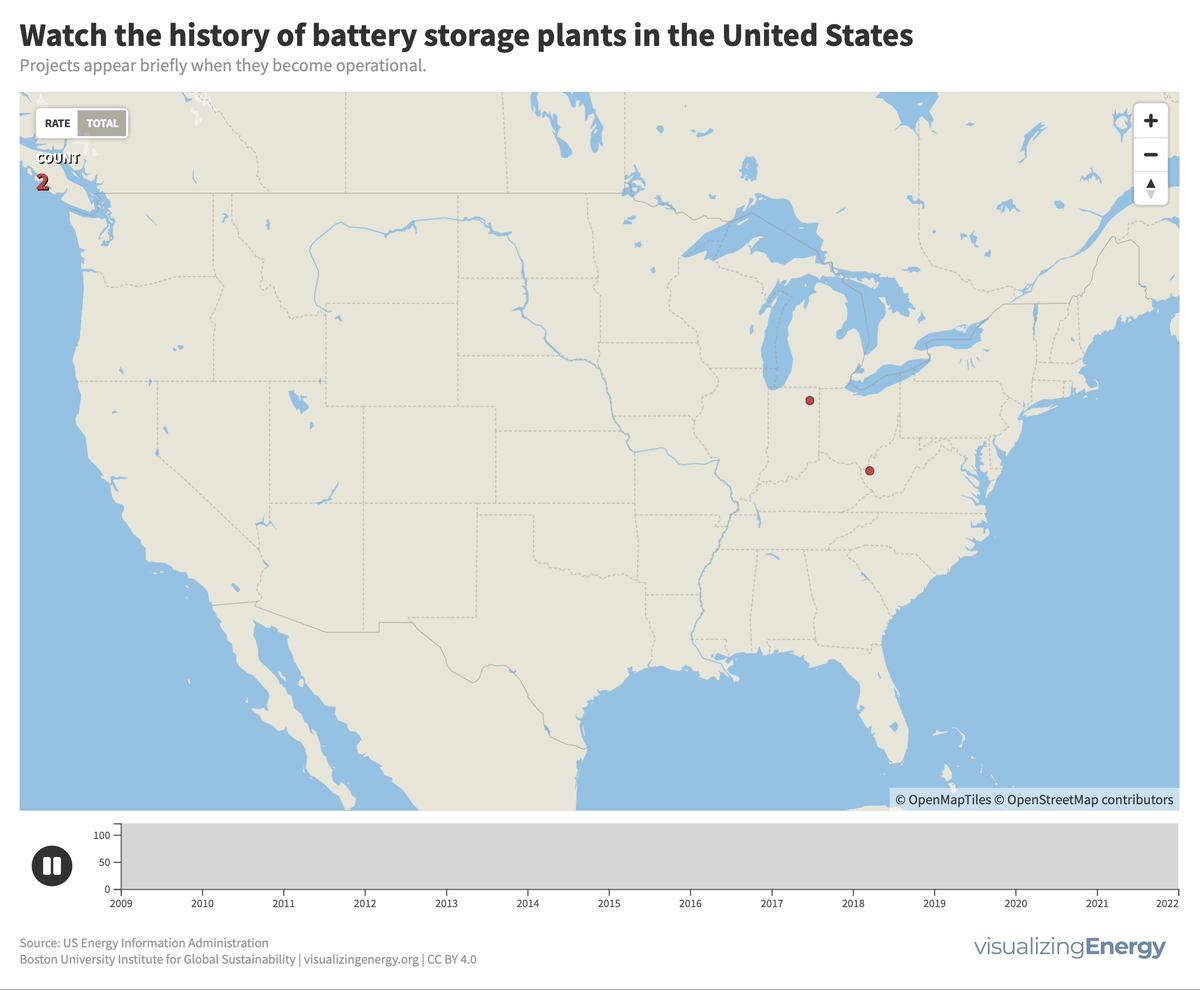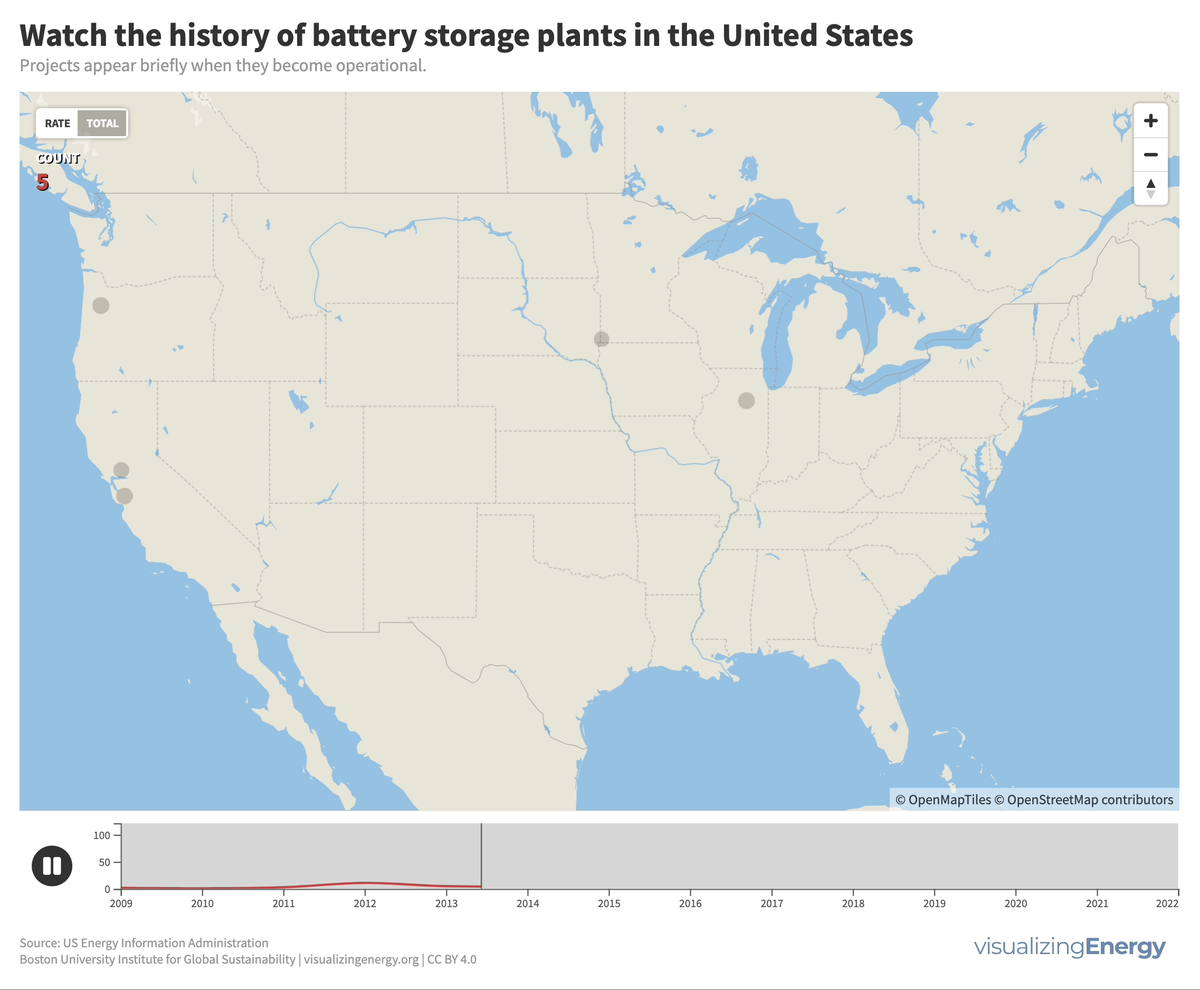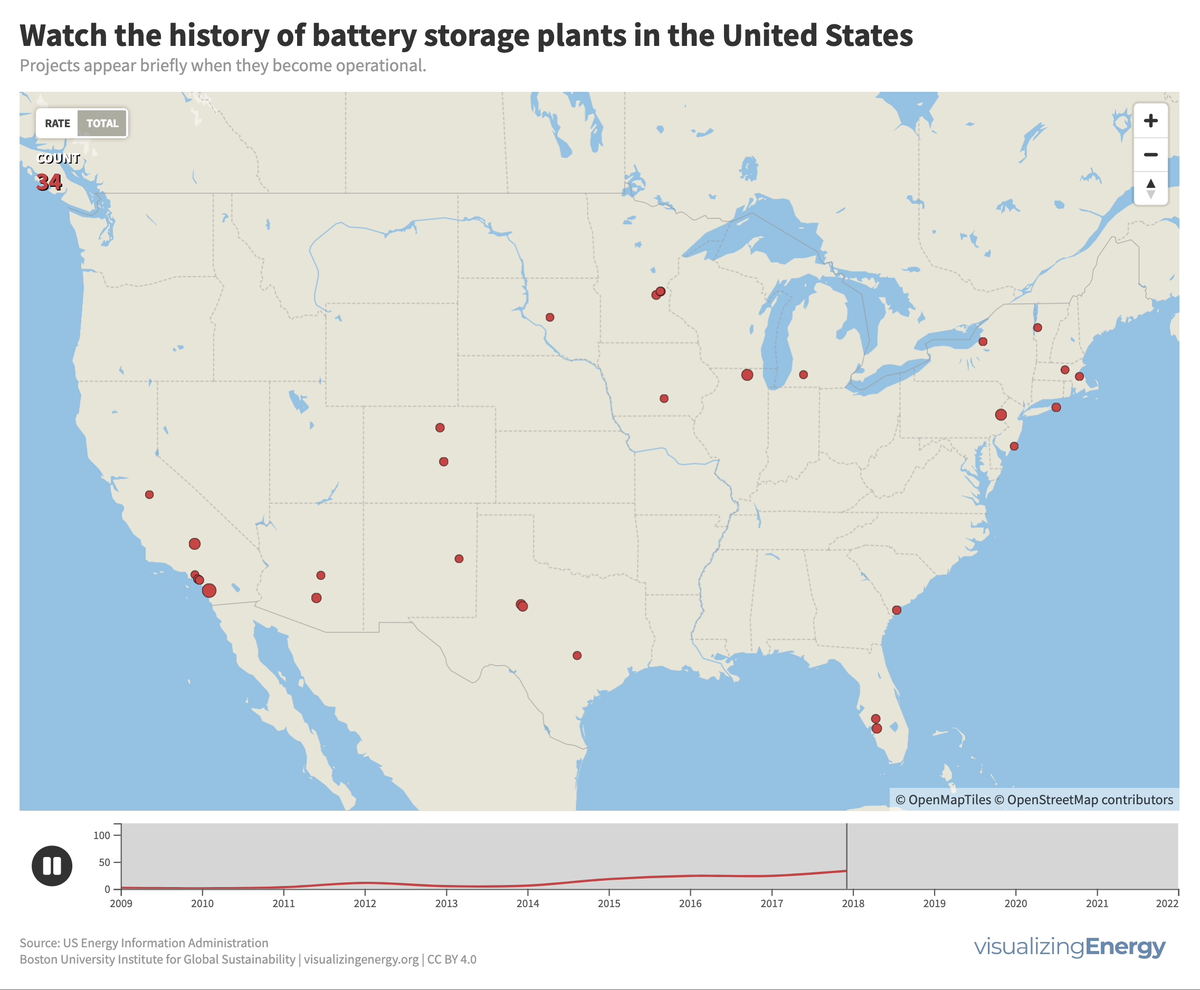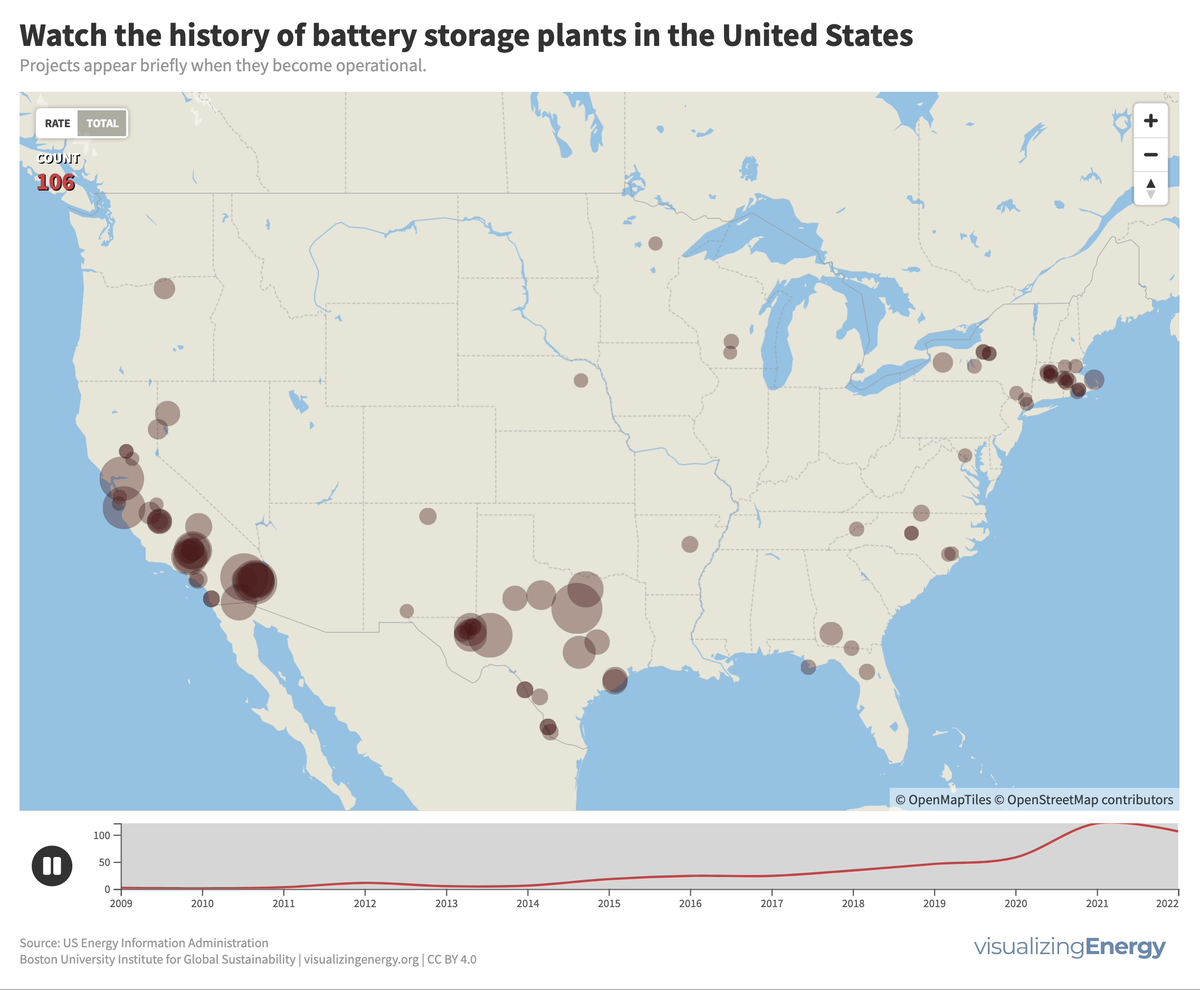
Utility-scale battery storage (BESS) systems store and distribute large-scale electricity