

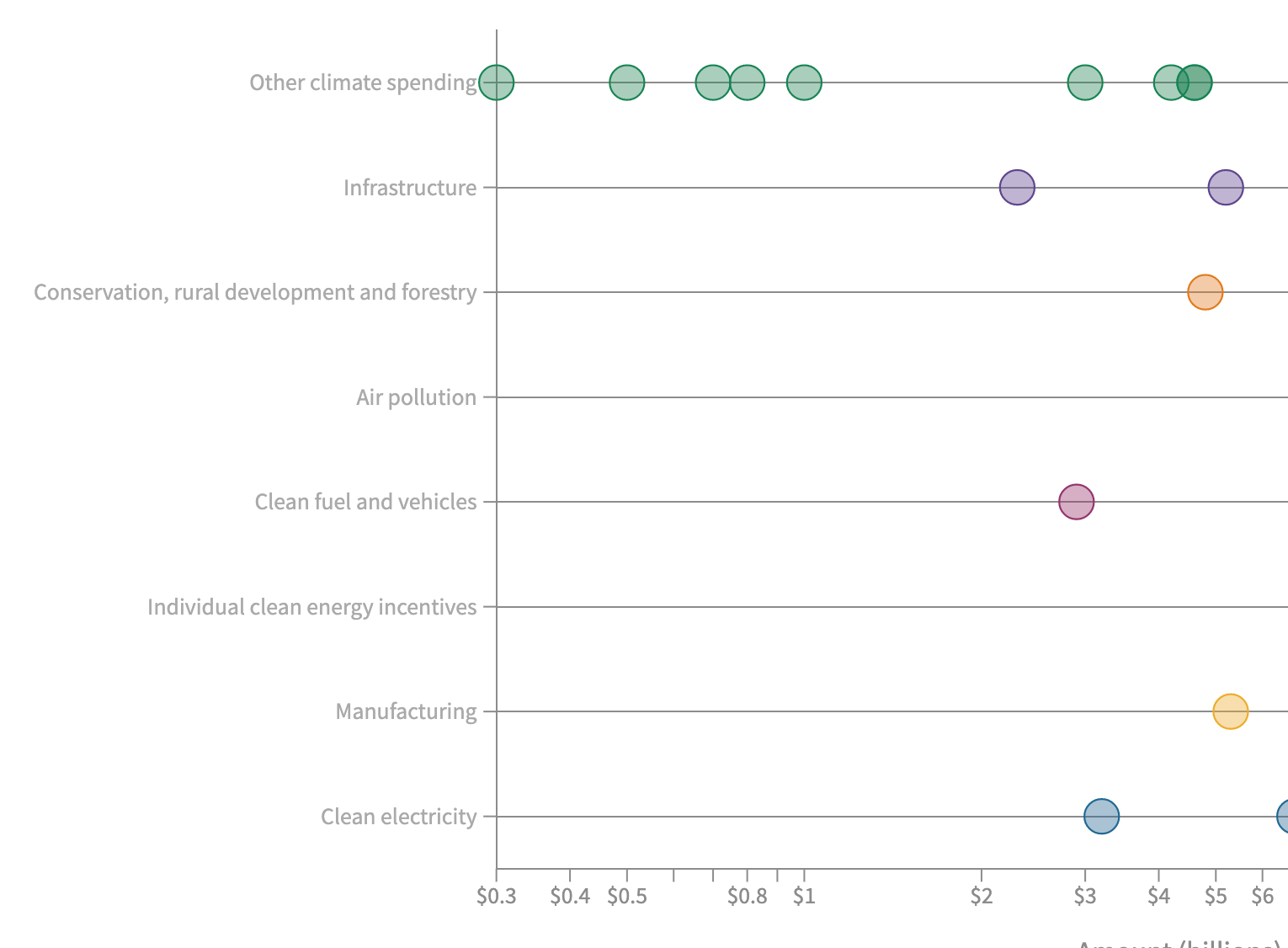
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) is the largest-ever federal program focused on energy and the environment, allocating $369 billion over a decade. With a laser focus on climate change, the IRA aims to cut greenhouse gas emissions, promote clean energy, and enhance climate resilience. Its provisions have the potential to create jobs, lower electricity costs, and significantly contribute to meeting the US climate targets.
