Watch the history of biopower plants in the United States
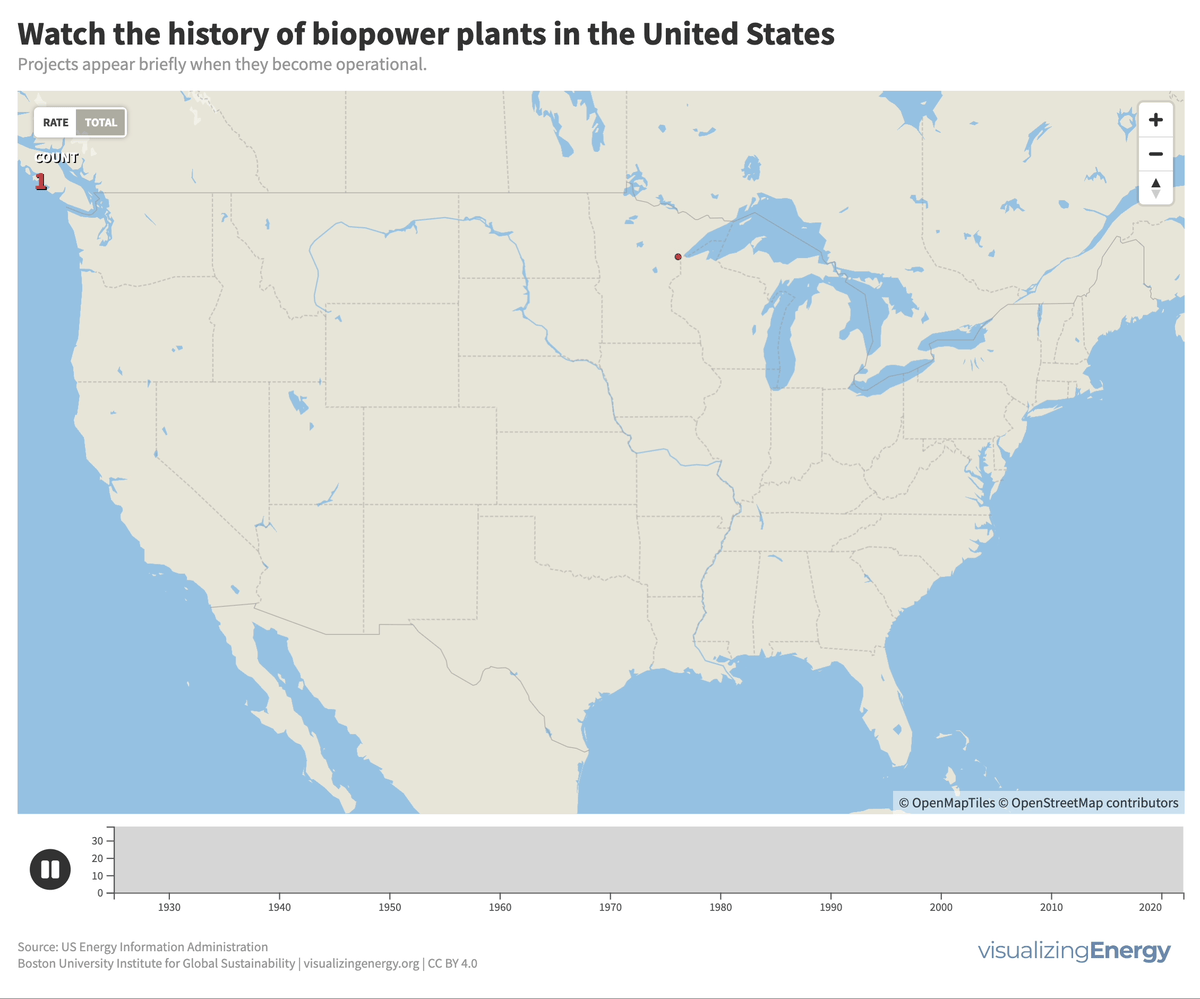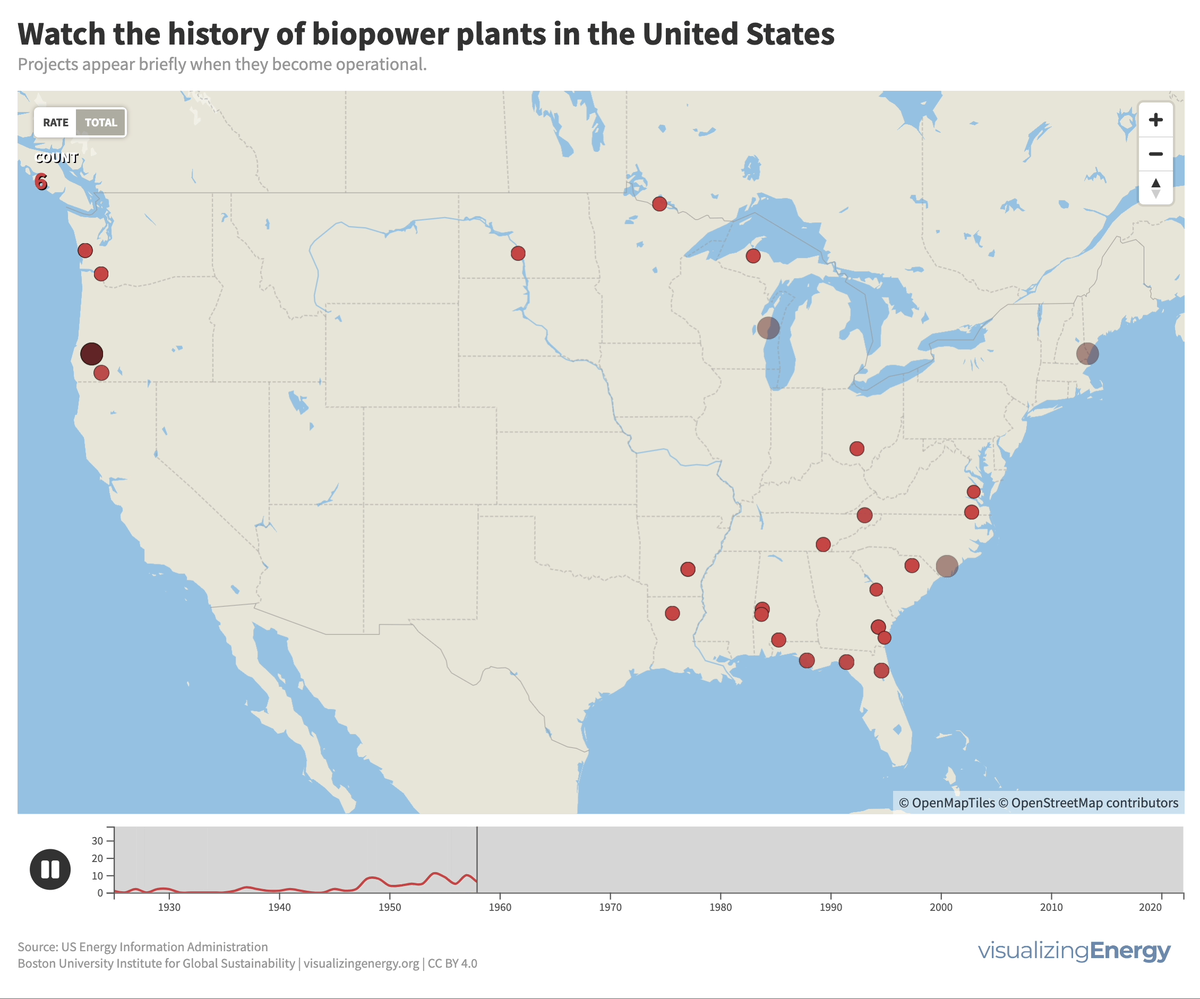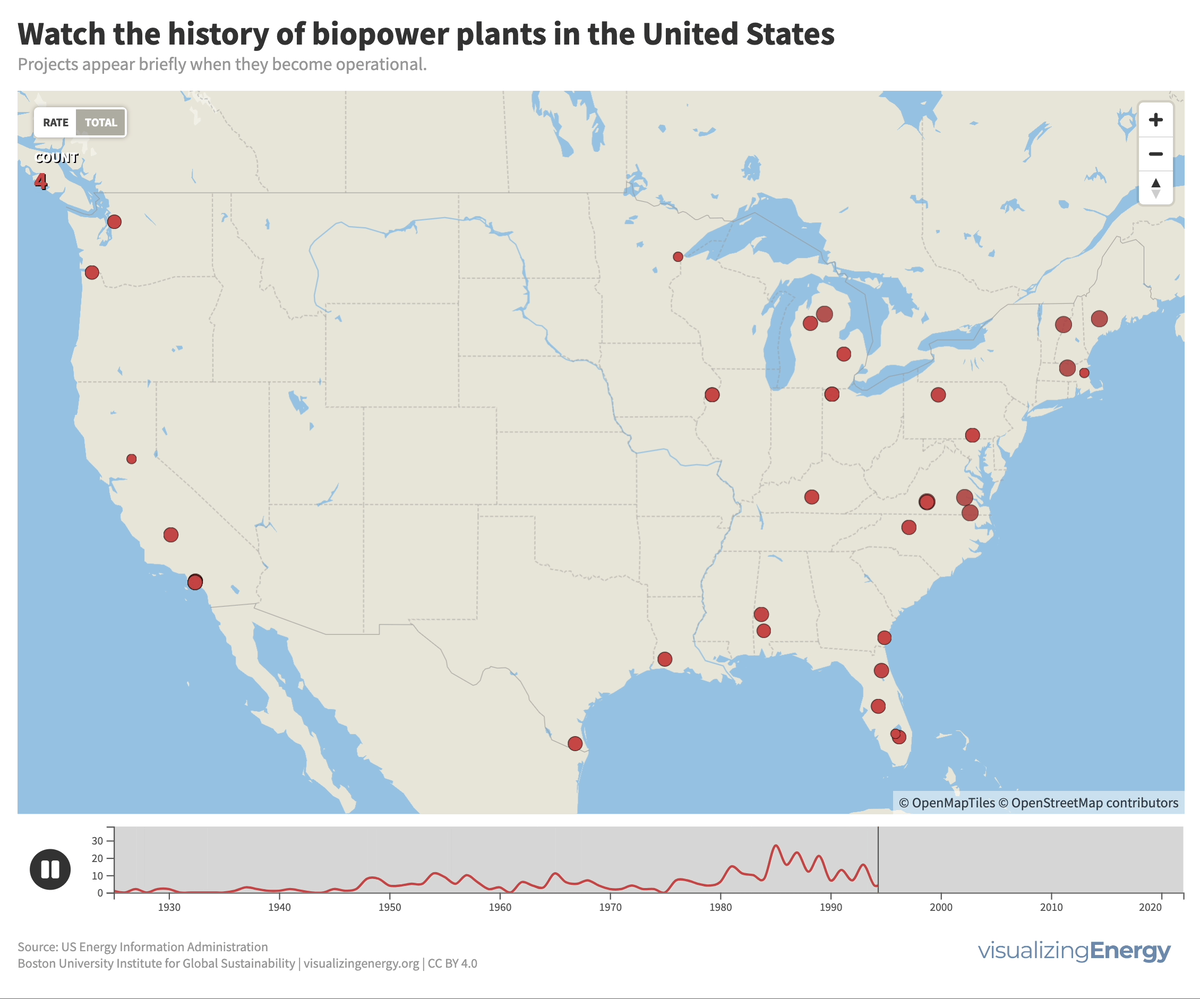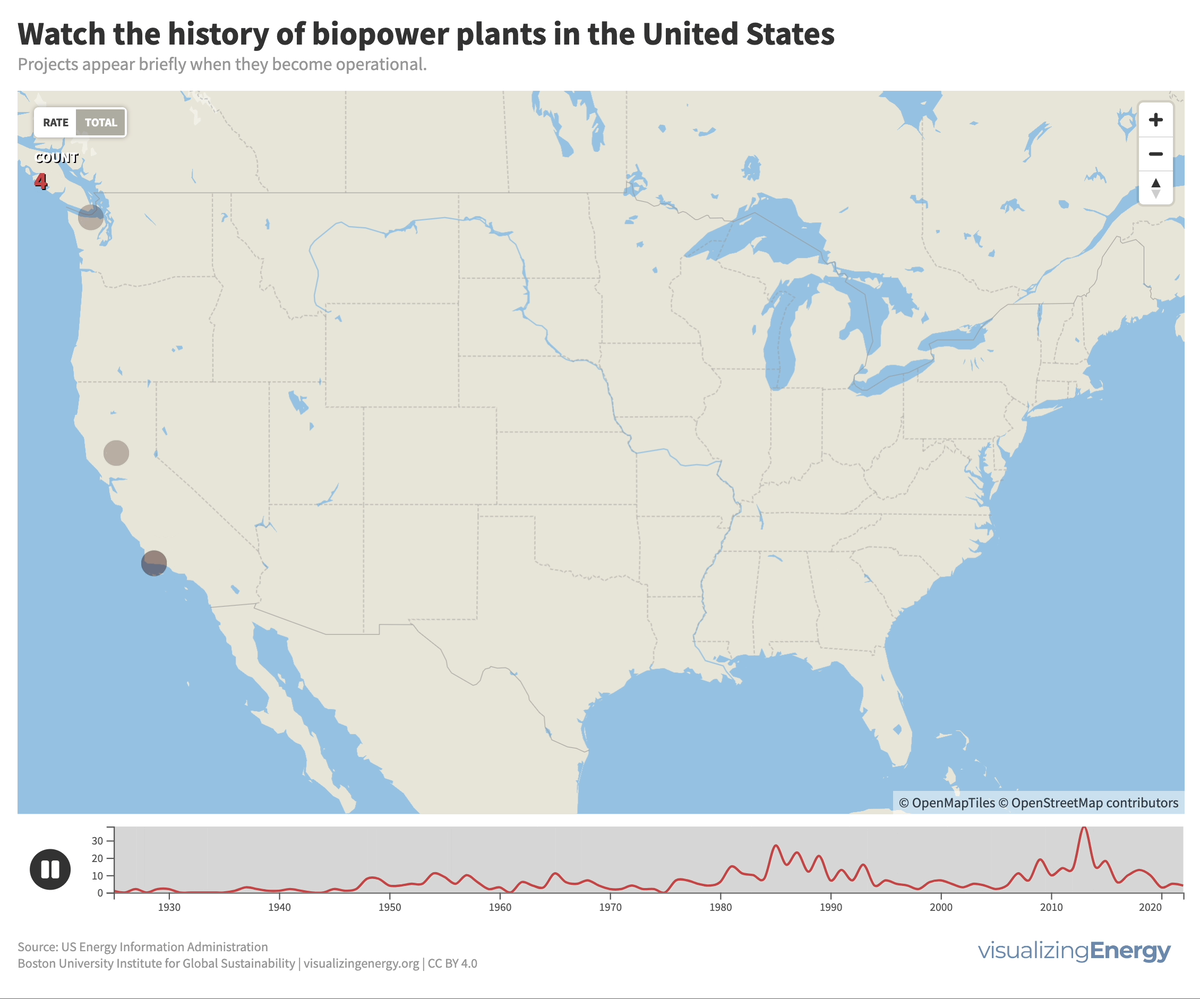
