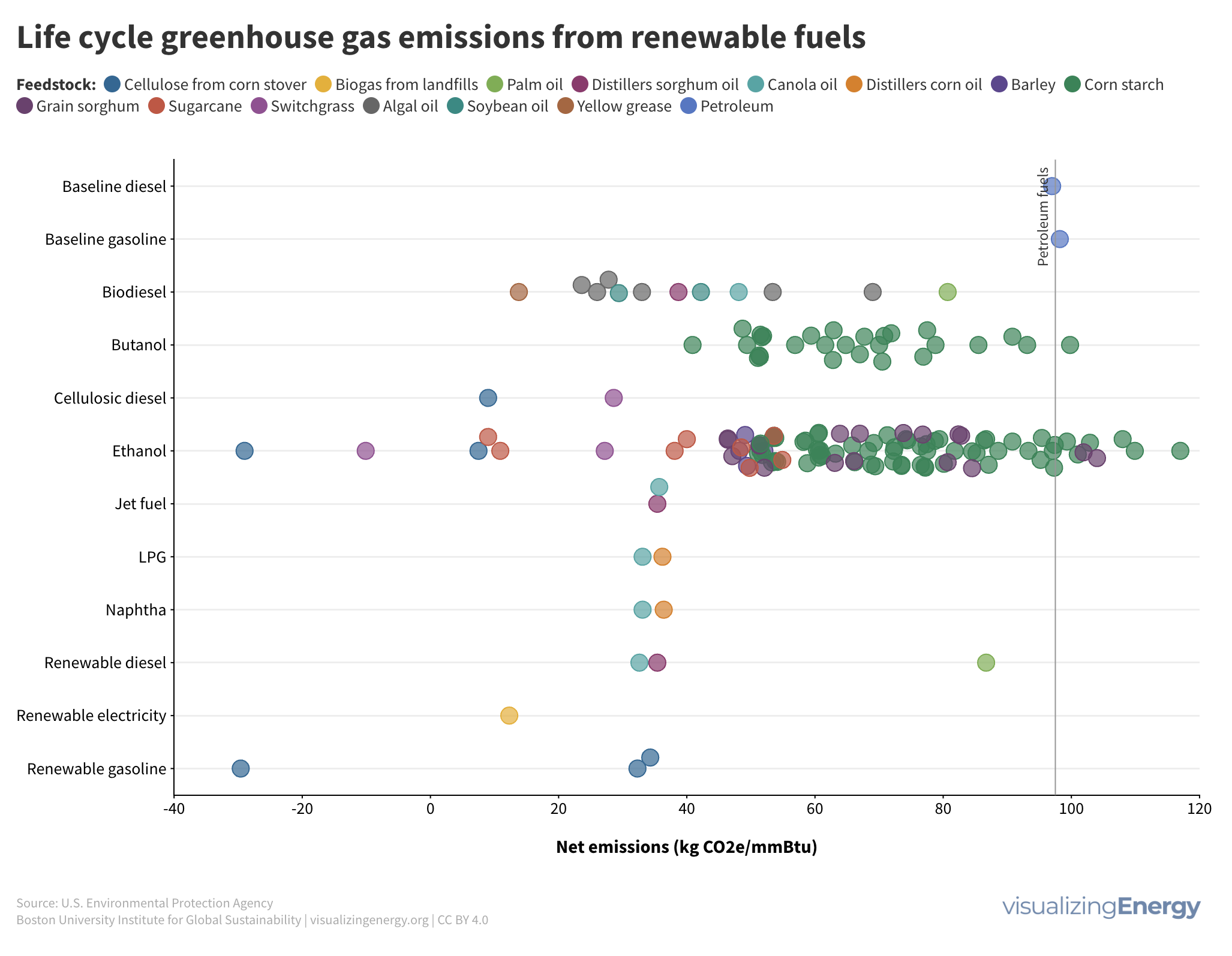
What renewable fuels have the largest climate benefit?
