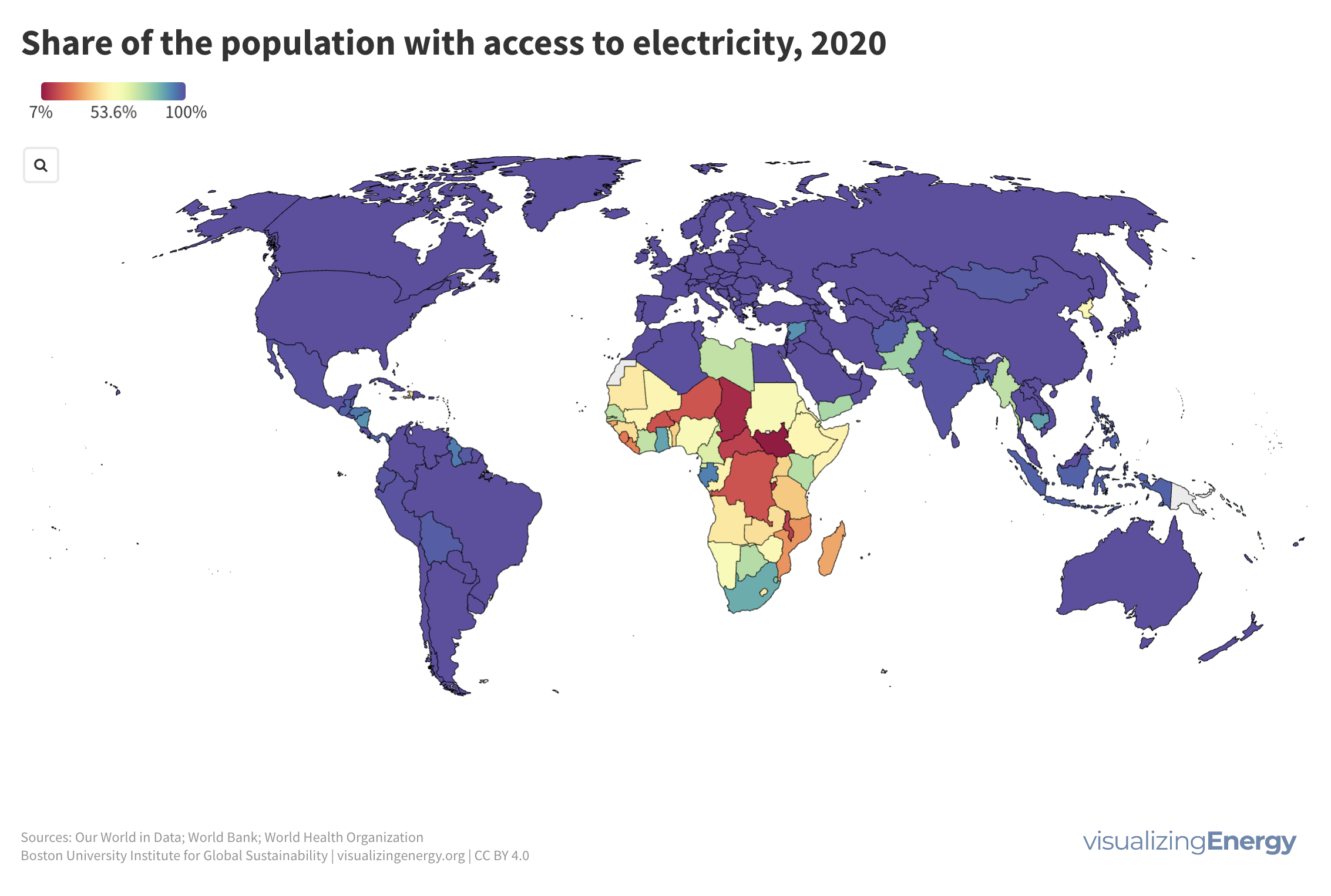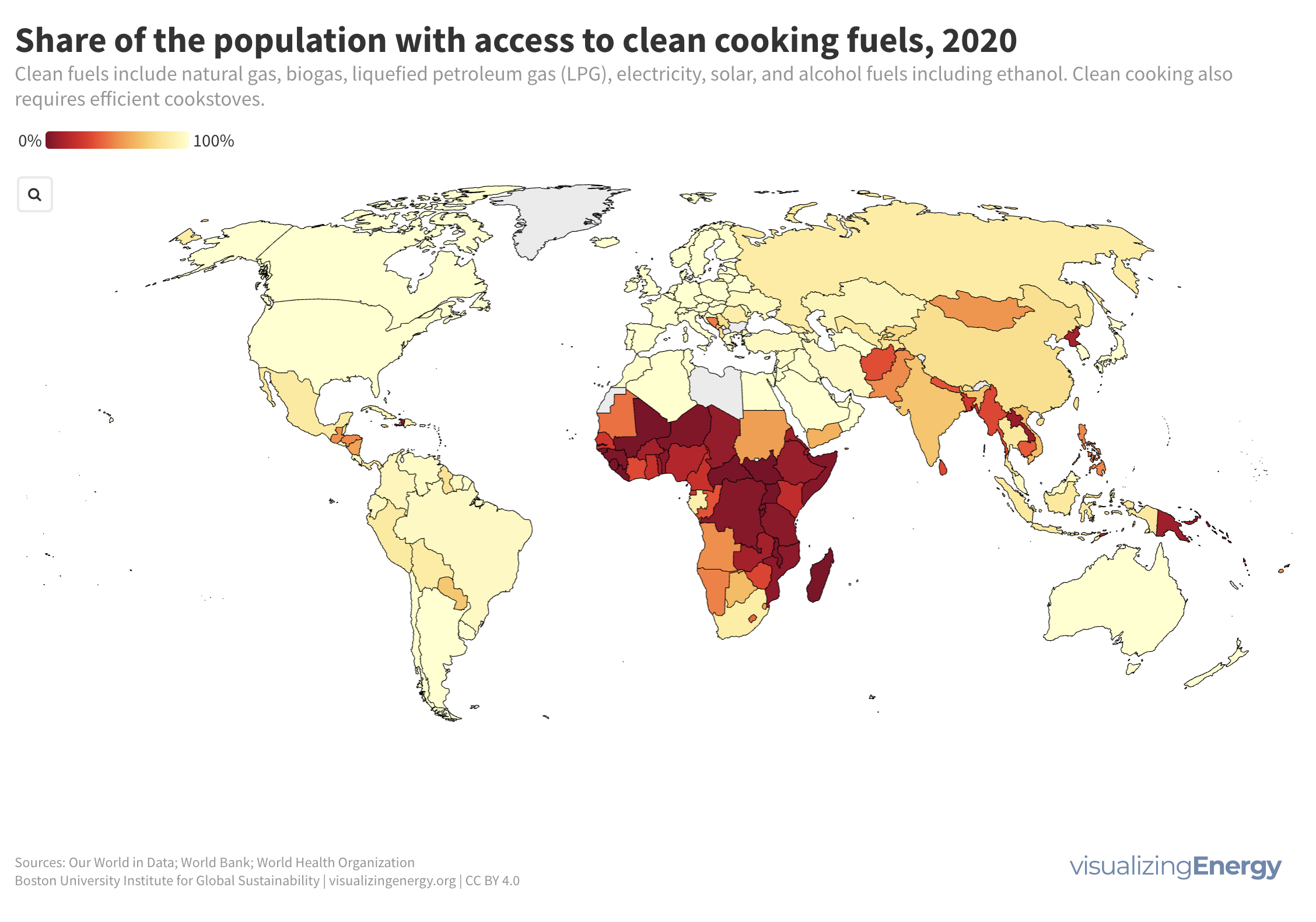