Biomass generates electricity, or biopower, from sources like wood, agricultural residues, and urban waste. In the US, it accounts for 1.2% of electricity.

Biomass generates electricity, or biopower, from sources like wood, agricultural residues, and urban waste. In the US, it accounts for 1.2% of electricity.
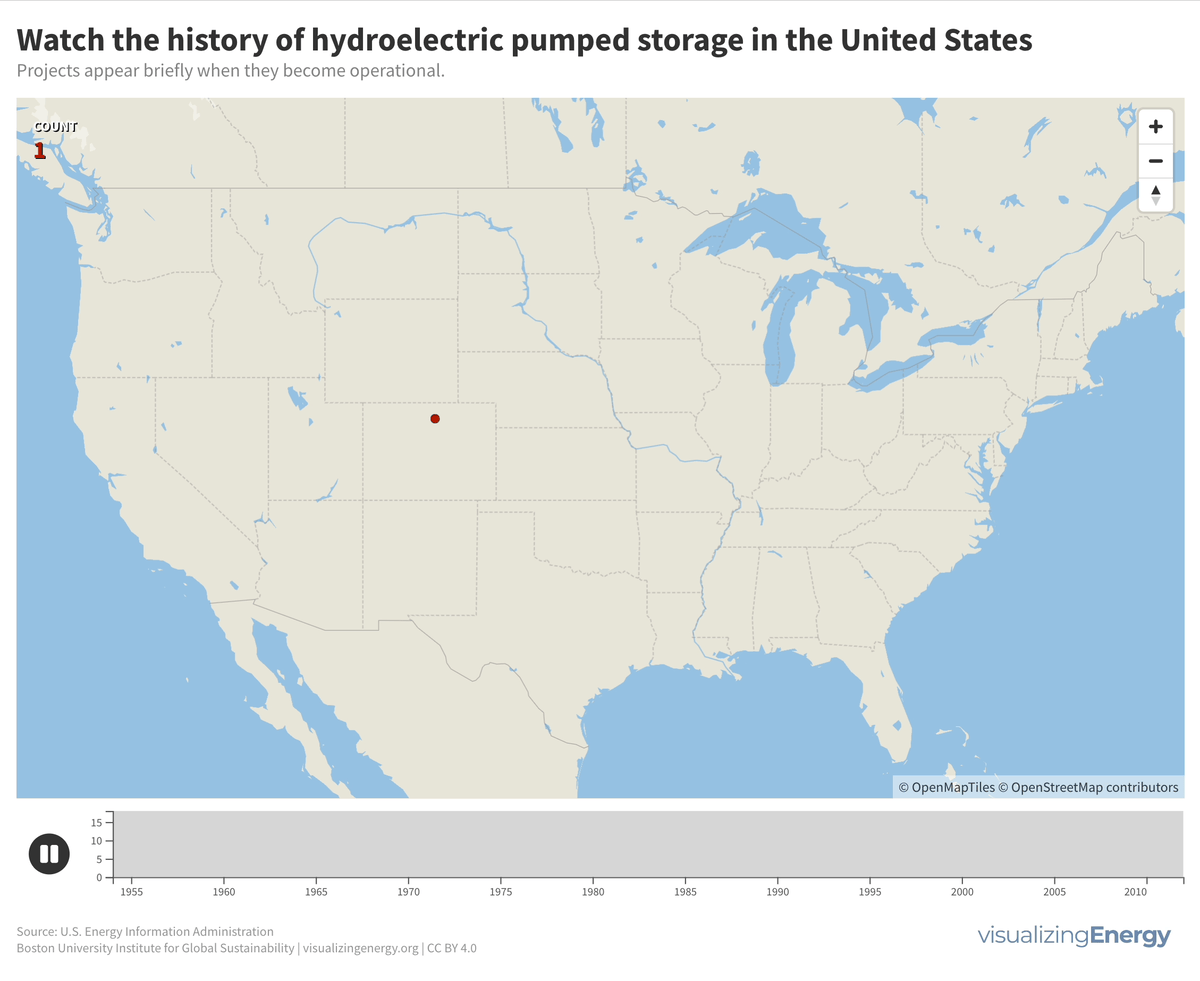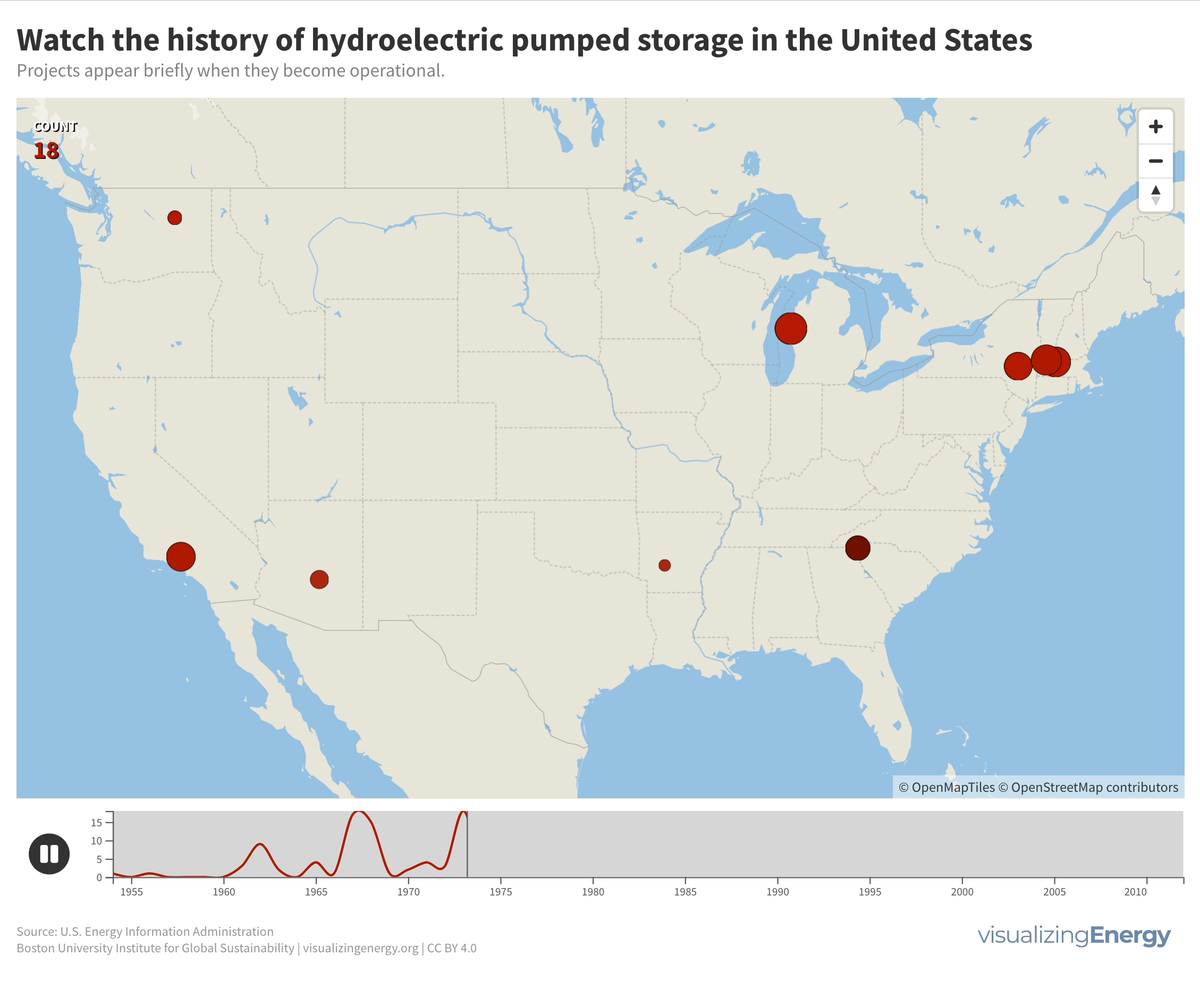