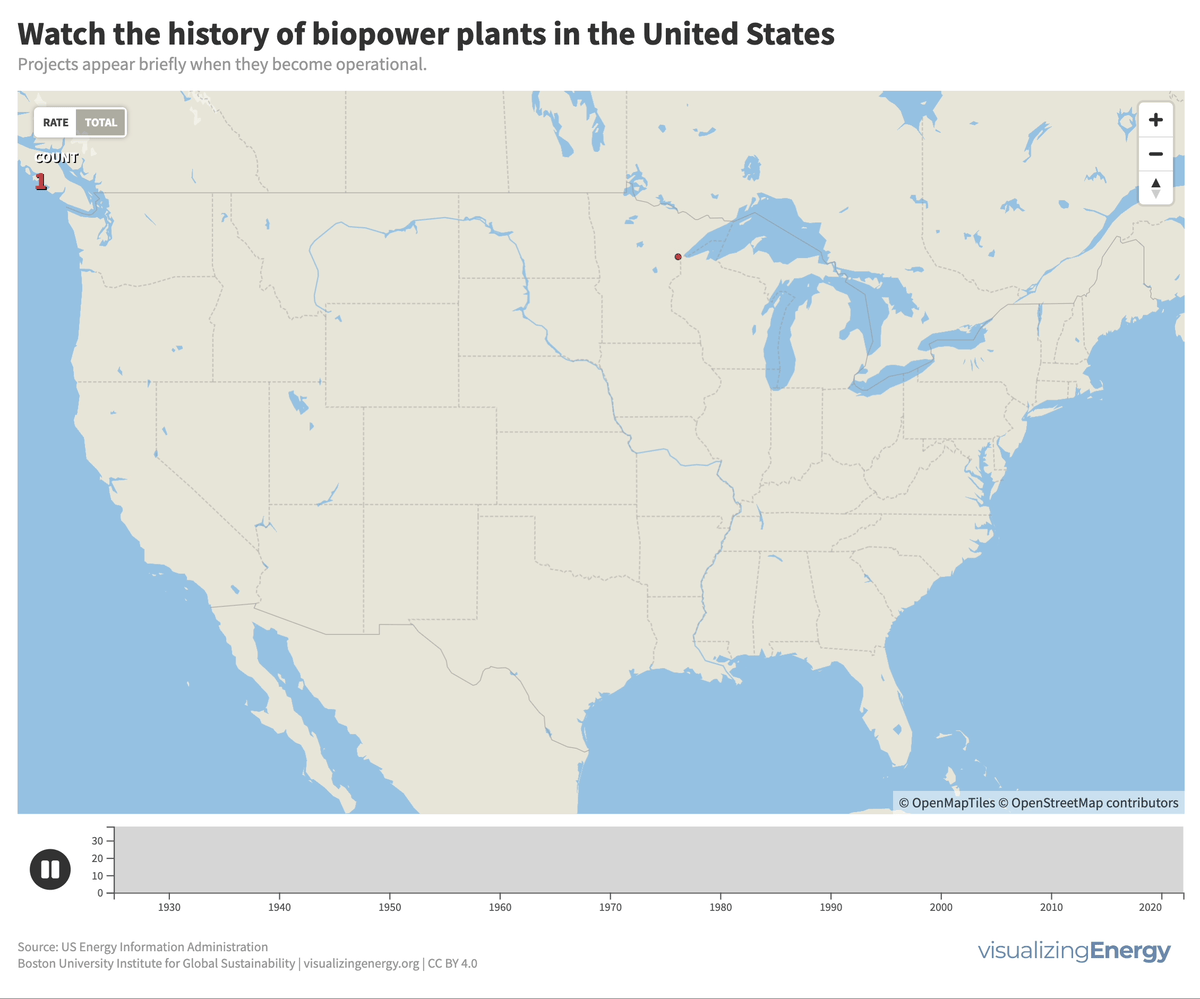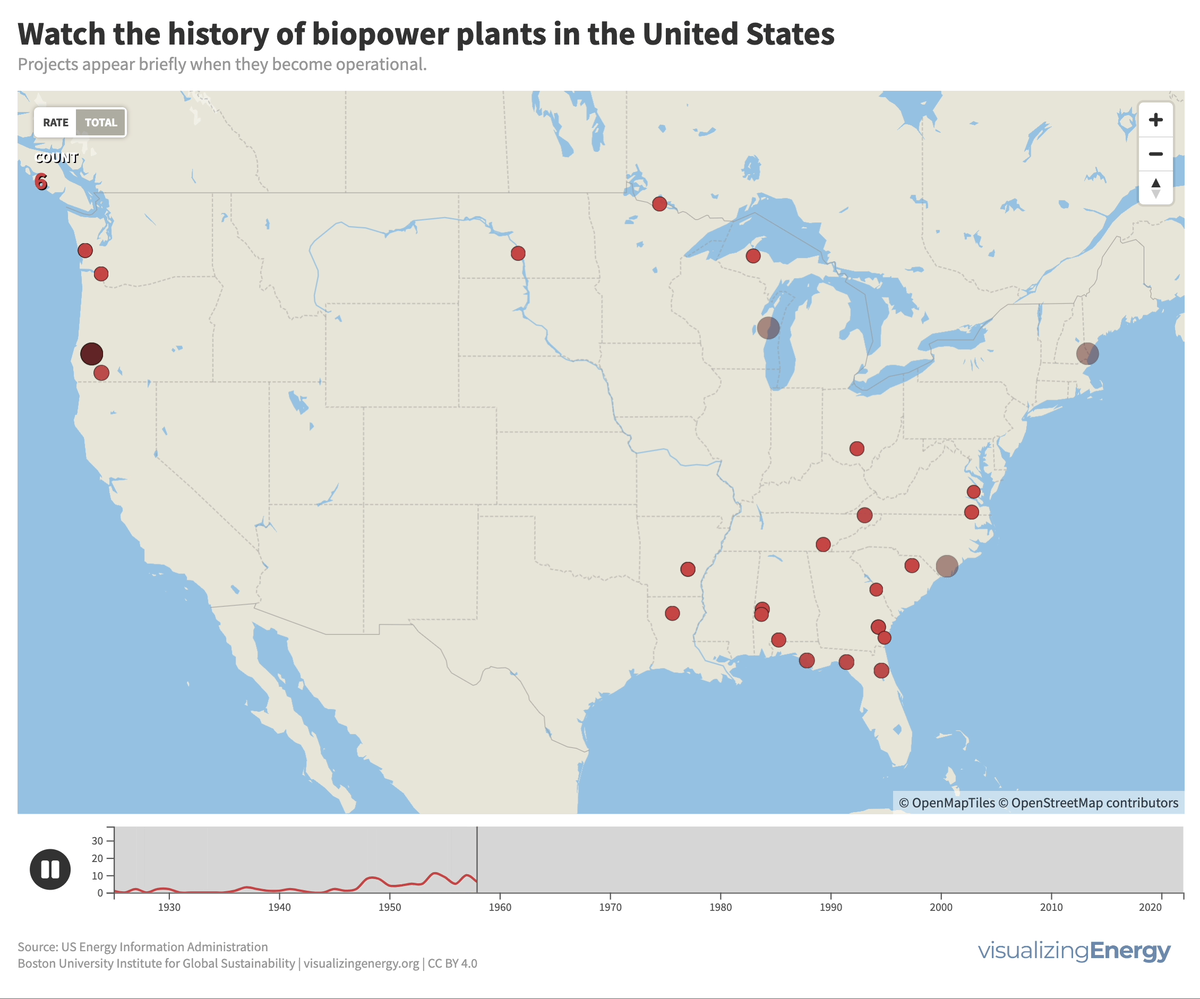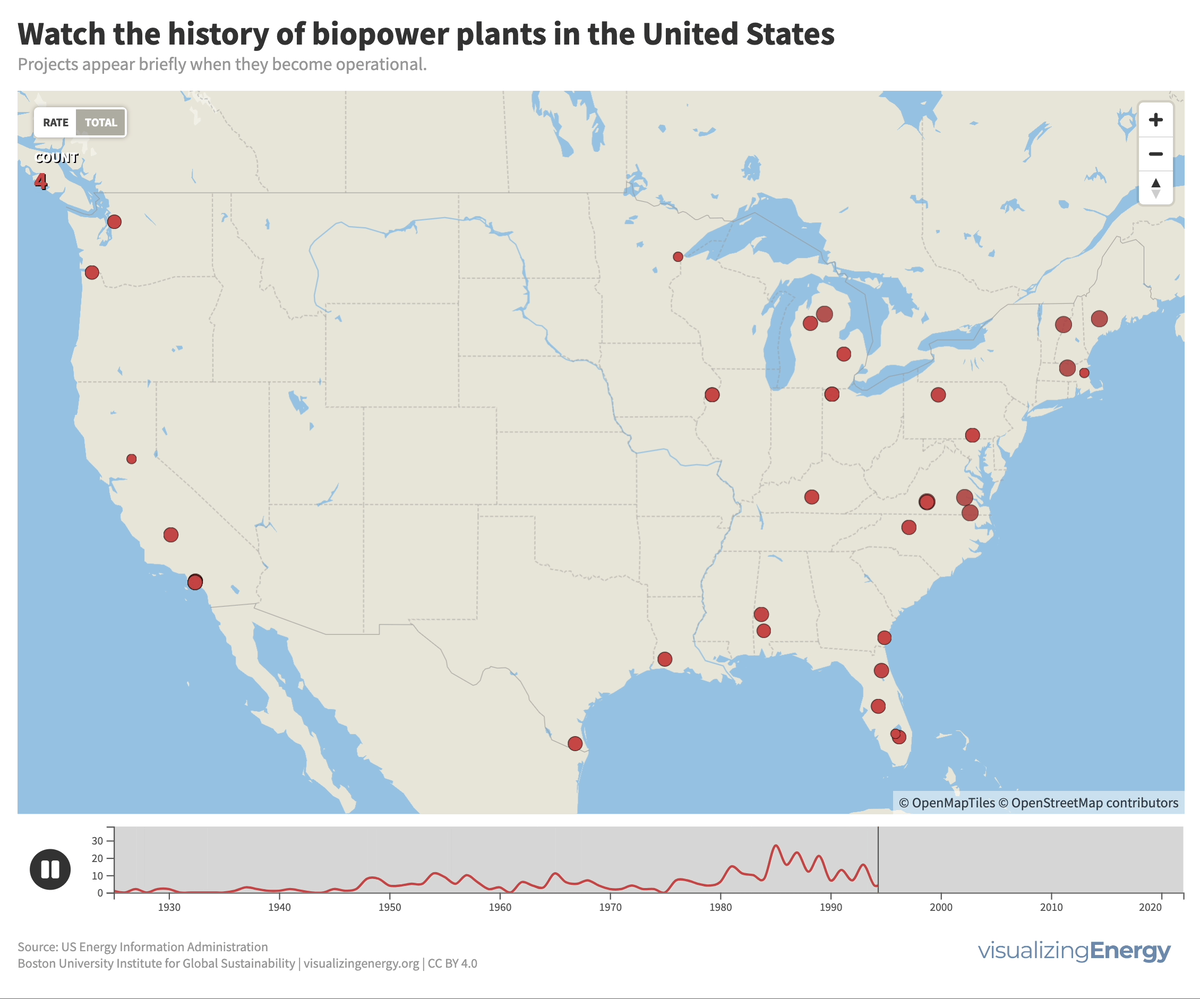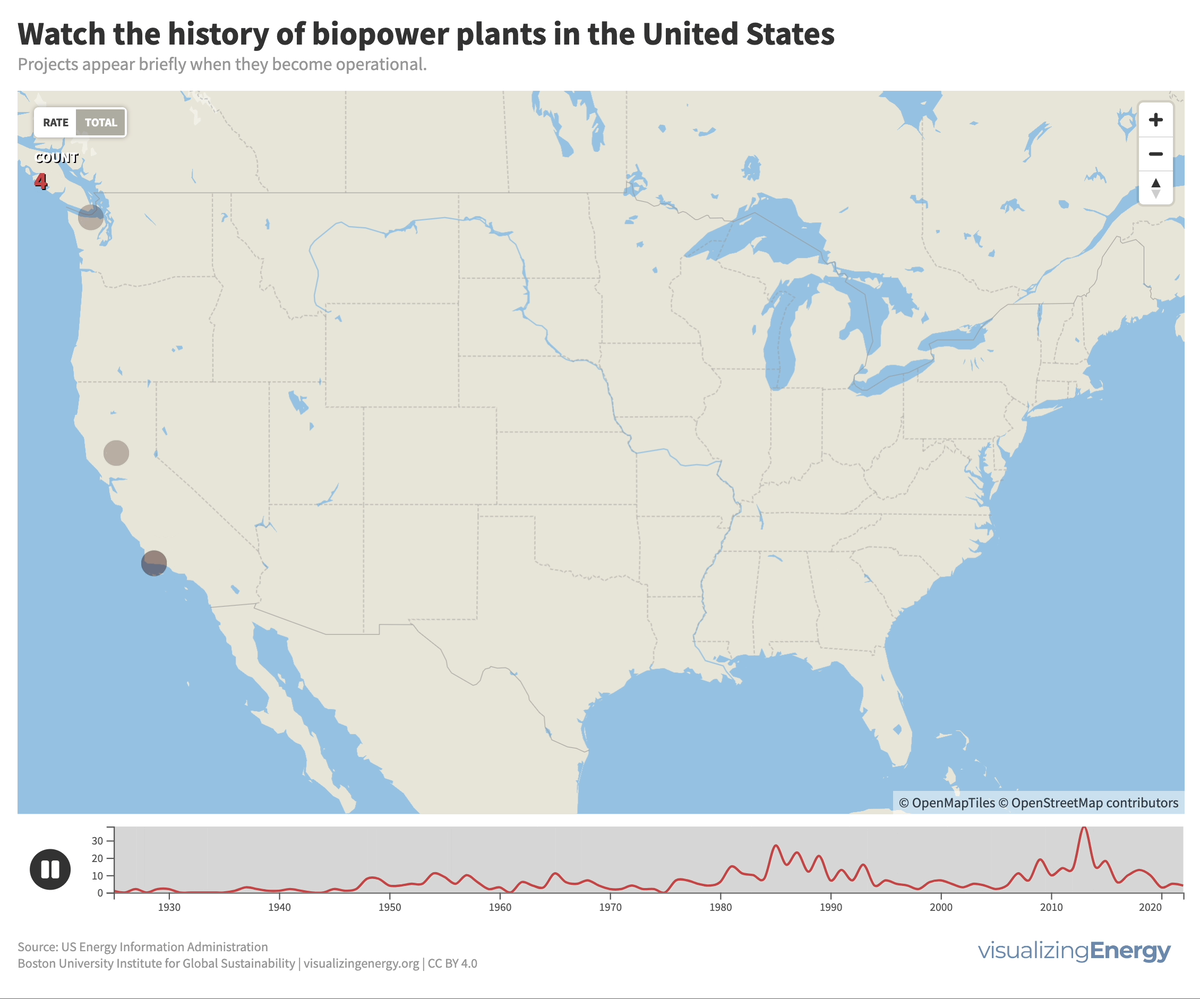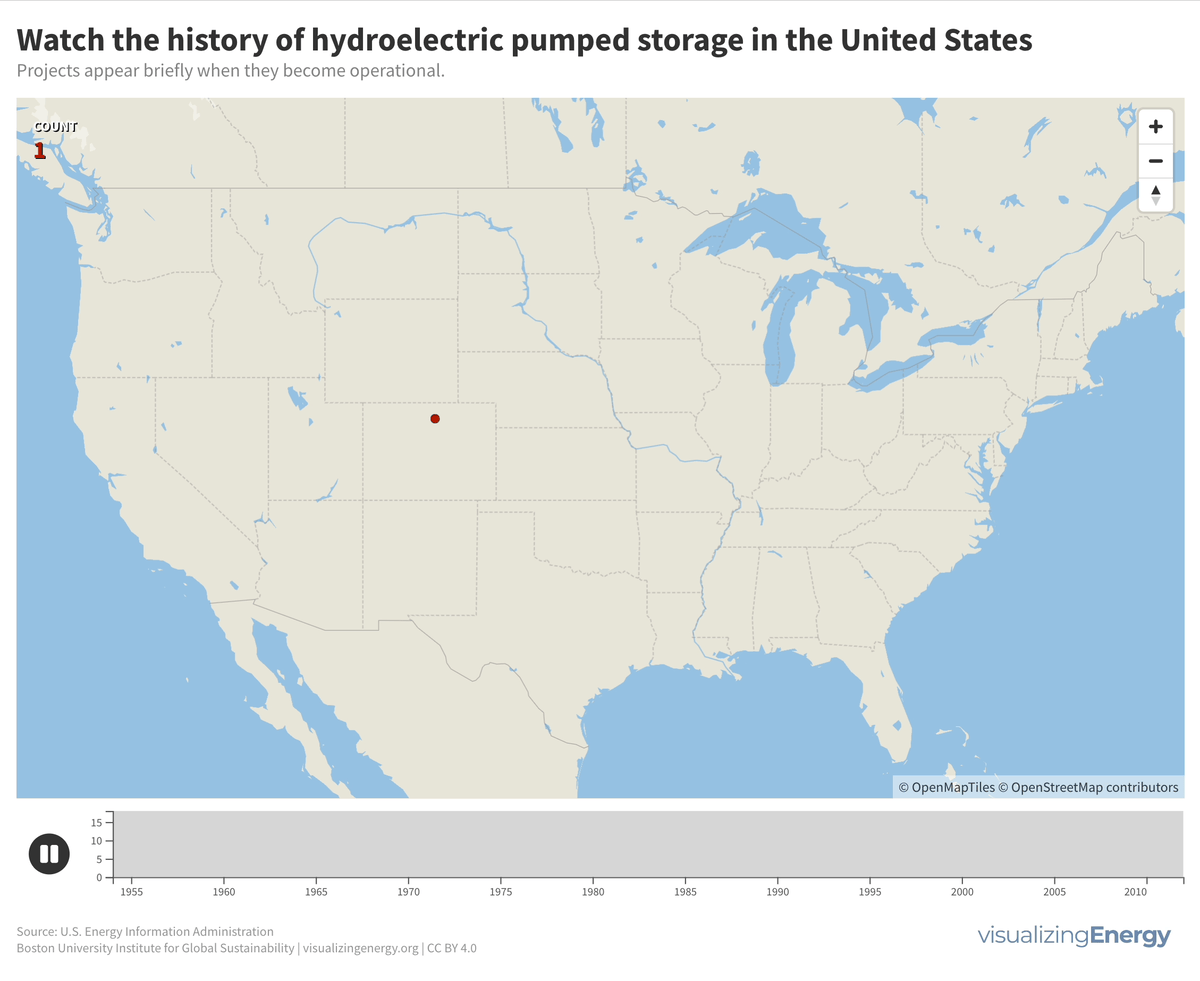