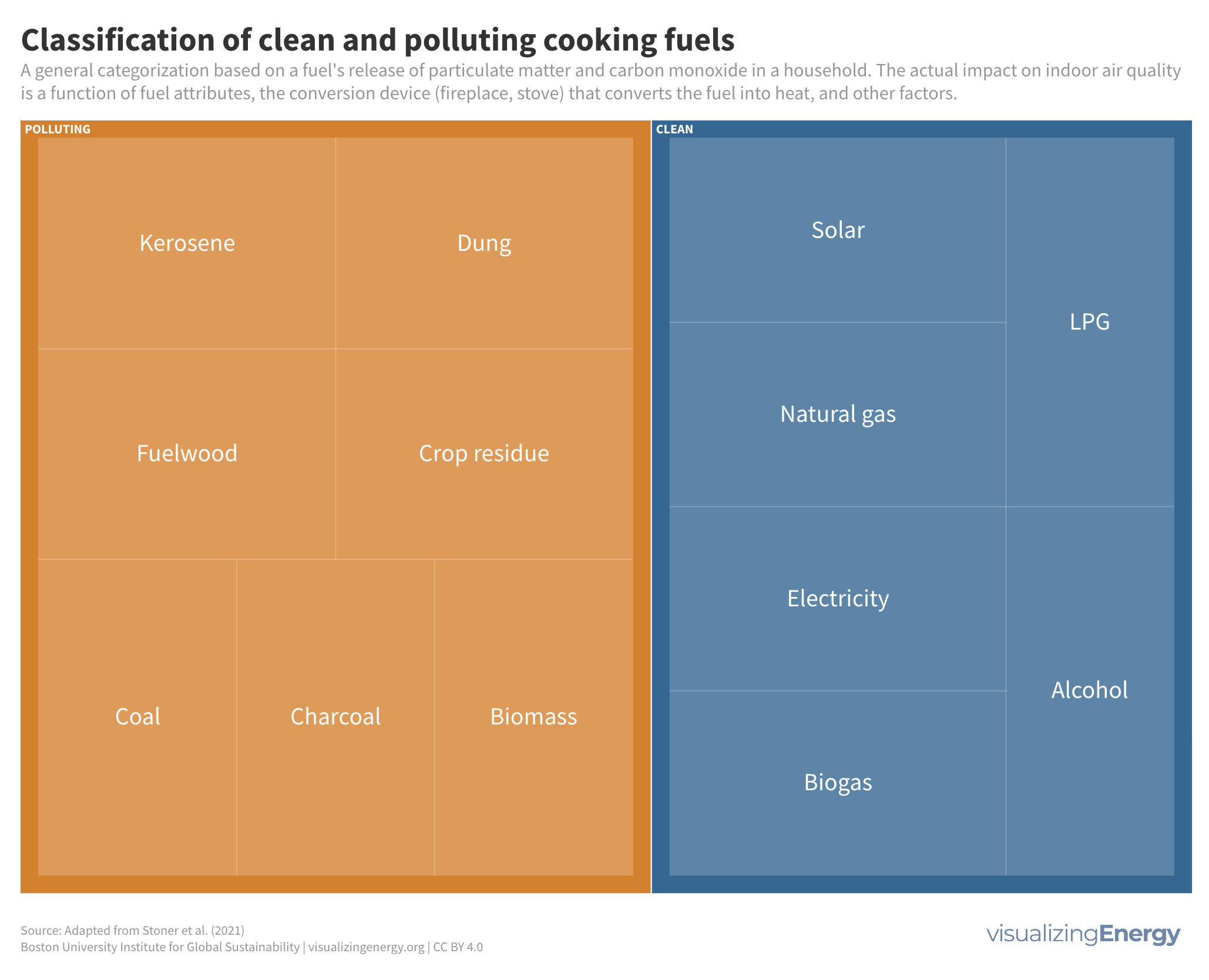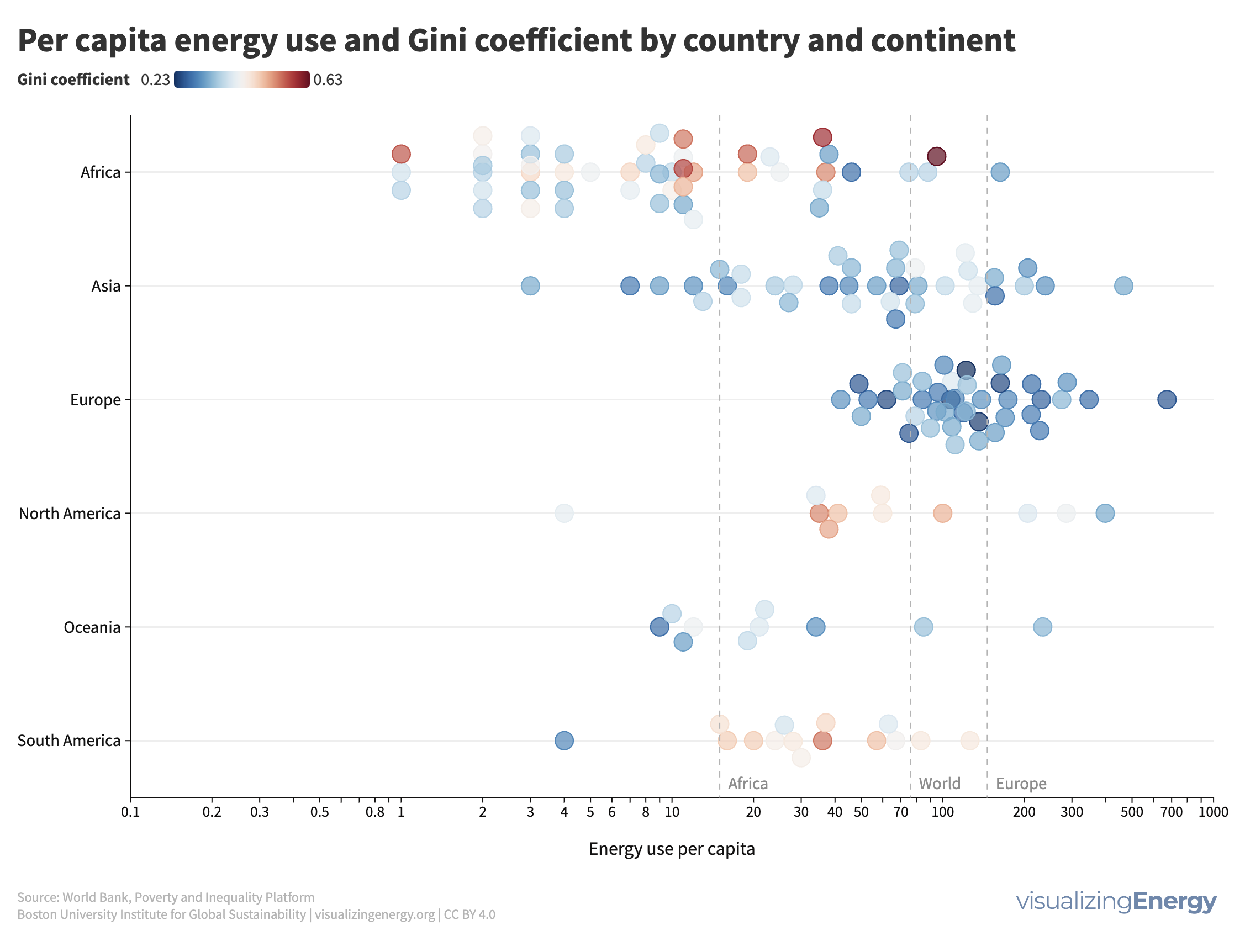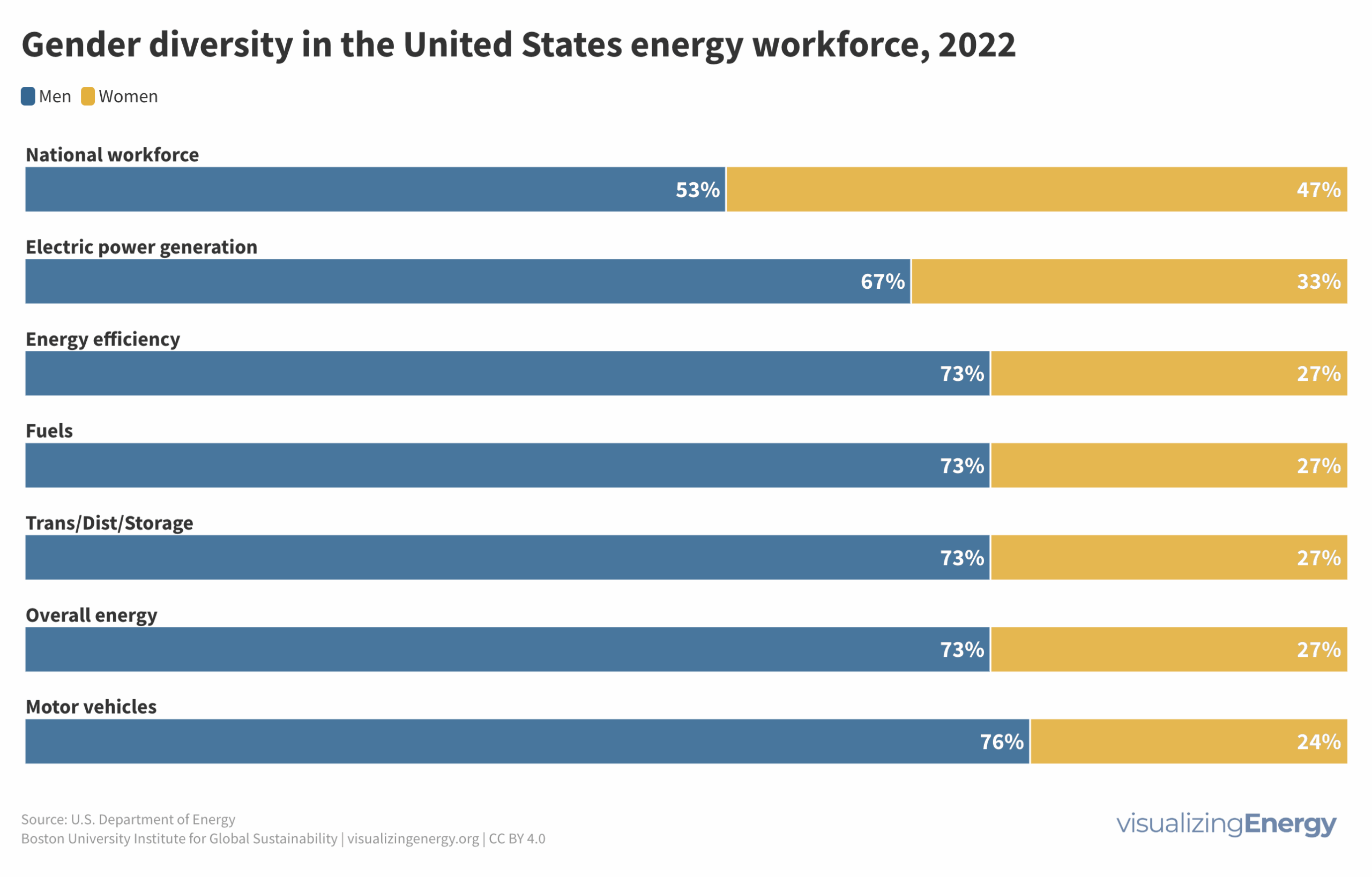