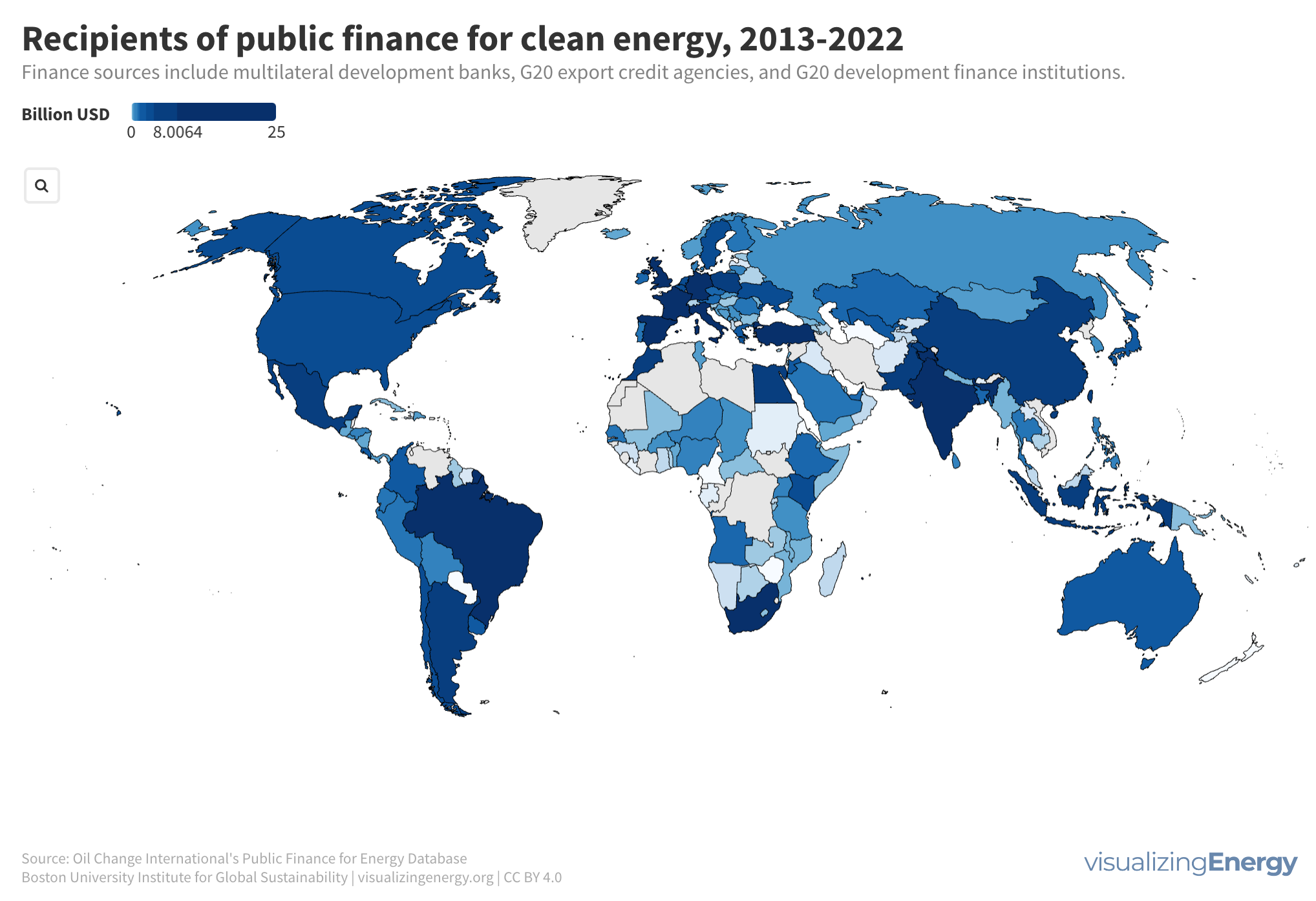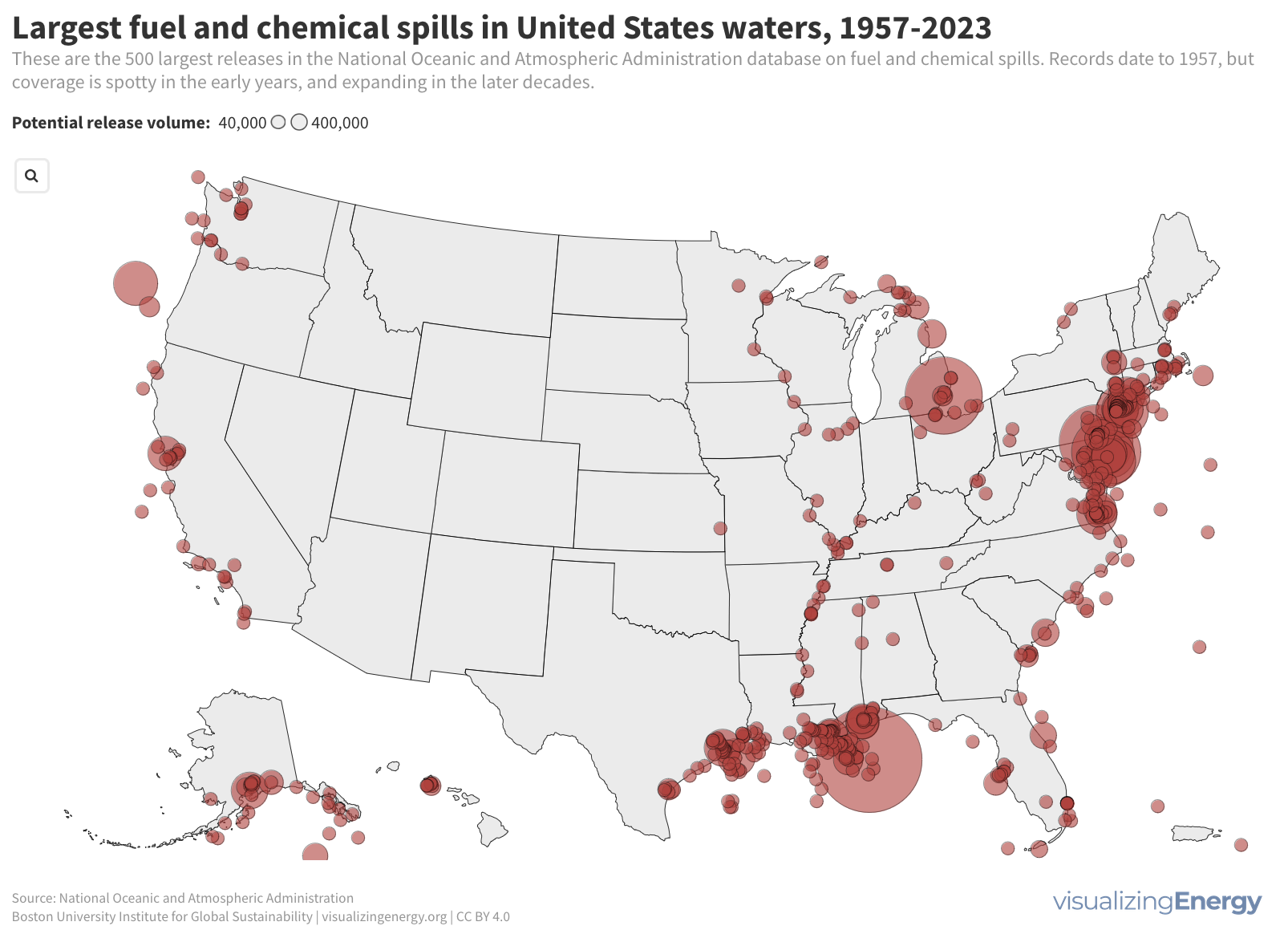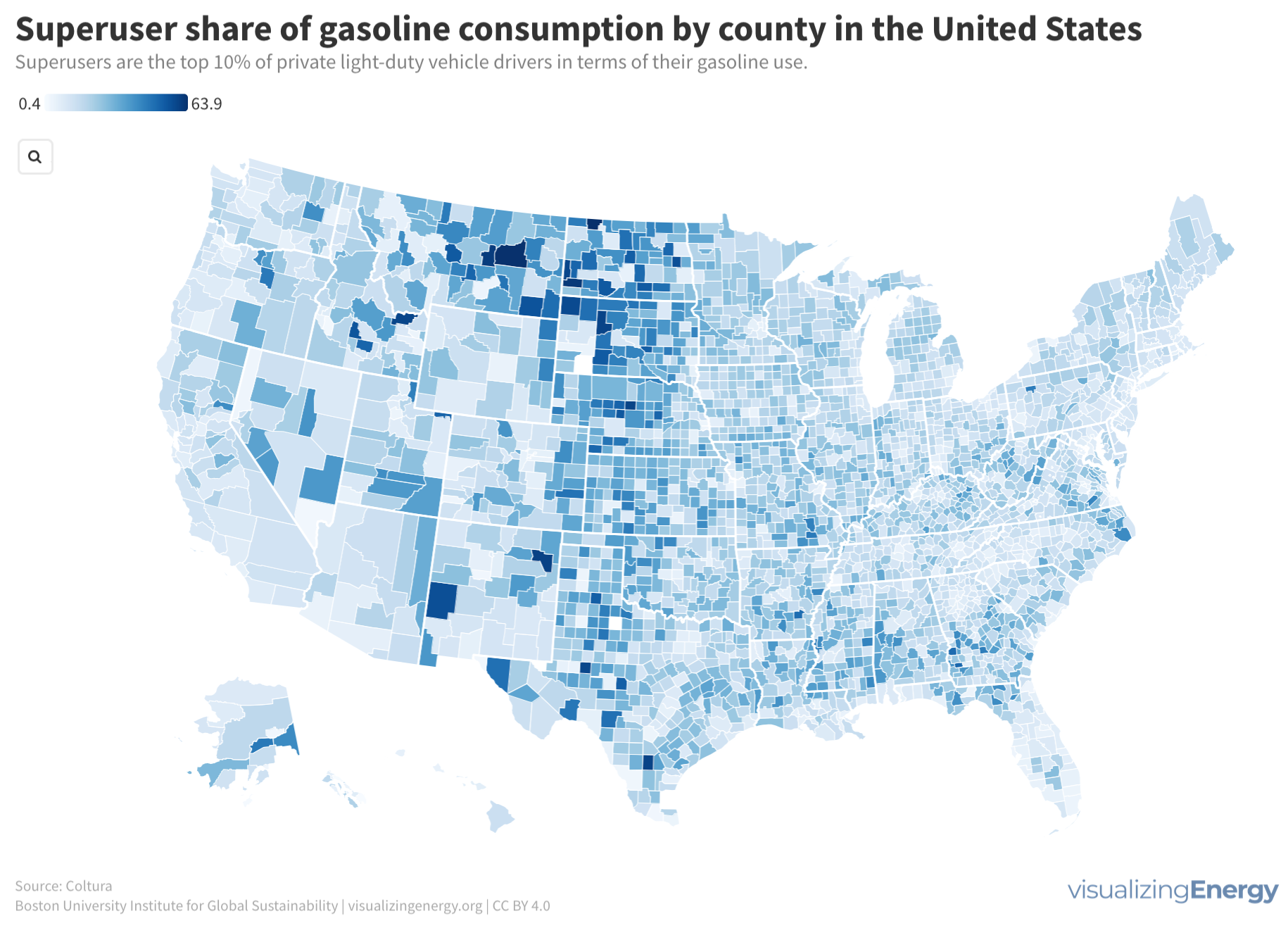