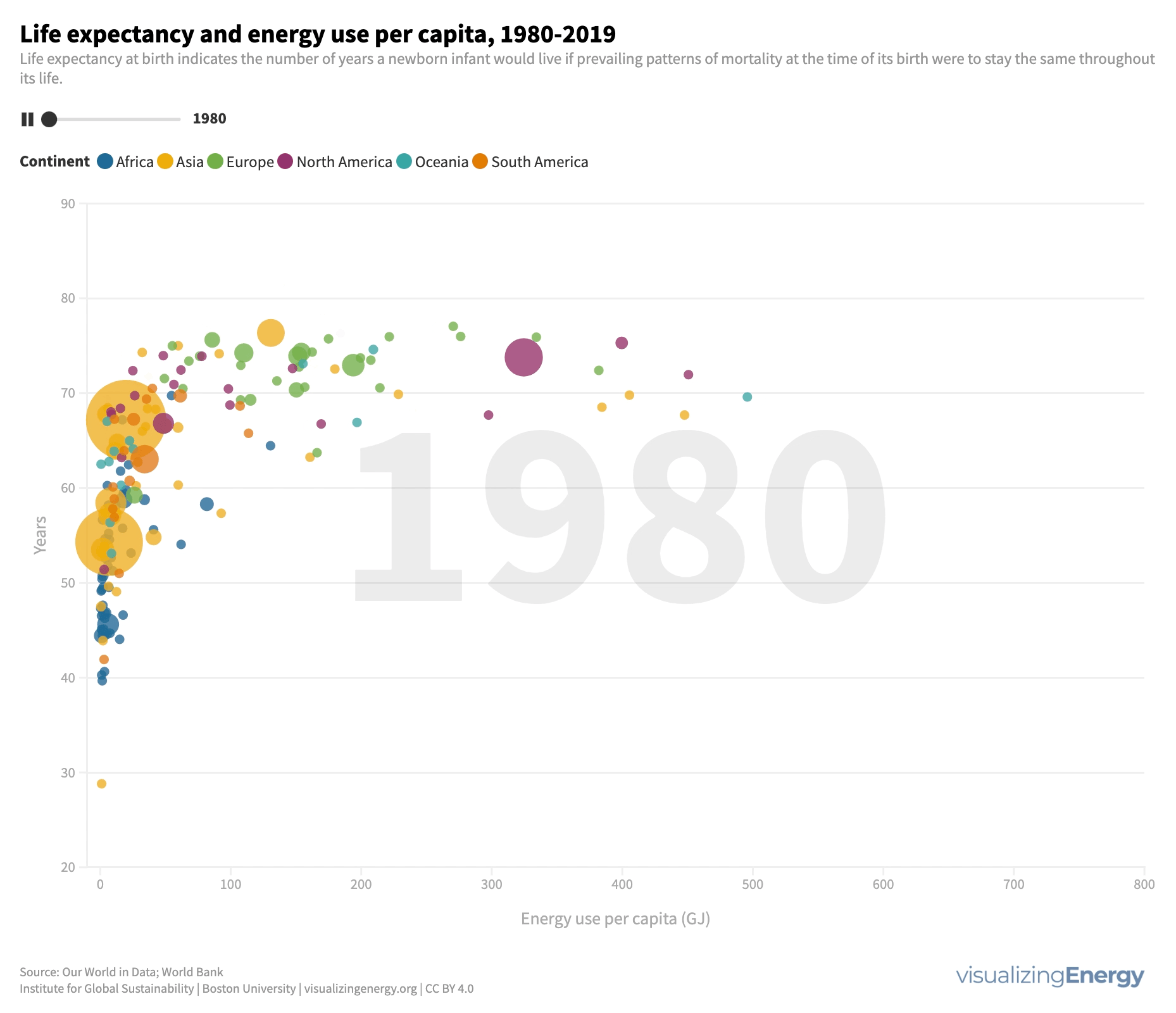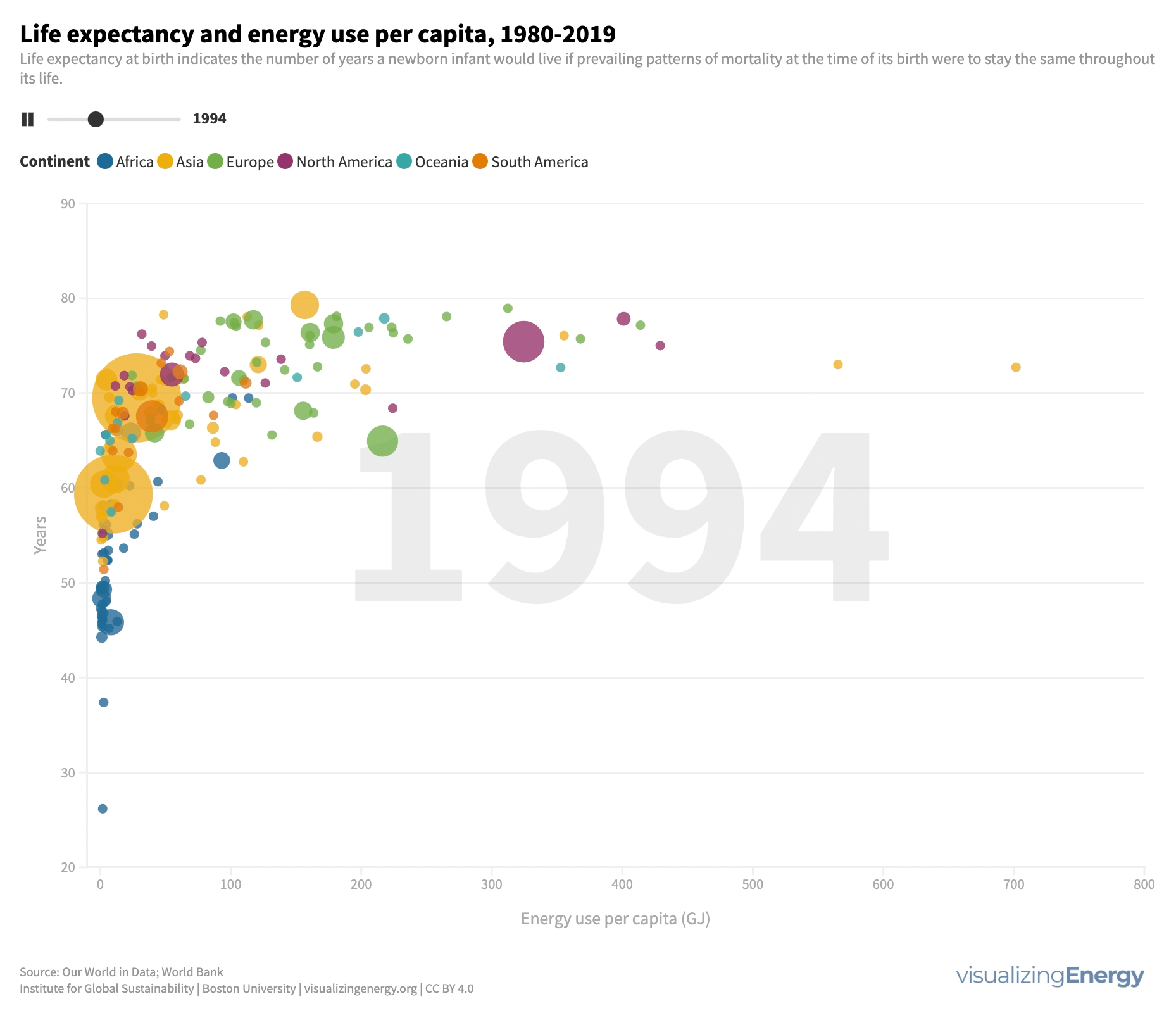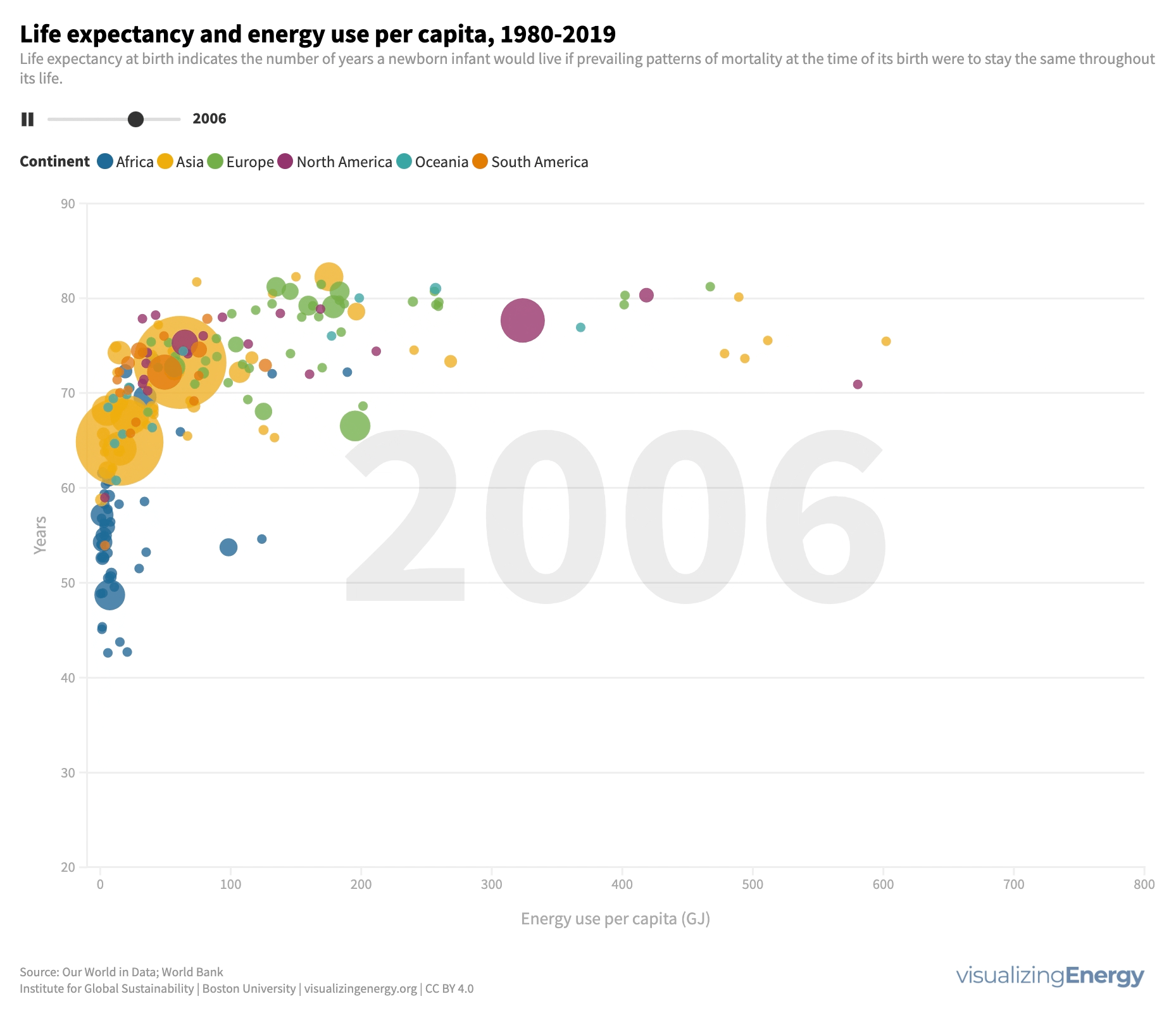