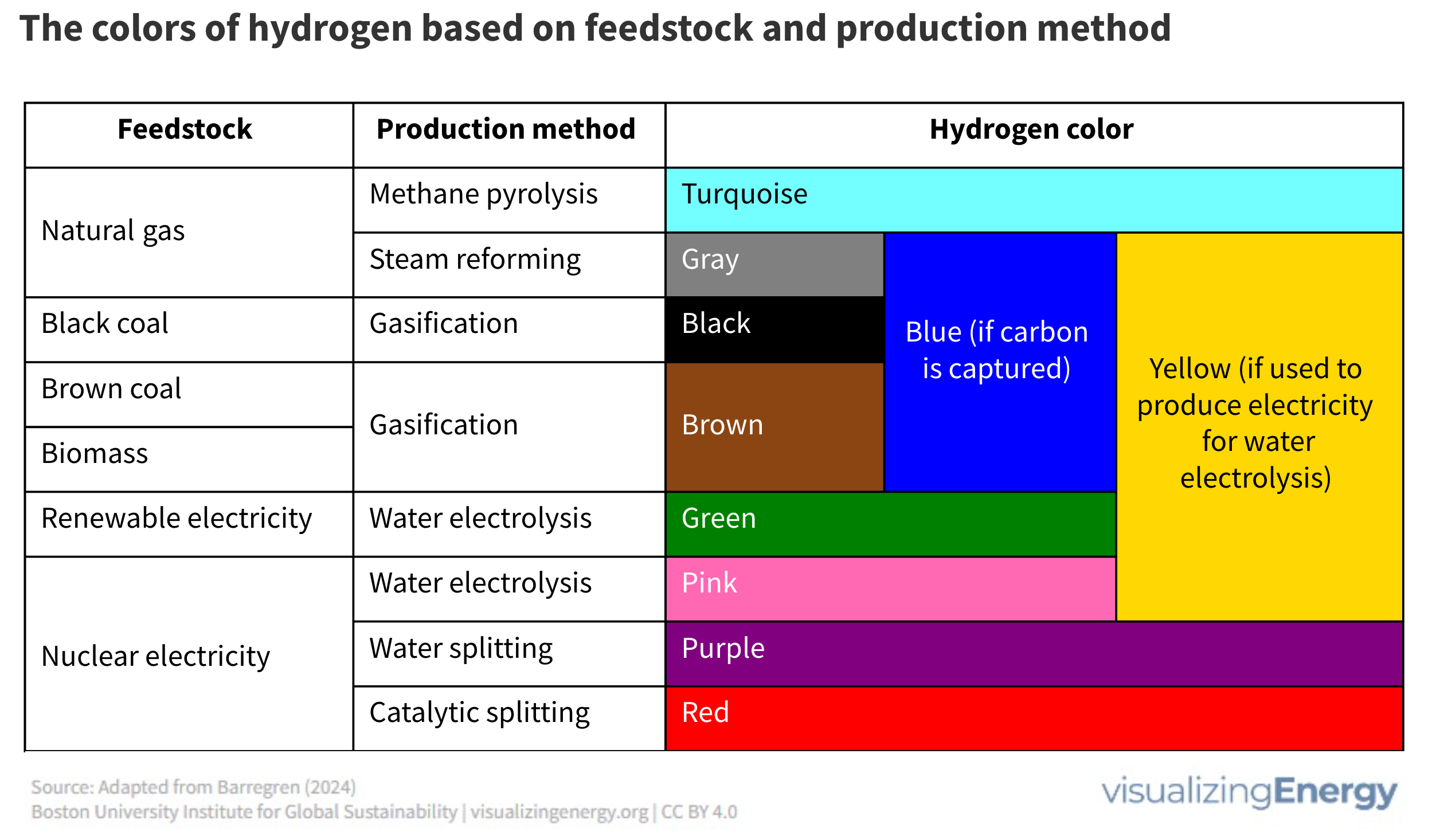
Why is hydrogen assigned different colors?
In 1875 the French Novelist Jules Verne published The Mysterious Island in which the protagonist Cyrus Smith envisioned a solution to the perceived inevitable exhaustion

In 1875 the French Novelist Jules Verne published The Mysterious Island in which the protagonist Cyrus Smith