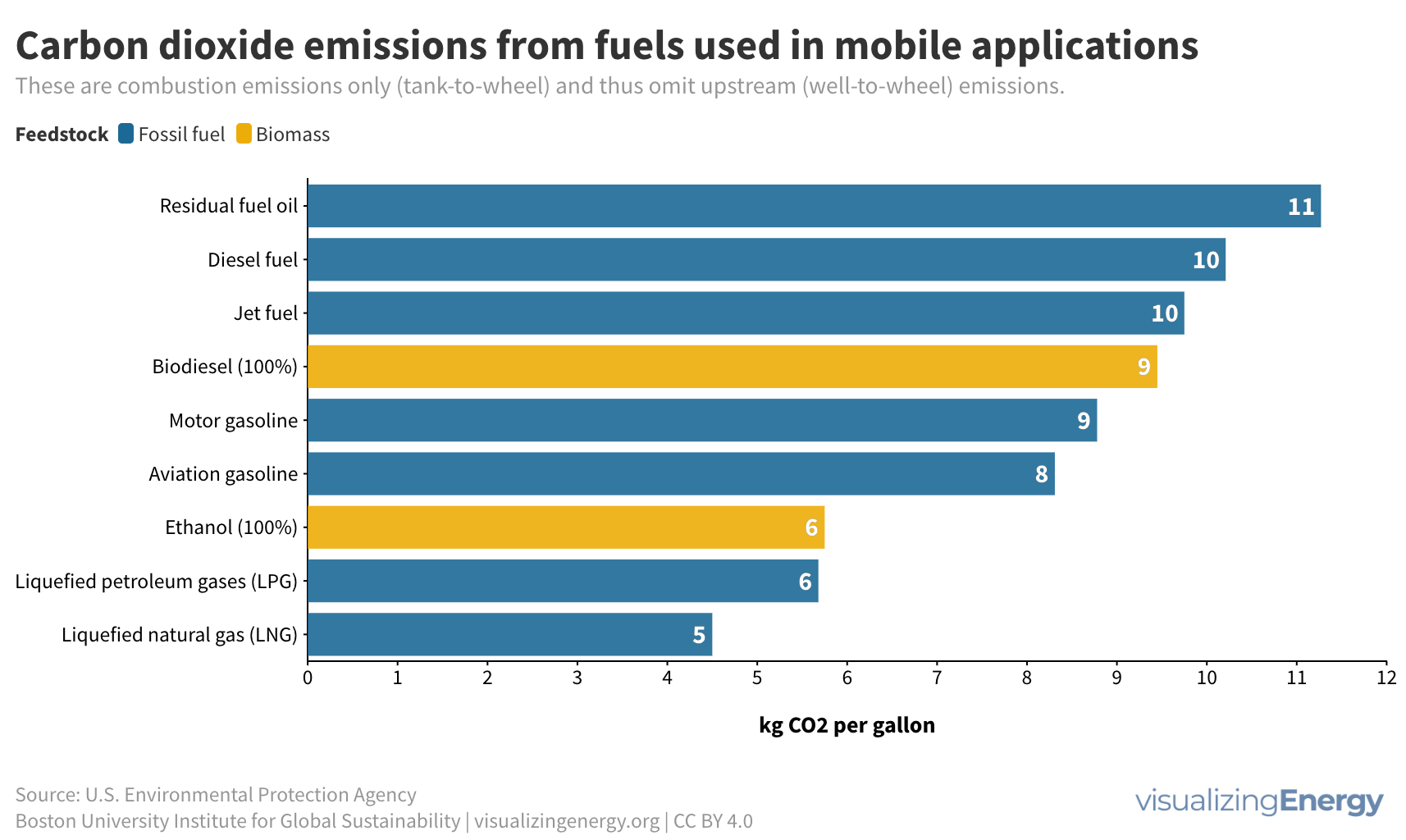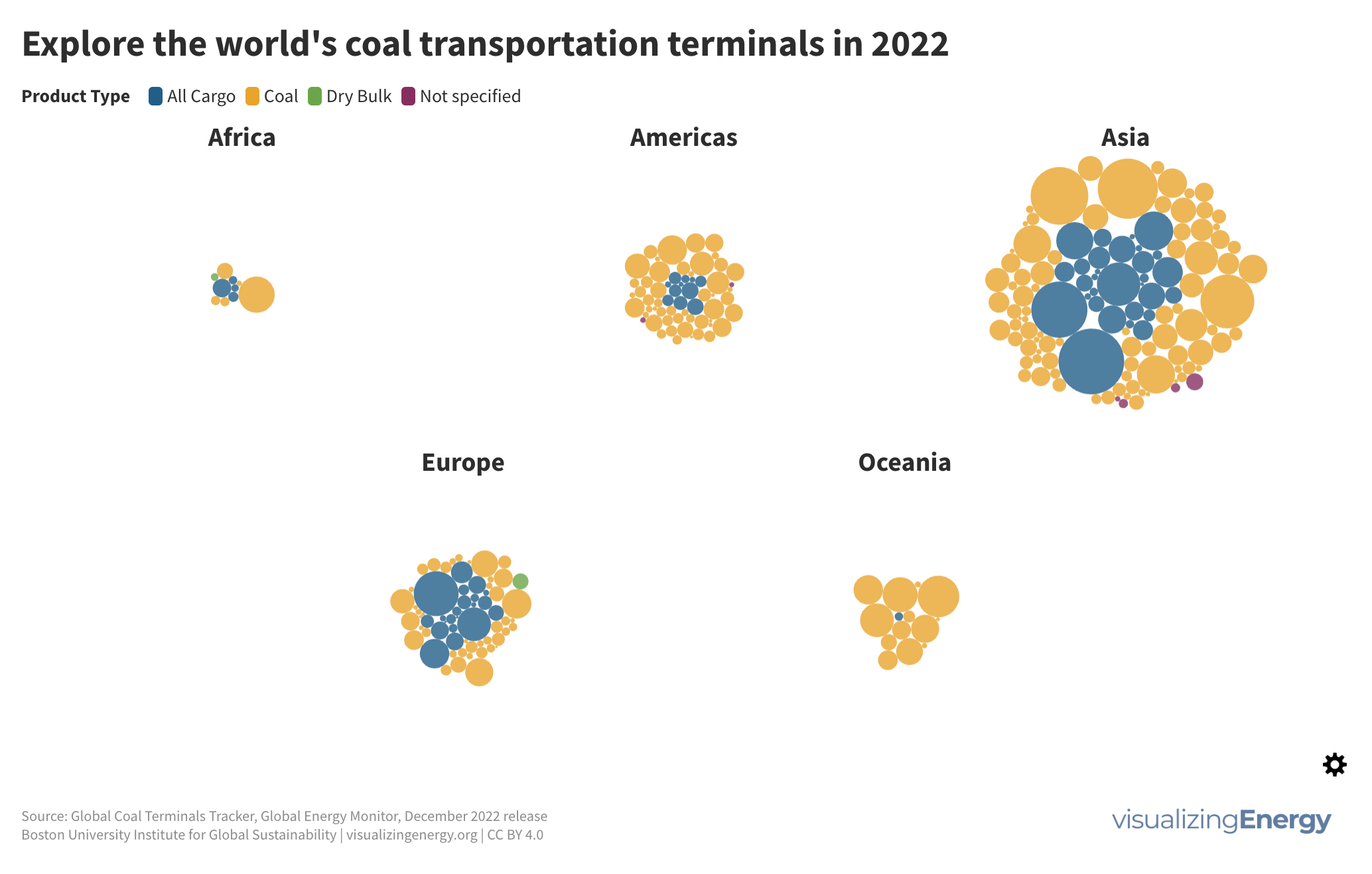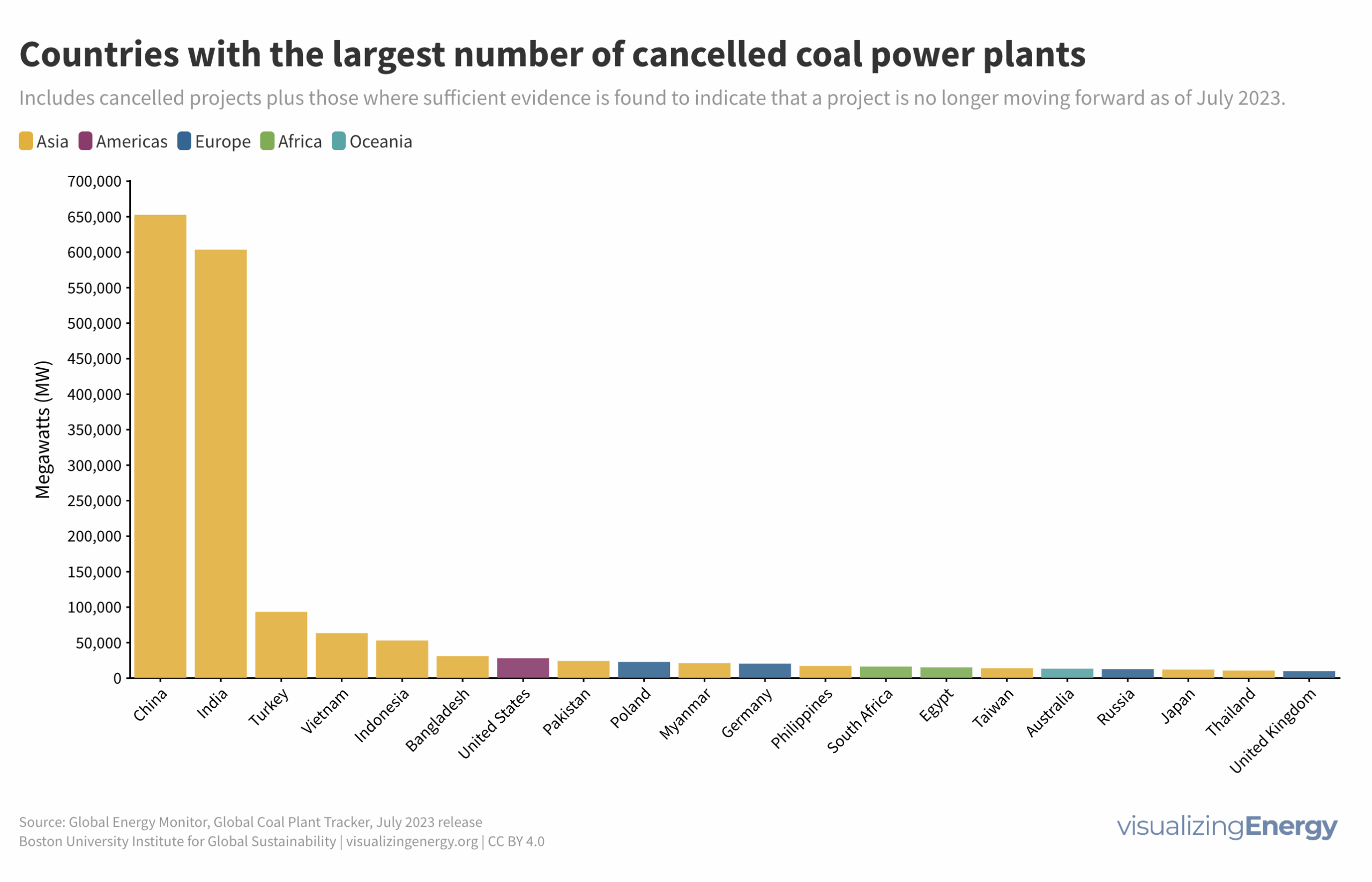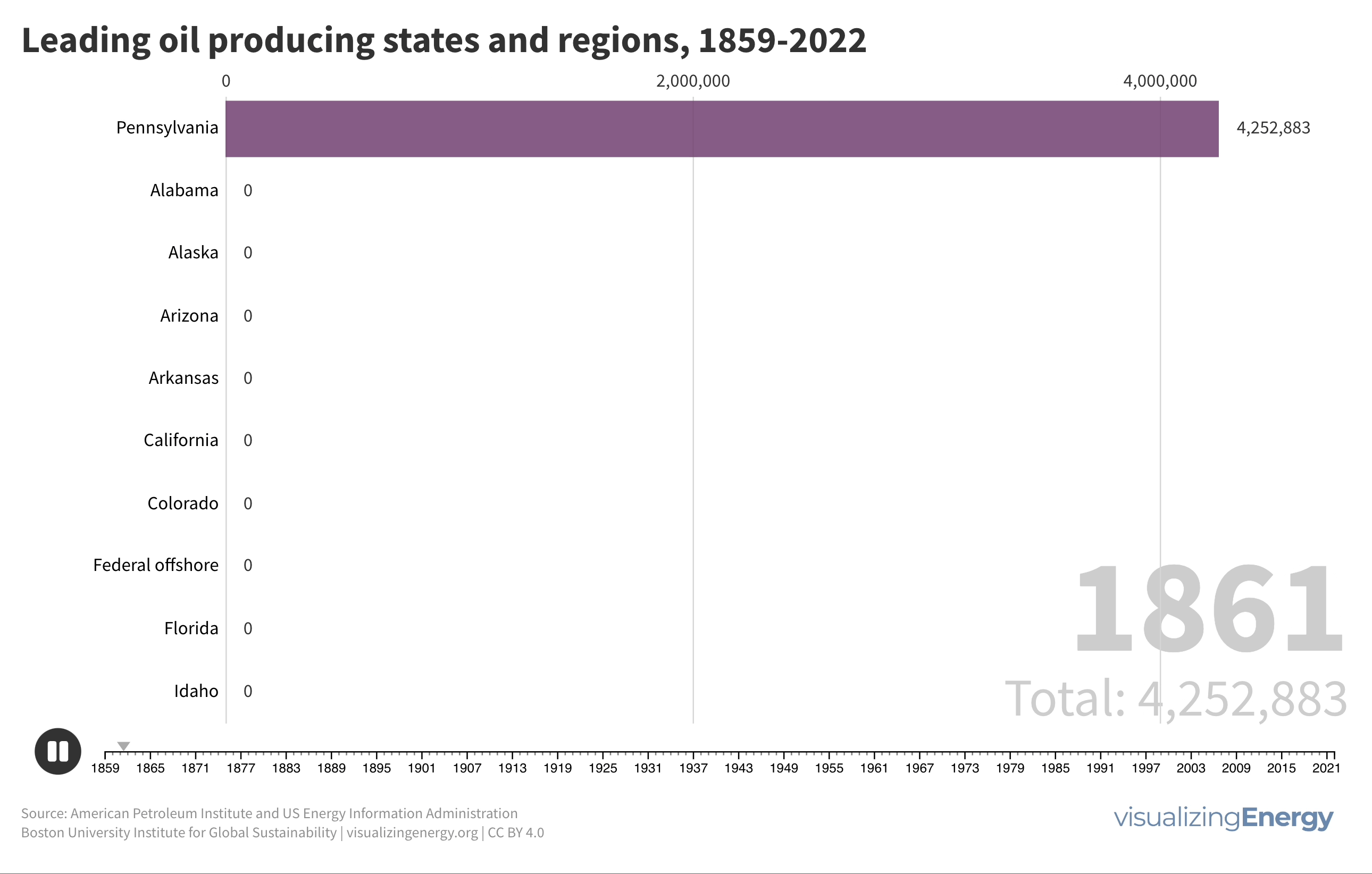