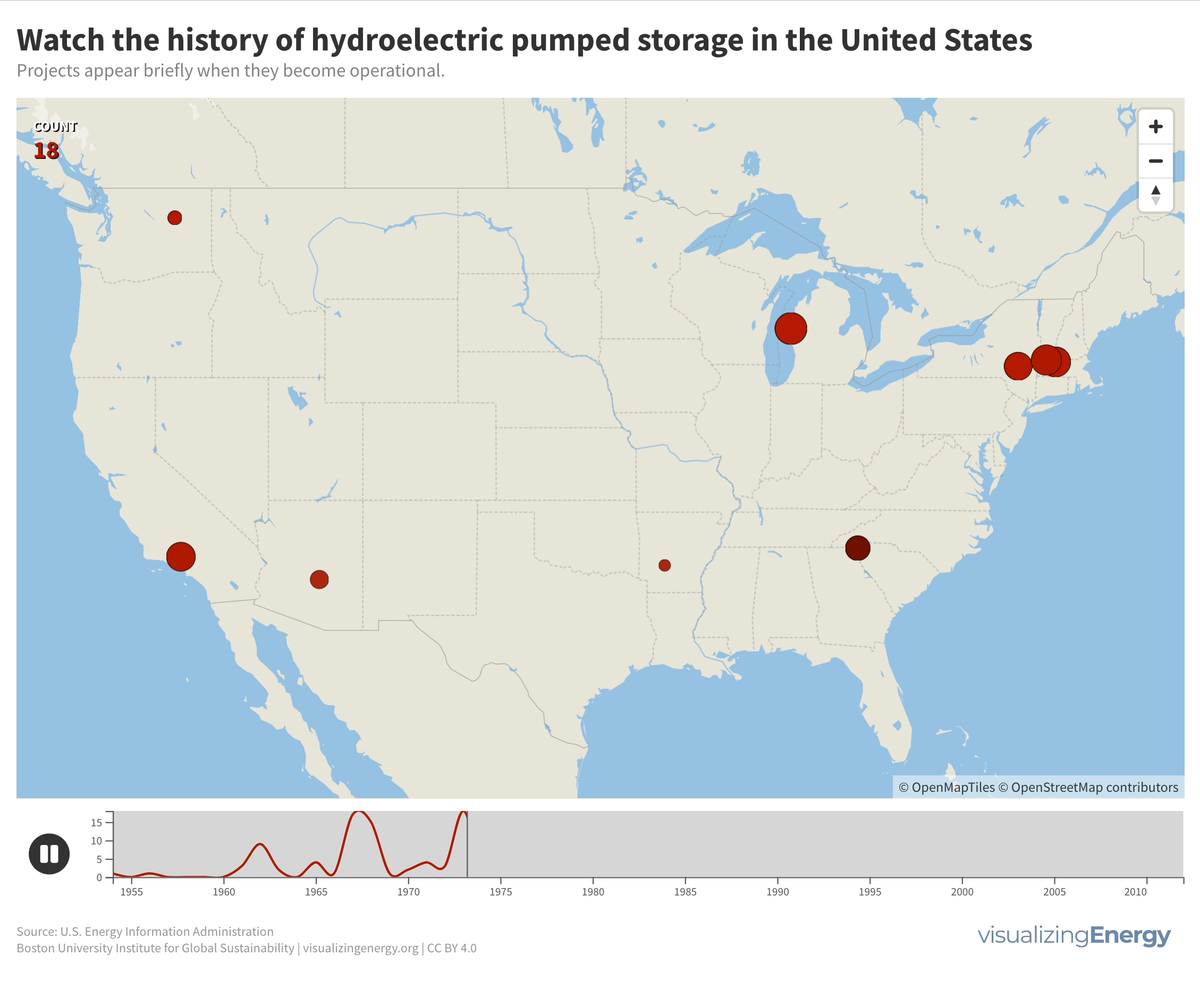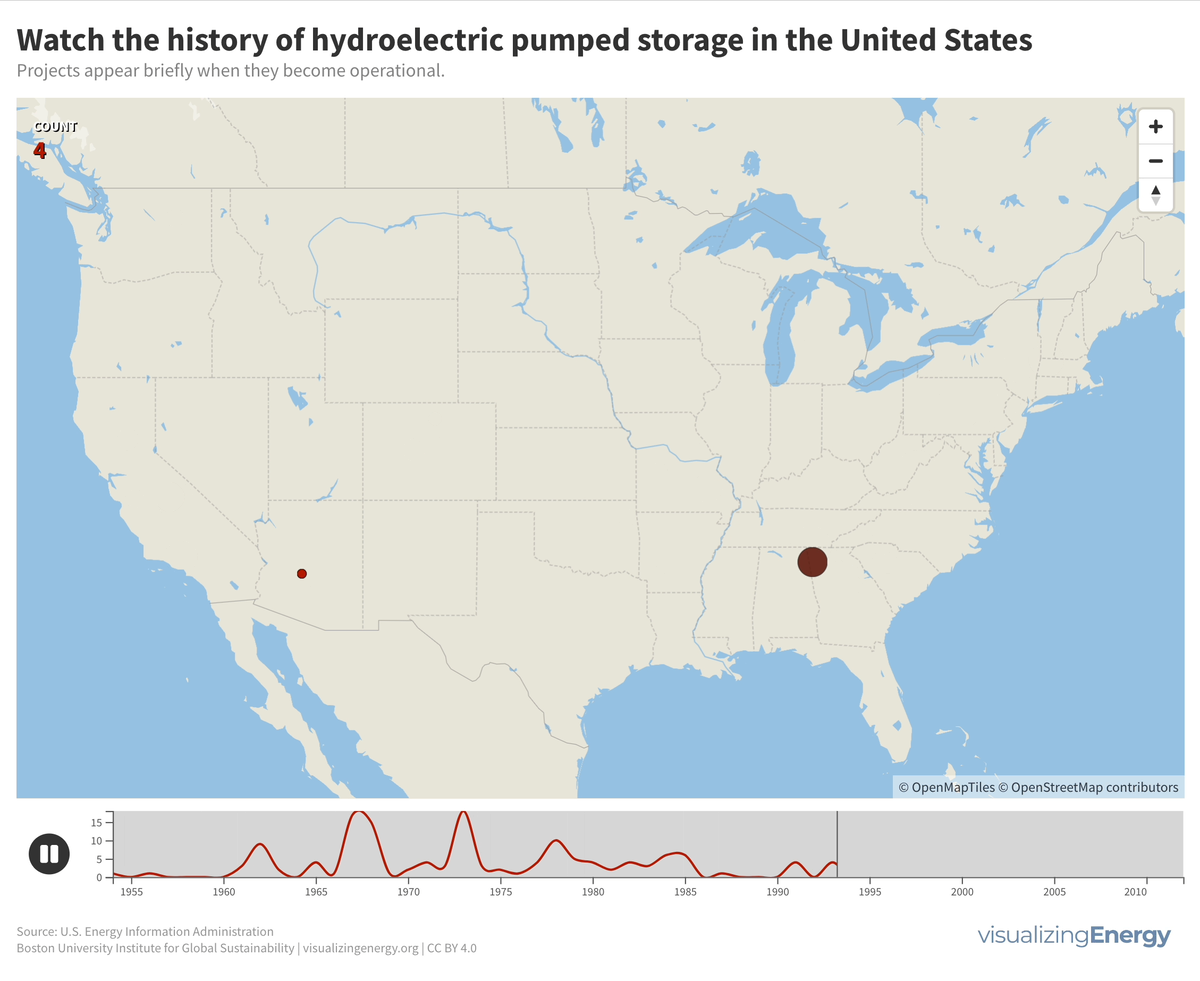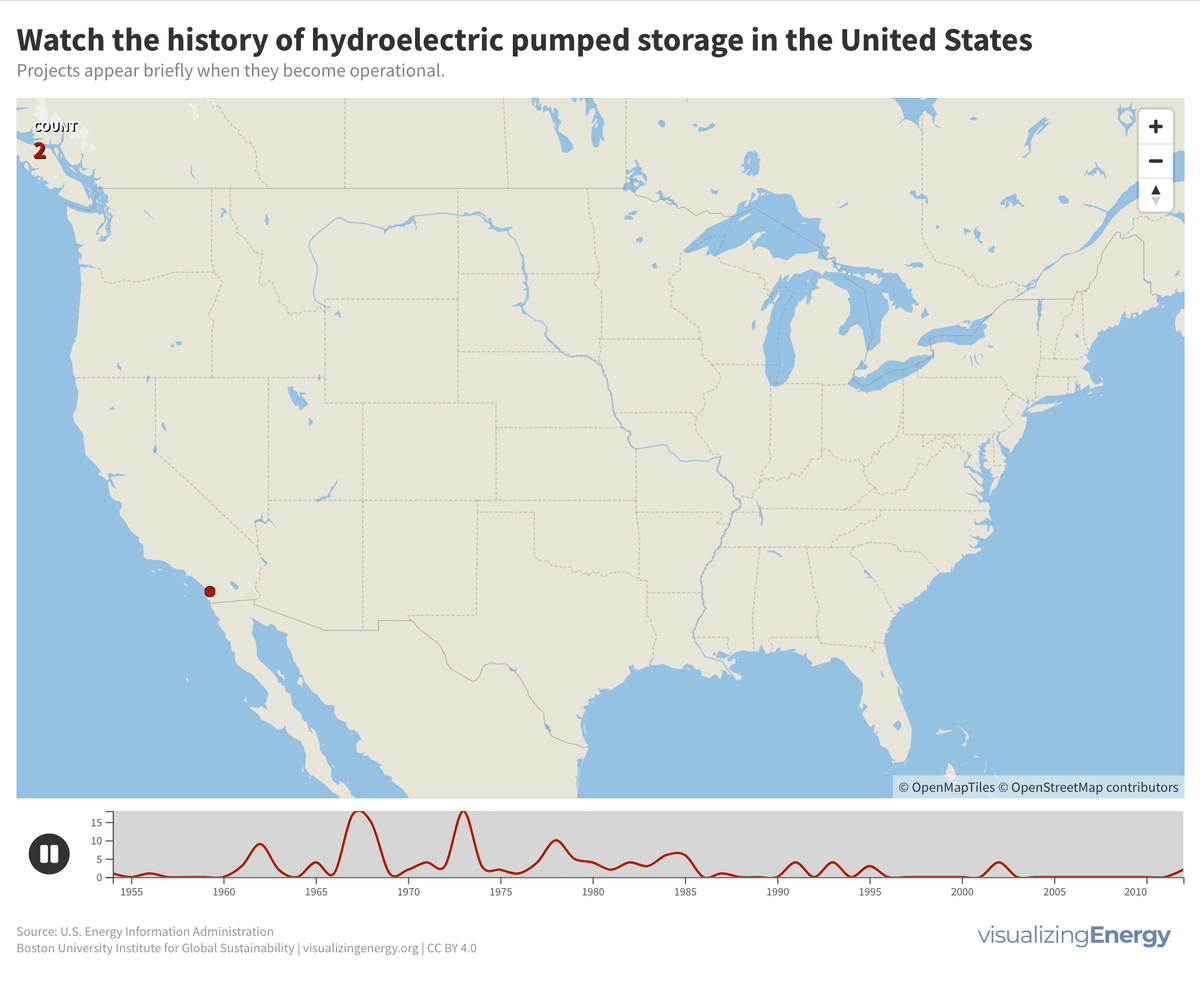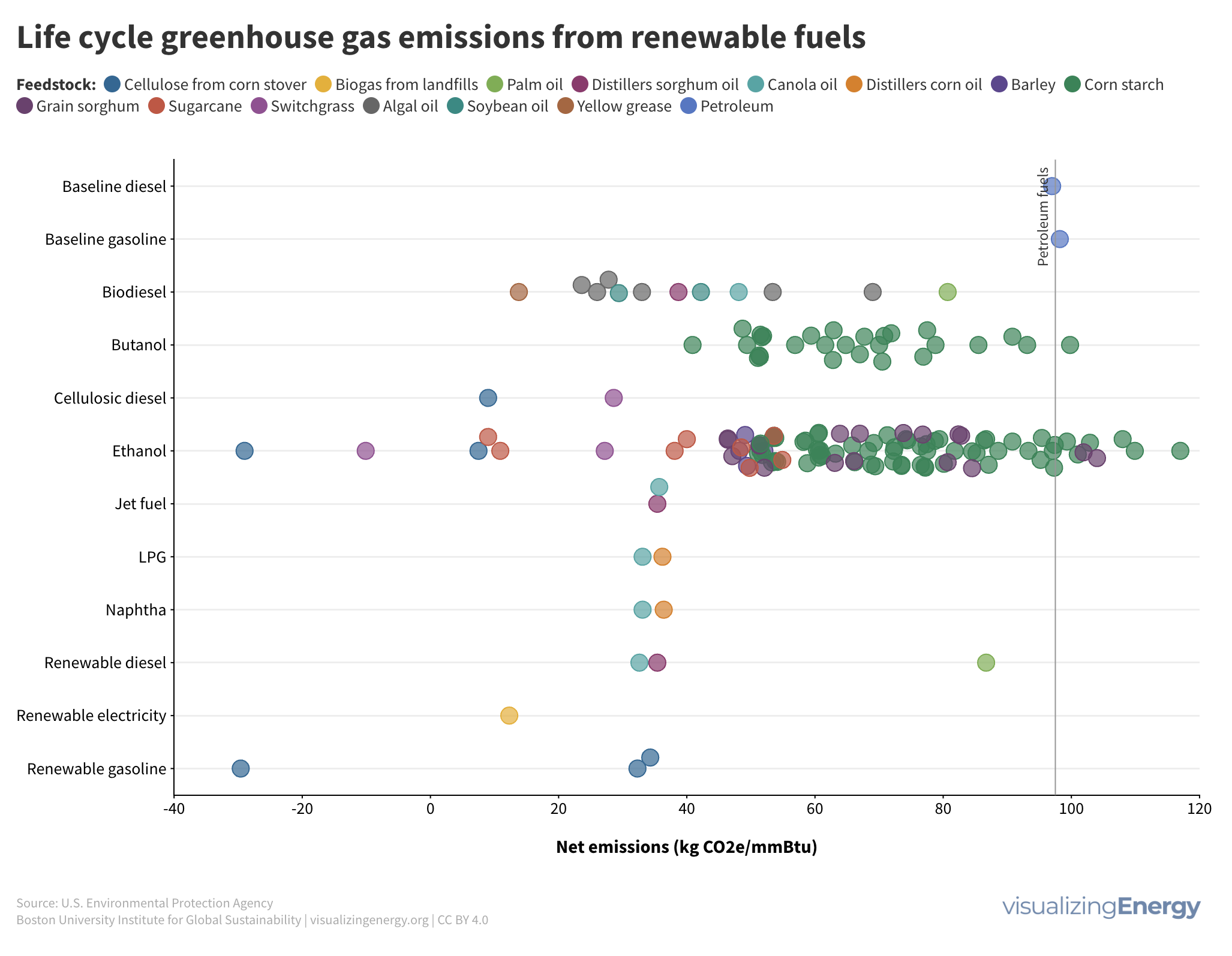