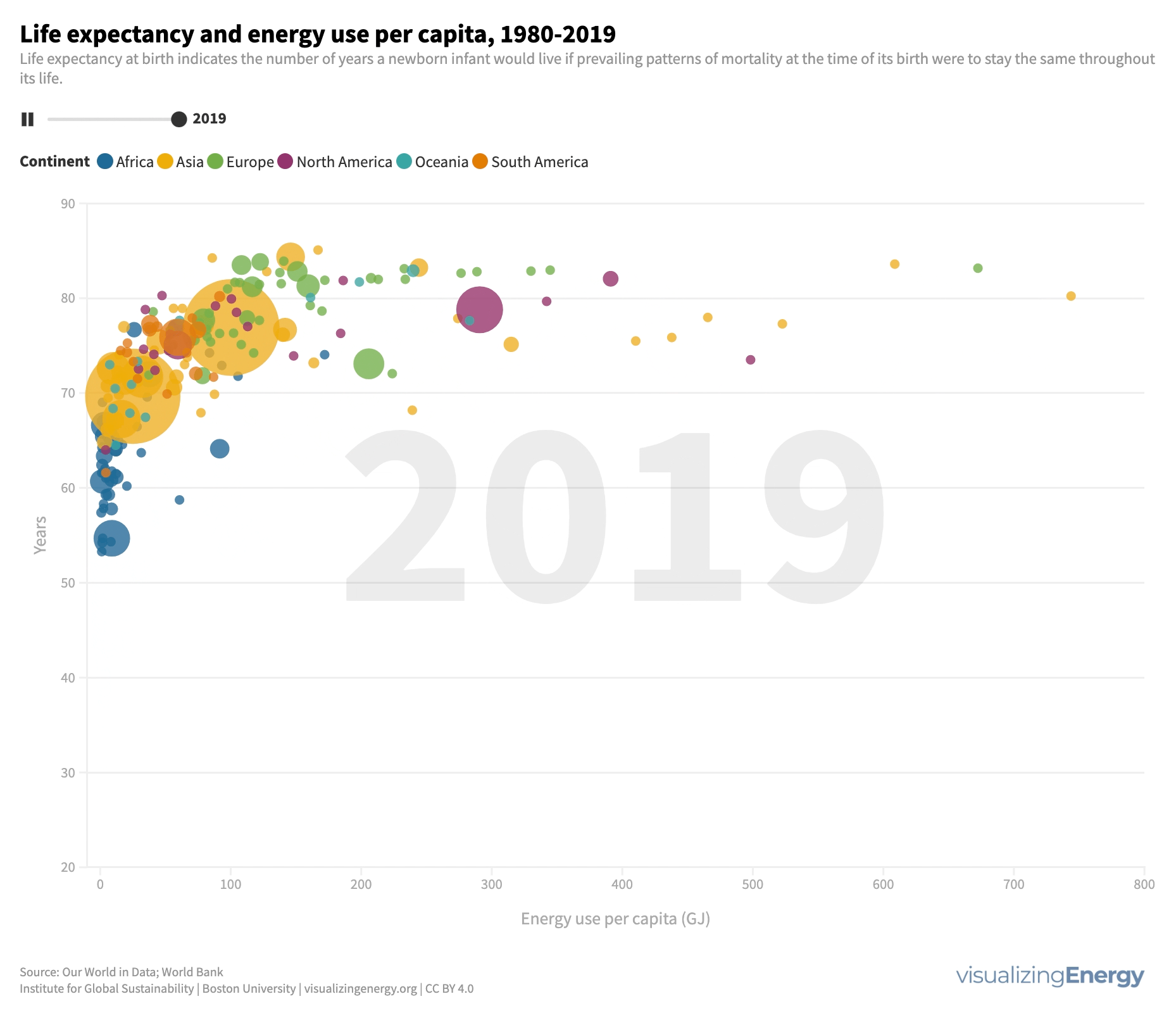
Energy use influences life expectancy. Access to energy services improves well-being and extends lifespan, while deprivation has the opposite effect. Modest energy increases positively impact longevity, especially in low-energy regions. However, beyond a certain point, additional energy use has diminishing returns for life expectancy.