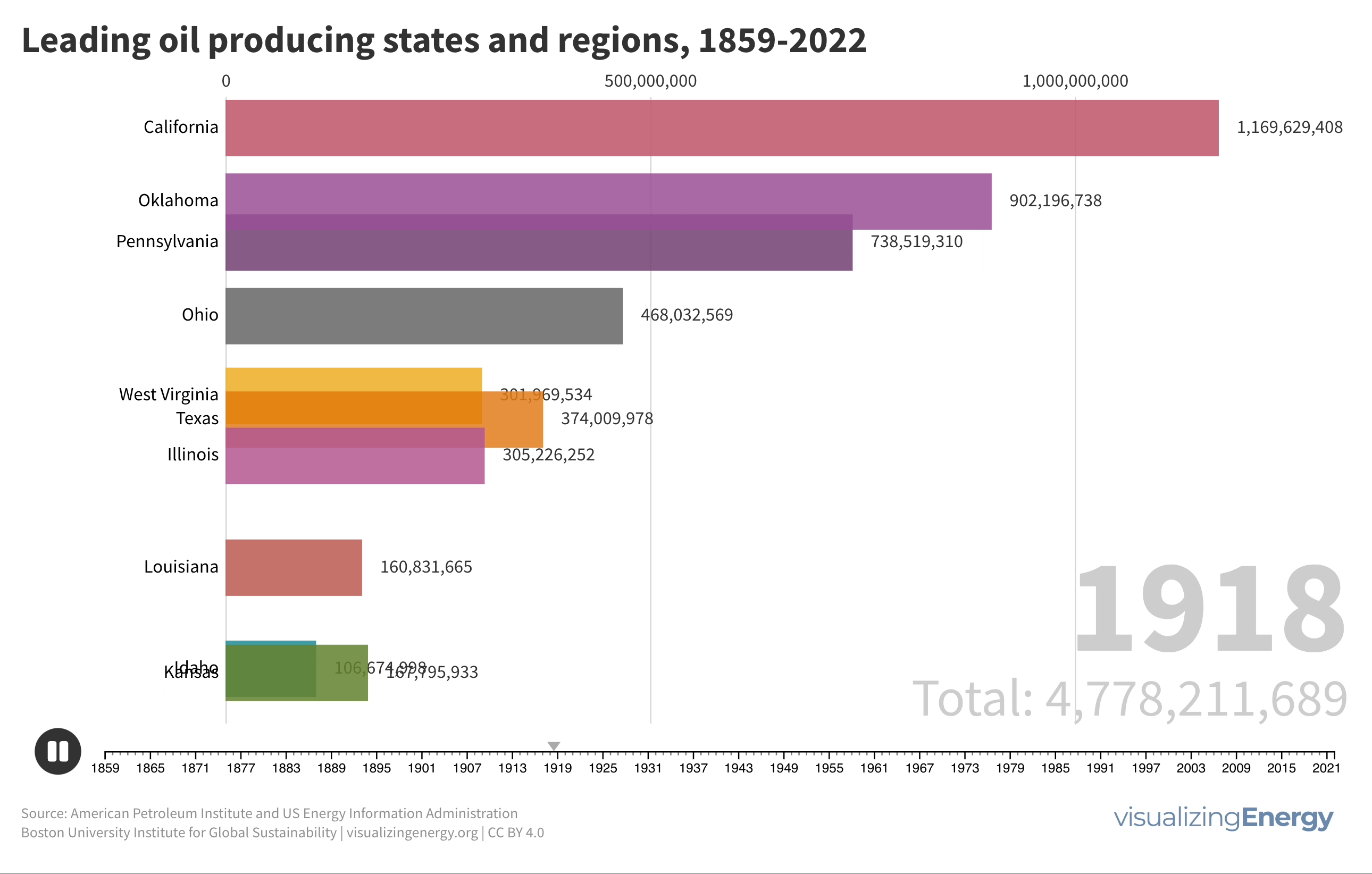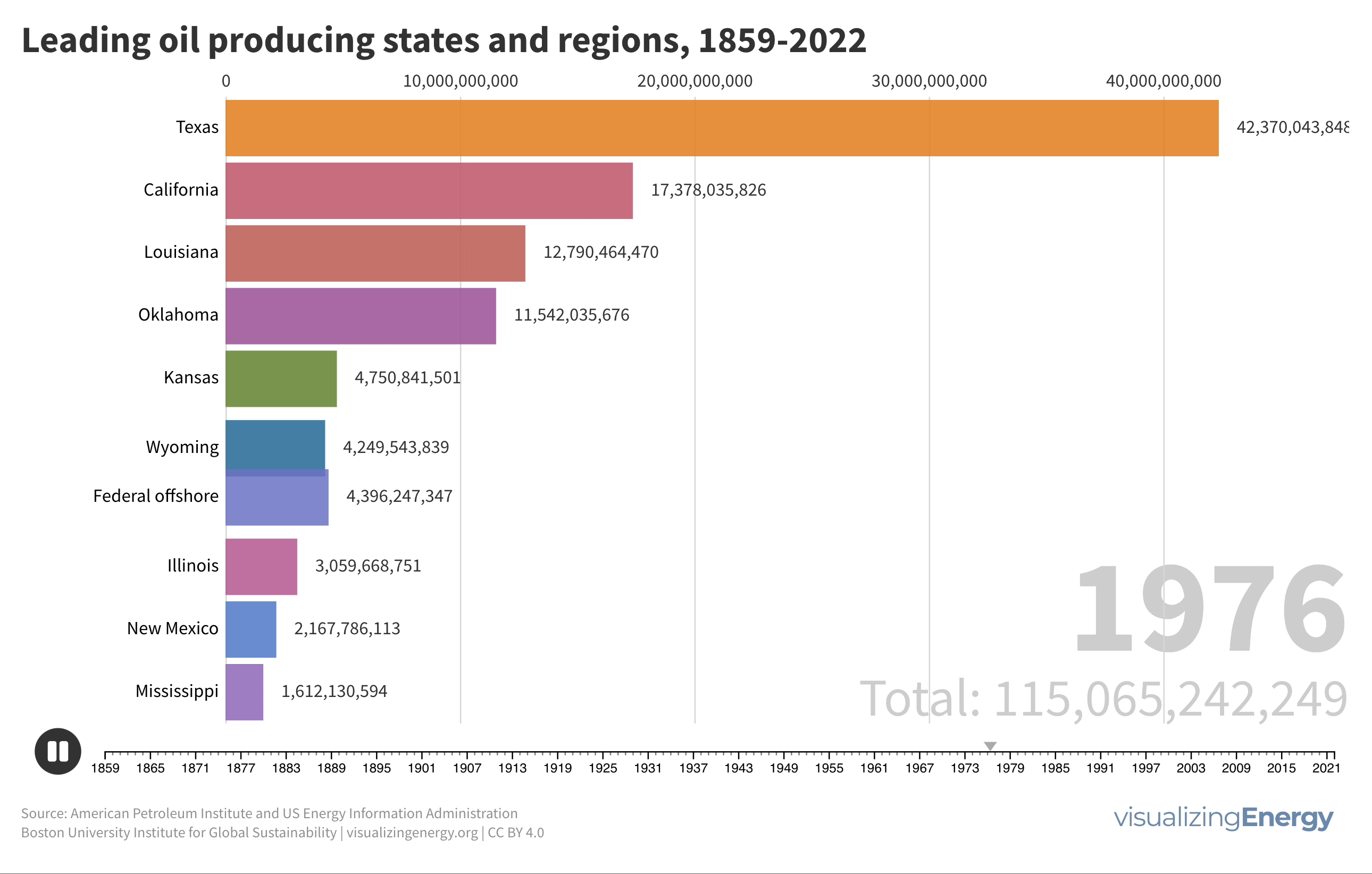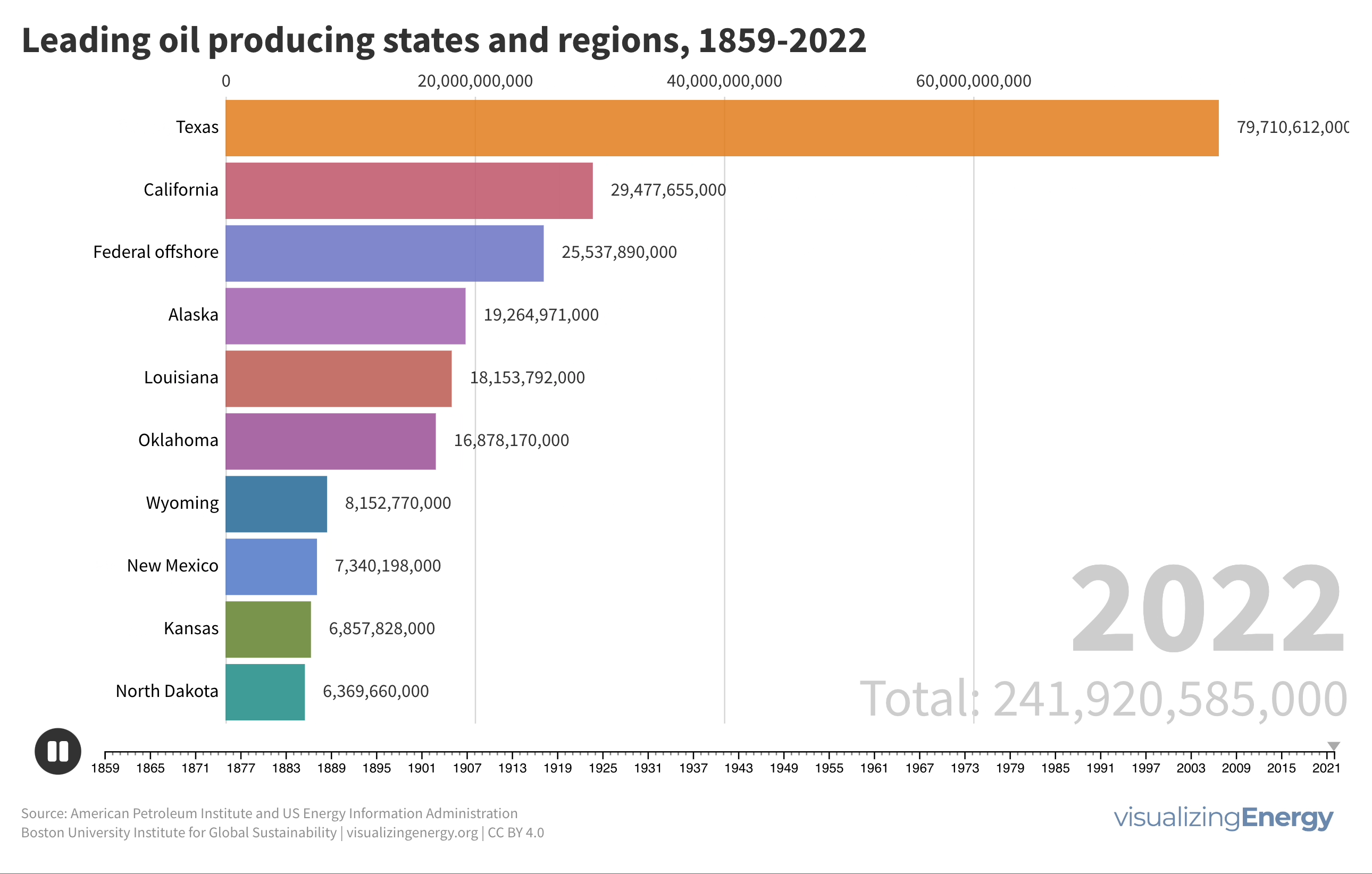