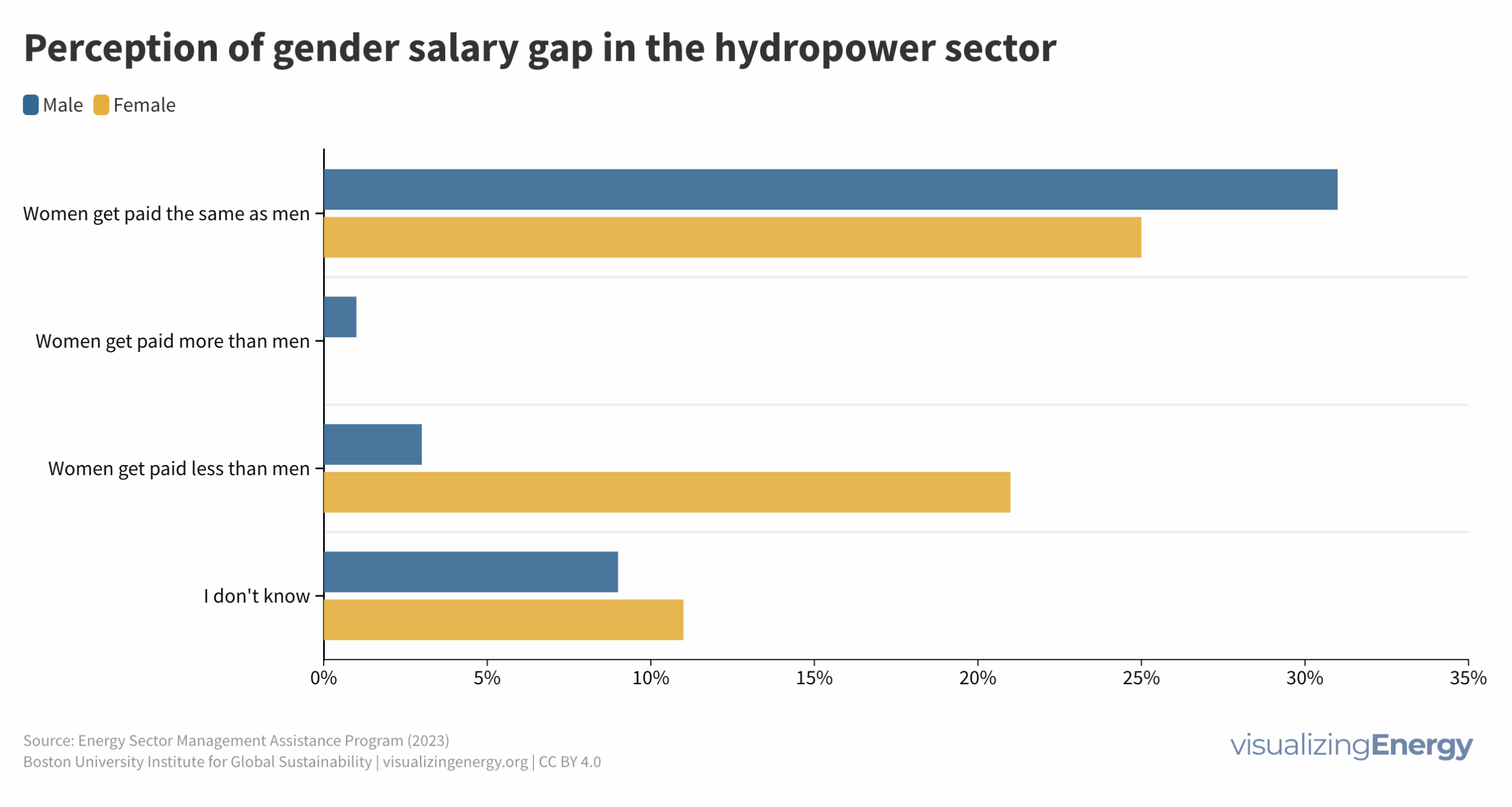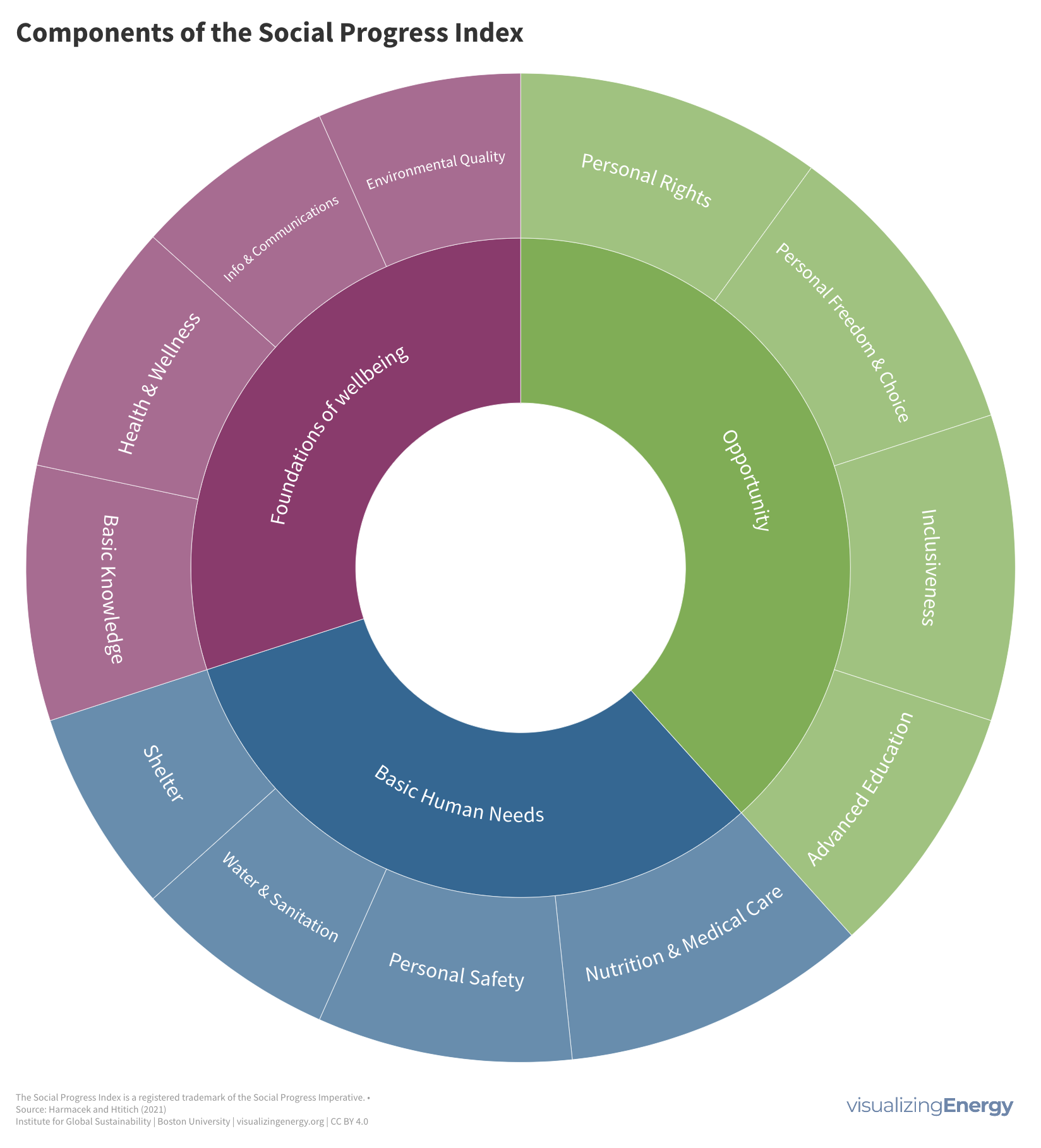