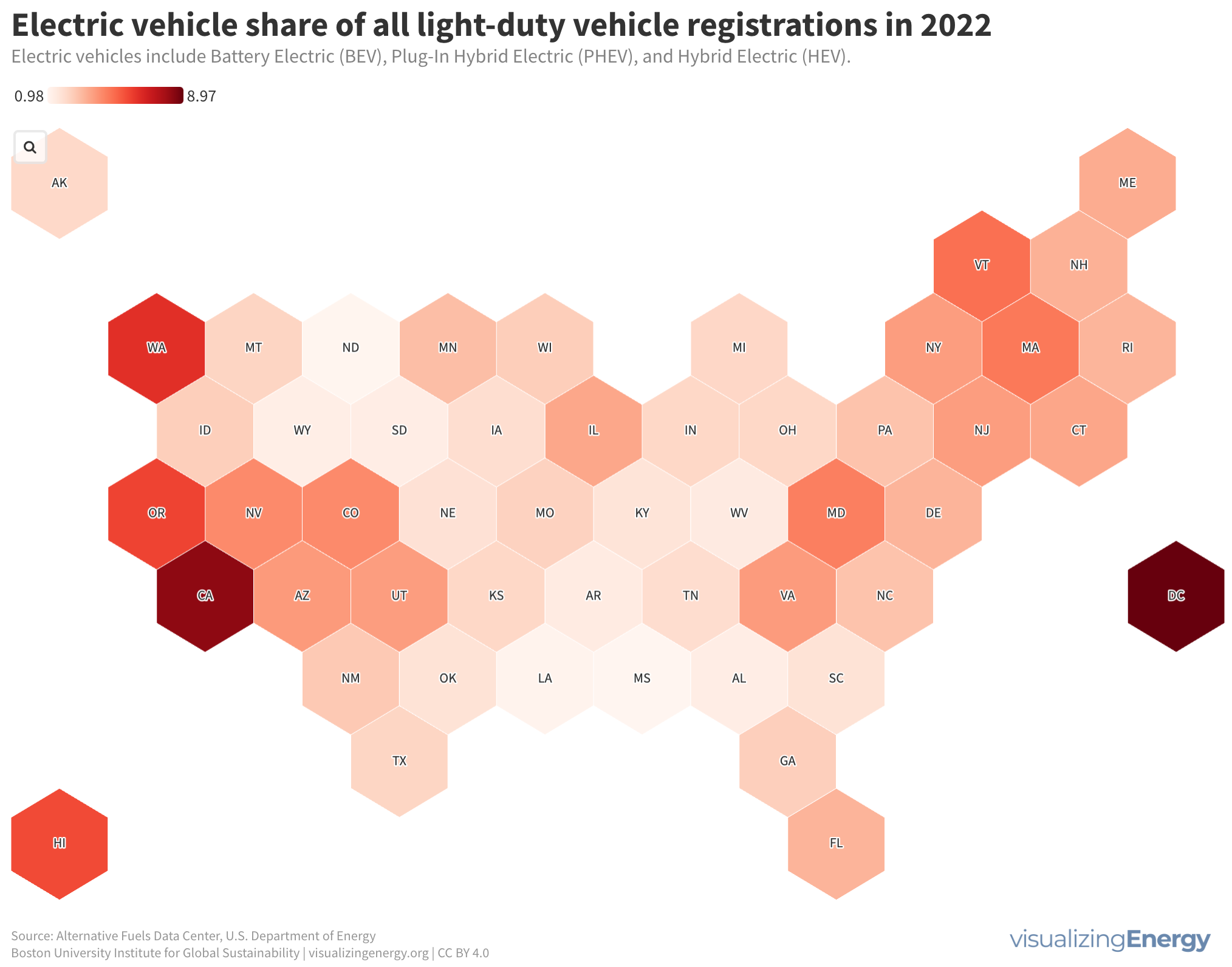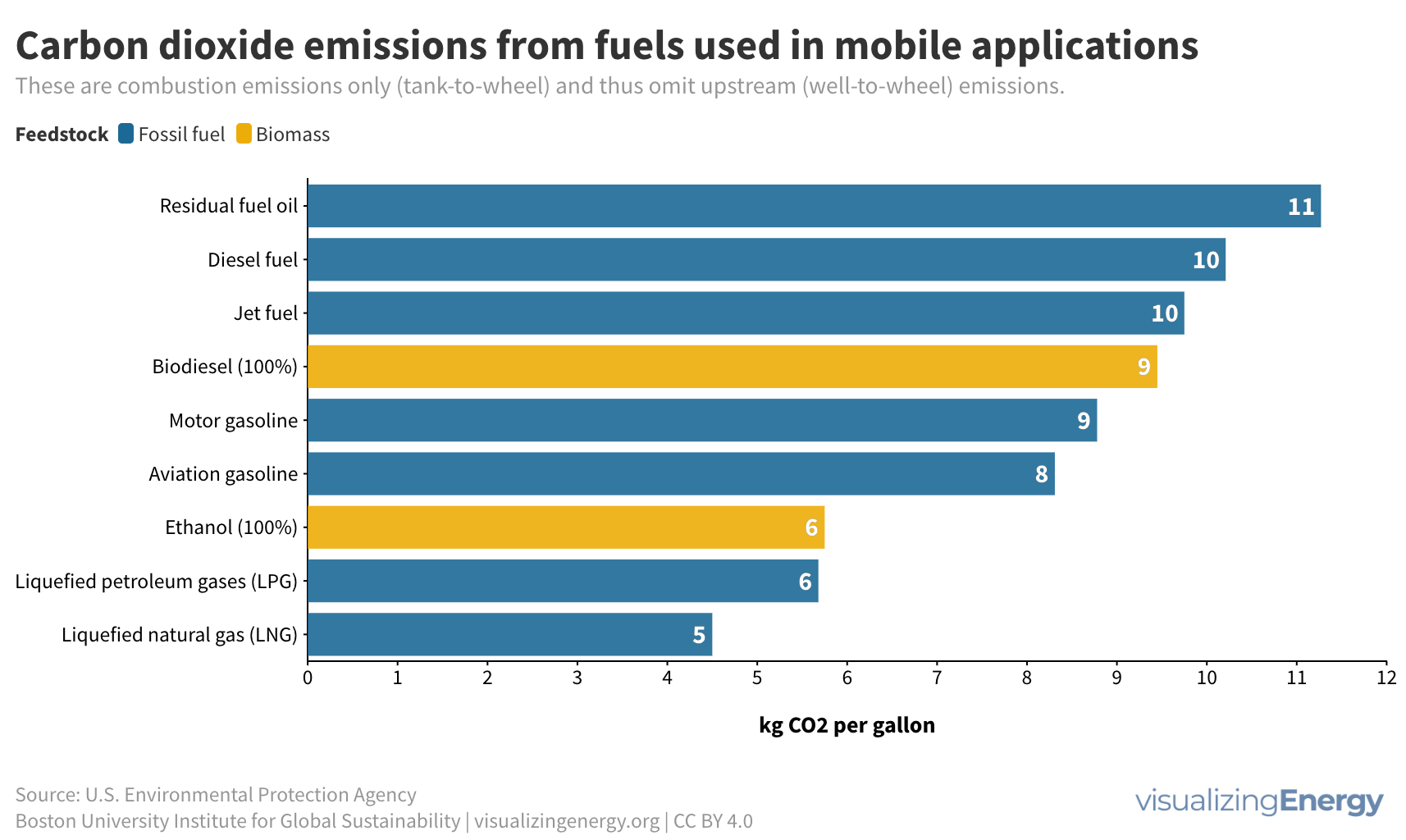