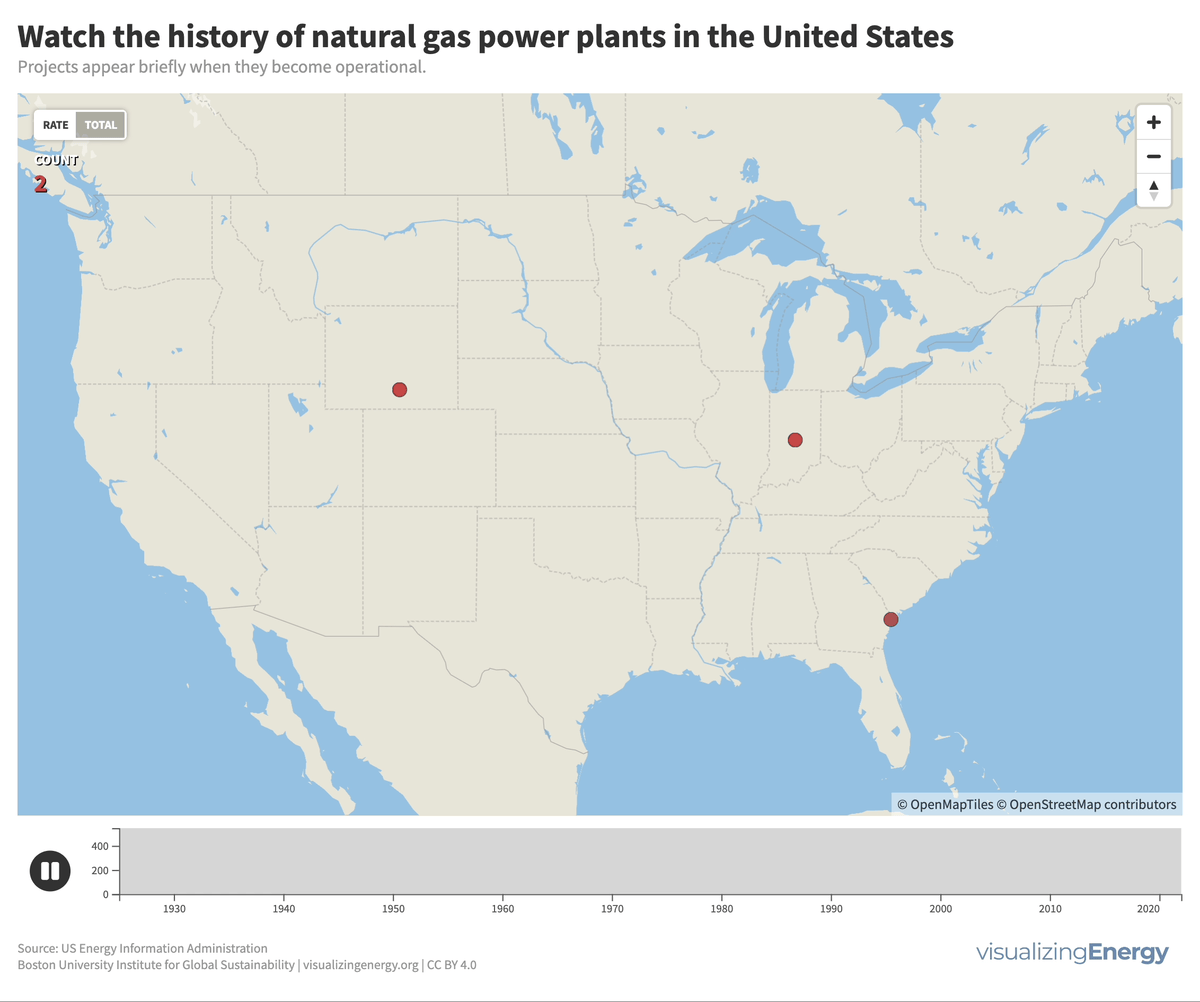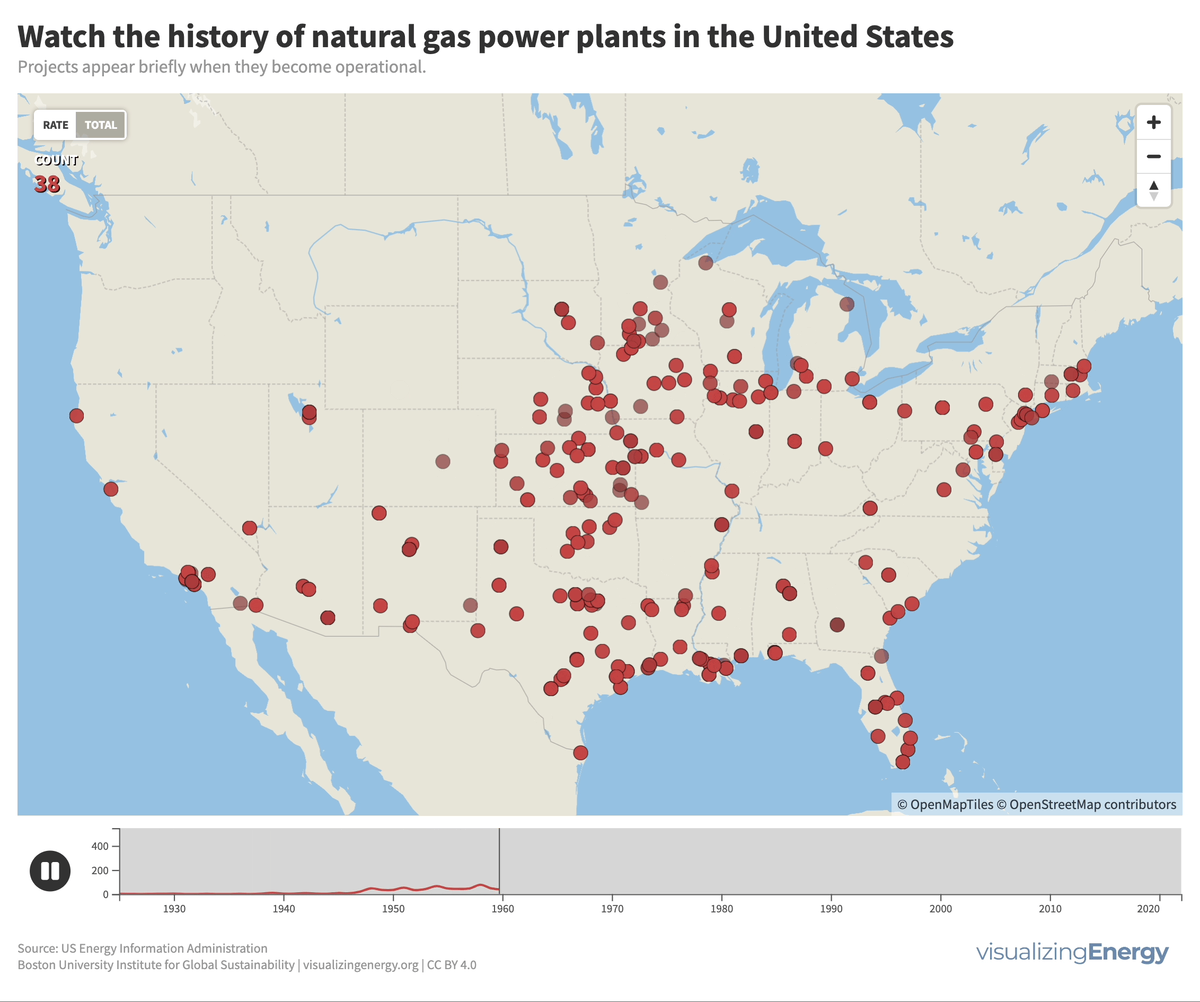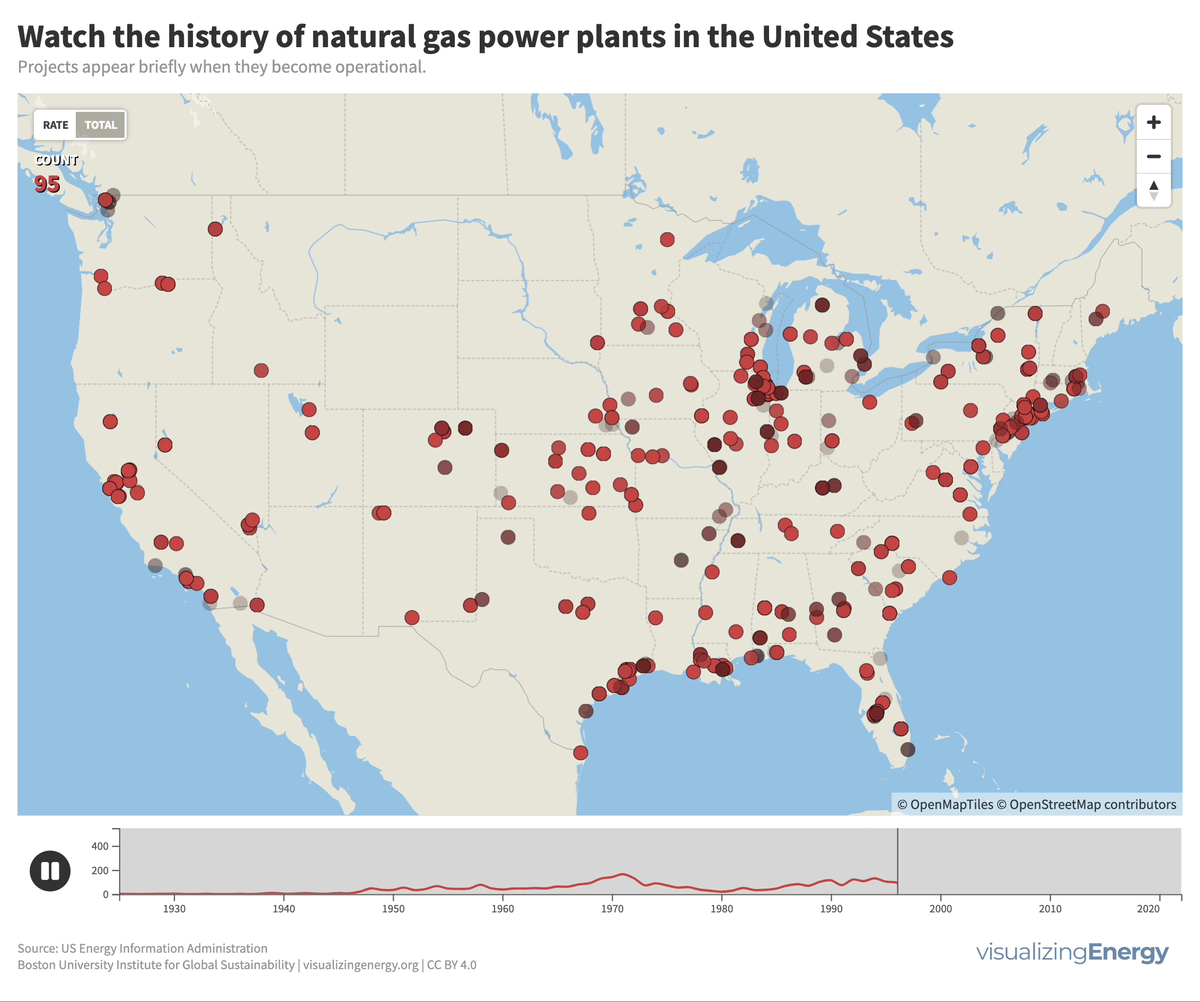