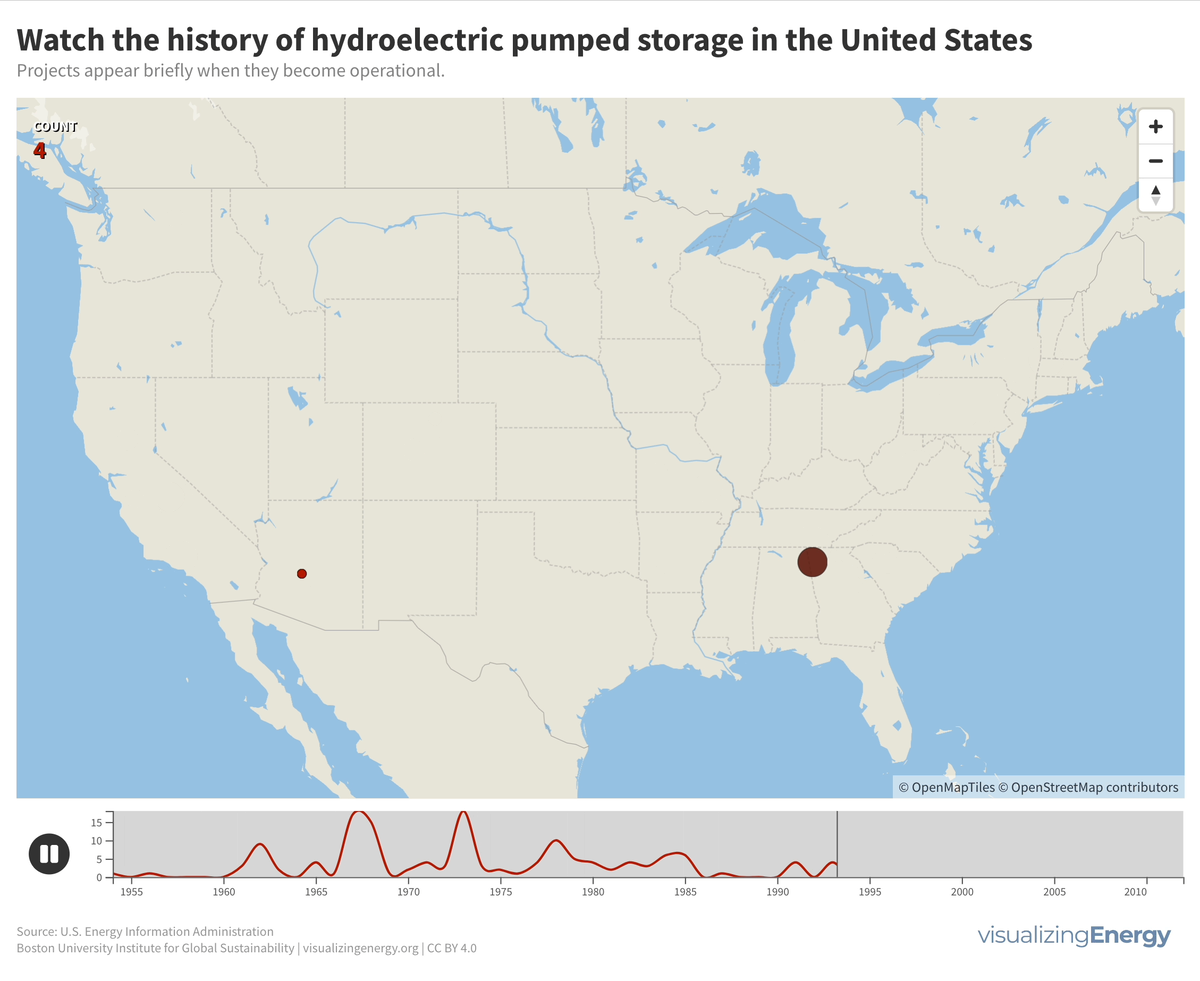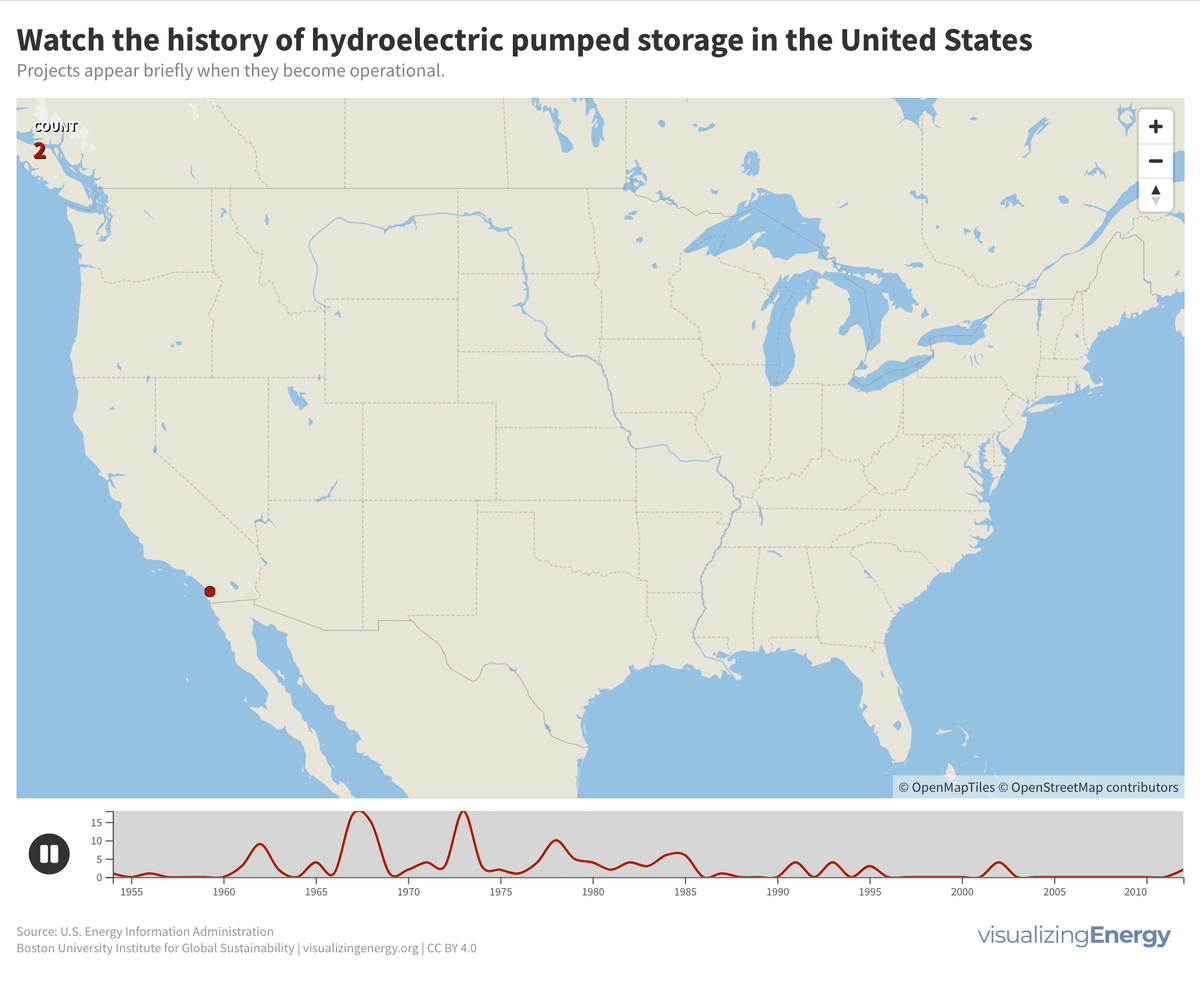
Pumped storage plants for hydroelectric power in the United States were primarily built between 1960 and 1990. There have been no new projects since 2012, but three new ones have been proposed, potentially adding 2.6 GW to the existing 22 GW capacity. The largest facility is the Bath County Pumped Storage Station in Virginia, with 2.9 GW.