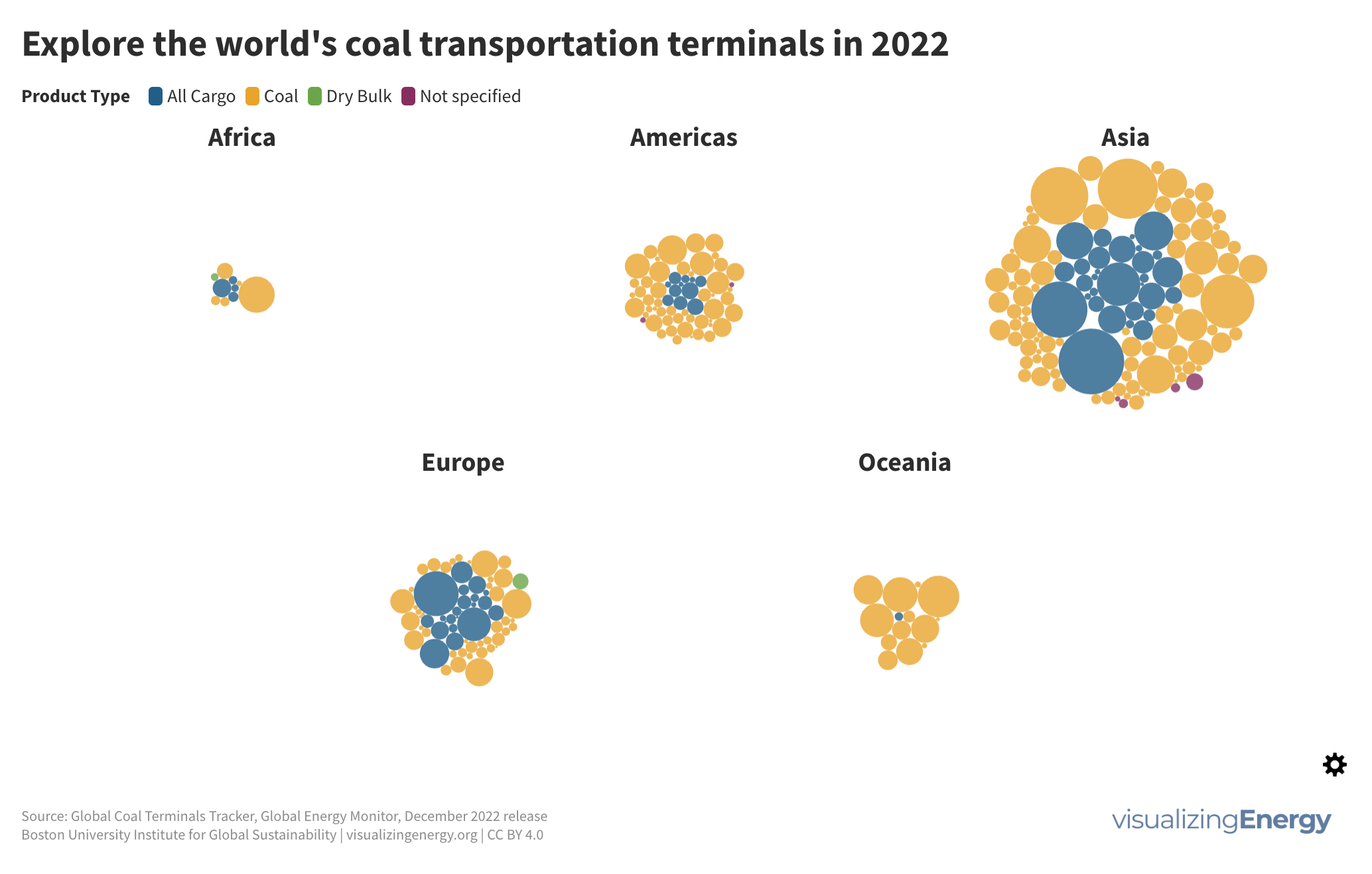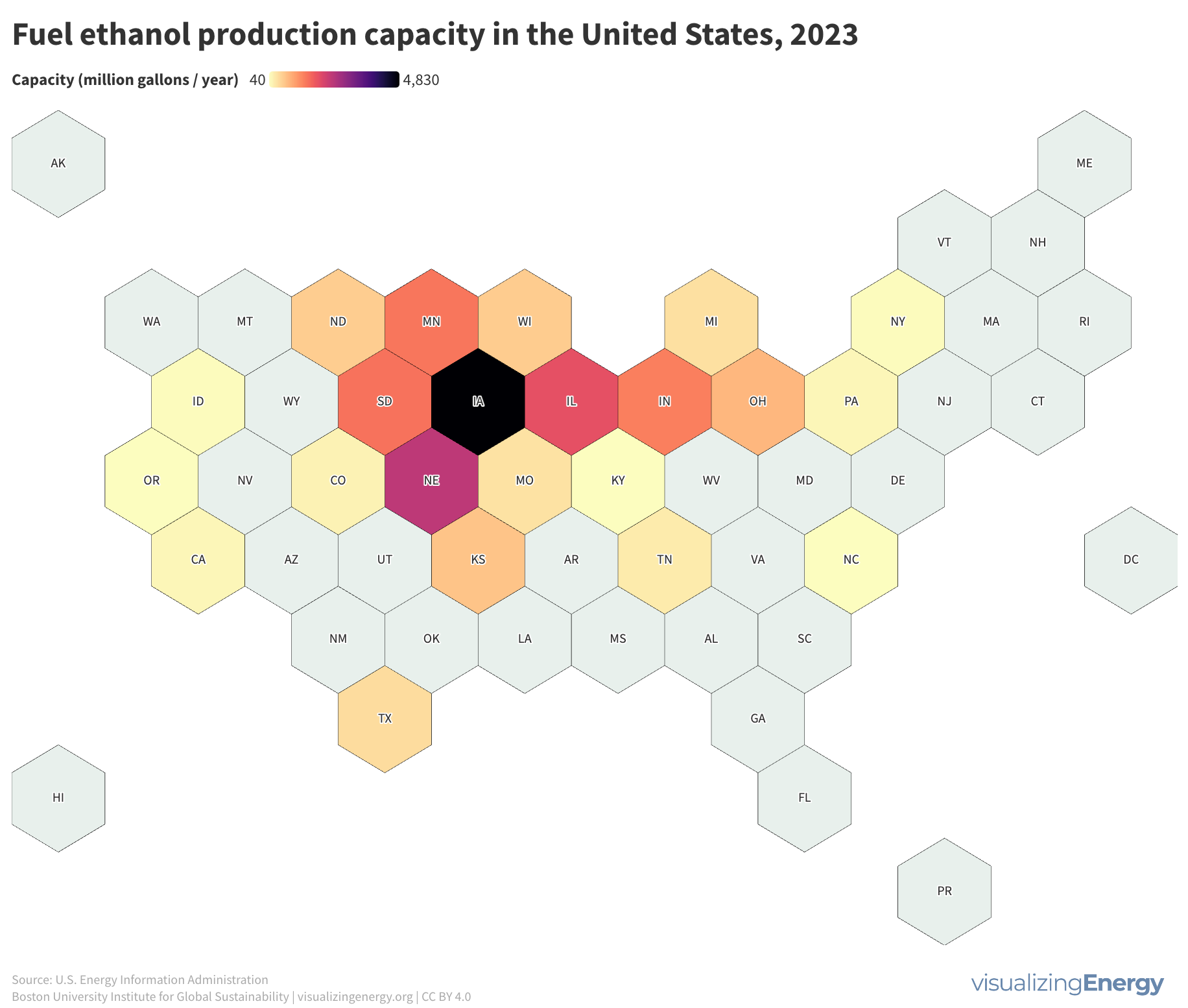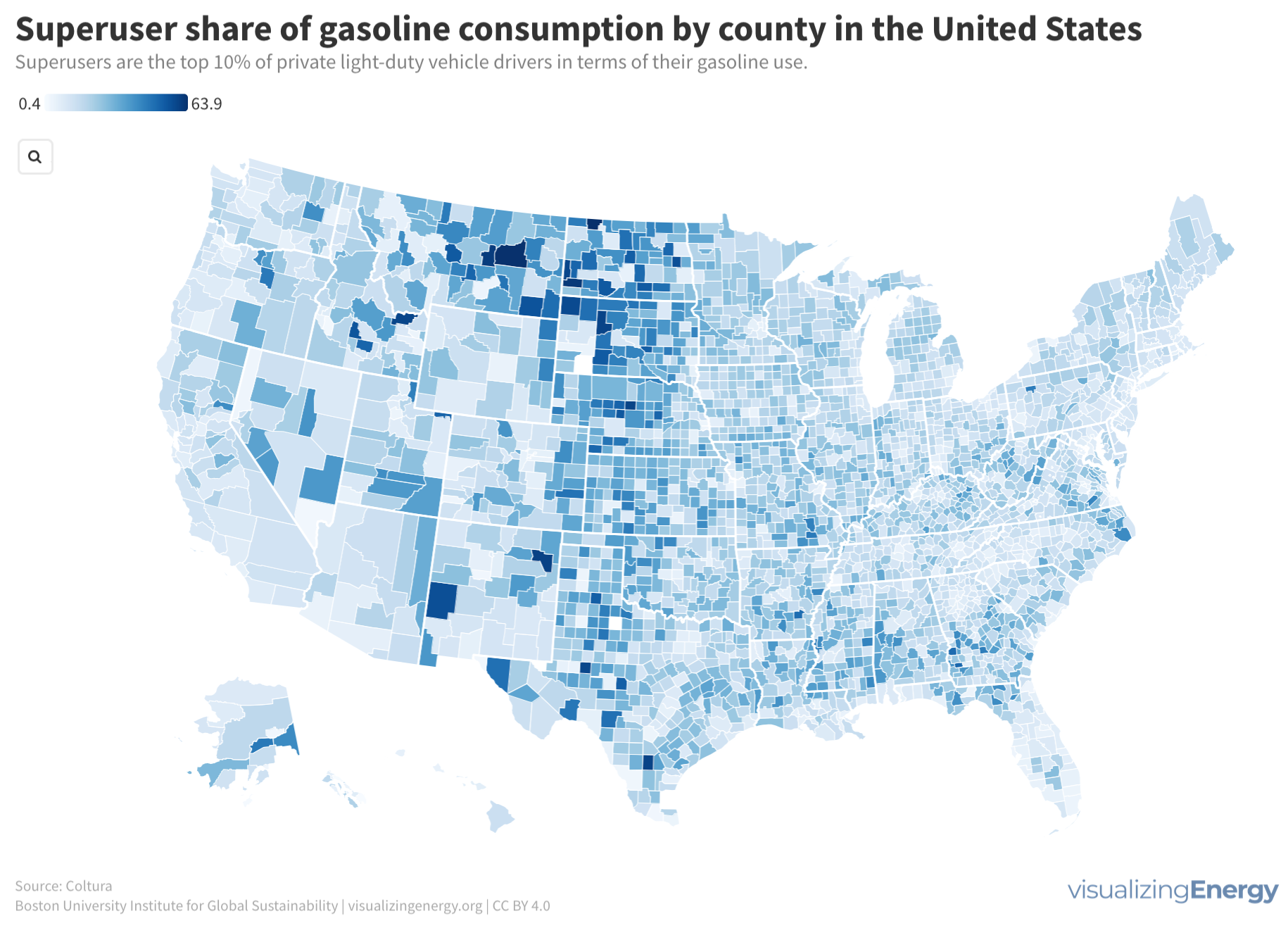