envisioned a solution to the perceived inevitable exhaustion
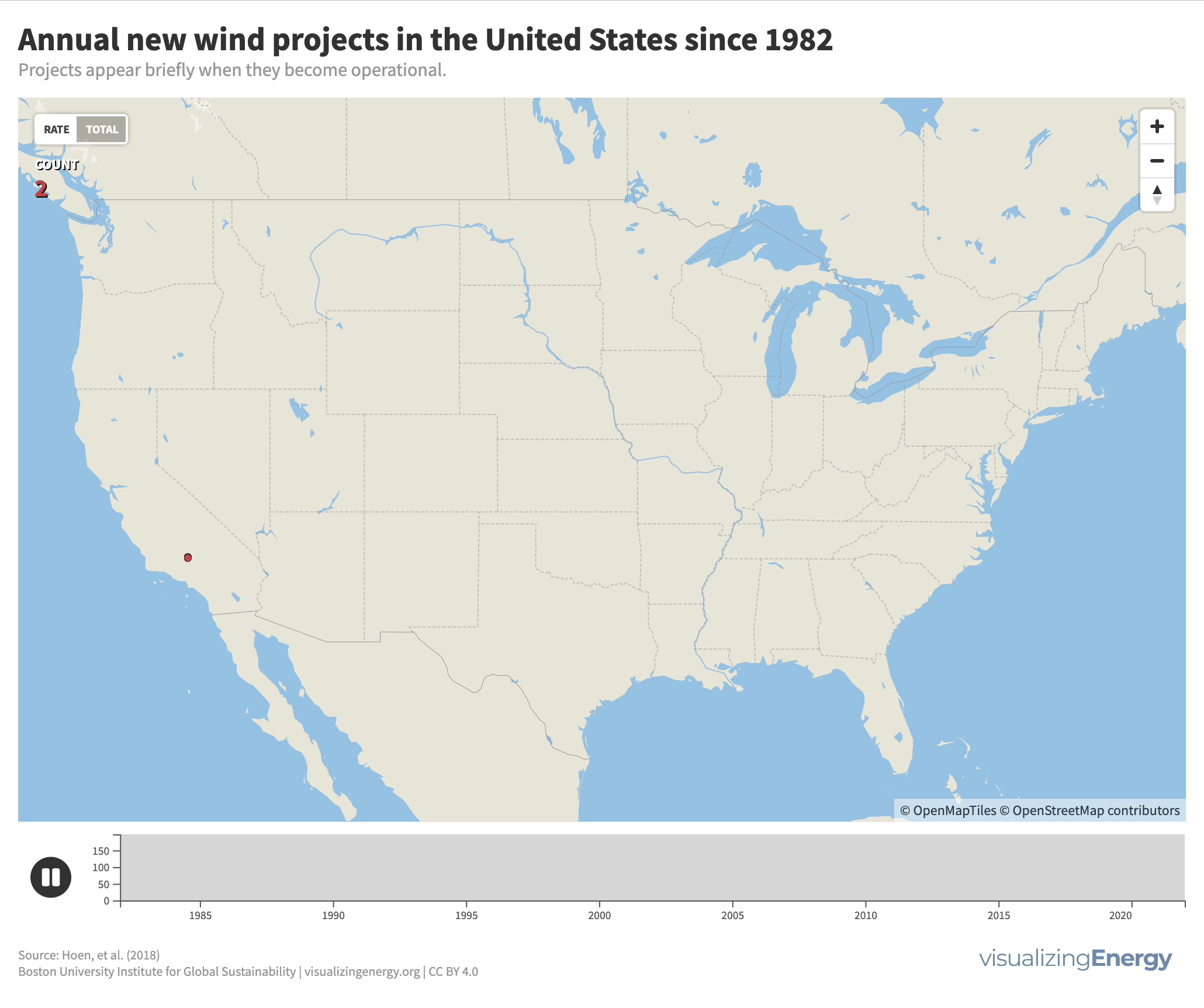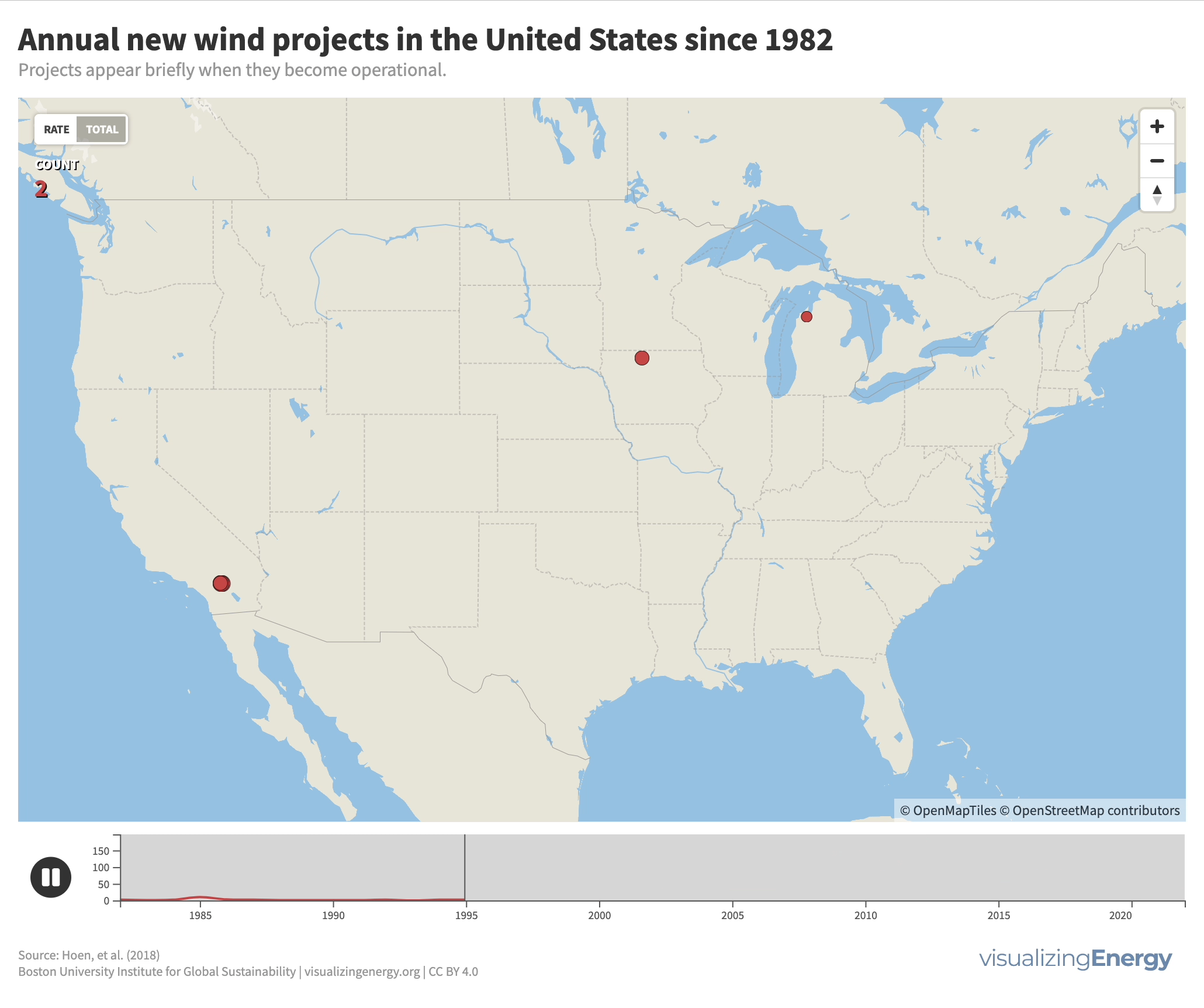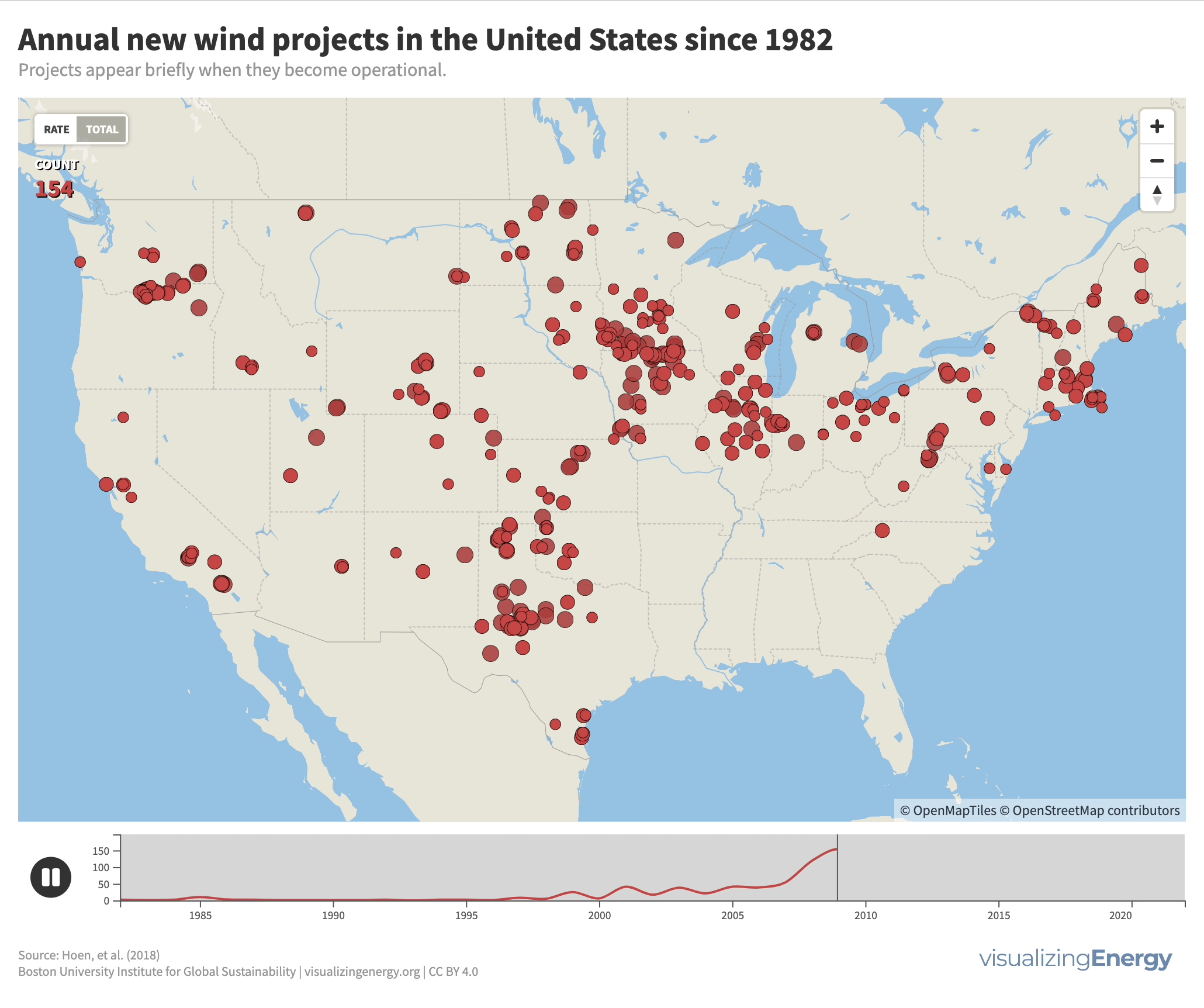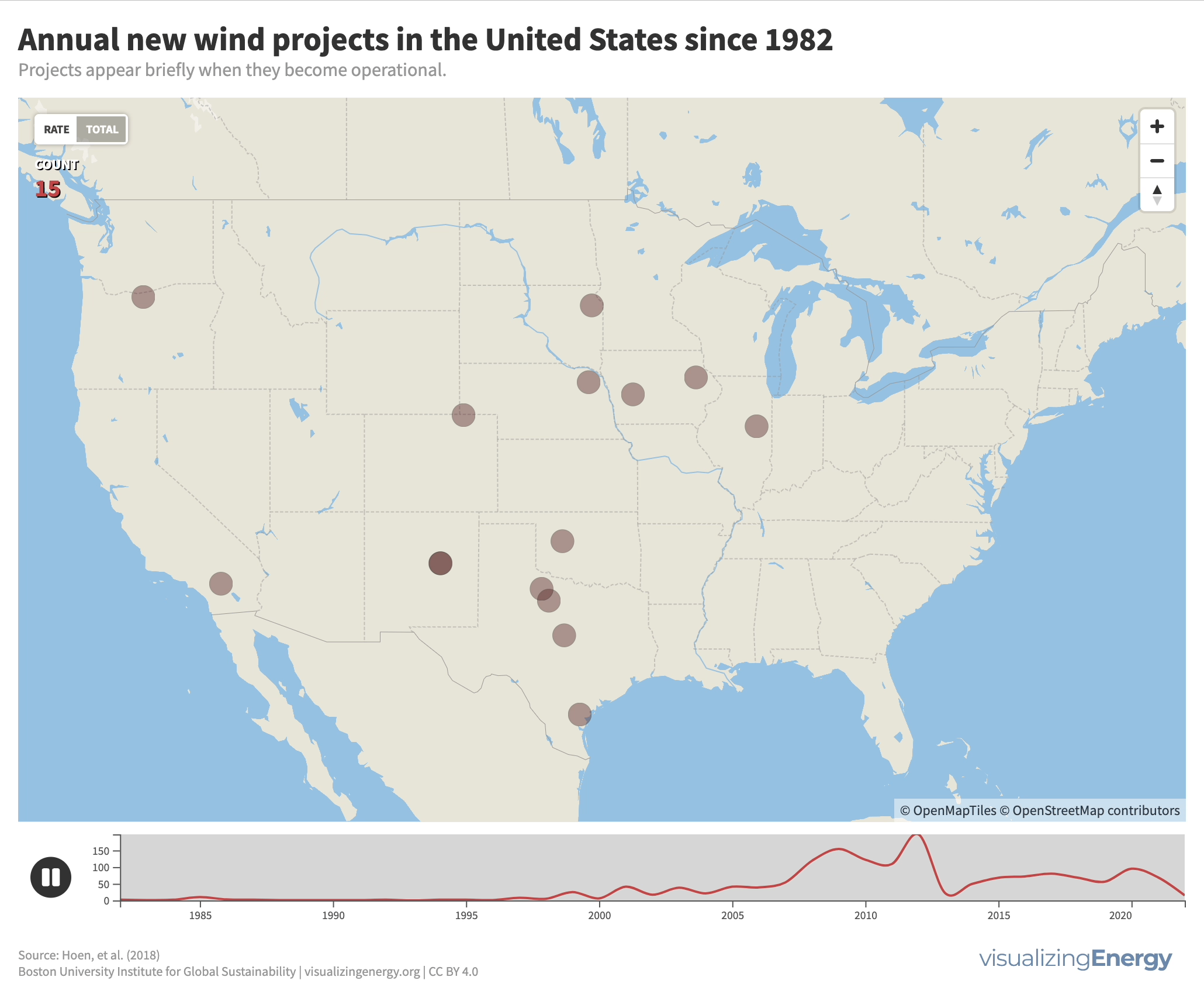
Modern wind energy in the United States began in California in the early 1980s with several wind farms in mountain passes in central and Southern