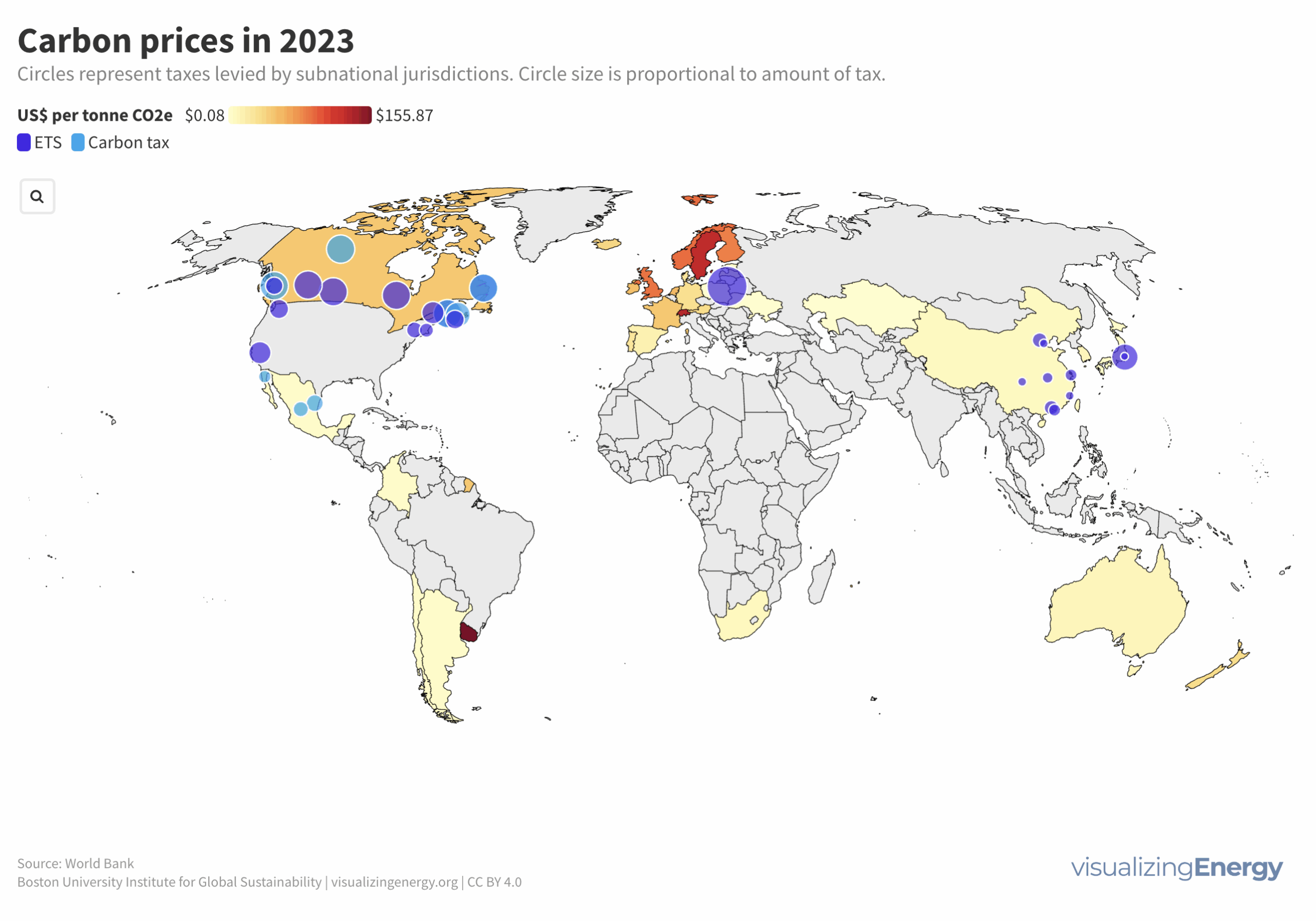
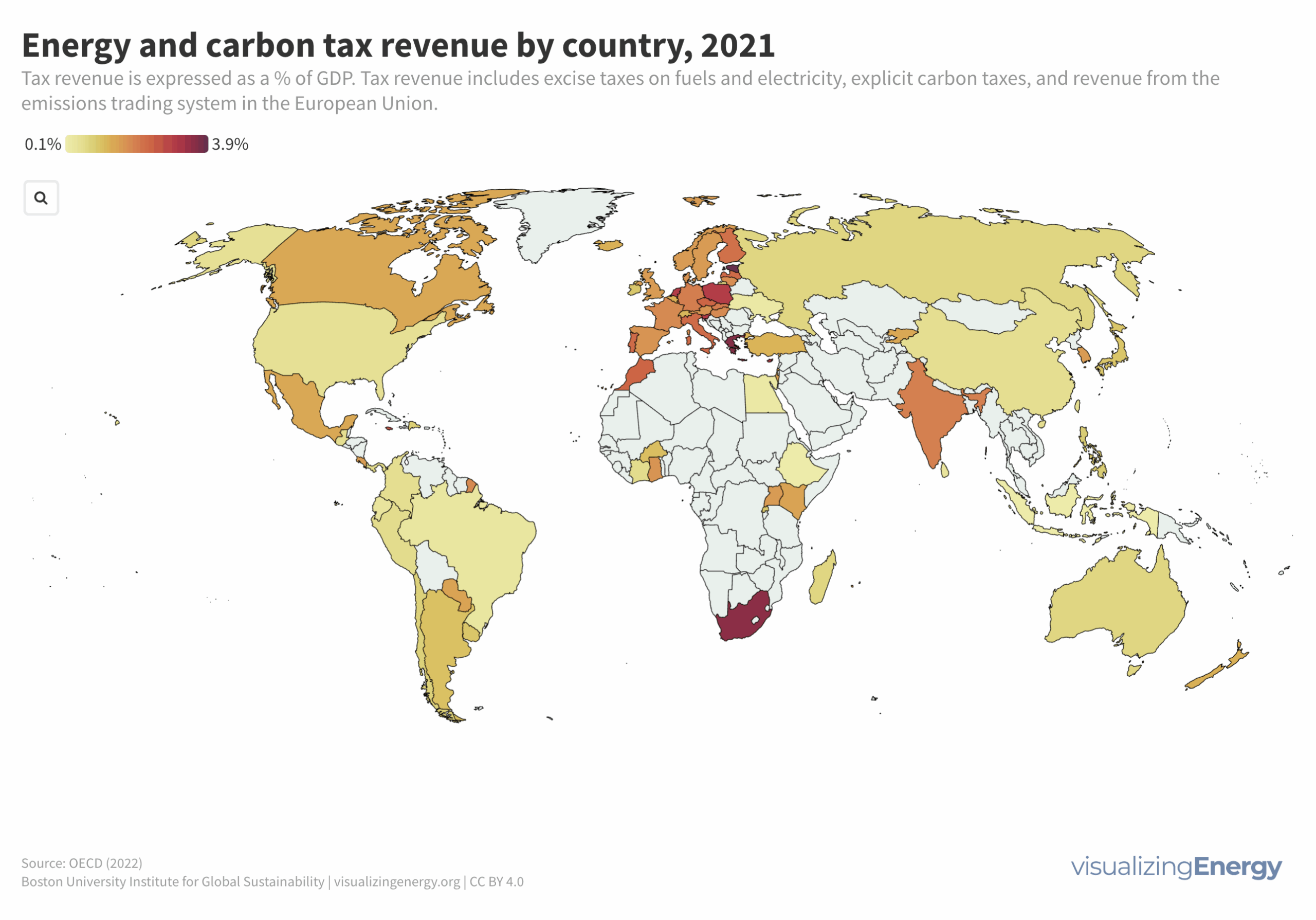
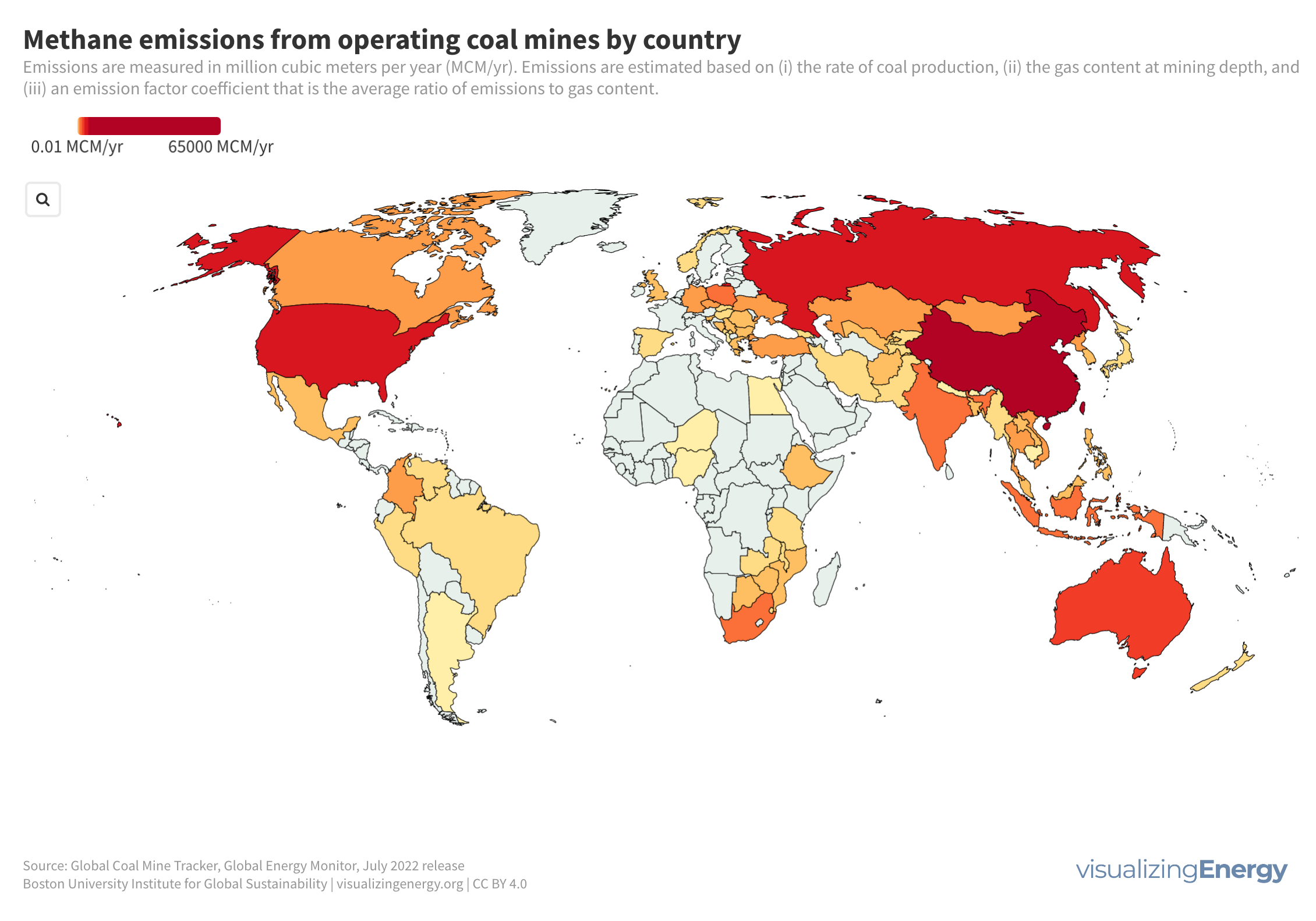
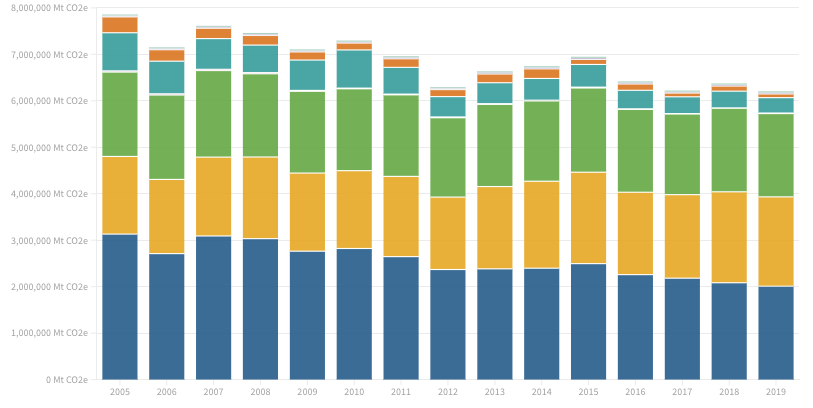
Approximately 91% of transportation energy globally comes from petroleum fuels, creating 29% of US and 20% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Biofuels offer potential emission reductions but raise land use concerns. Ethanol’s carbon emissions have decreased, and ongoing research aims to further reduce them. Government support and investments are driving biofuel expansion.