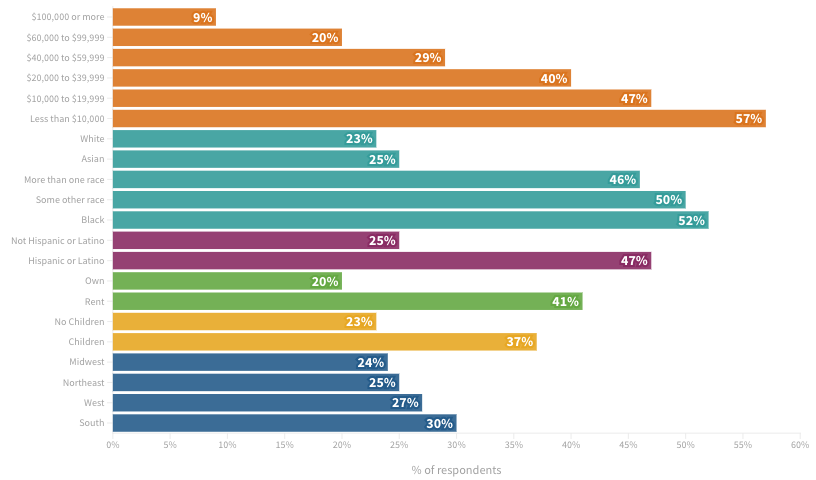
Many US households, particularly low-income, minority, and renting households, face a high energy burden, spending a significant portion of their income on fuel and electricity. In 2020, 27% of households reported difficulty paying energy bills. Federal programs provide some relief, but addressing the underlying causes of social inequity is crucial for long-term energy security.
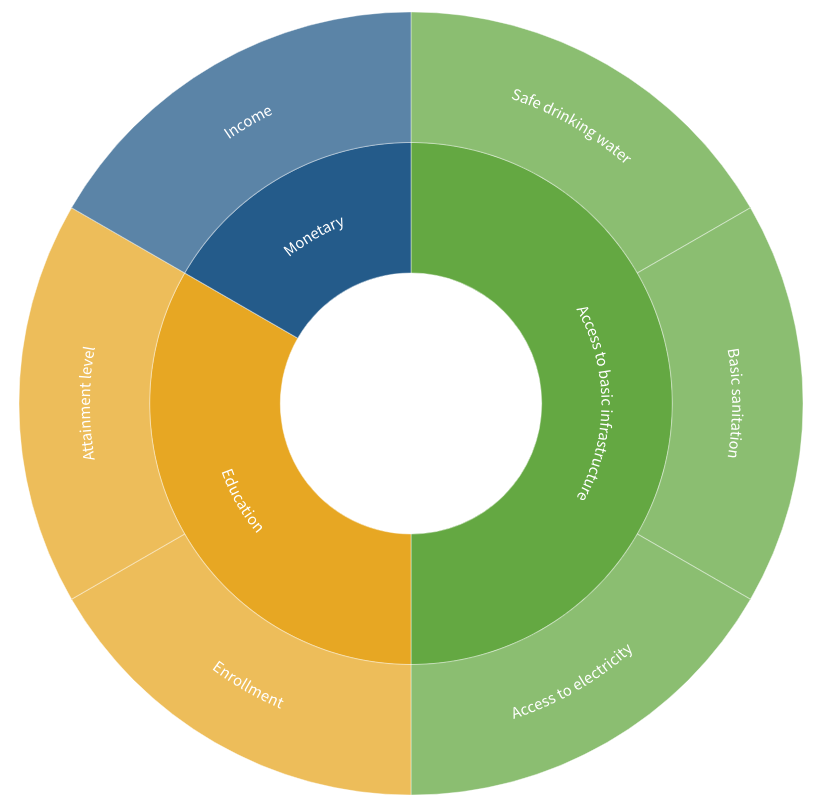
Increased energy use per capita is linked to decreased poverty rates. Modest energy increases can lead to significant poverty reduction, but the relationship is not always linear. Factors like governance and social policies also influence poverty levels. Beyond a certain threshold, further energy increases have diminishing returns.