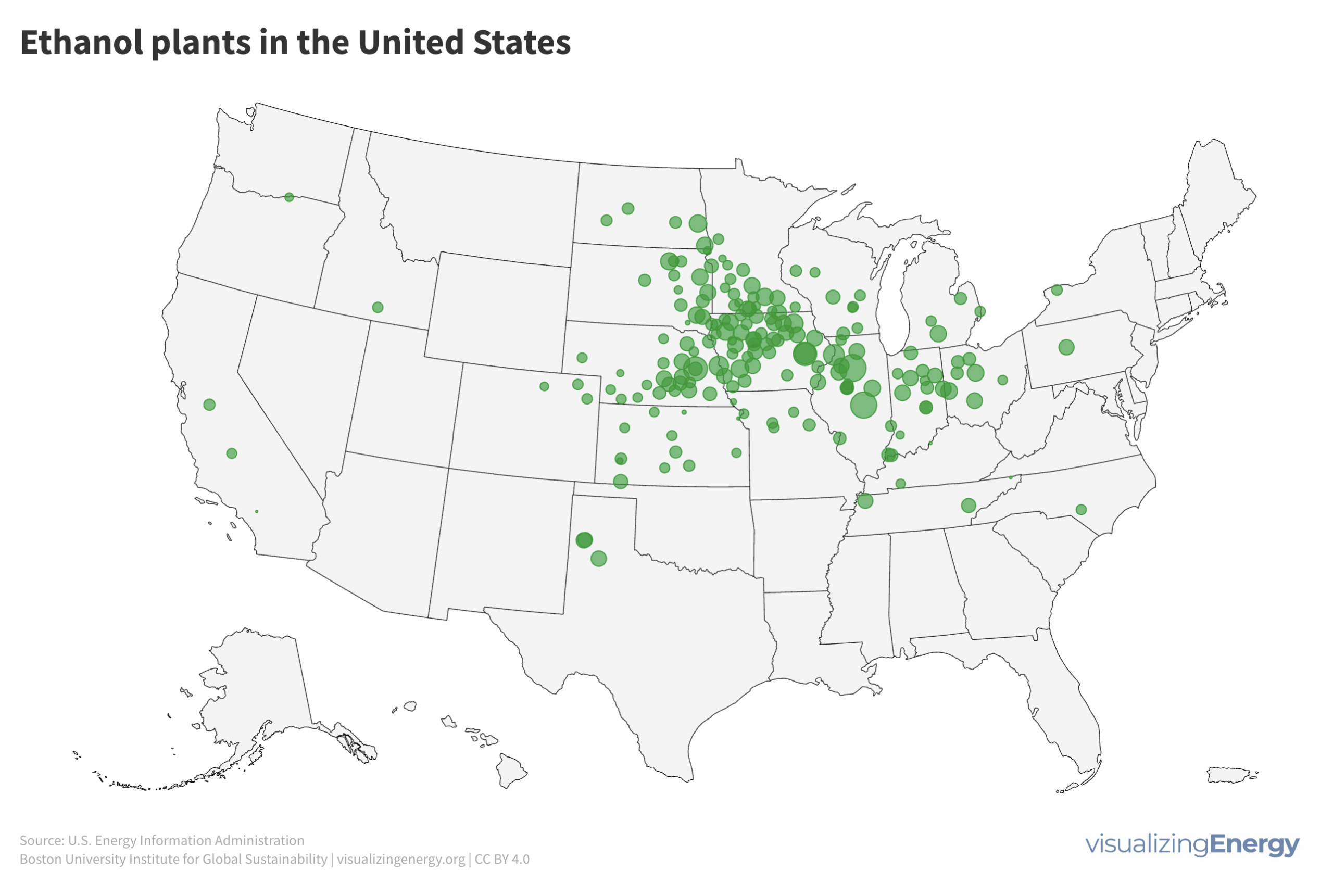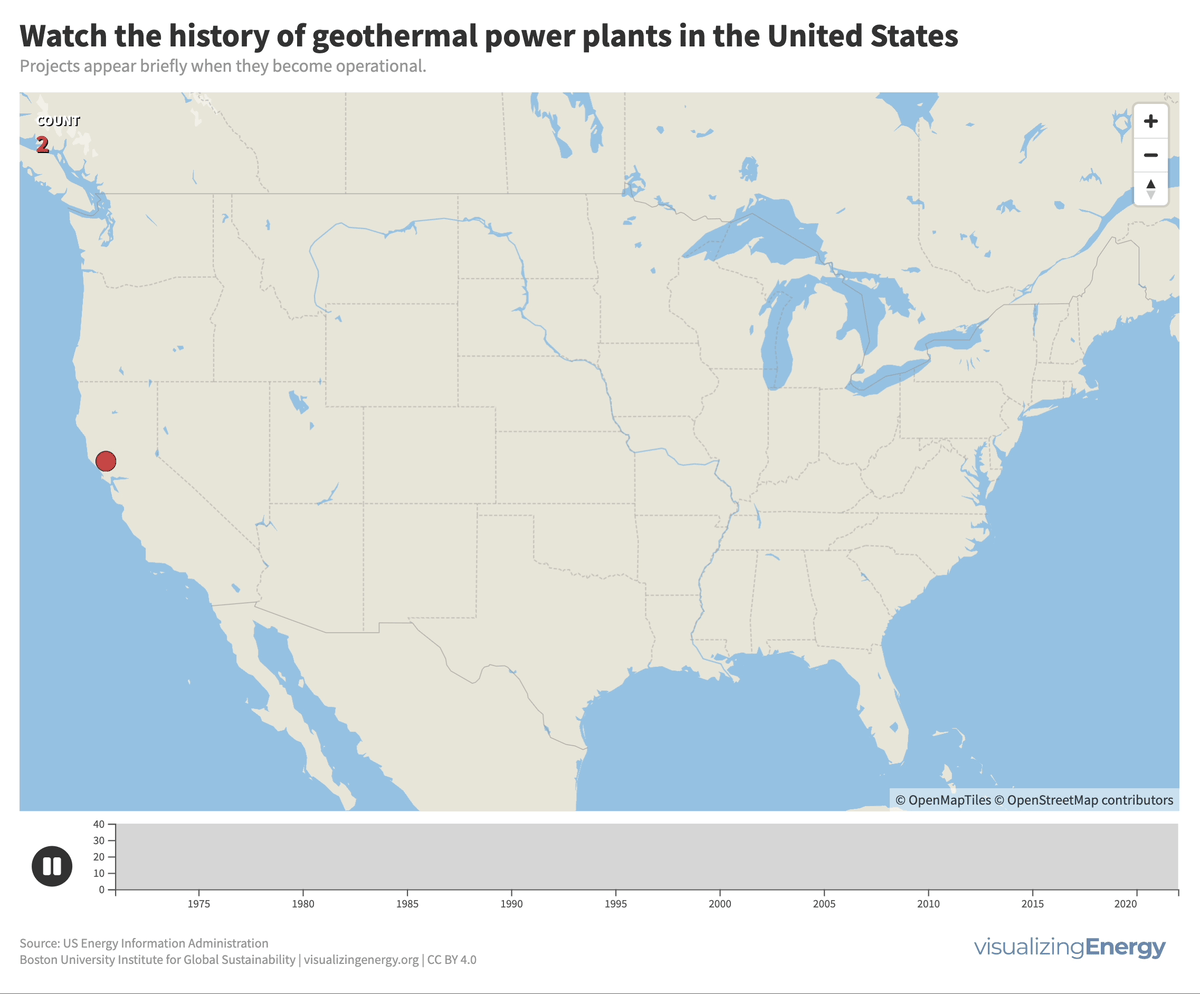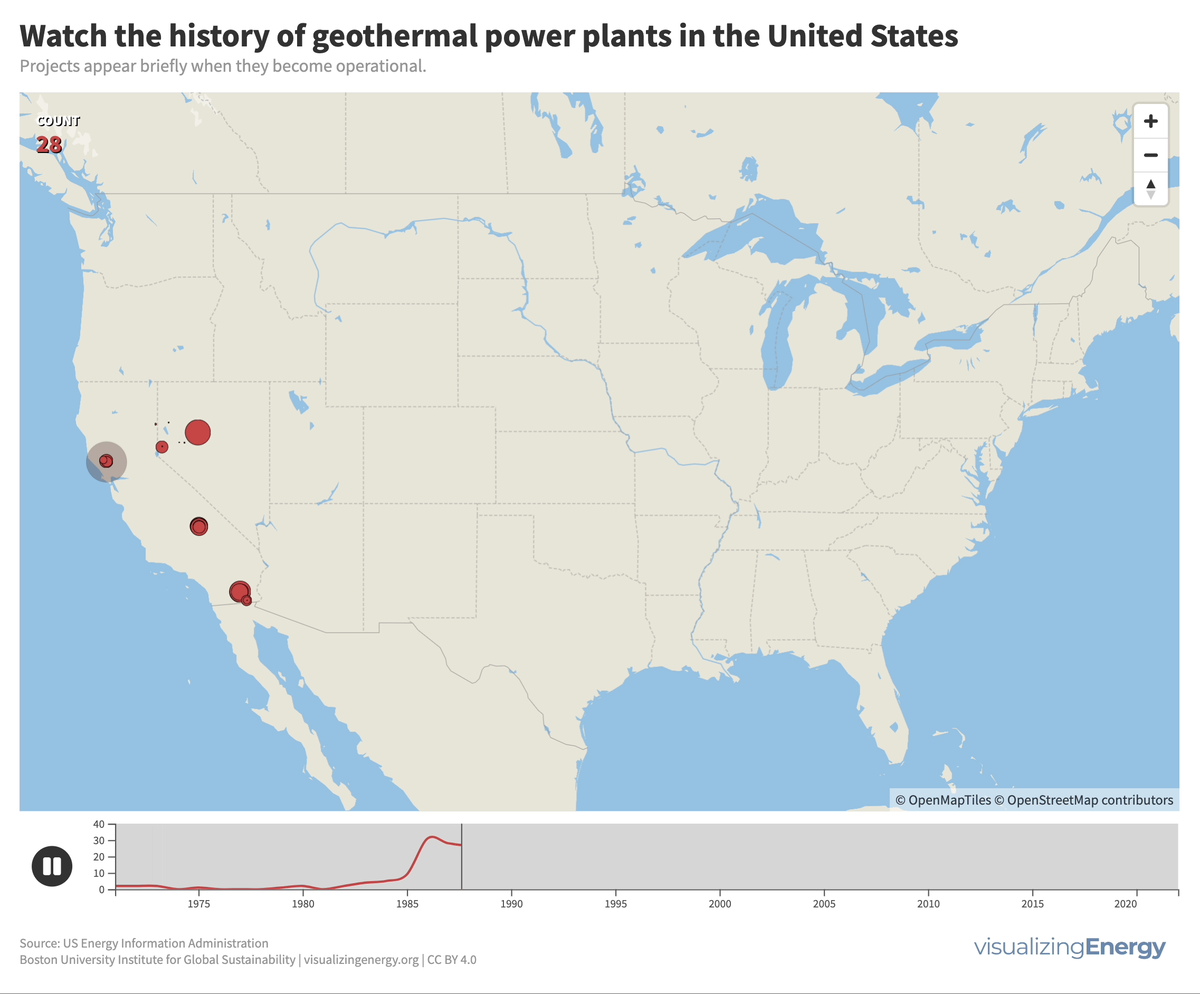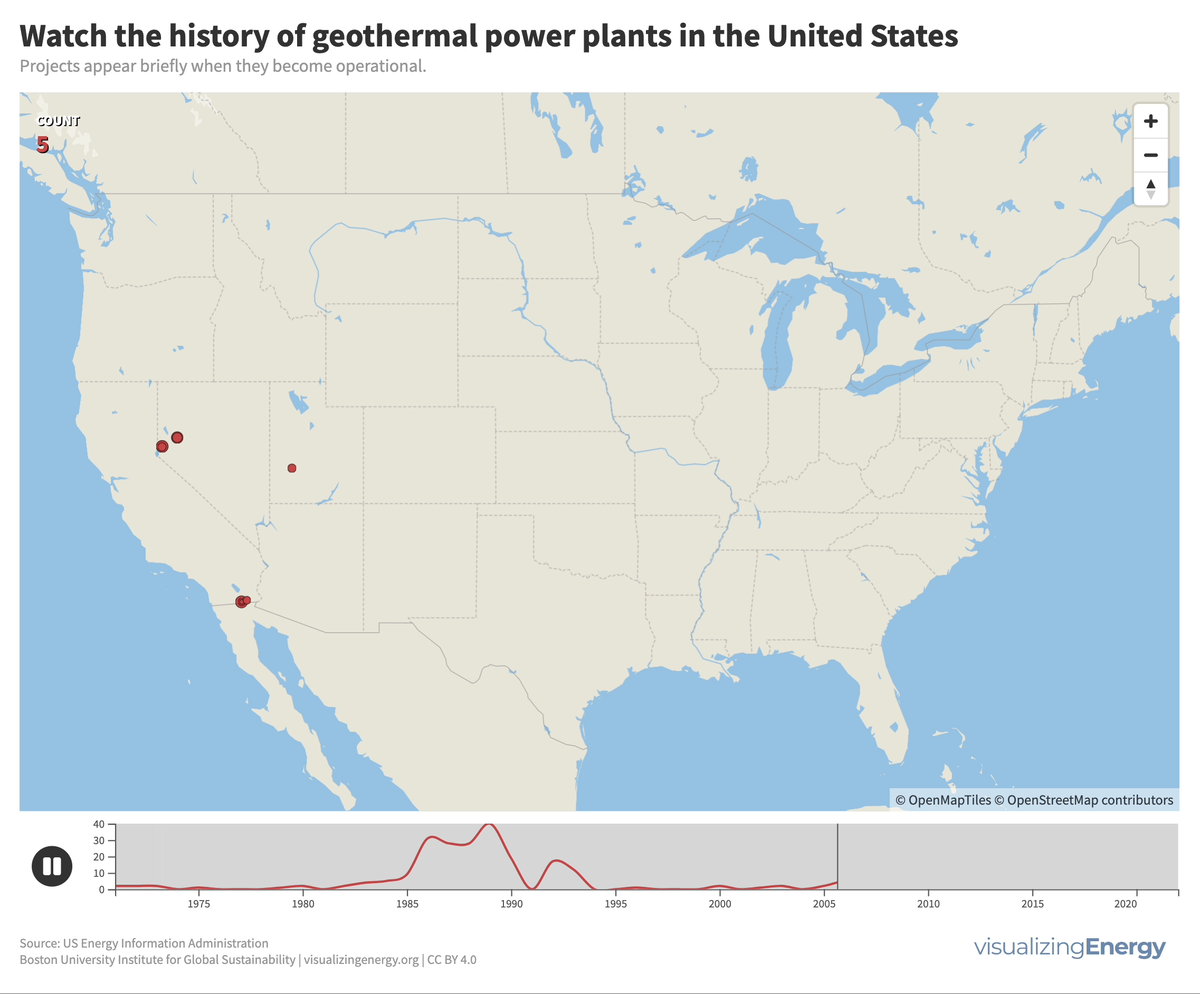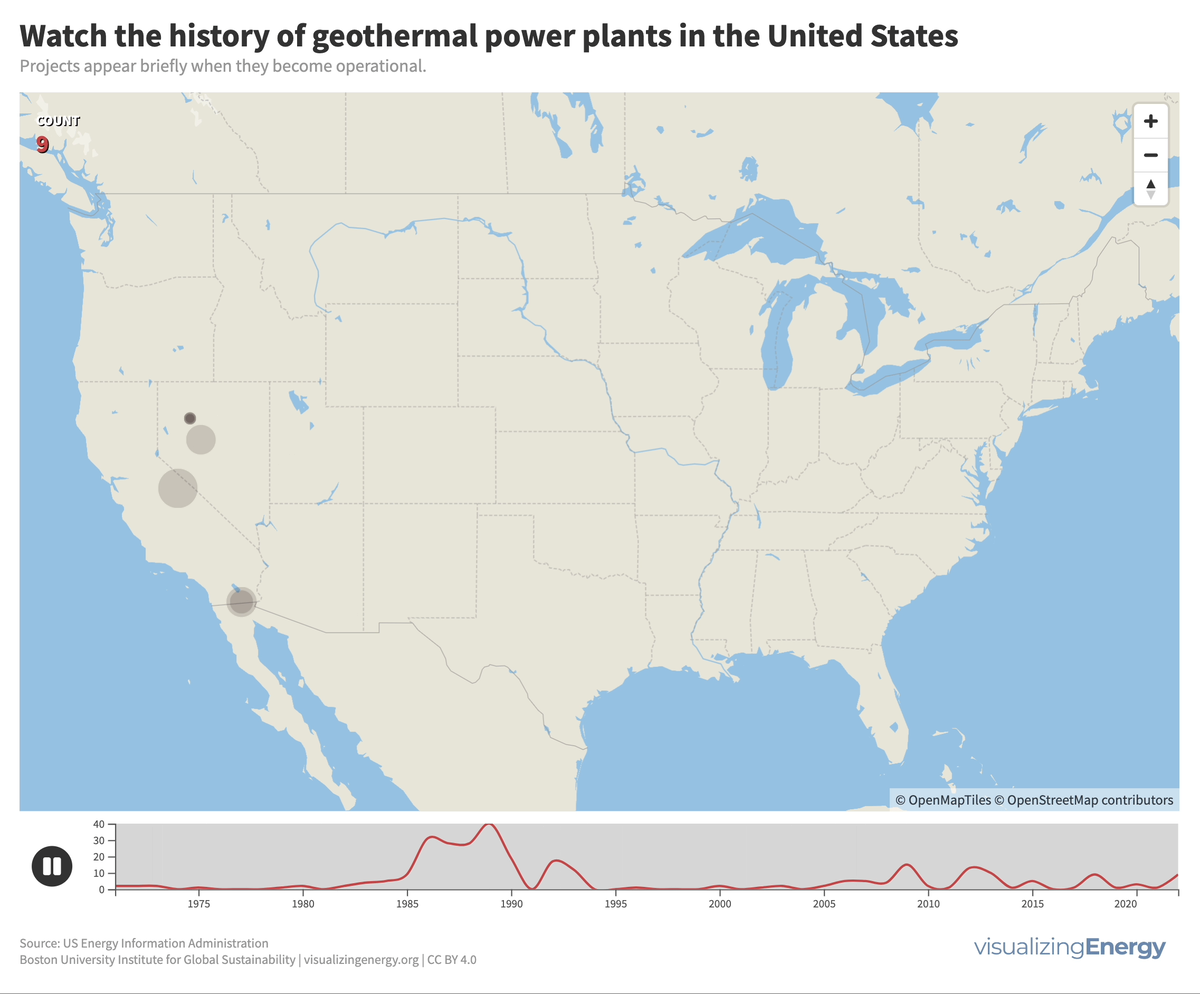