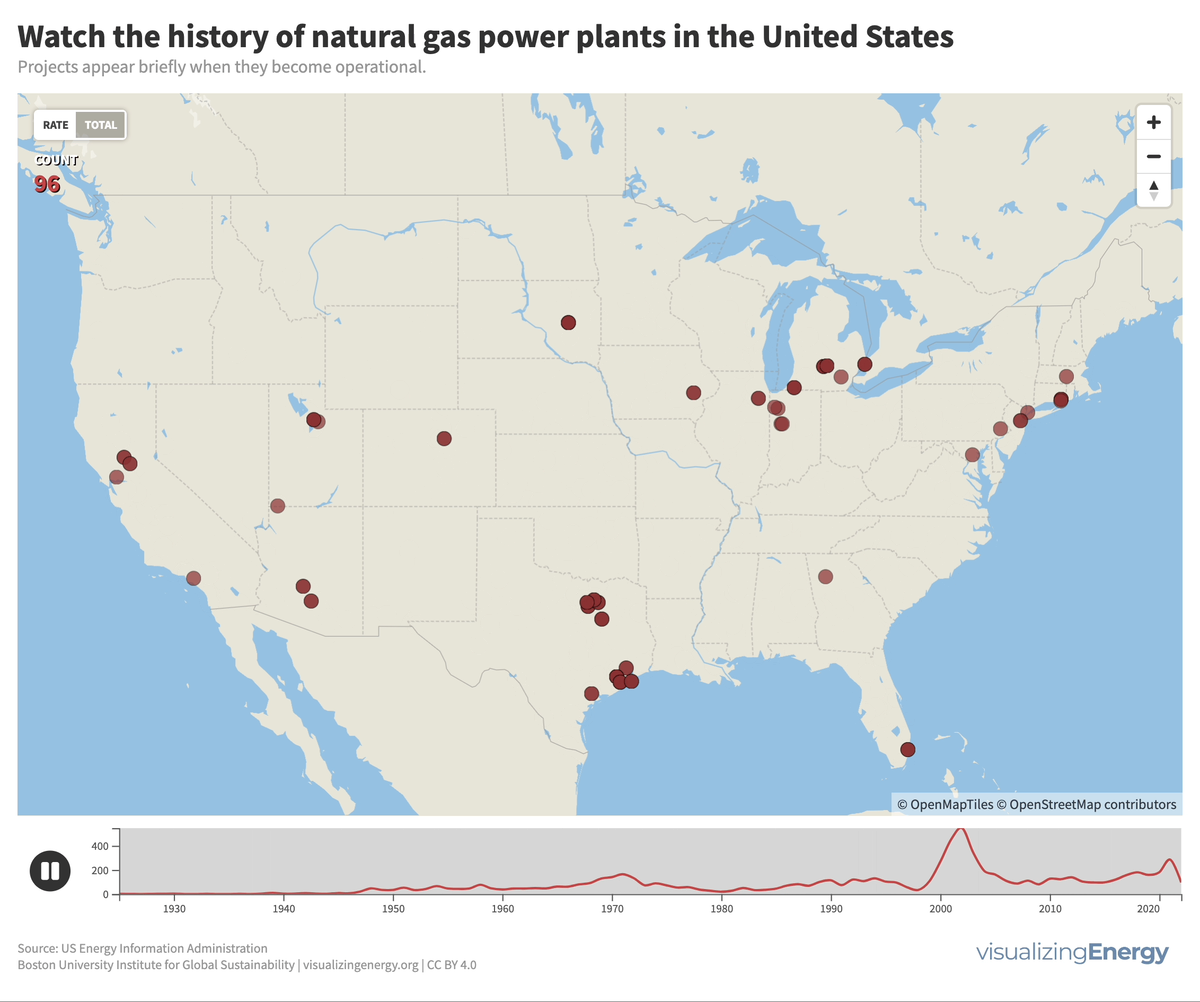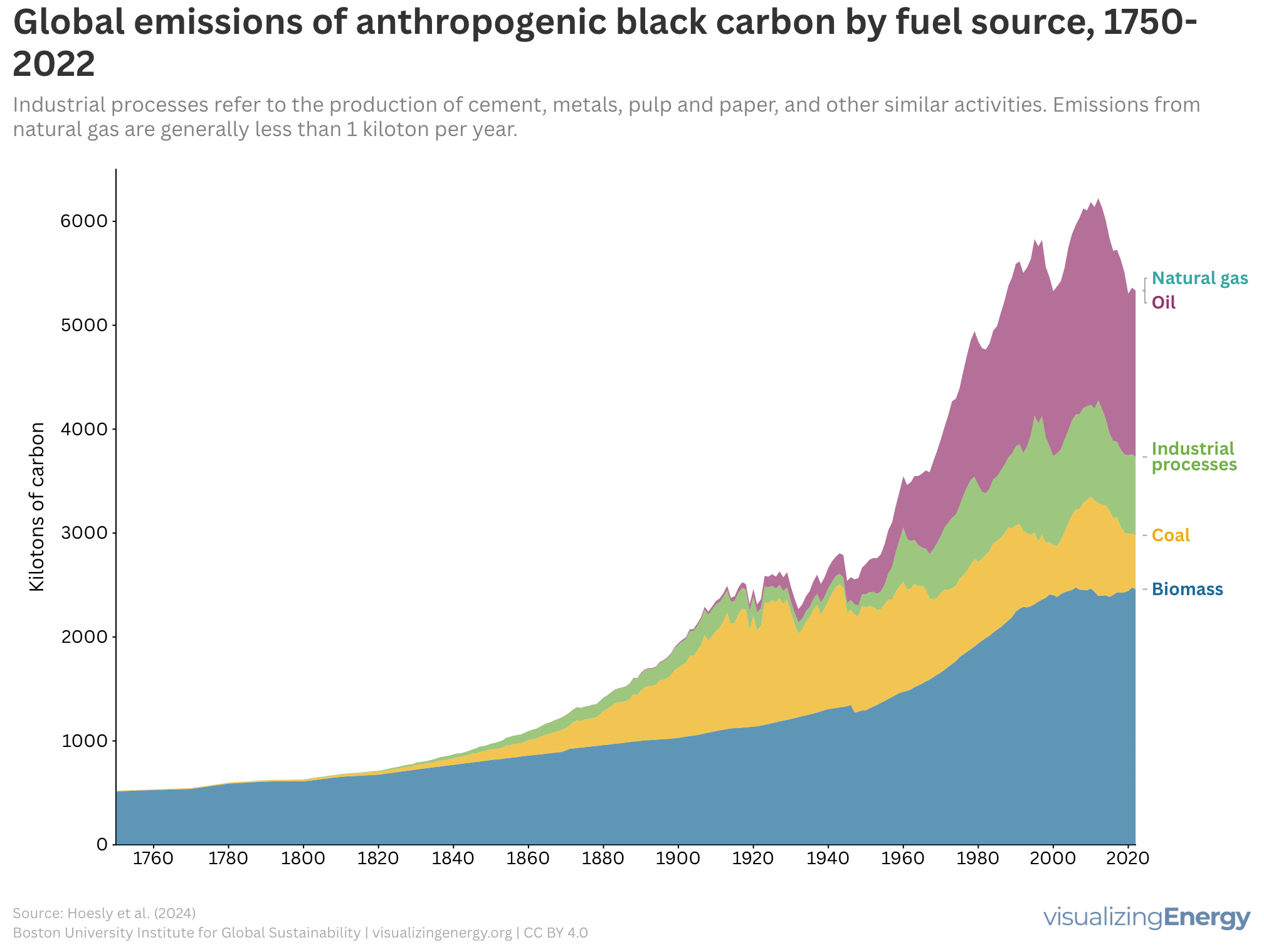
Global black carbon emissions, 1750-2022
Anthropogenic black carbon, or soot, arises from incomplete combustion of organic materials, significantly impacting climate change and public health. It causes global warming, degrades air quality, and leads to various health issues. Major contributors include residential fuel usage and transportation emissions. Reducing black carbon relies on cleaner fuel access and improved combustion technologies.