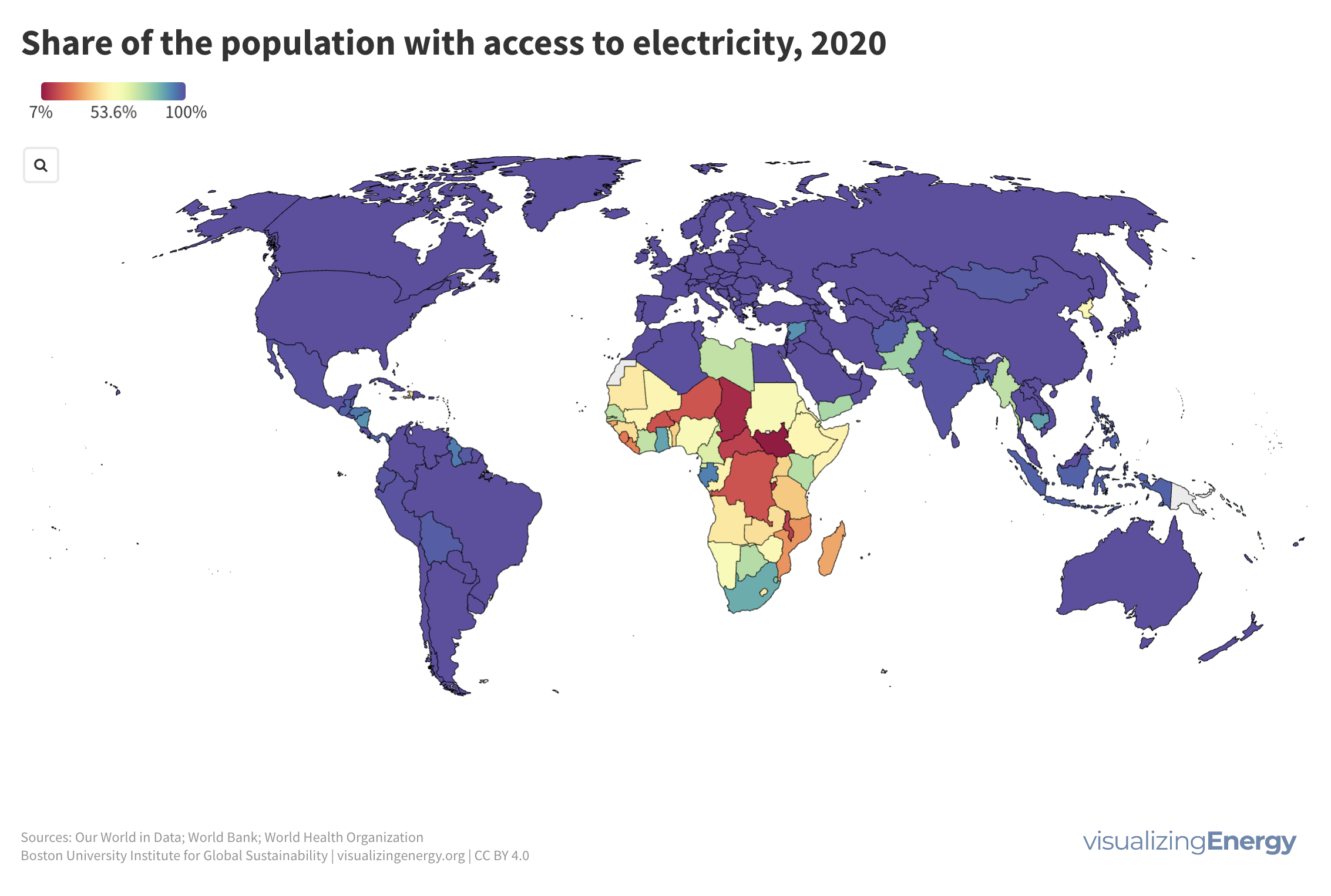
The United Nations’ 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) include SDG7, which aims to ensure affordable and sustainable energy for all. The share of global population with access to electricity has increased to 90% in 2022, yet around 800 million people are still without access, mostly in sub-Saharan Africa. Various factors influence access to electricity, impacting income and well-being.
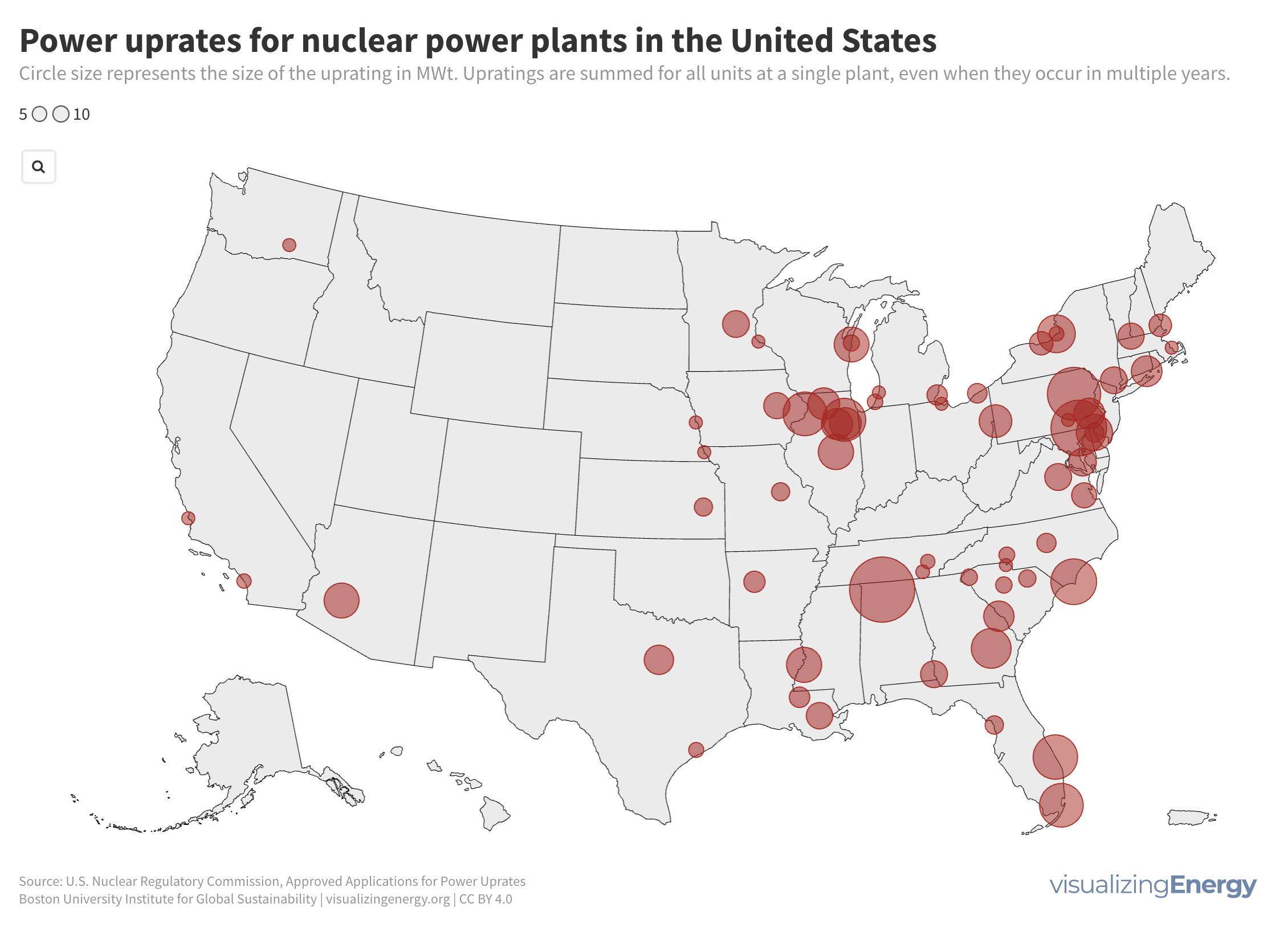
Nuclear power in the US has steadily contributed 19% of electricity since 1990, mainly through uprates. These uprates, approved by the NRC, have boosted capacity by 24,080 MWt or 8030 MWe, equivalent to over 7 new plant units. Most uprates range from 0-5%.