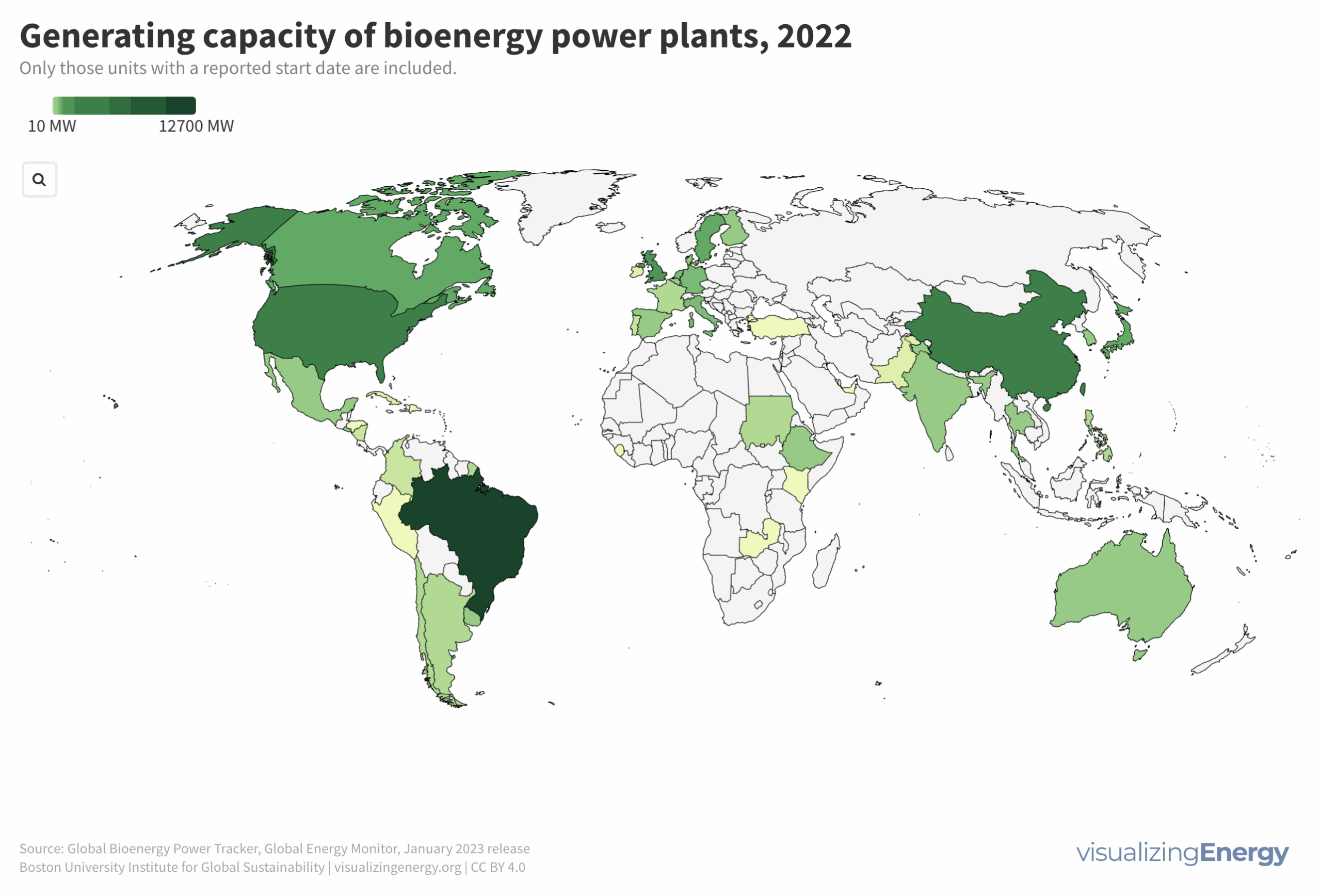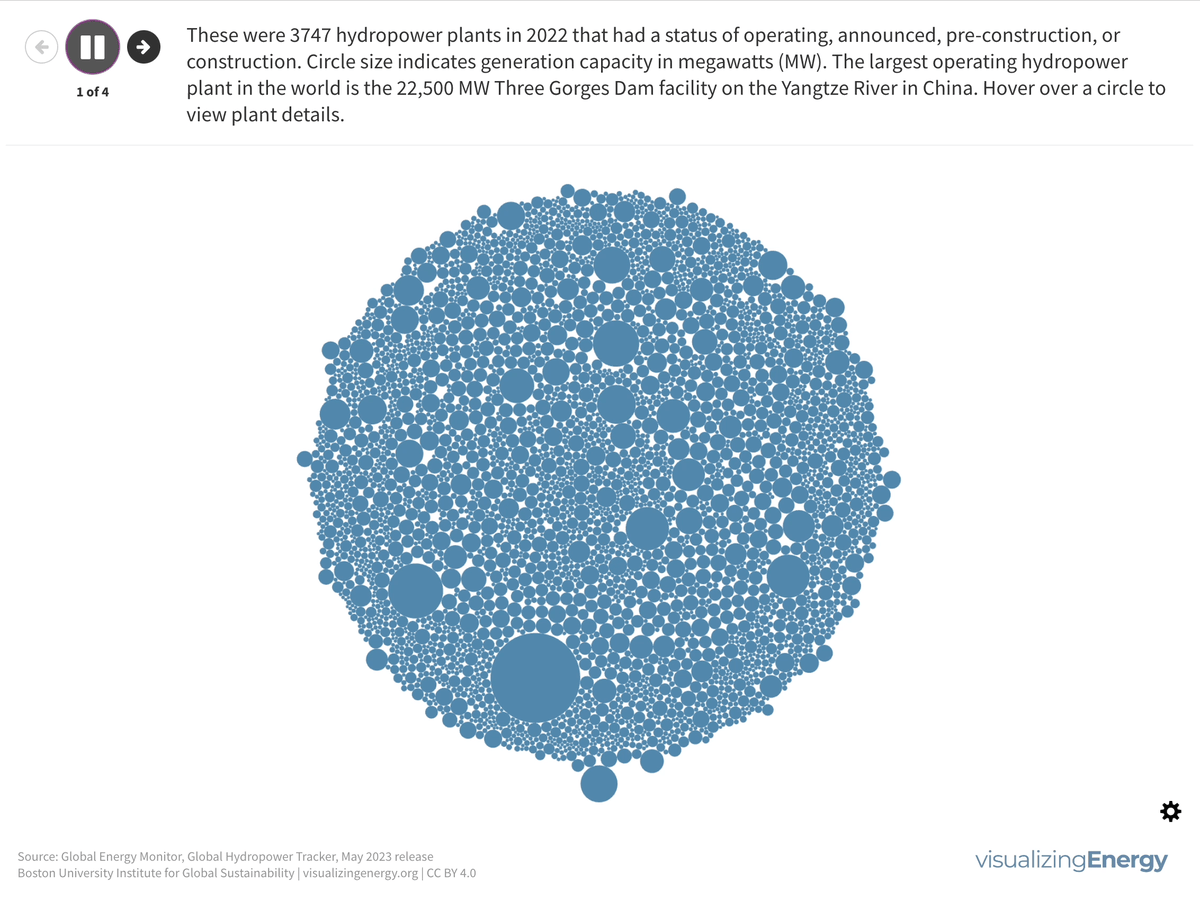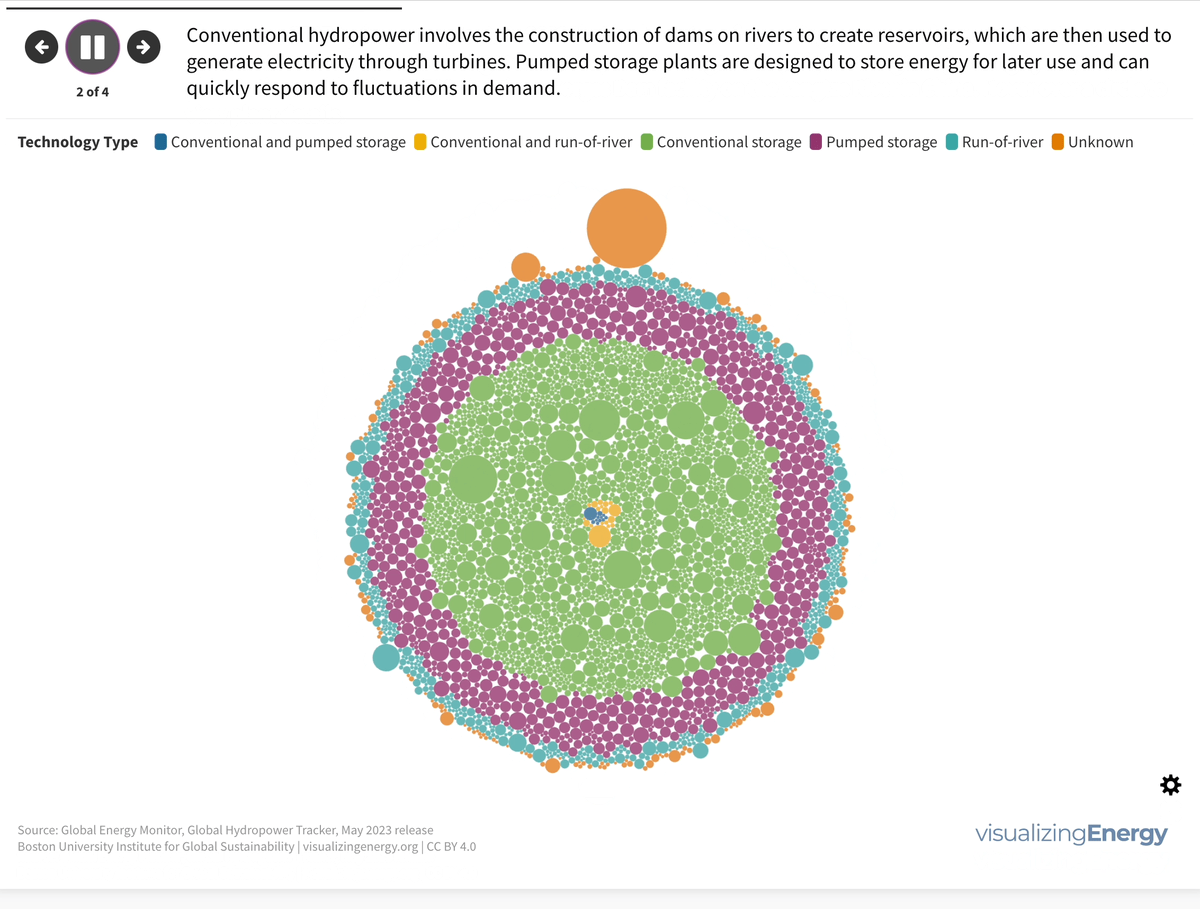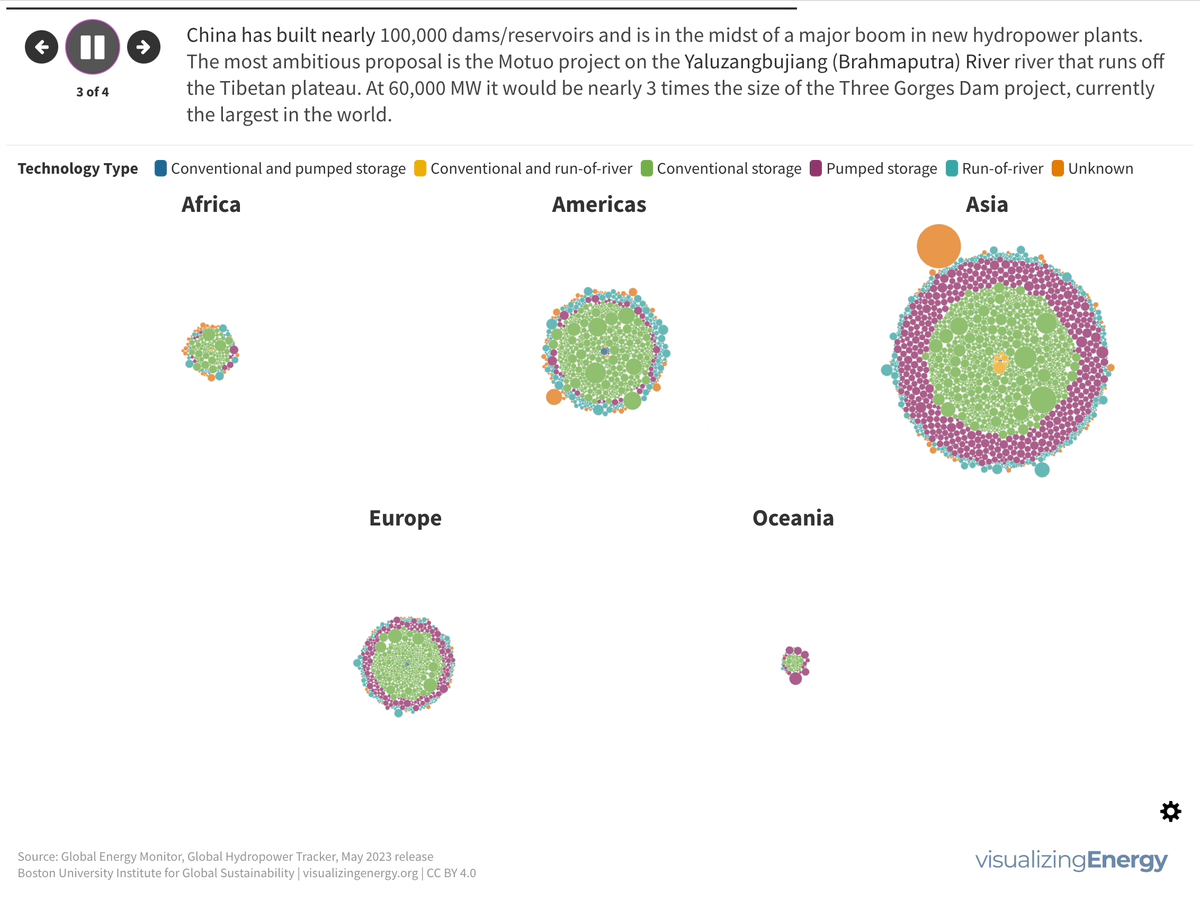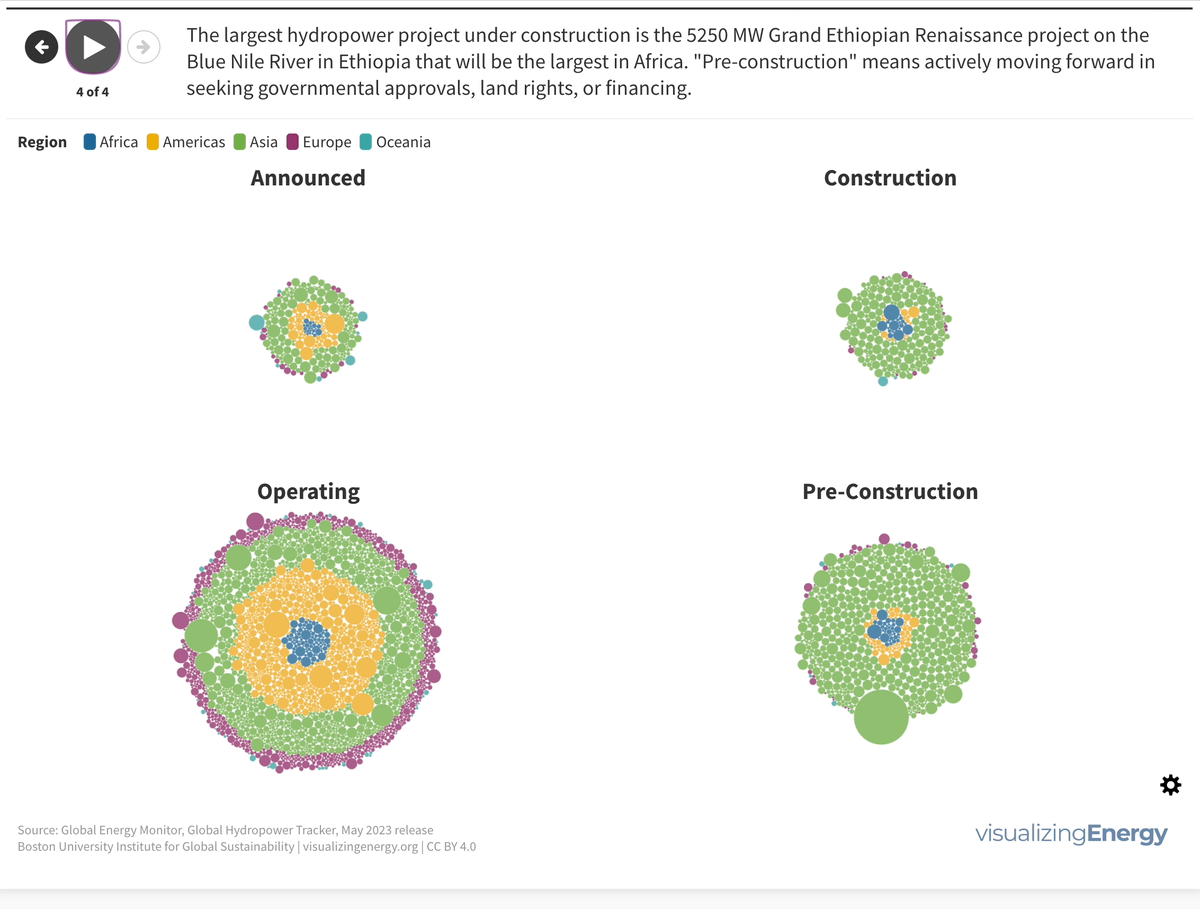