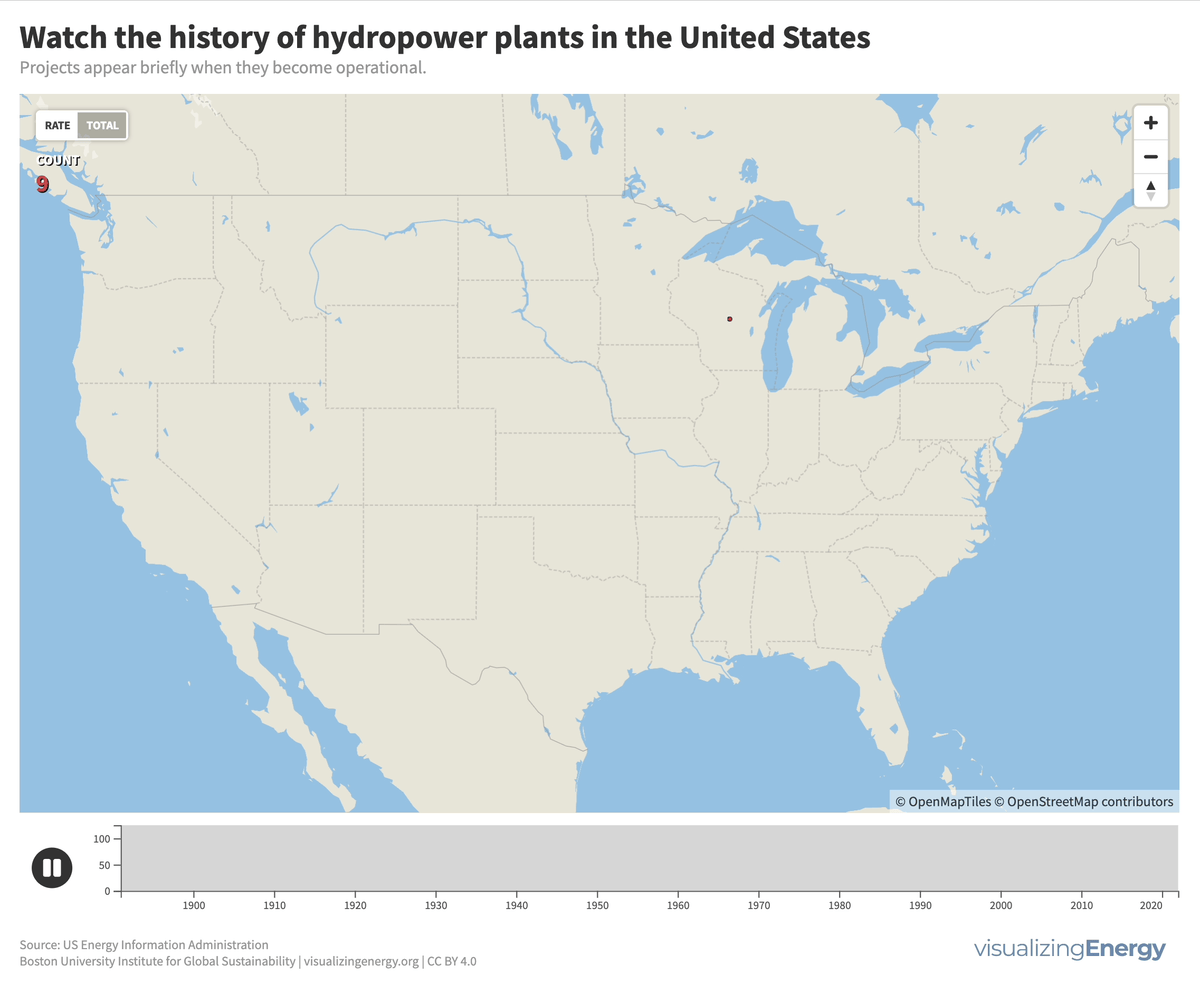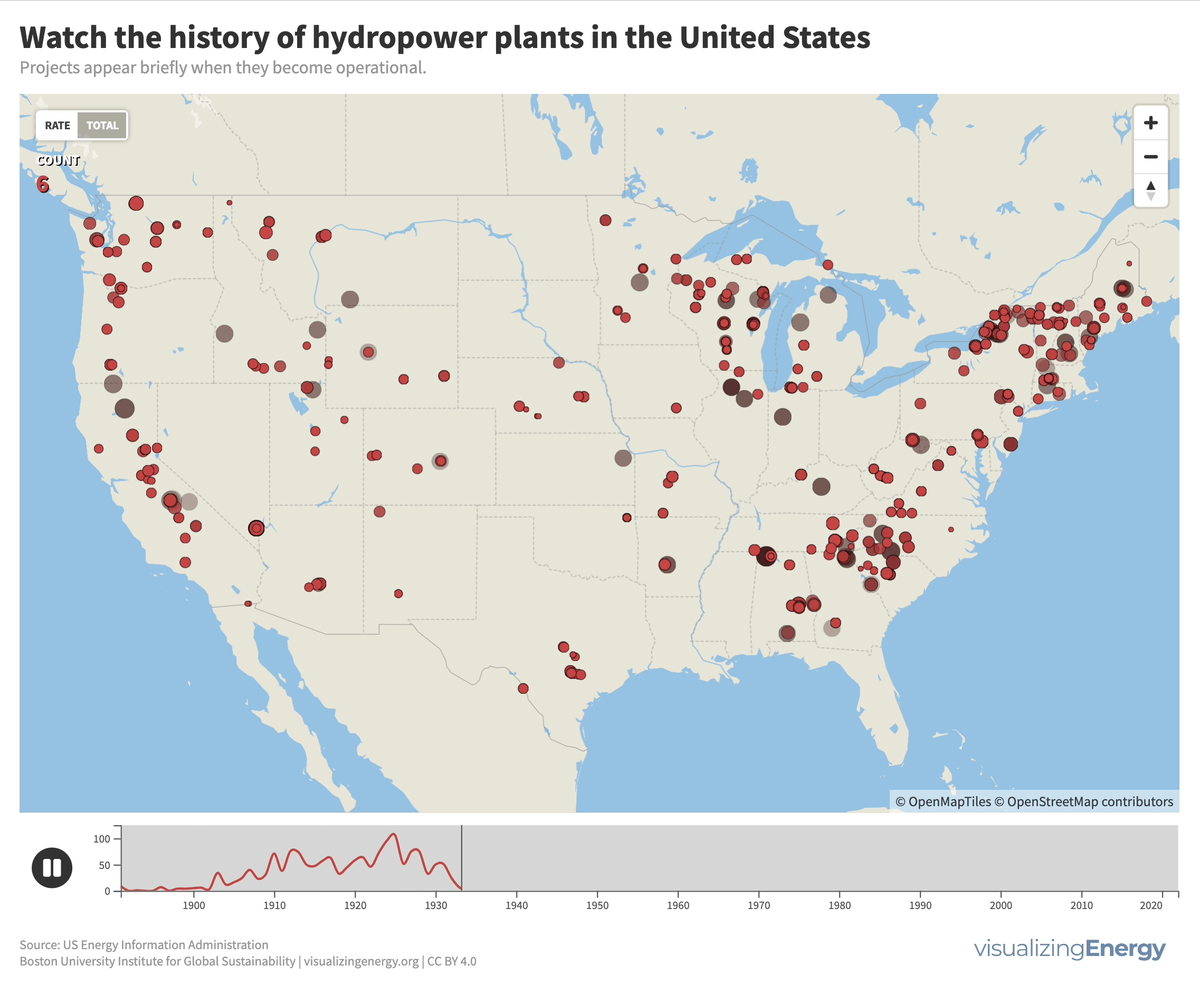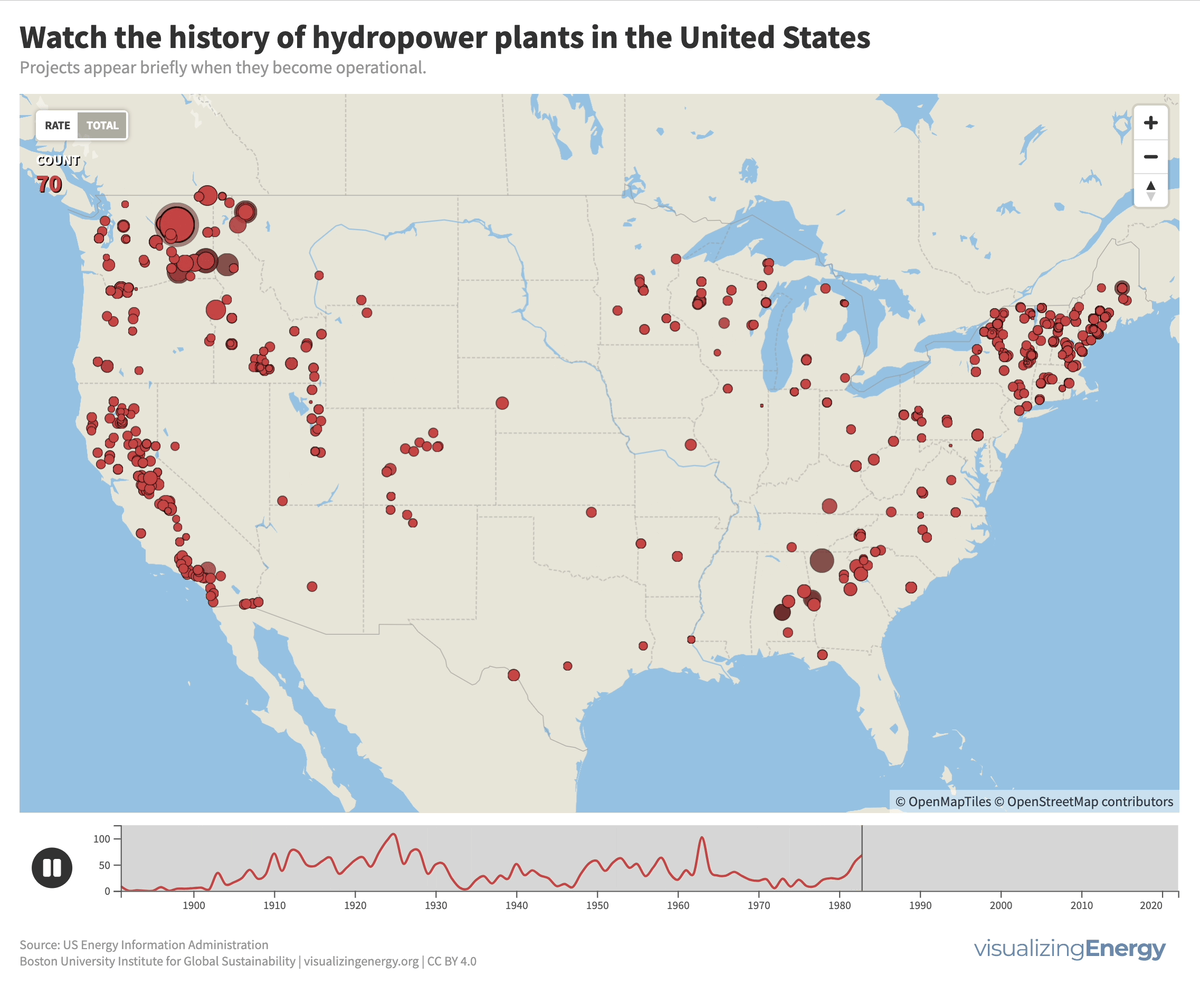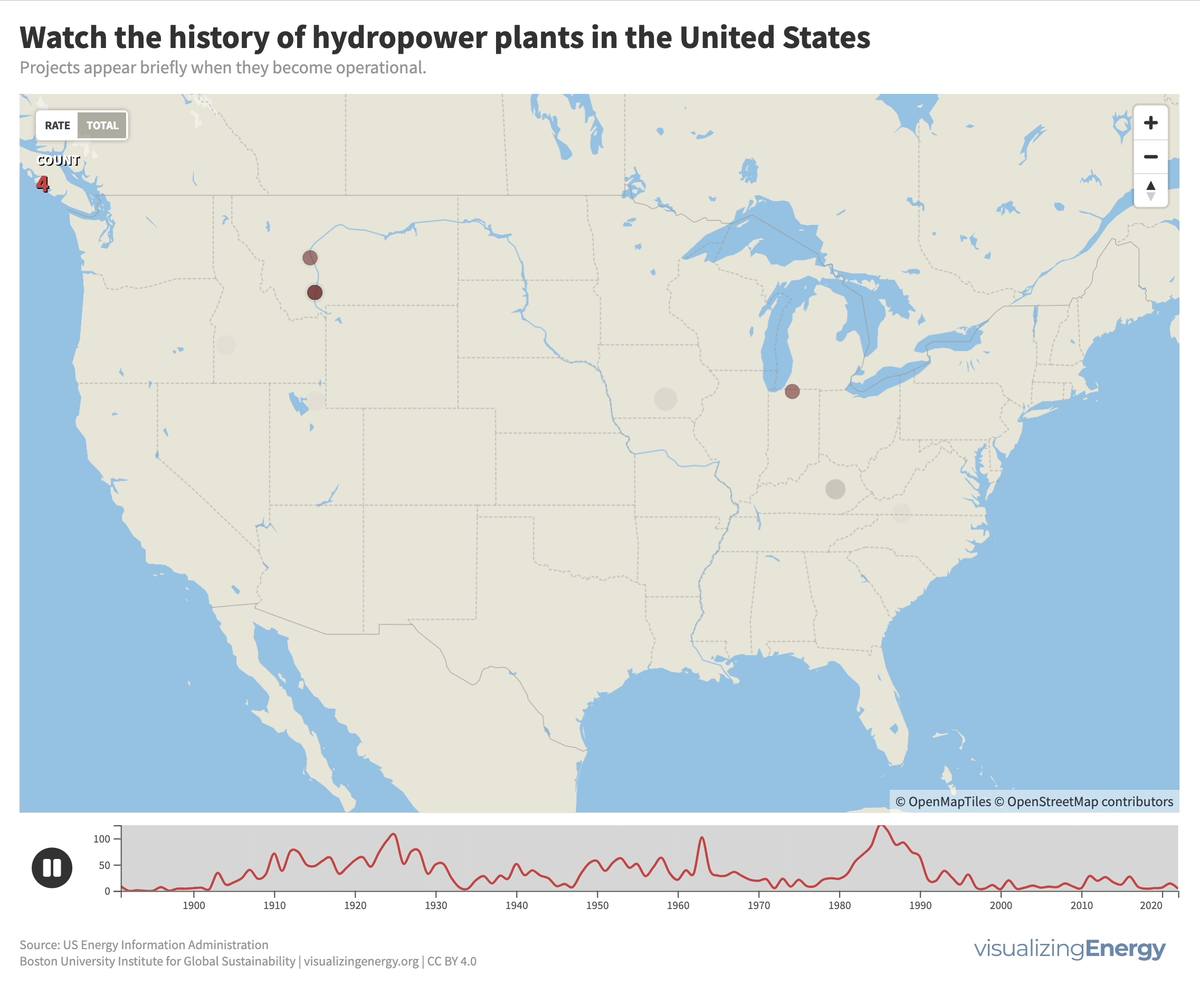
More than 4000 hydroelectric dams have been built in the United States since the late 19th century, representing six percent of all-time additions to electric generation capacity from all sources.