Where are the gasoline superusers in the United States?
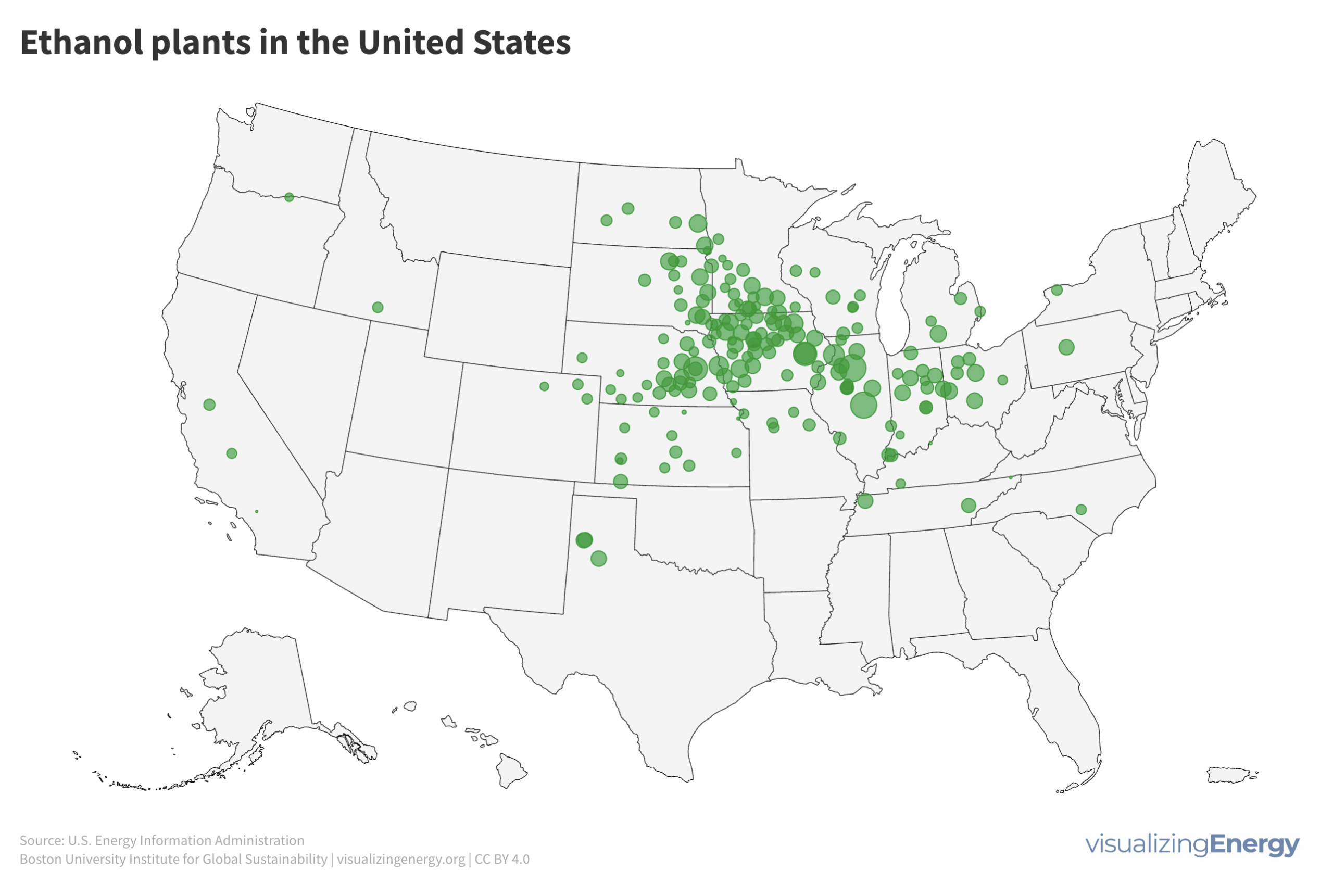