Explore the world’s hydropower plants in 2022
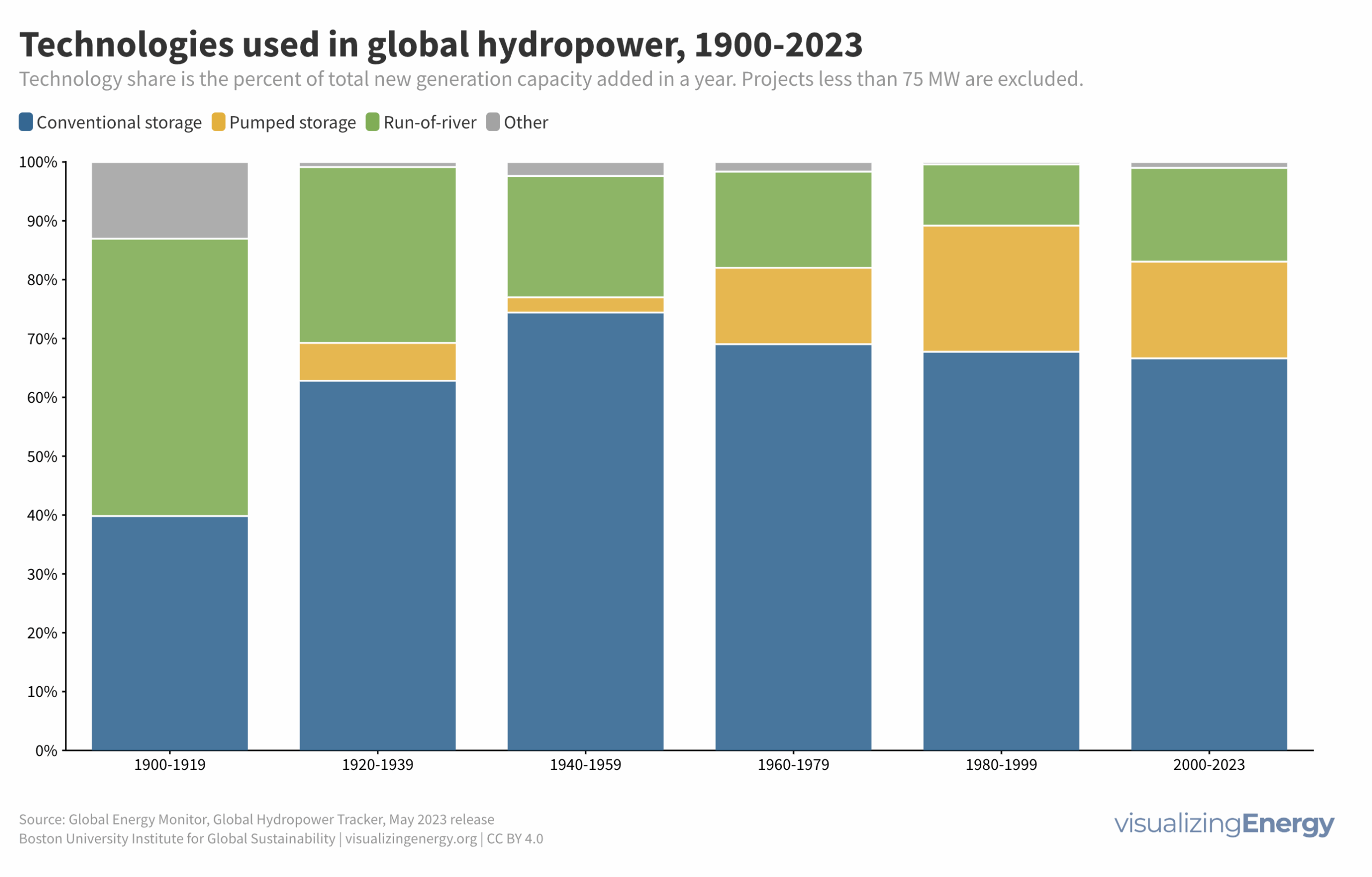
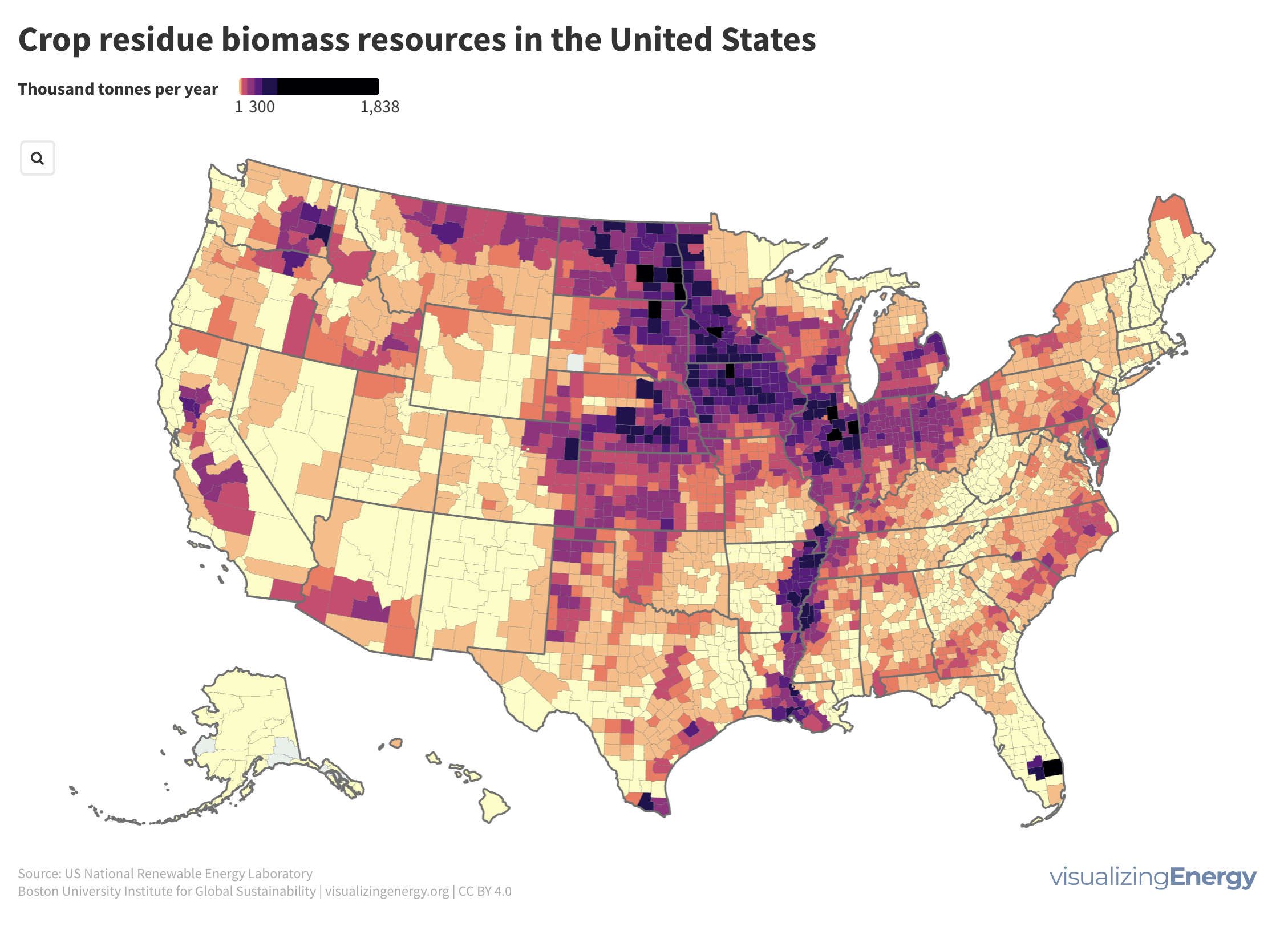
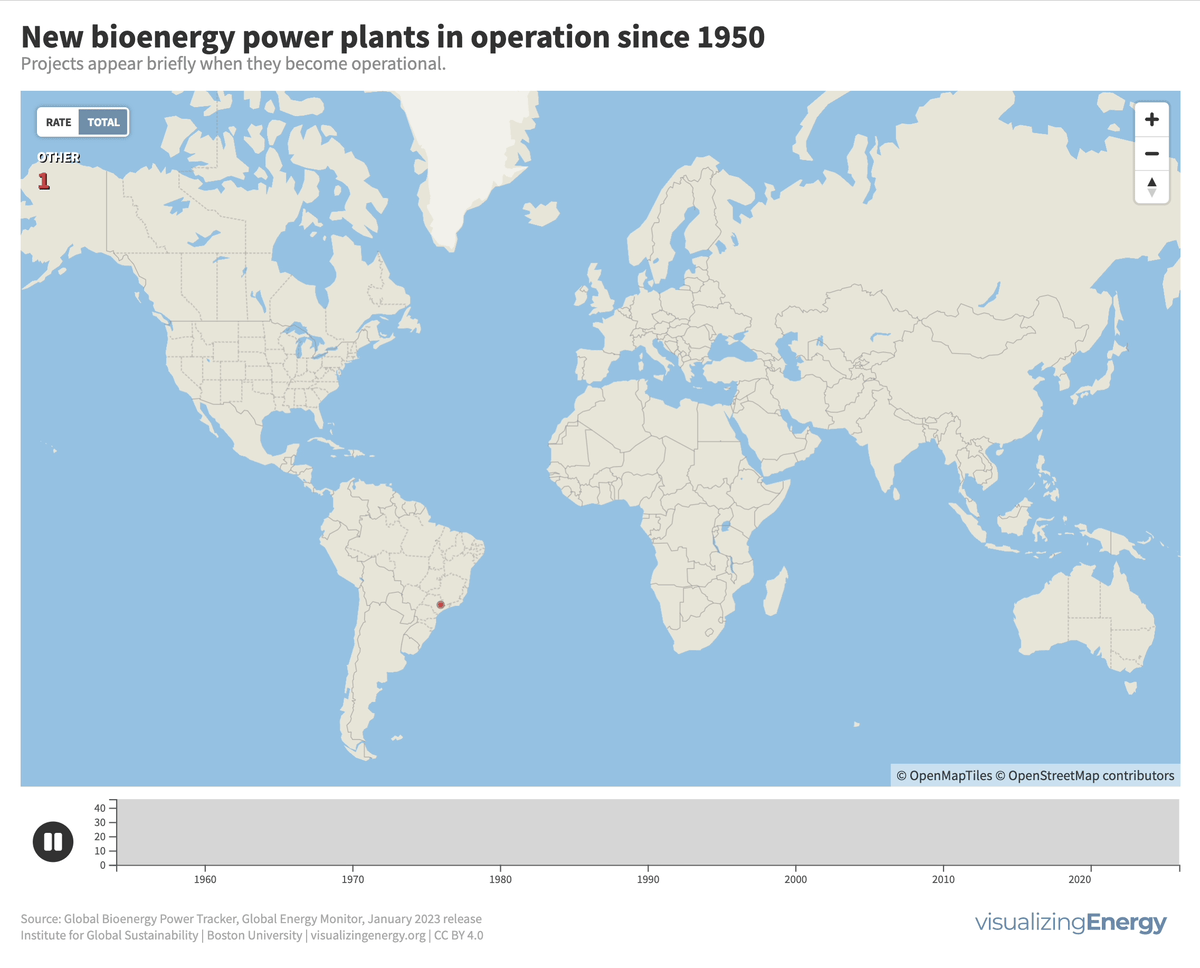