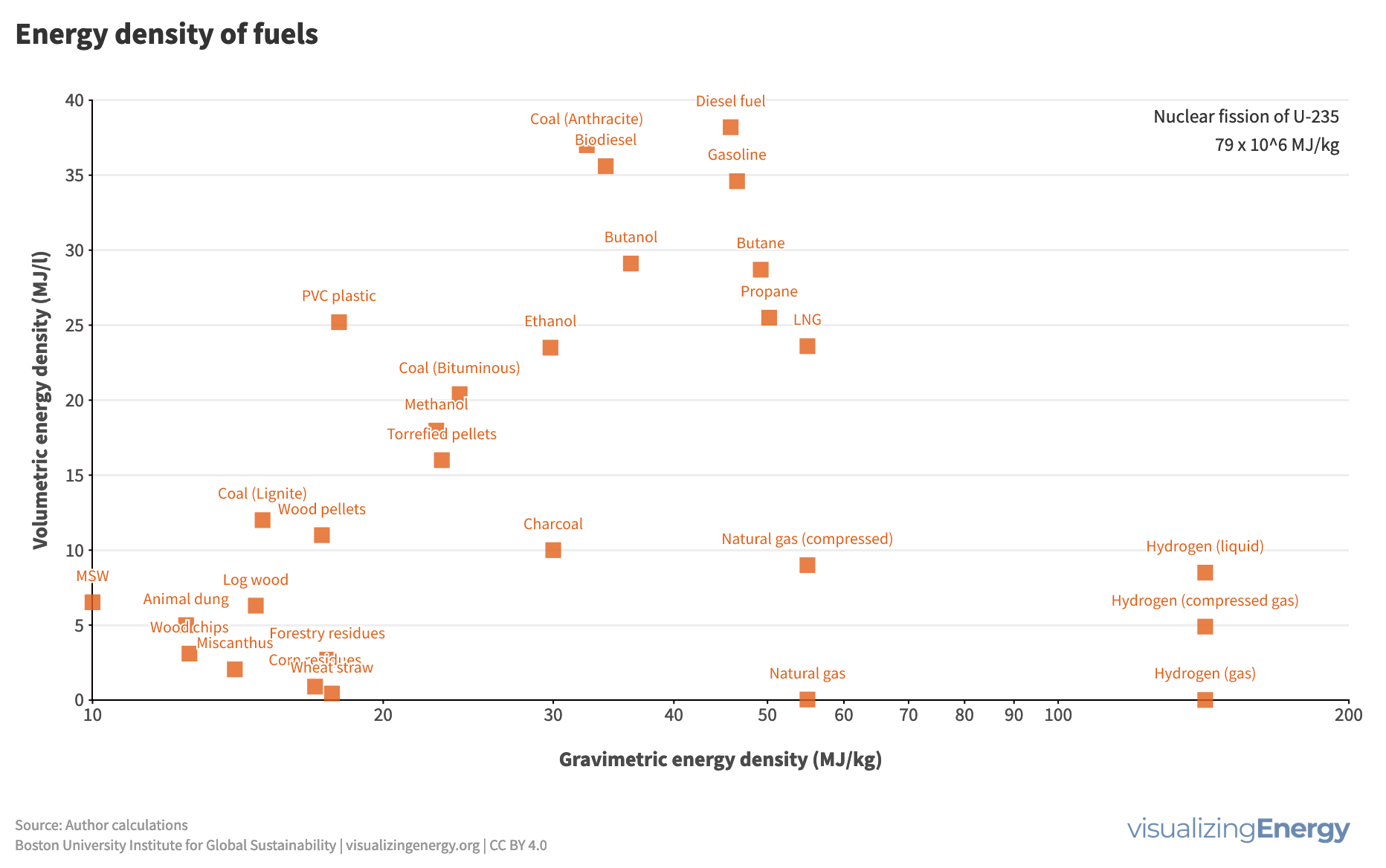
Fuels like wood, diesel, and natural gas have shaped human energy history, driven by technological, economic, and environmental forces. Liquid fuels from oil, with their high mass and volumetric energy density, led to their supremacy in transportation. Shifts in fuel types also influence the devices that convert them into energy services.