and are crucial for renewable energy integration. Since the mid-2000s, about 460 such systems were built in the U.S., the largest being the 409 MW Manatee Energy Storage Center.

Major financial institutions’ practices are not climate-friendly, with policies disconnecting short-term targets from required long-term climate actions. A Columbia University report highlights financial institutions’ political influence, using lobbying and campaign contributions, often obstructing climate policy. The report suggests measures for shifting towards positive climate action.
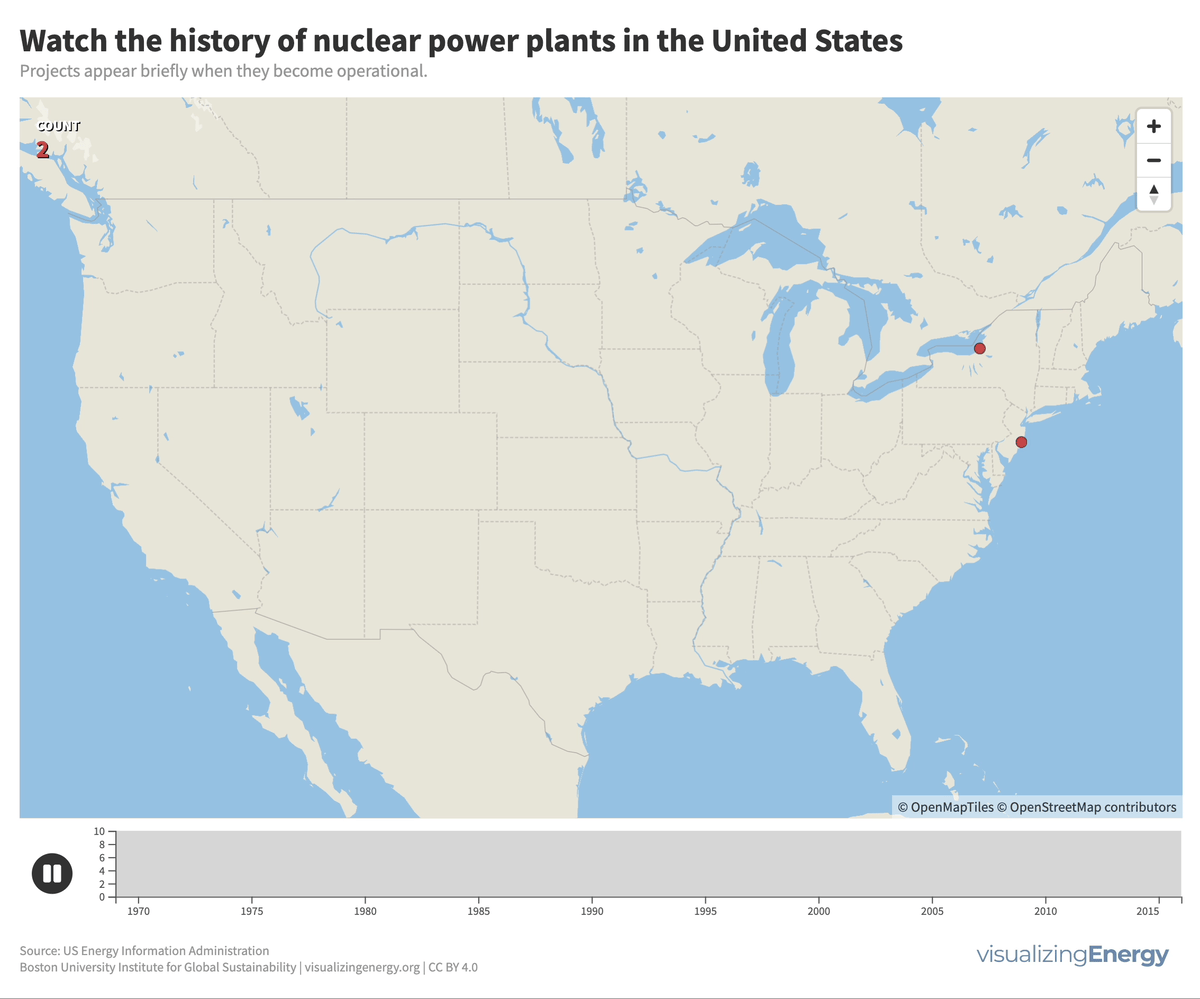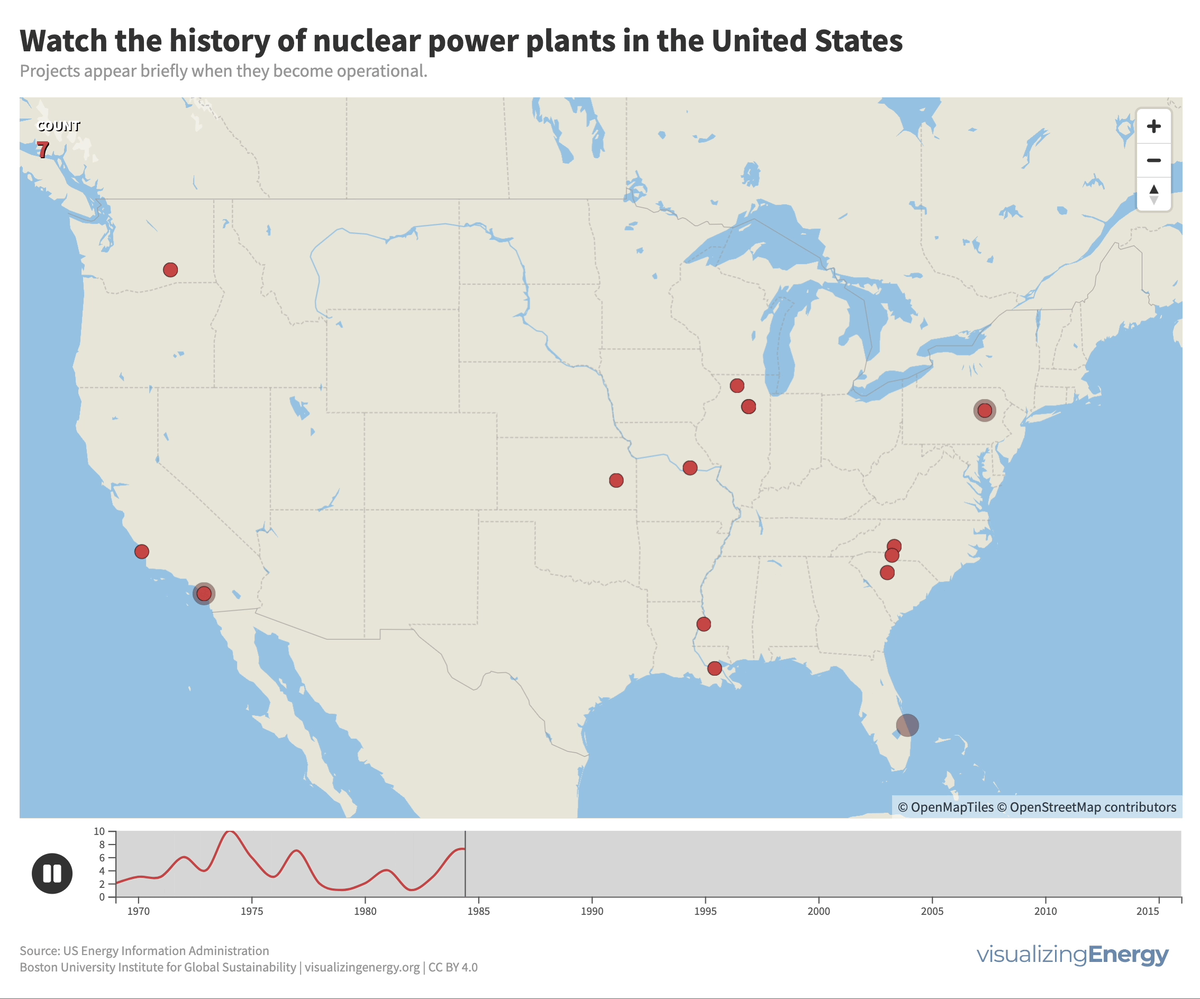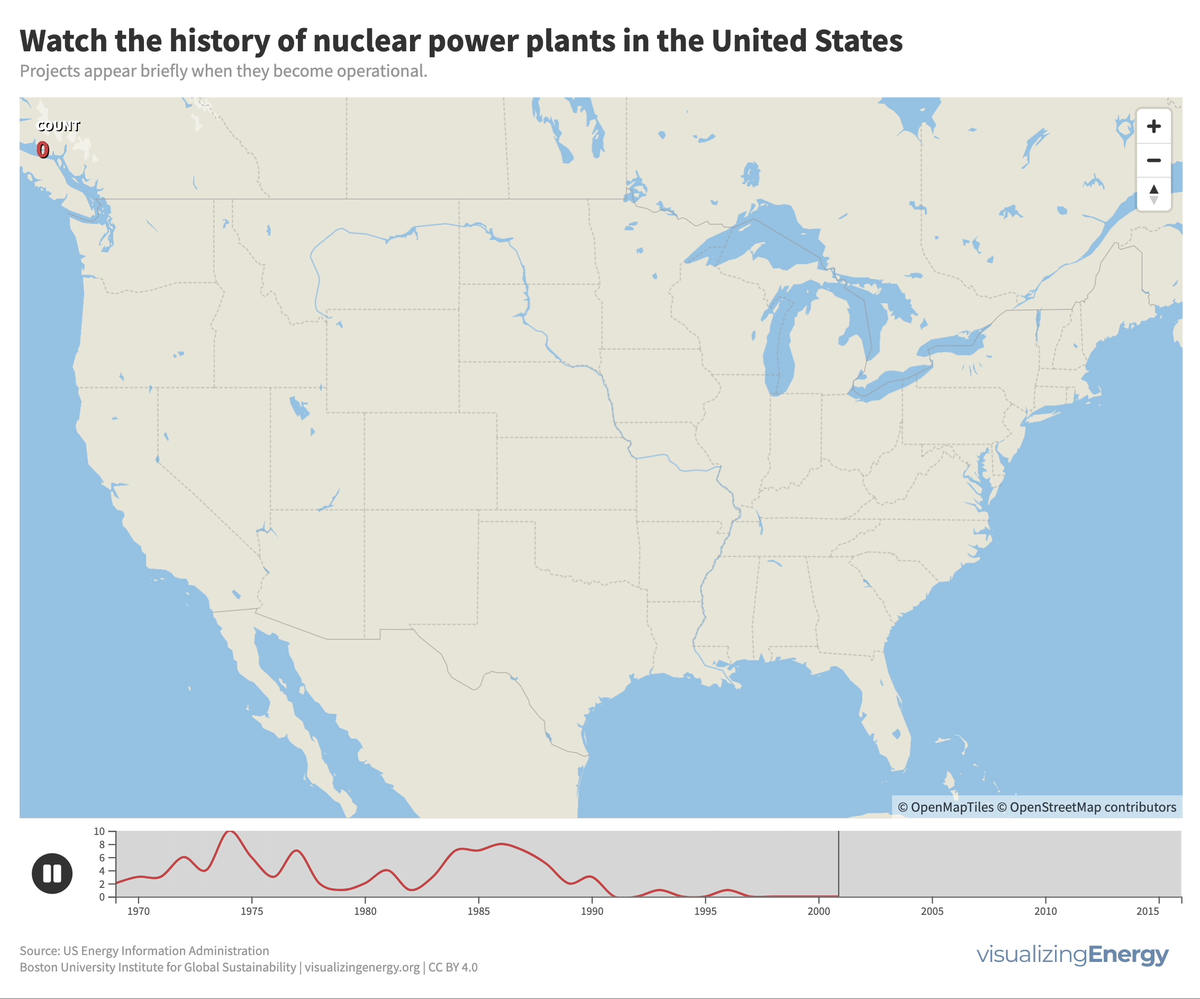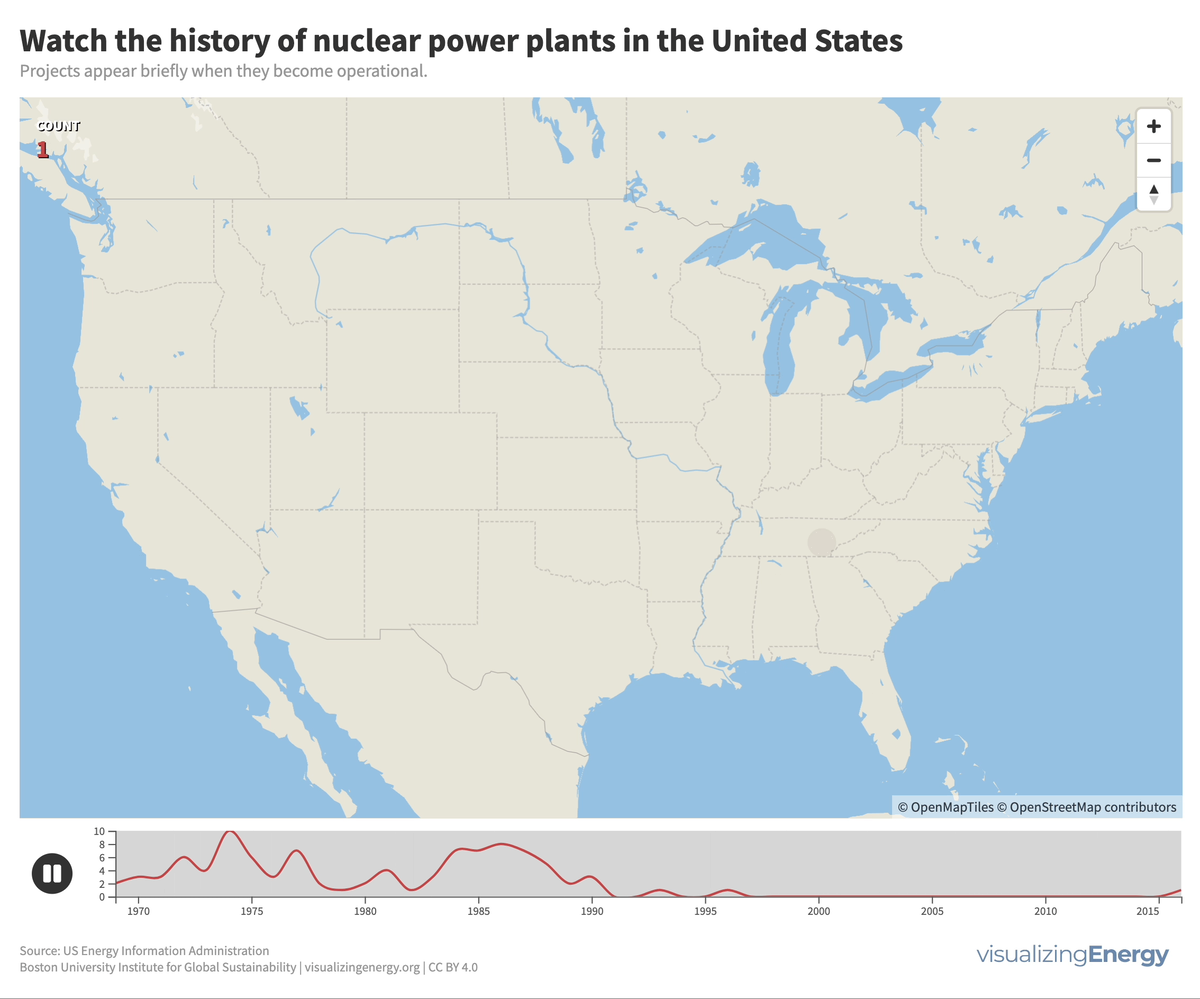