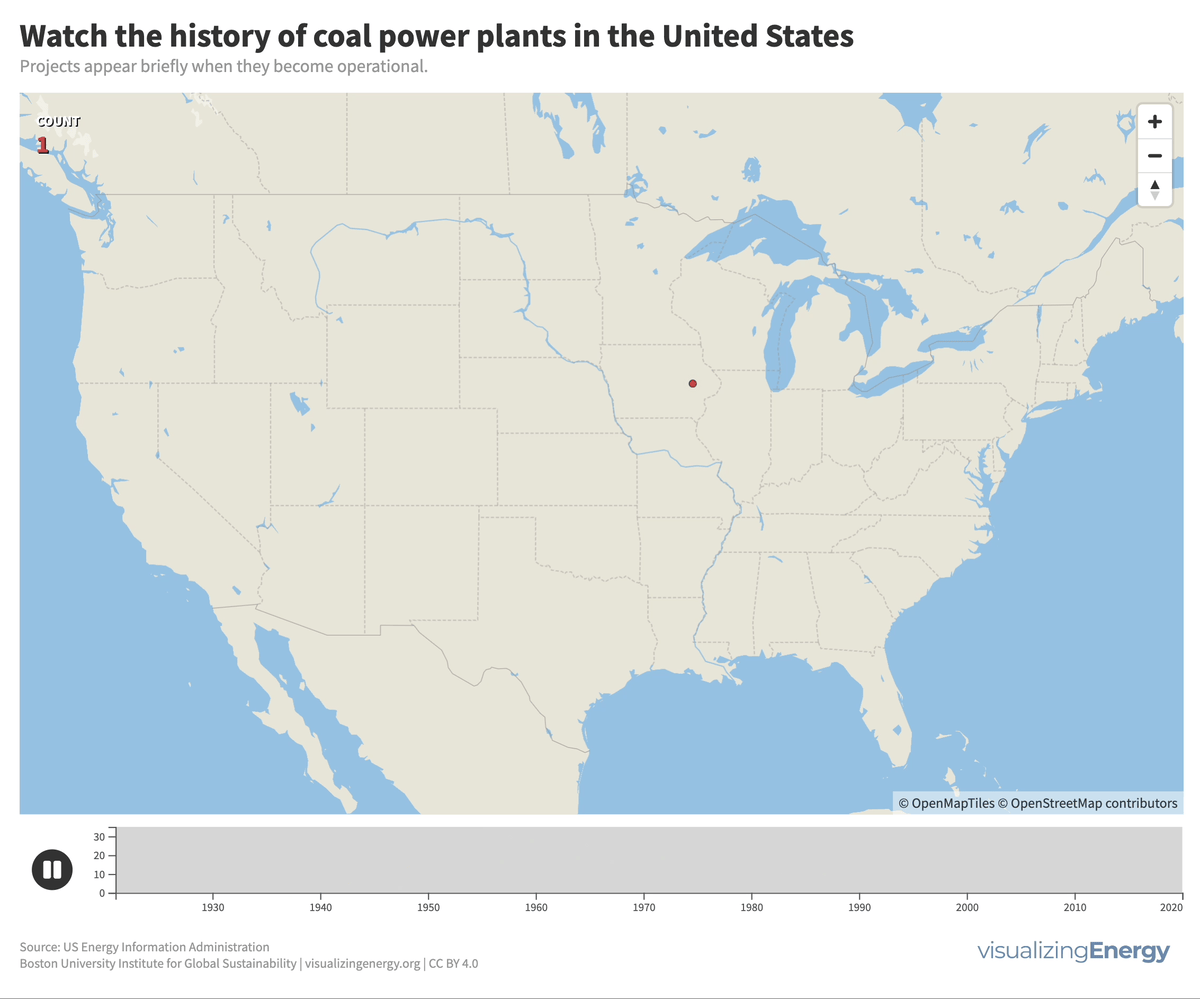