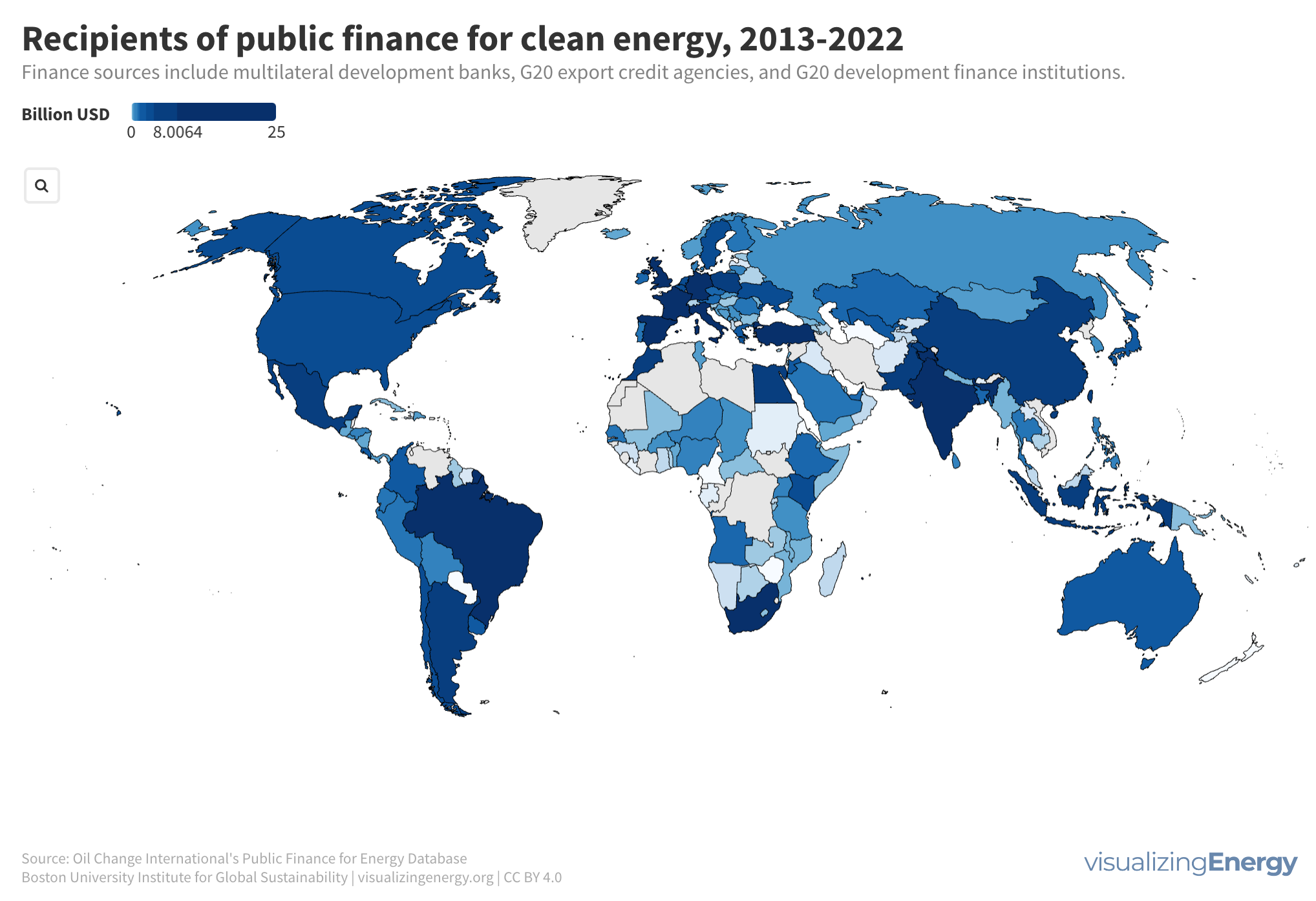
The global energy system encompasses diverse infrastructure requiring extensive investment, with USD 2.8 trillion spent in 2023. Public finance significantly supports energy projects, where fossil fuels received 56% of funding from 2013 to 2022. Clean energy finance increased until 2021, highlighting varying regional priorities and the dominance of large projects in funding distribution.
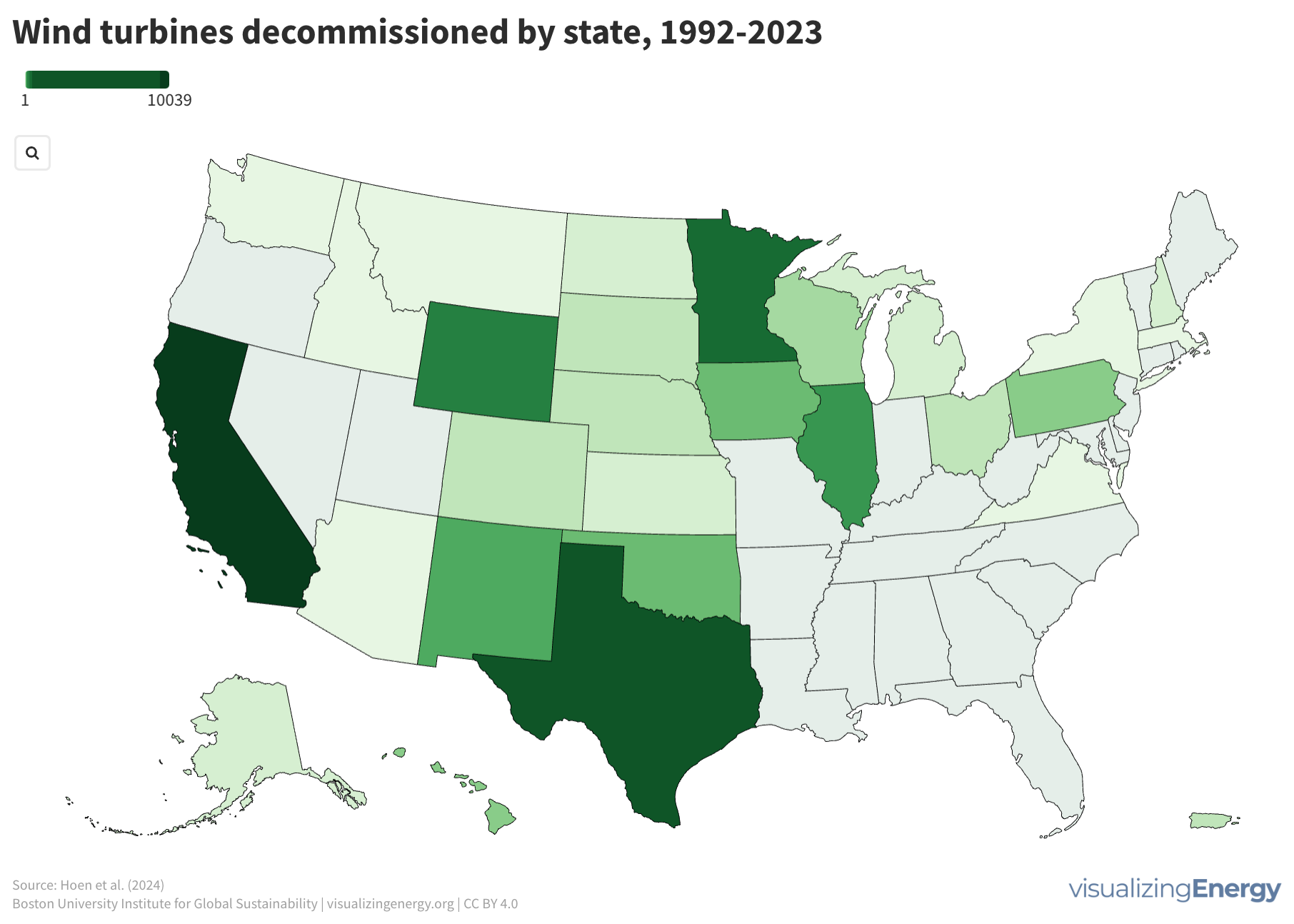
More than 86,000 wind turbines were built in the US from 1981 to early 2024, with over 11,000 decommissioned since 1992. Decommissioning presents waste management challenges, especially with the difficult-to-recycle turbine blades. Research is ongoing for recyclable blades, such as those made from plant material, to address the issue.