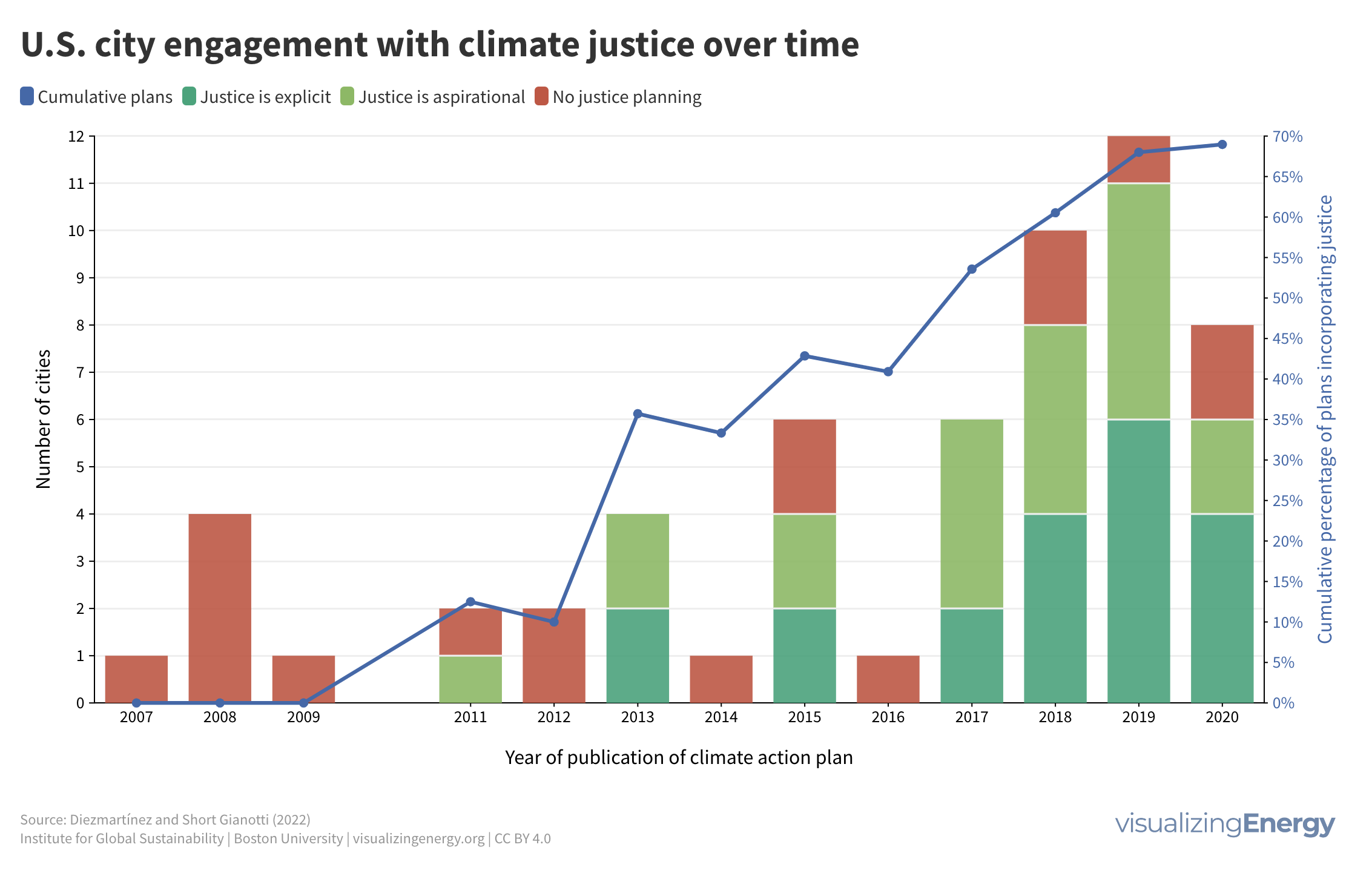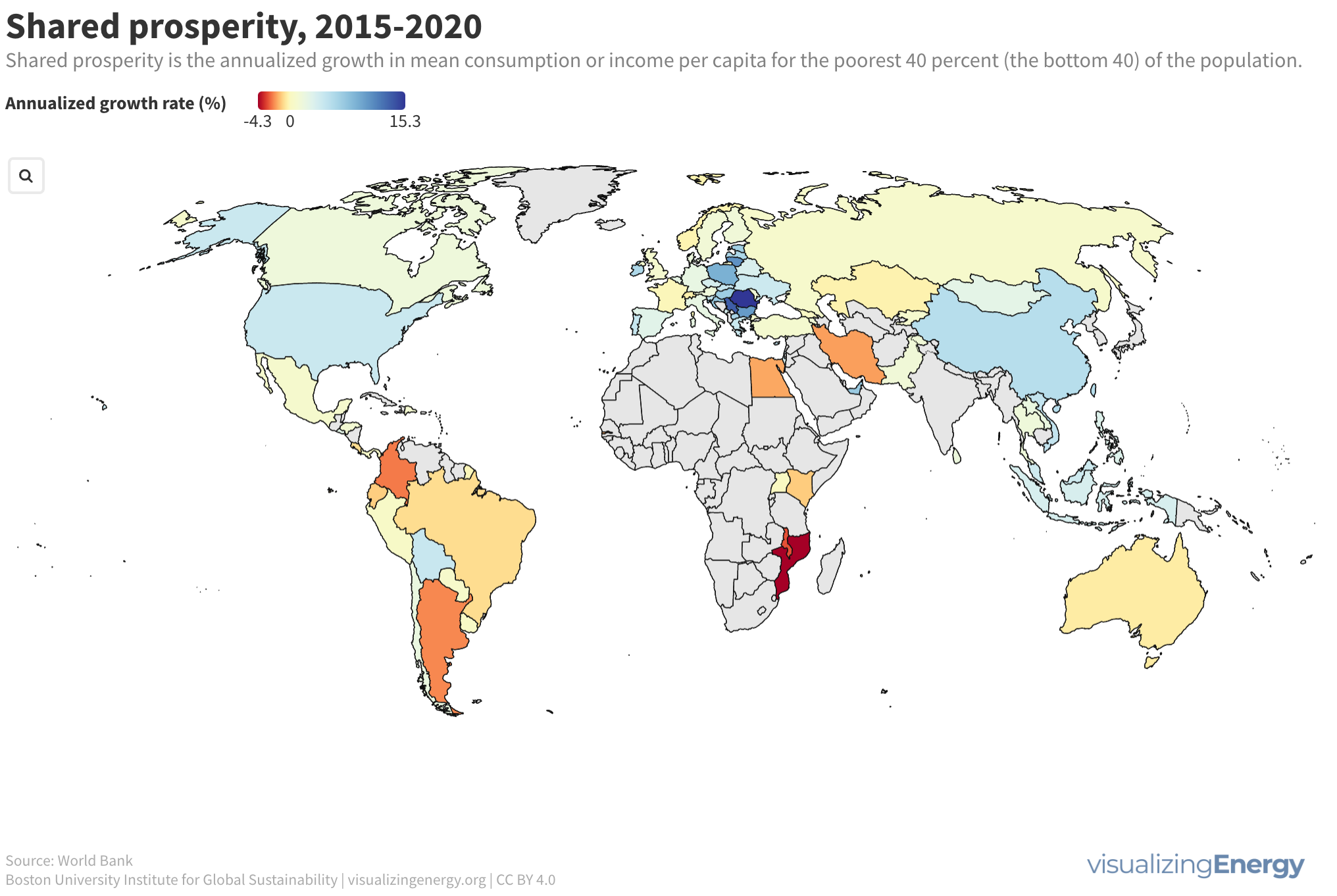
Is shared prosperity connected to per capita energy use?
Shared prosperity measures economic growth inclusiveness, focusing on the income growth of the poorest compared to the overall population. It reduces poverty and inequality and is relevant even in high-income countries. Energy use can impact shared prosperity, but other factors like social safety nets and education also play a crucial role.