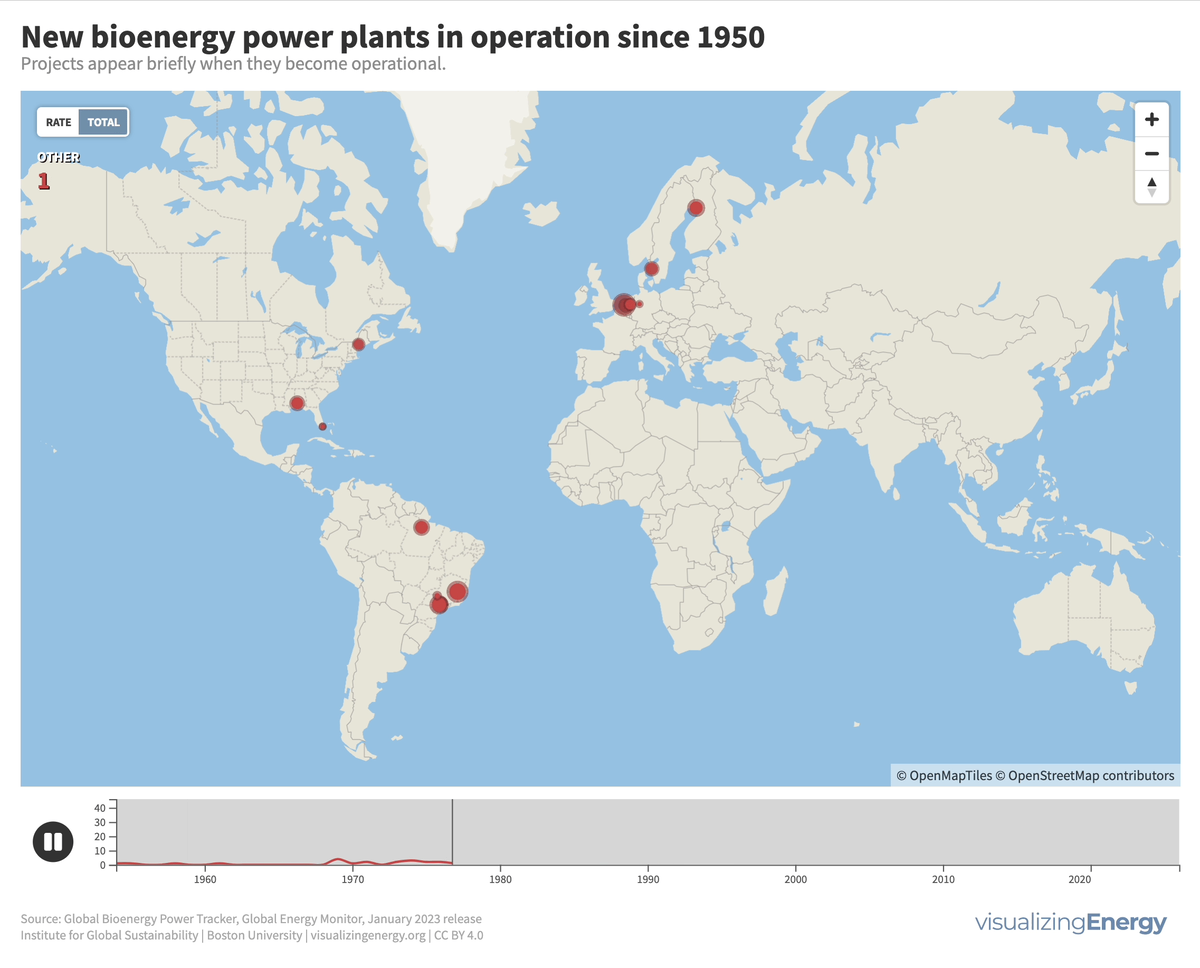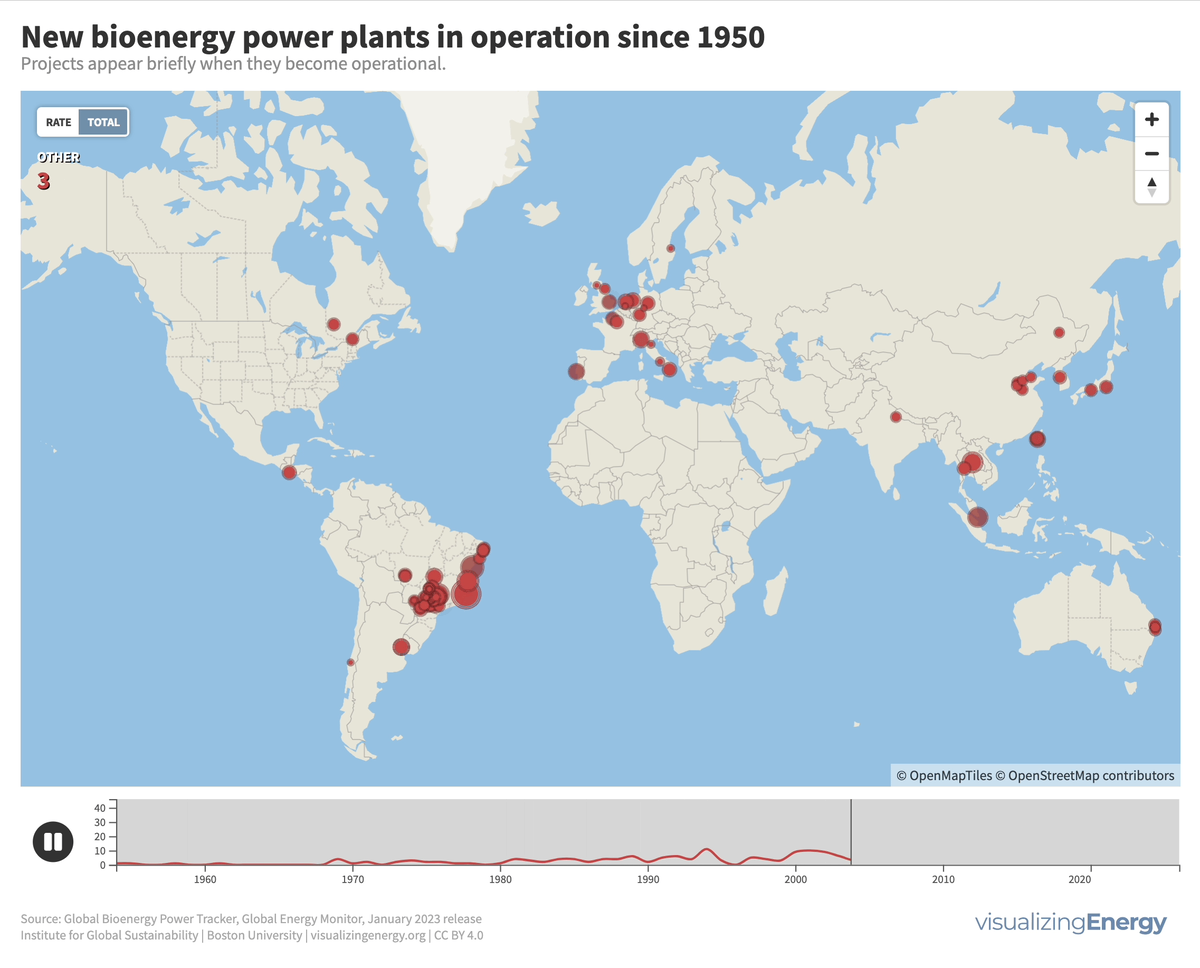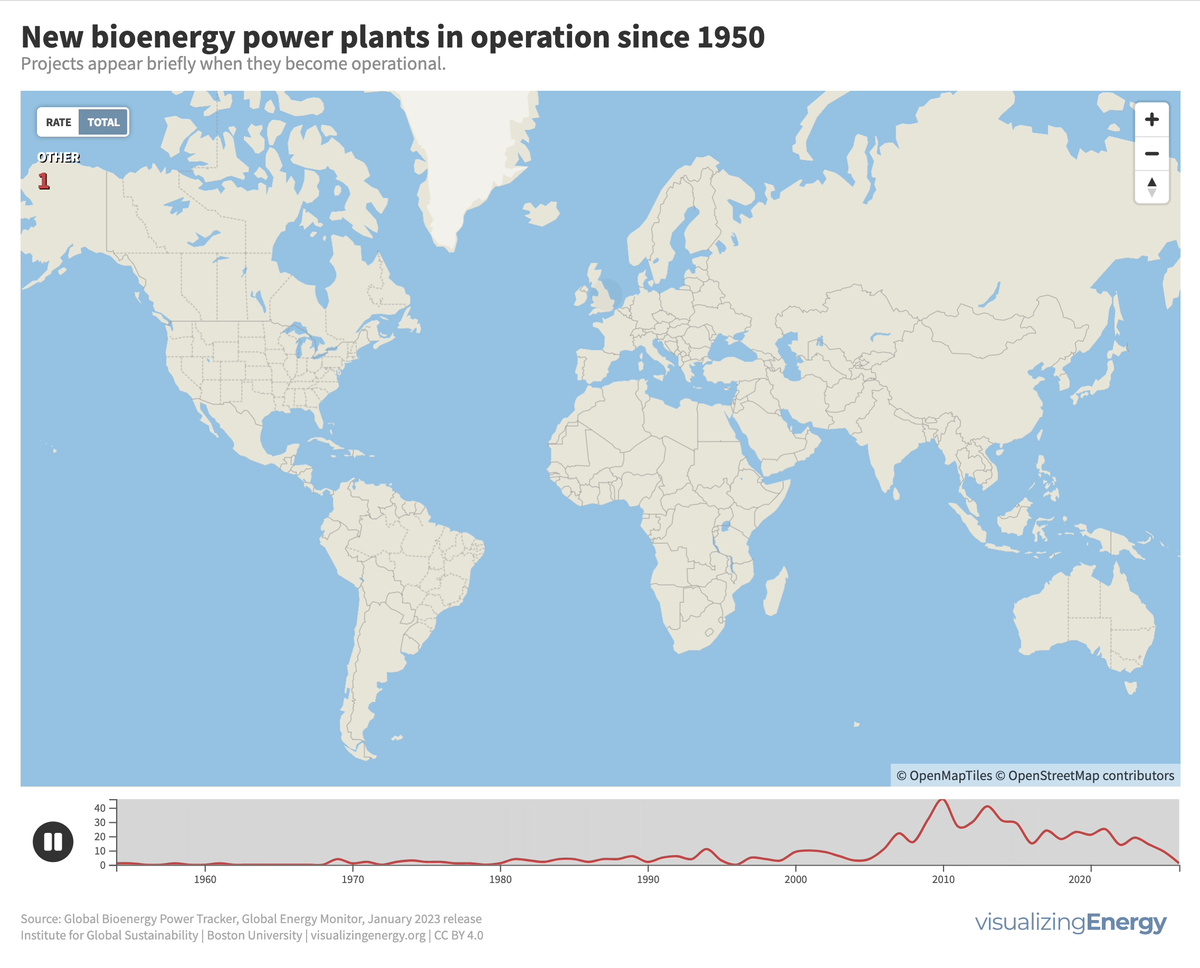
Hydropower, a pioneer in grid-scale electricity generation since the late 19th century, now provides 17% of global electricity, surpassing nuclear, wind, solar, bioenergy, and geothermal combined. While the US and Europe have well-established capacity with limited room for expansion, China, India, Africa, and South America are developing new projects to meet rising electricity demand and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.