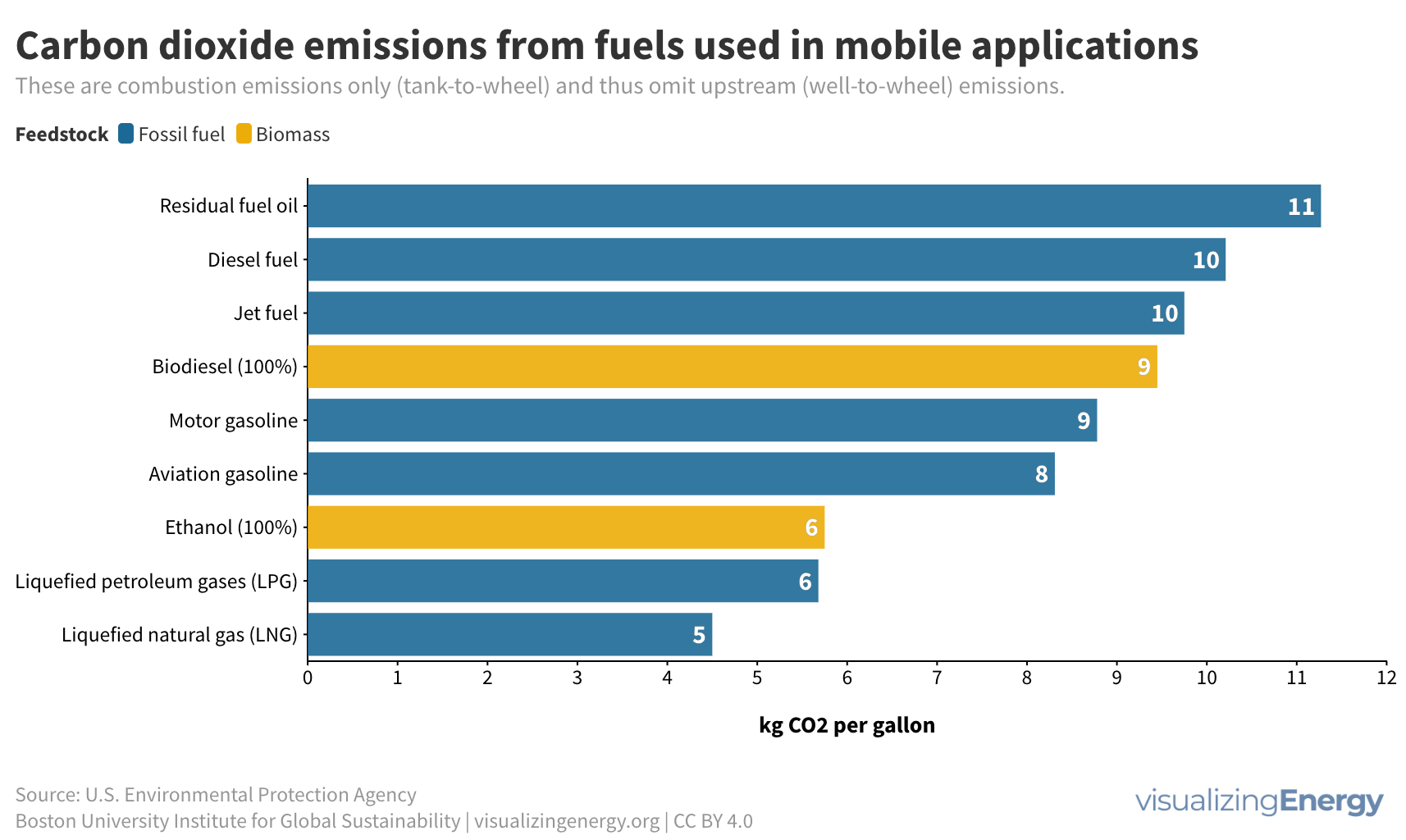
There are two main sources of greenhouse gas emissions: stationary (e.g., power plants, refineries) and mobile (e.g., cars, trucks). Transportation contributes 24% of energy-related CO2 emissions, with fossil fuels dominating. LNG in maritime transport shows potential for reduced CO2 emissions, but methane leakages must be addressed. Coal has the highest CO2 emissions factor among widely used fuels.
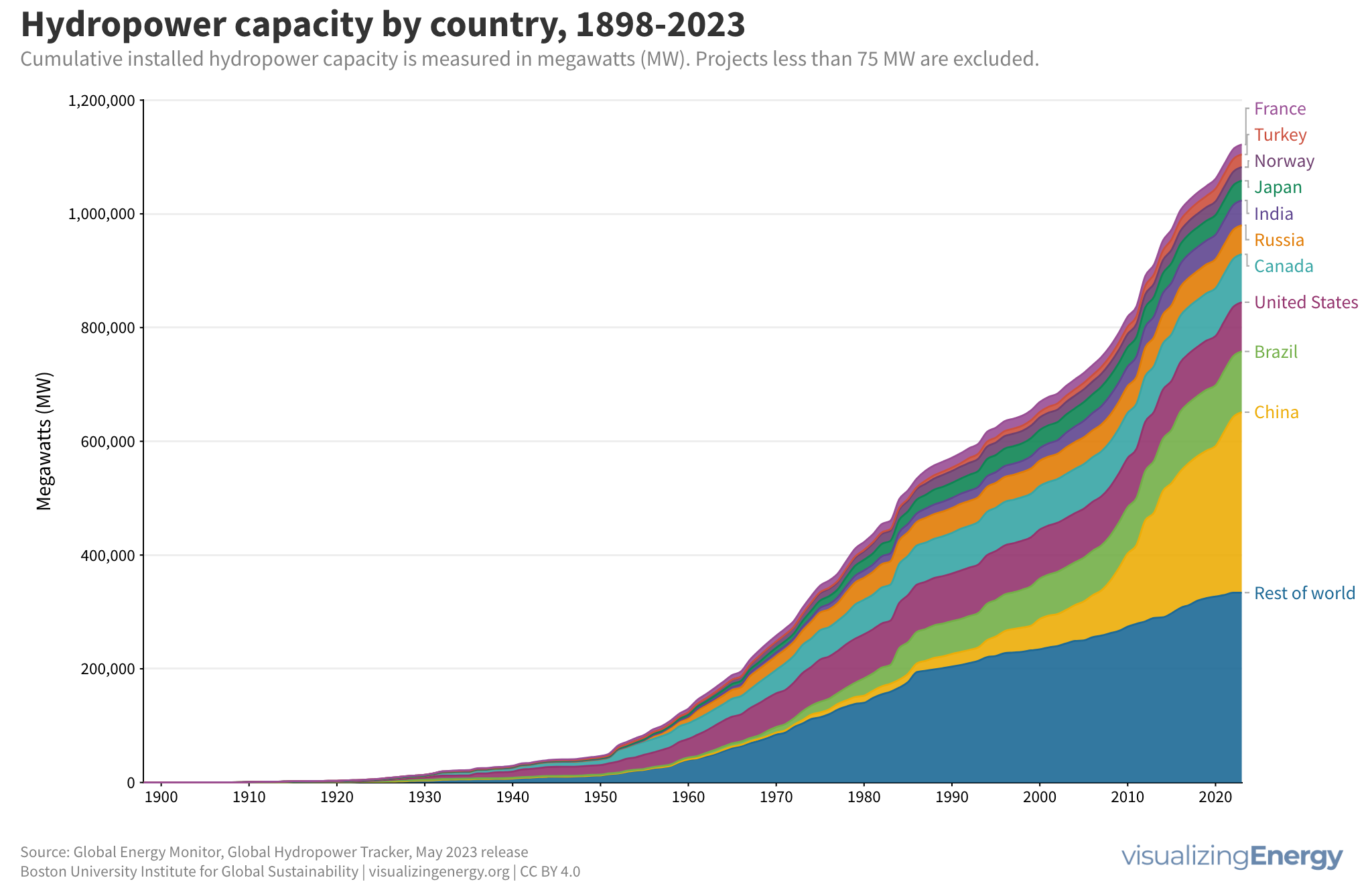
Dams serve various purposes such as navigation improvement, flood control, and electricity generation. There are over 40,000 dams worldwide, with significant hydroelectric capacity. The environmental impact of these large projects, including disturbance of ecosystems and displacement of communities, must be carefully assessed and balanced with their low-cost and low-carbon benefits.