In 2022, the U.S. had 92 nuclear power plants generating 18% of total electricity. The industry, once a major player, declined due to high costs, long construction timelines, decreased demand, accidents, regulations, and market deregulation. There’s renewed interest in nuclear power to combat climate change, with the first new plant in 30 years, though debates continue on cost, safety, and alternative energy sources.
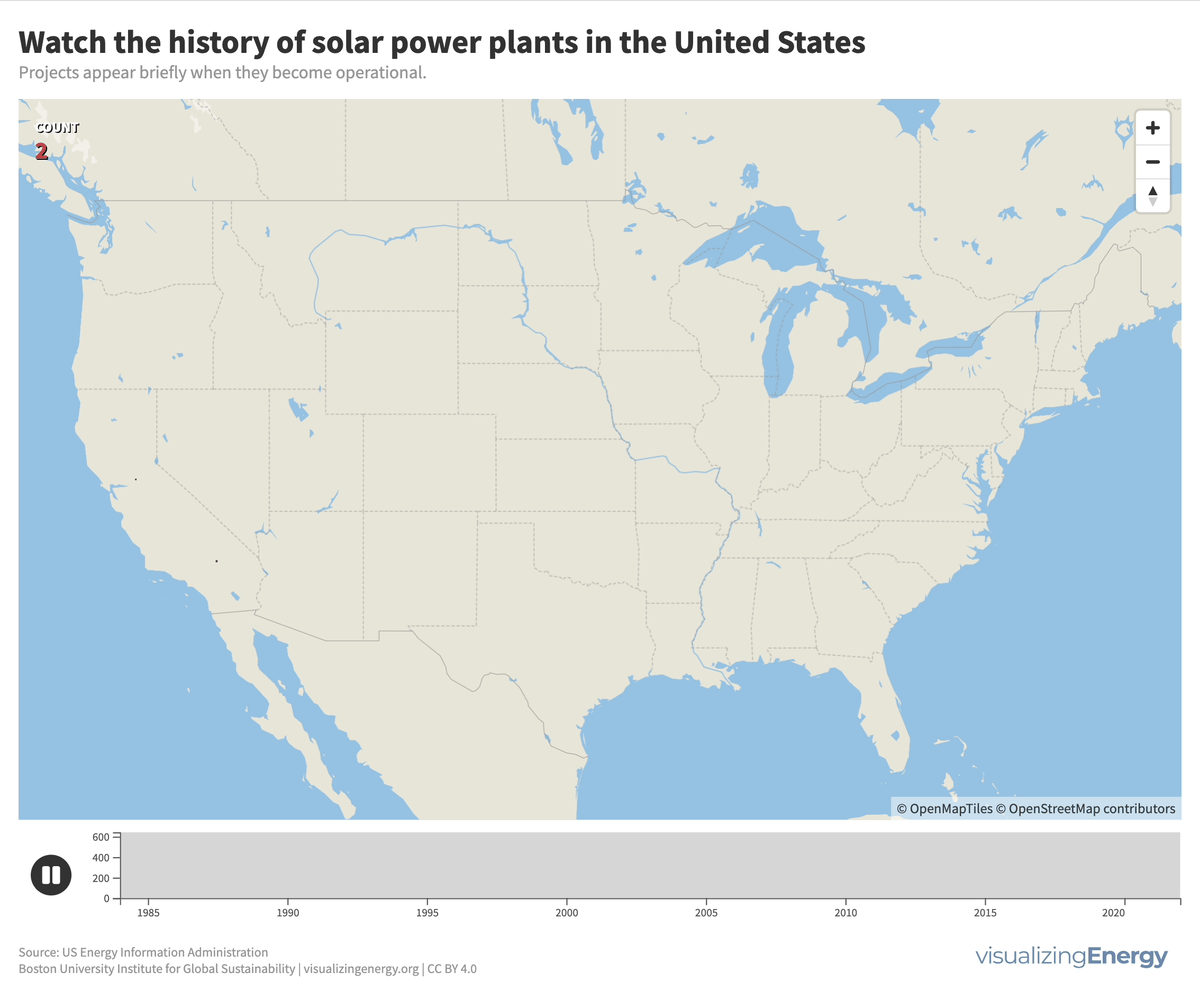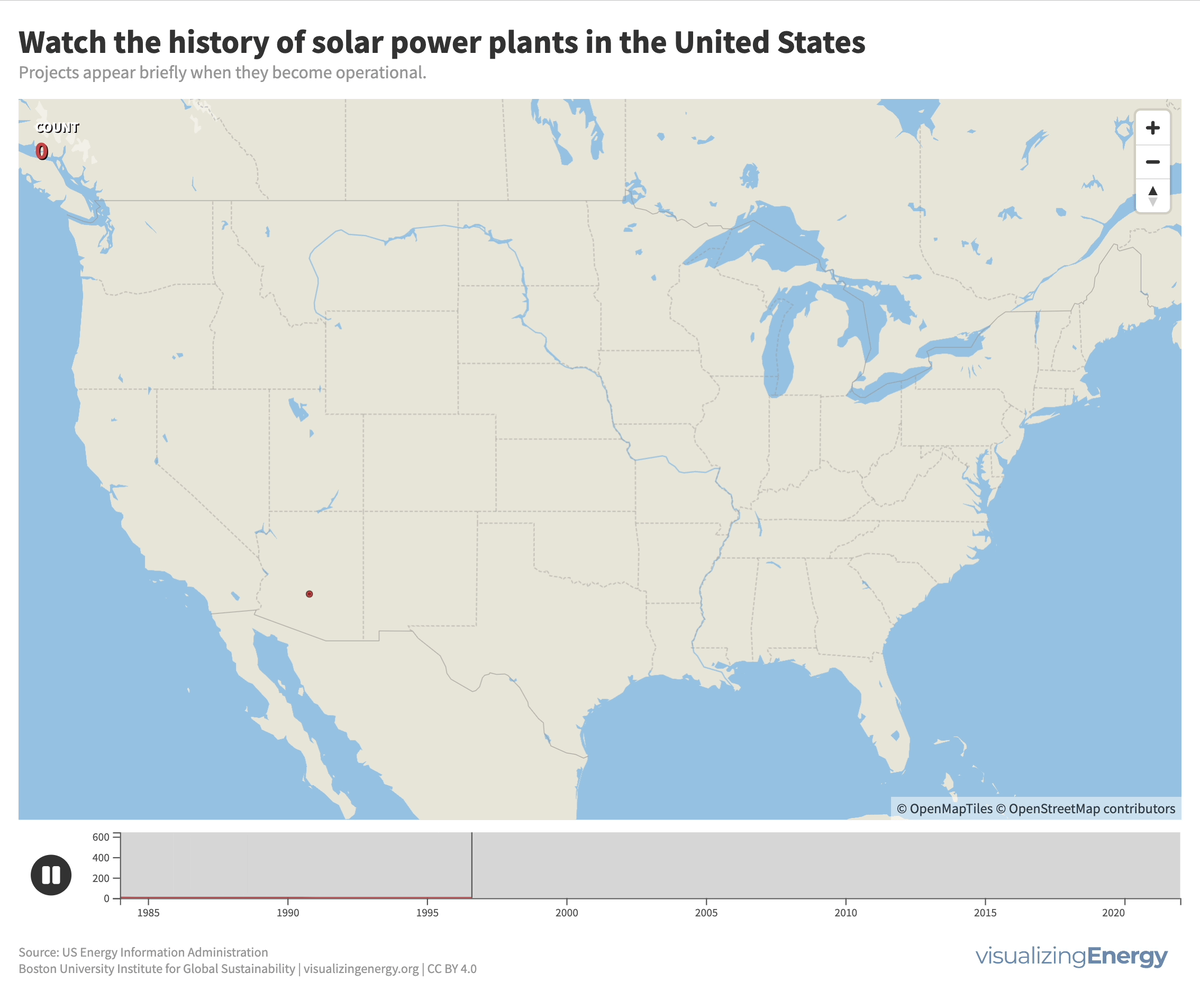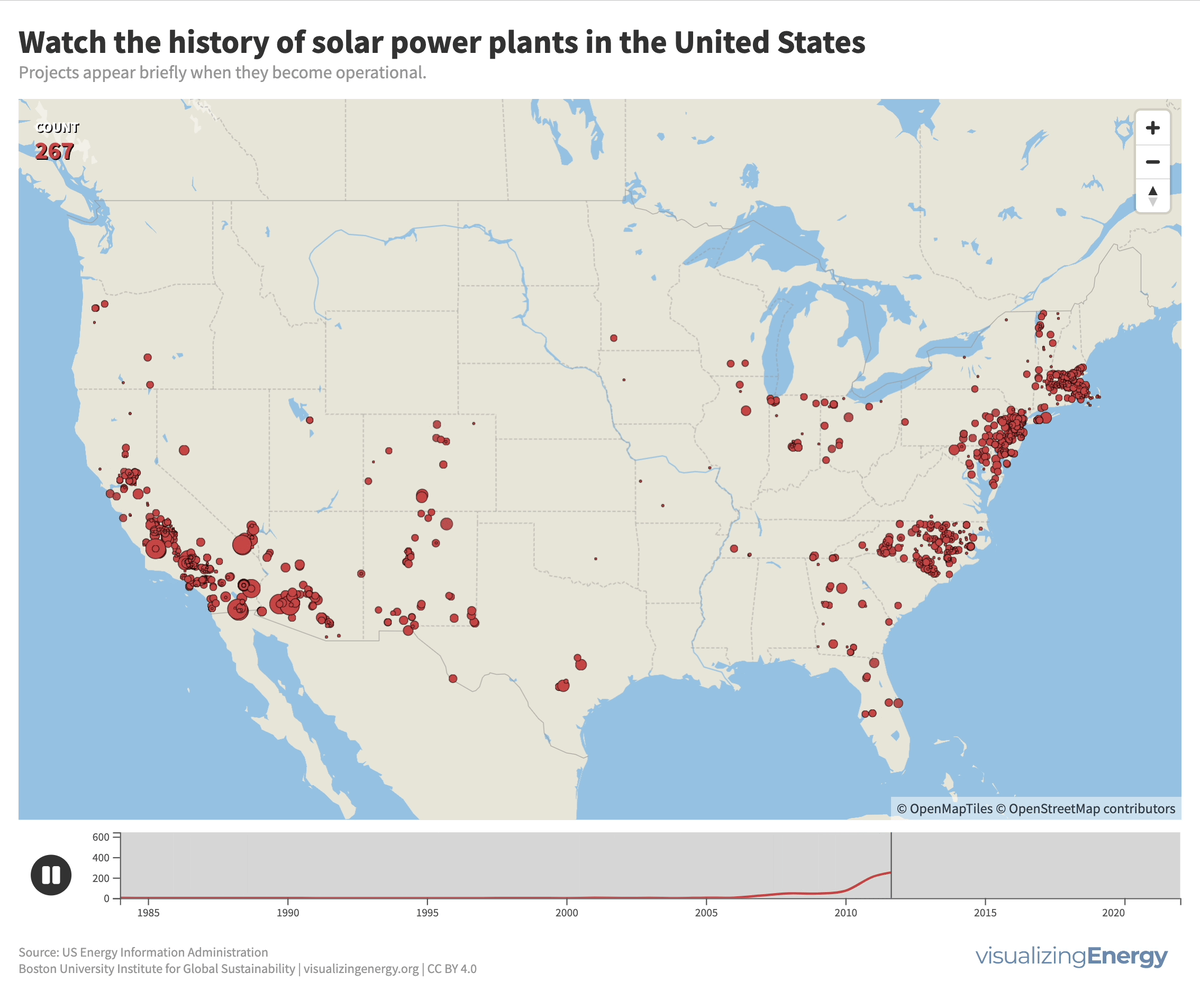