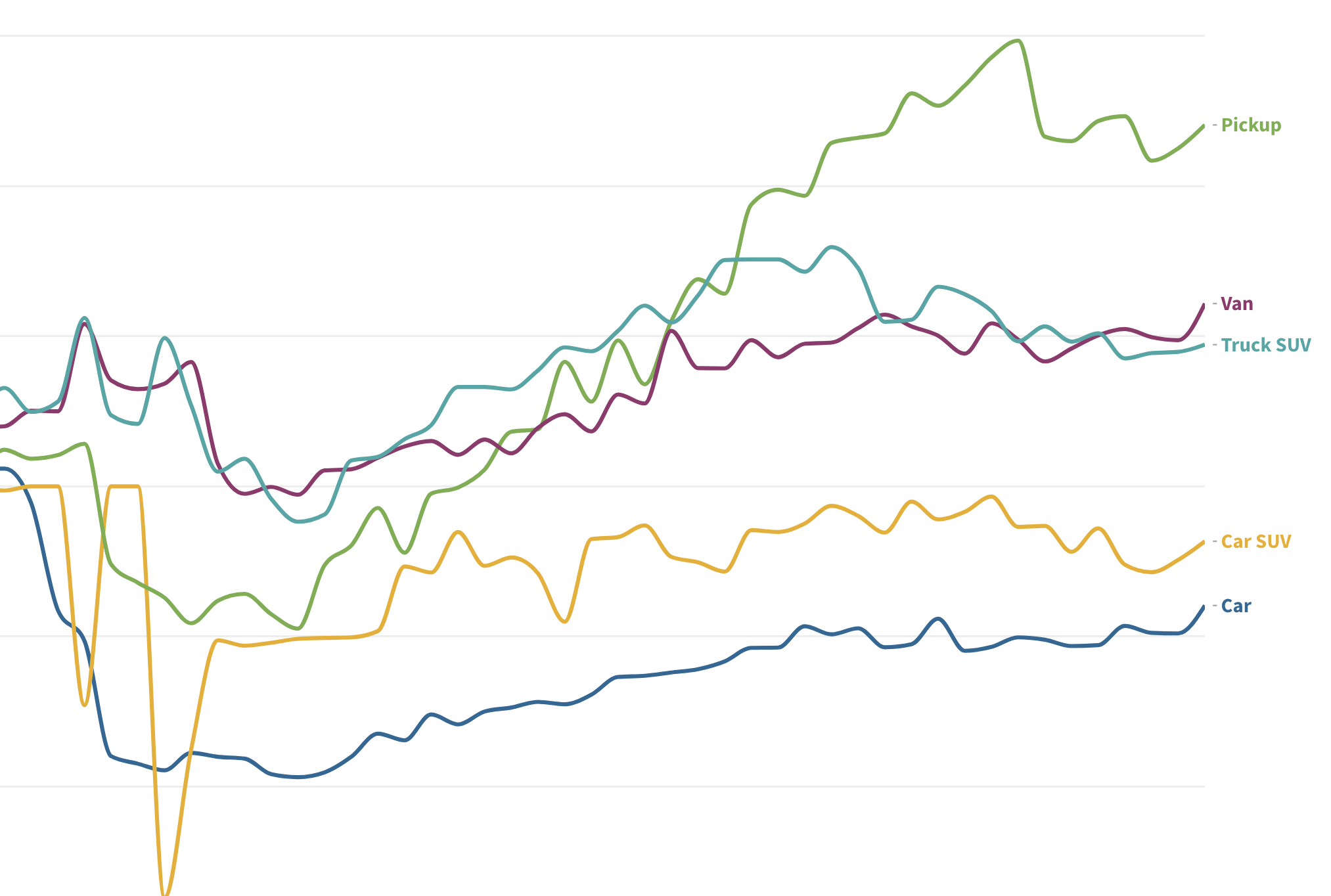
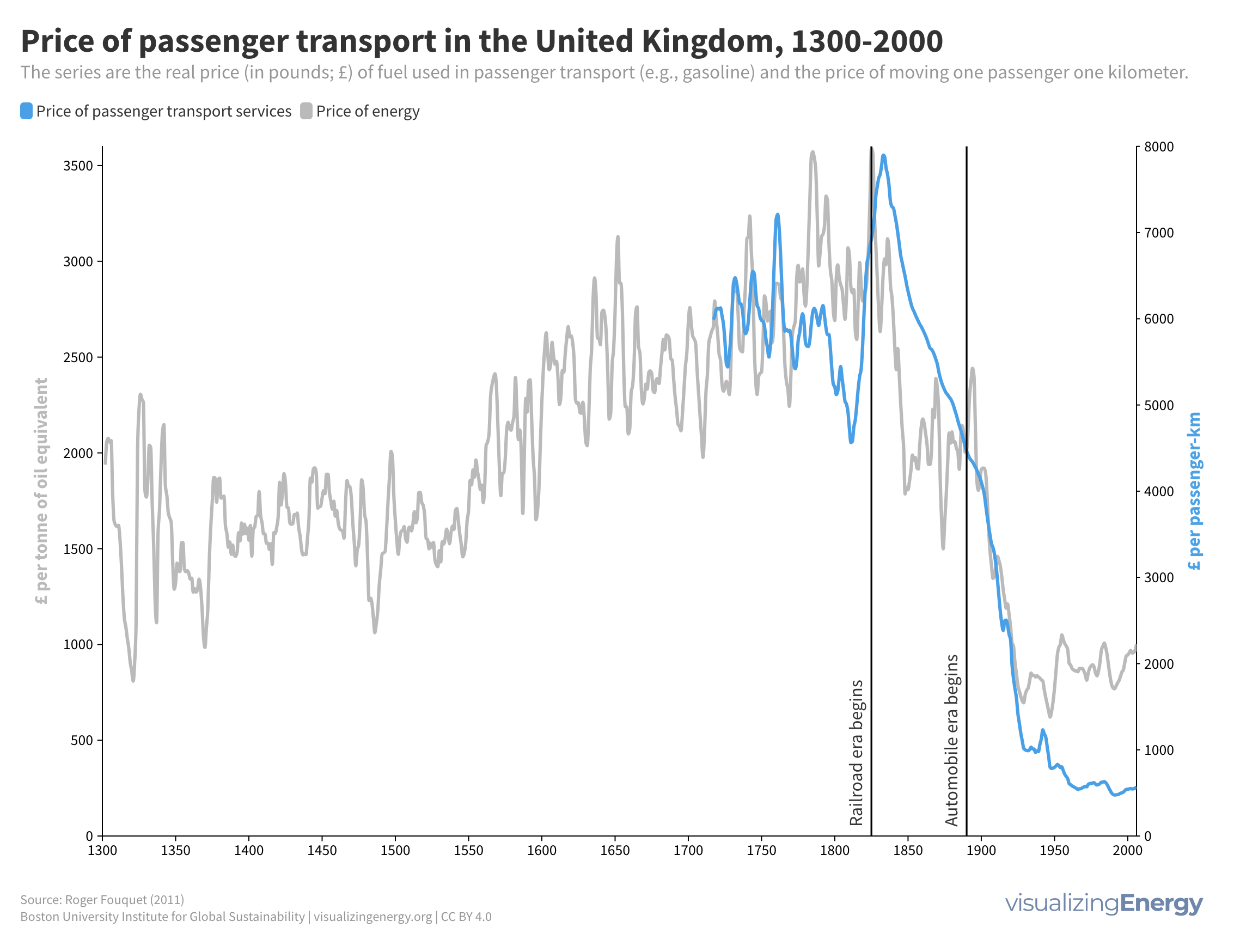
In 2023, US drivers consumed 376 million gallons of gasoline daily, with superusers accounting for 35% of usage. Rural areas have more superusers, spending 10.2% of their income on gasoline. They also tend to drive larger, less fuel-efficient vehicles. Electric vehicle policies targeting superusers could reduce energy burdens and emissions, benefiting low-income households.