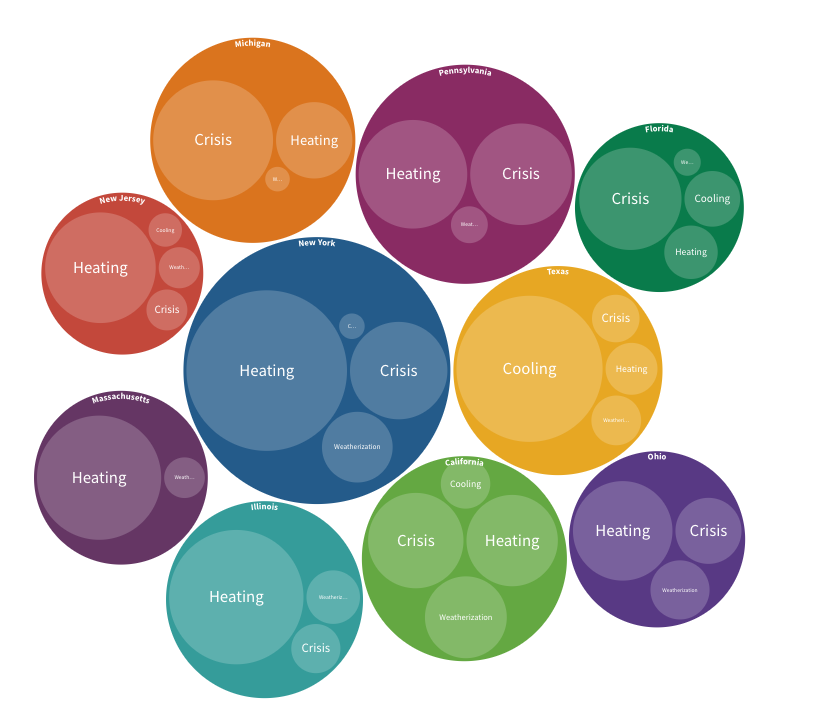
Energy poverty is a significant concern in the United States, with over one in four households experiencing insecurity. Government programs like LIHEAP and WAP aim to address this issue, but funding levels often fall short of the need. A more comprehensive approach is necessary, considering the impact on well-being and addressing racial and socioeconomic disparities.
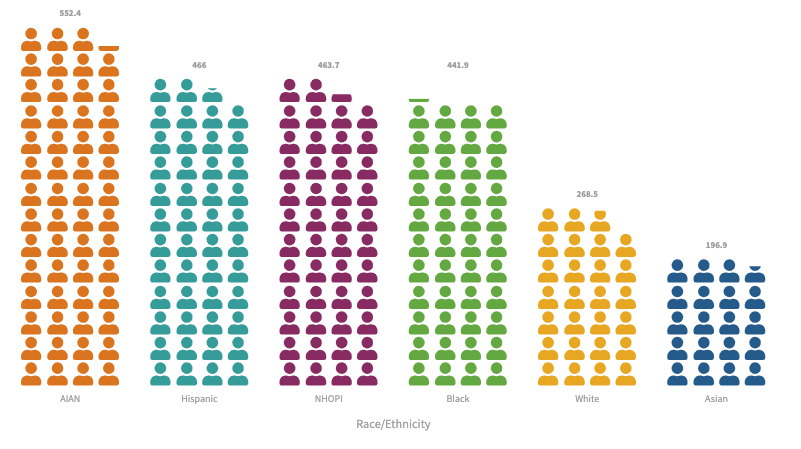
The COVID-19 pandemic worsened energy insecurity in the US, particularly for vulnerable populations. Prior to the pandemic, around 25% of low-income households struggled to pay energy bills, but during the early months of the pandemic, nearly 13% couldn’t afford them. Racial and ethnic disparities were exacerbated, with Black and Hispanic households facing higher odds of disconnection