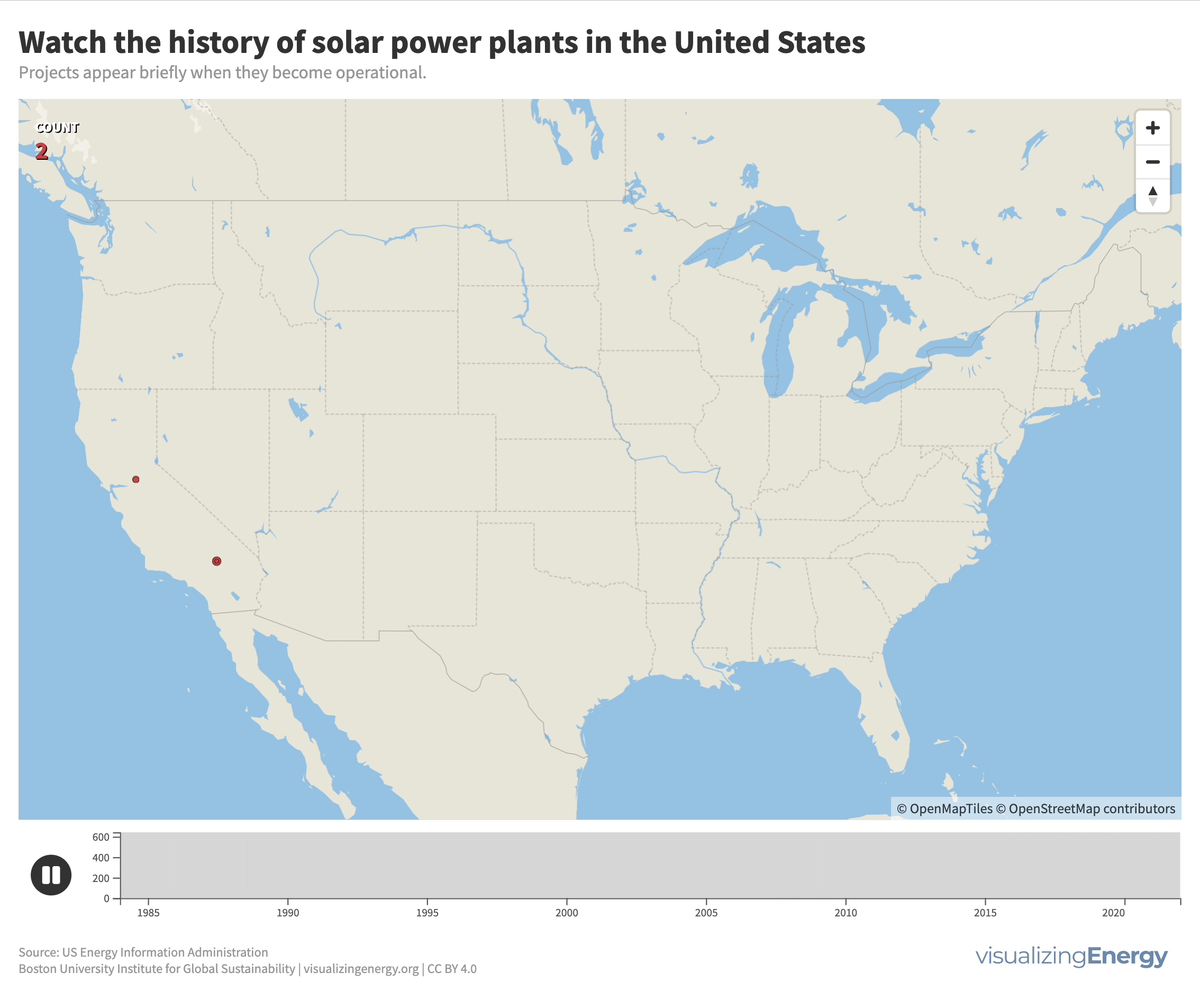
In 2022, the United States saw a significant rise in solar power generation, with 5730 utility-scale solar PV plants and 13 solar thermal plants producing 146 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity, equal to 3.4% of total utility-scale generation. This growth traces back to the 2000s, marked by falling solar system costs, enhanced efficiency, and government incentives like the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009.