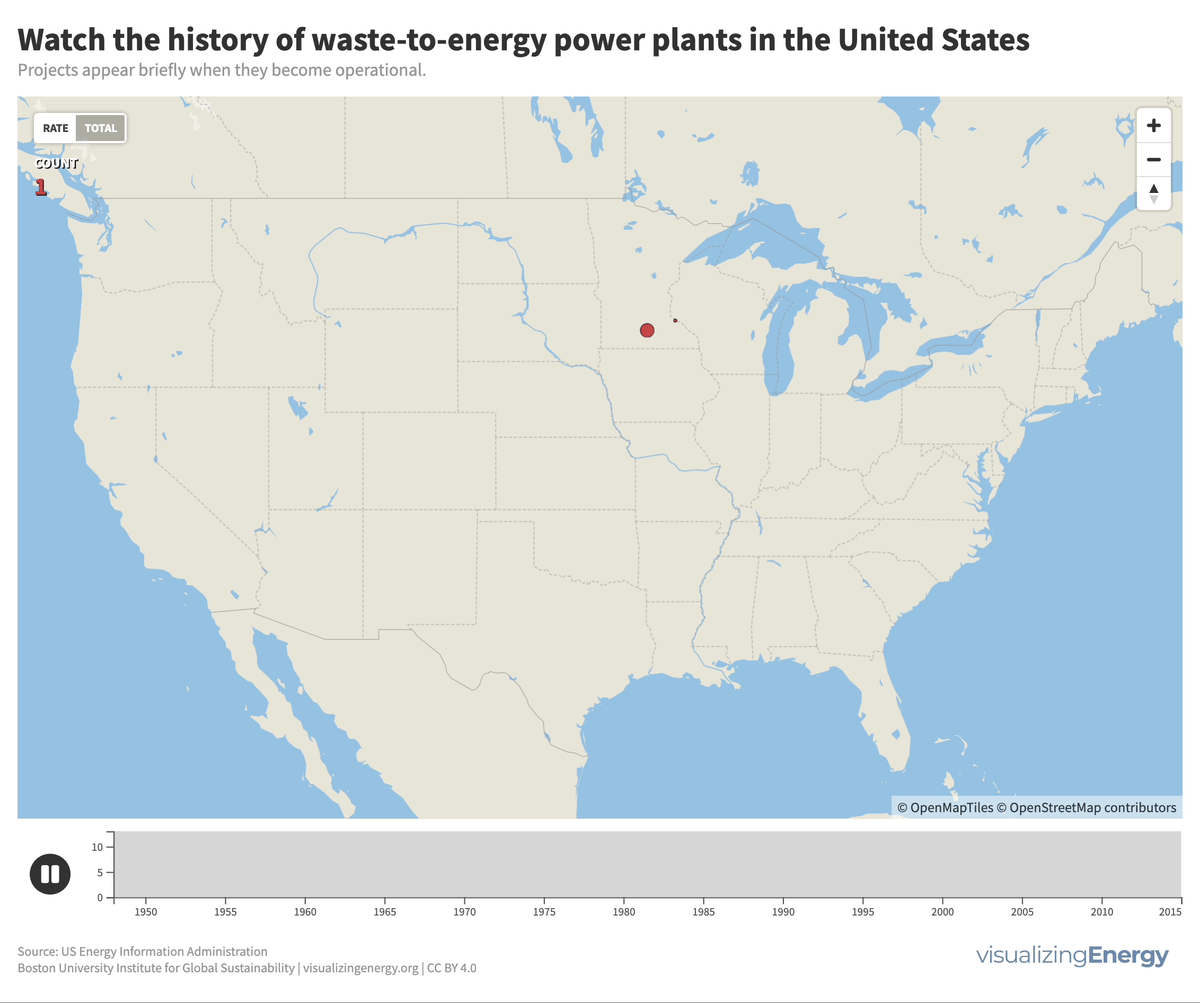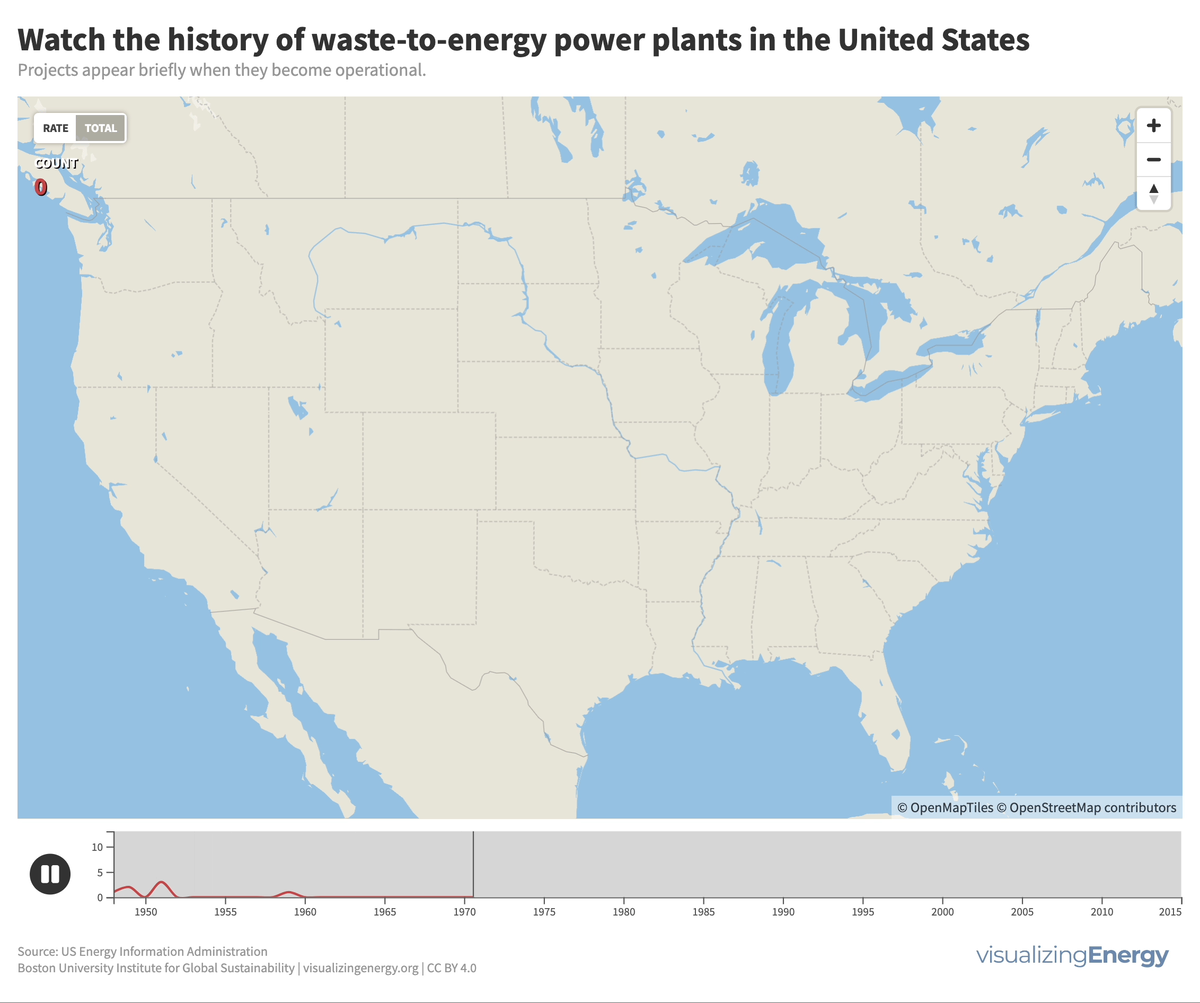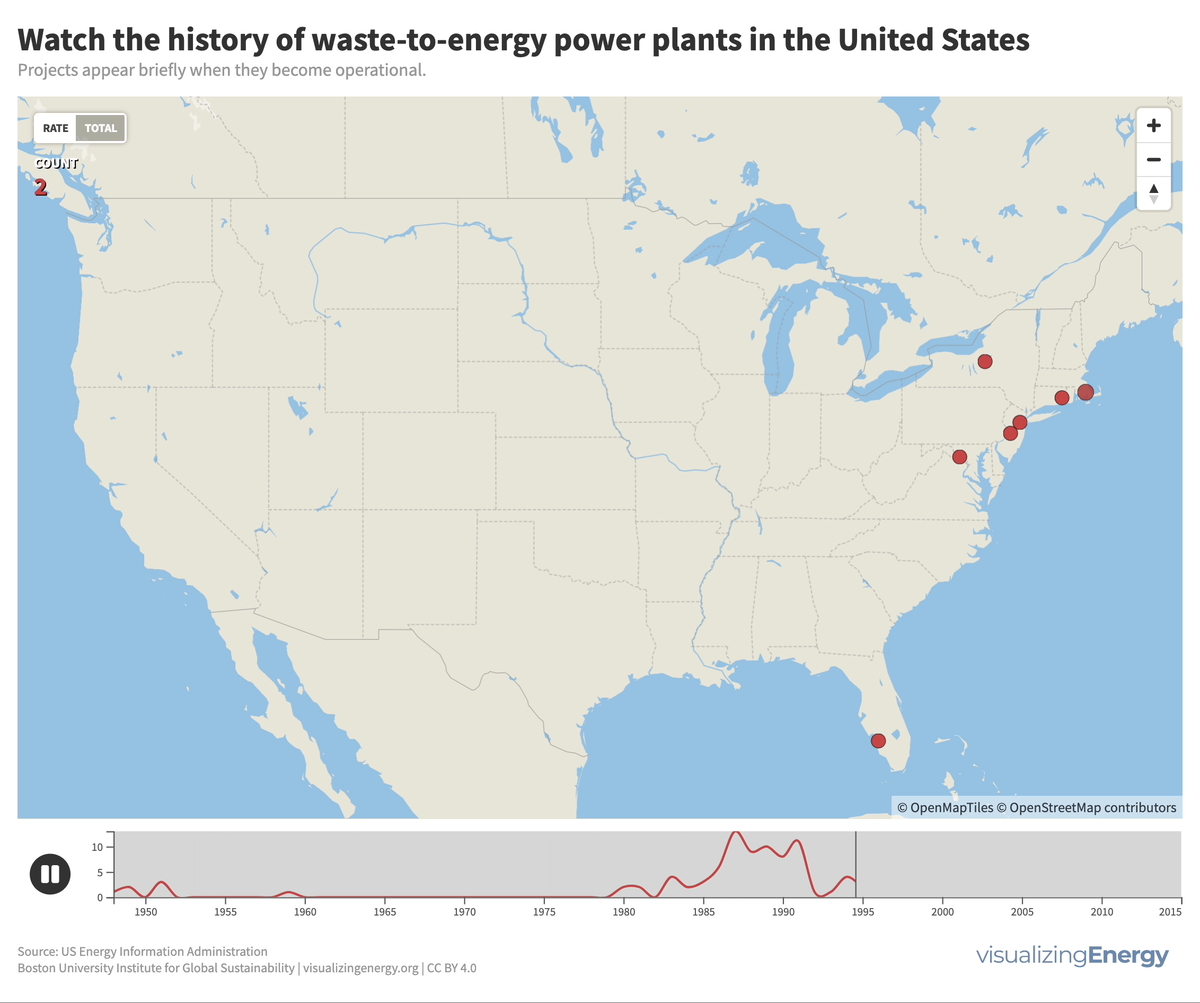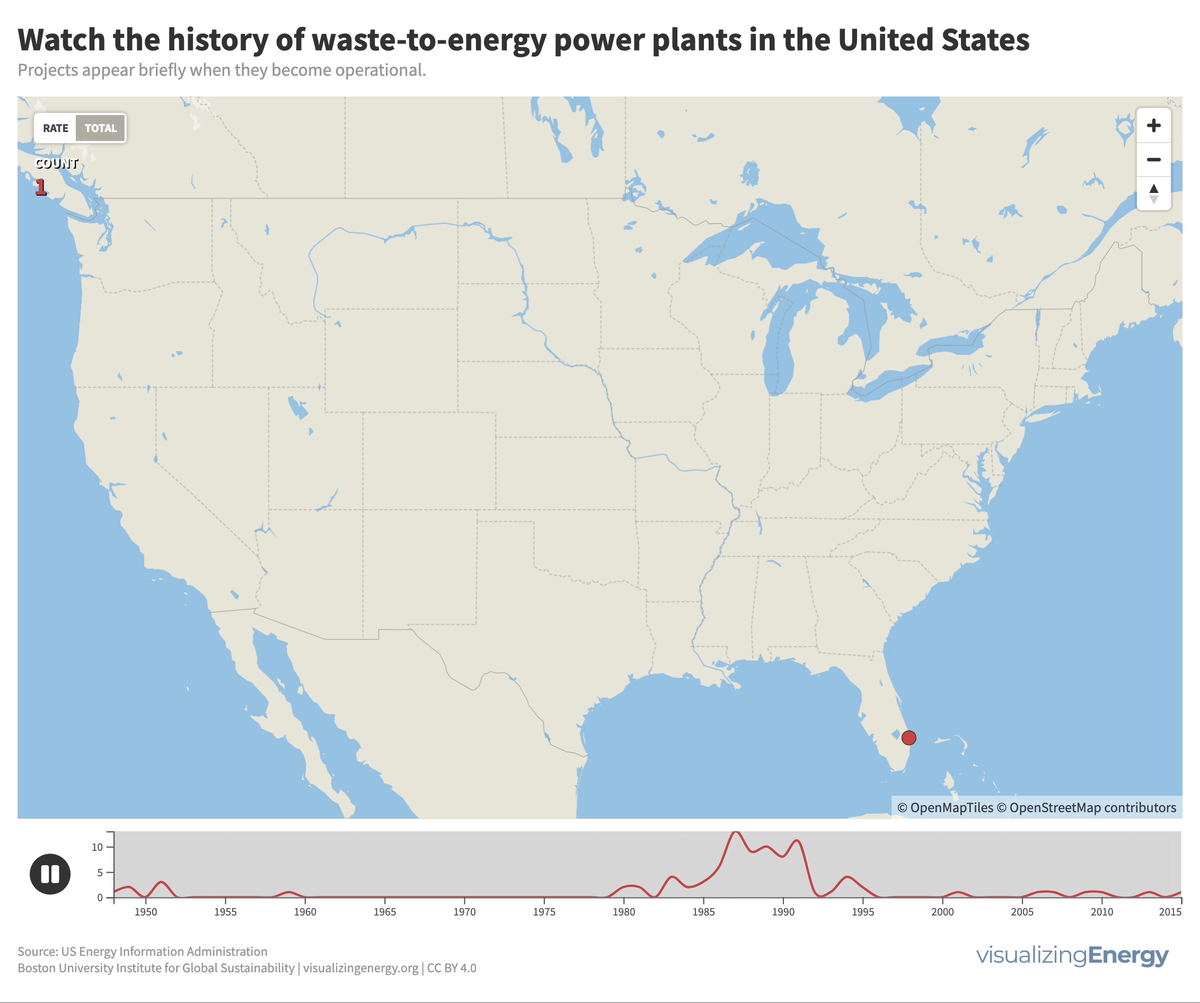
Waste-to-energy (WTE) plants in the US burn municipal solid waste to generate electricity, contributing less than one percent of the total. Initially developed due to landfill space scarcity, the renewable classification is disputed due to non-biogenic waste. Few new facilities have been built since the 1990s due to opposition, high costs, and increased focus on recycling and waste reduction.
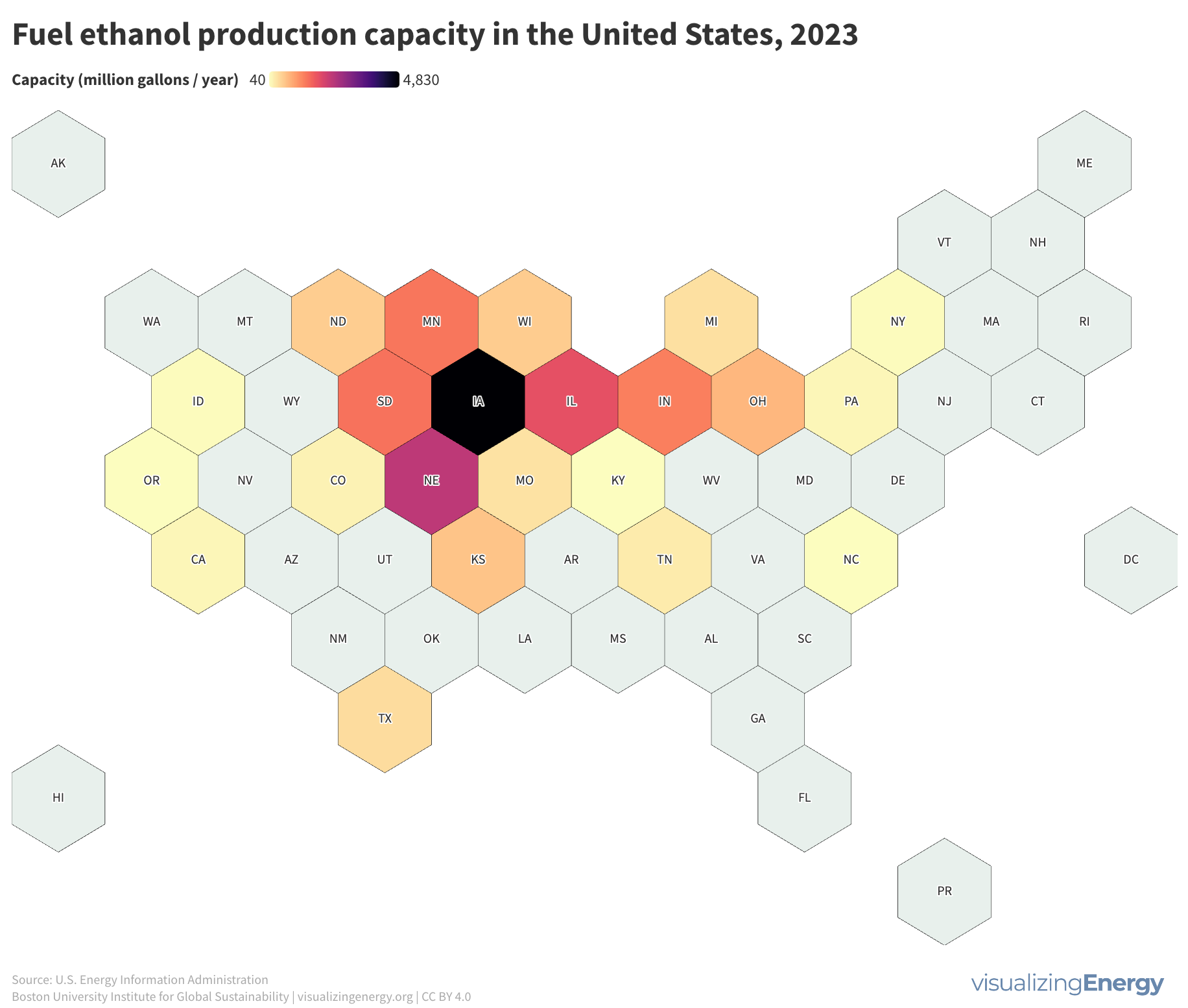
Henry Ford’s early vehicles ran on ethanol, which became commercially significant in the 1970s after the phase-out of lead in gasoline. Ethanol blending has been supported by various government policies, including tax incentives and the Renewable Fuel Standard. Ethanol production surged, particularly in the Midwest, driven by high corn production. While ethanol offers economic and environmental benefits, it also raises concerns about environmental impacts and the efficacy of subsidies. Changes in ethanol demand significantly affect corn prices and agricultural practices.