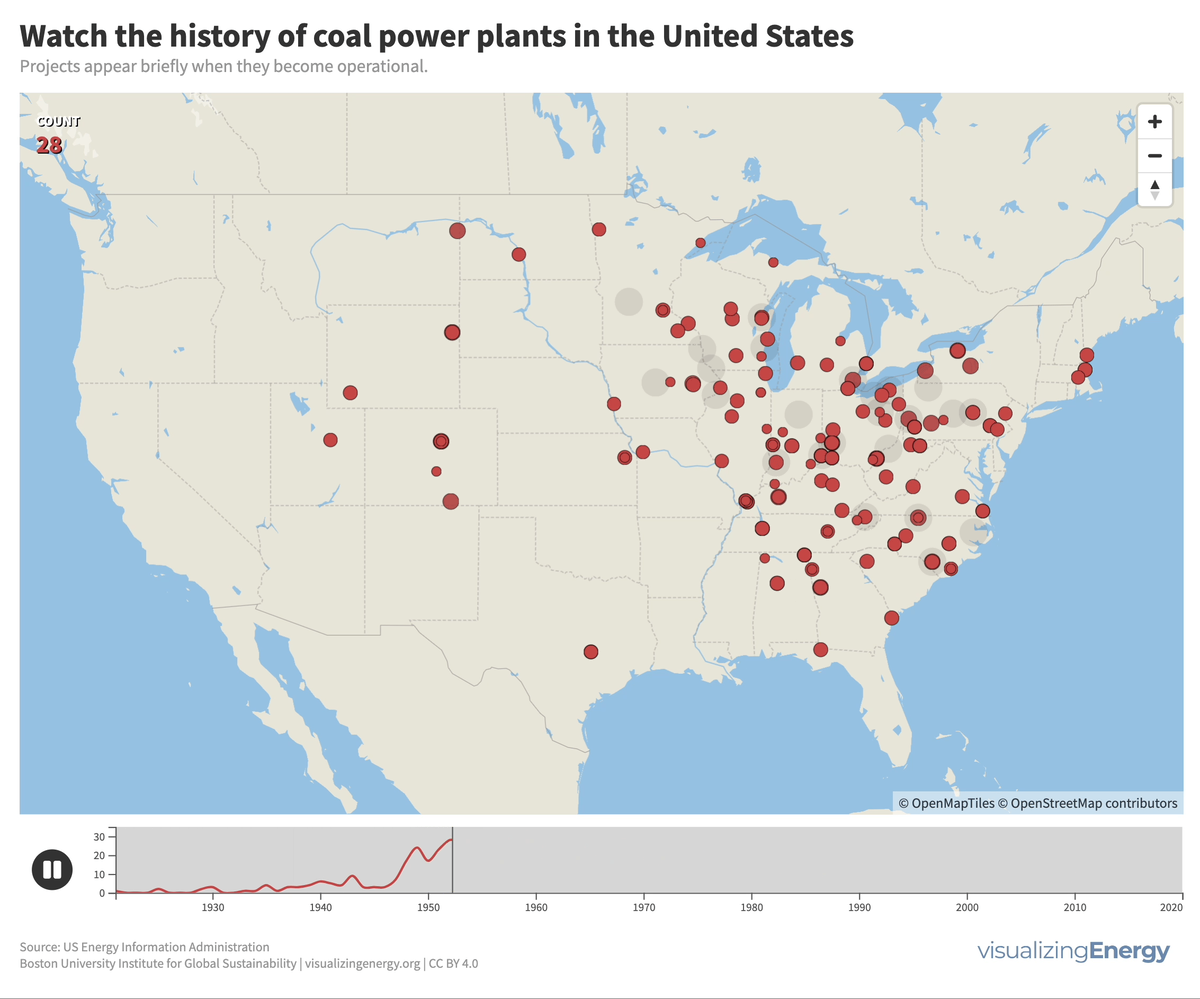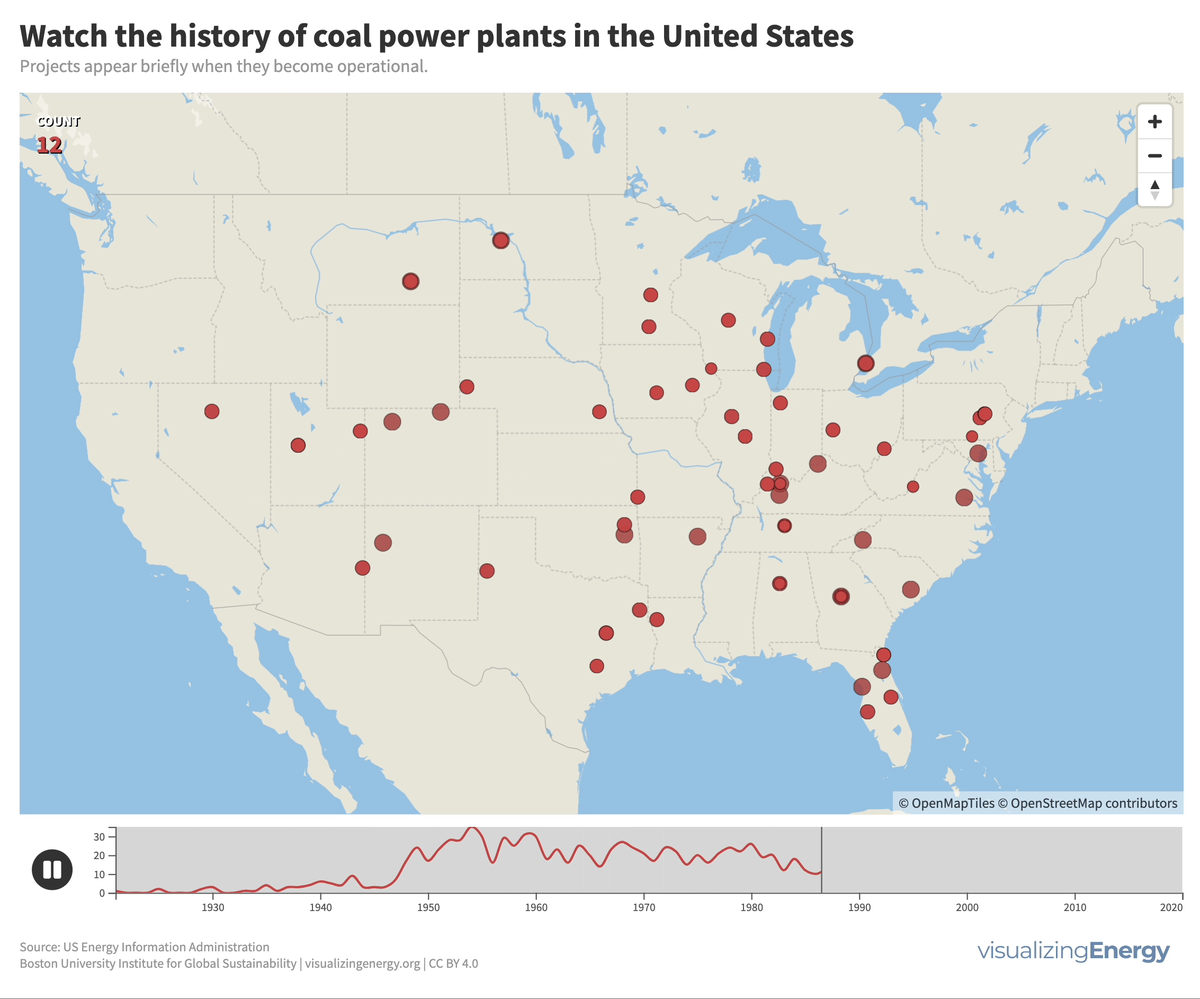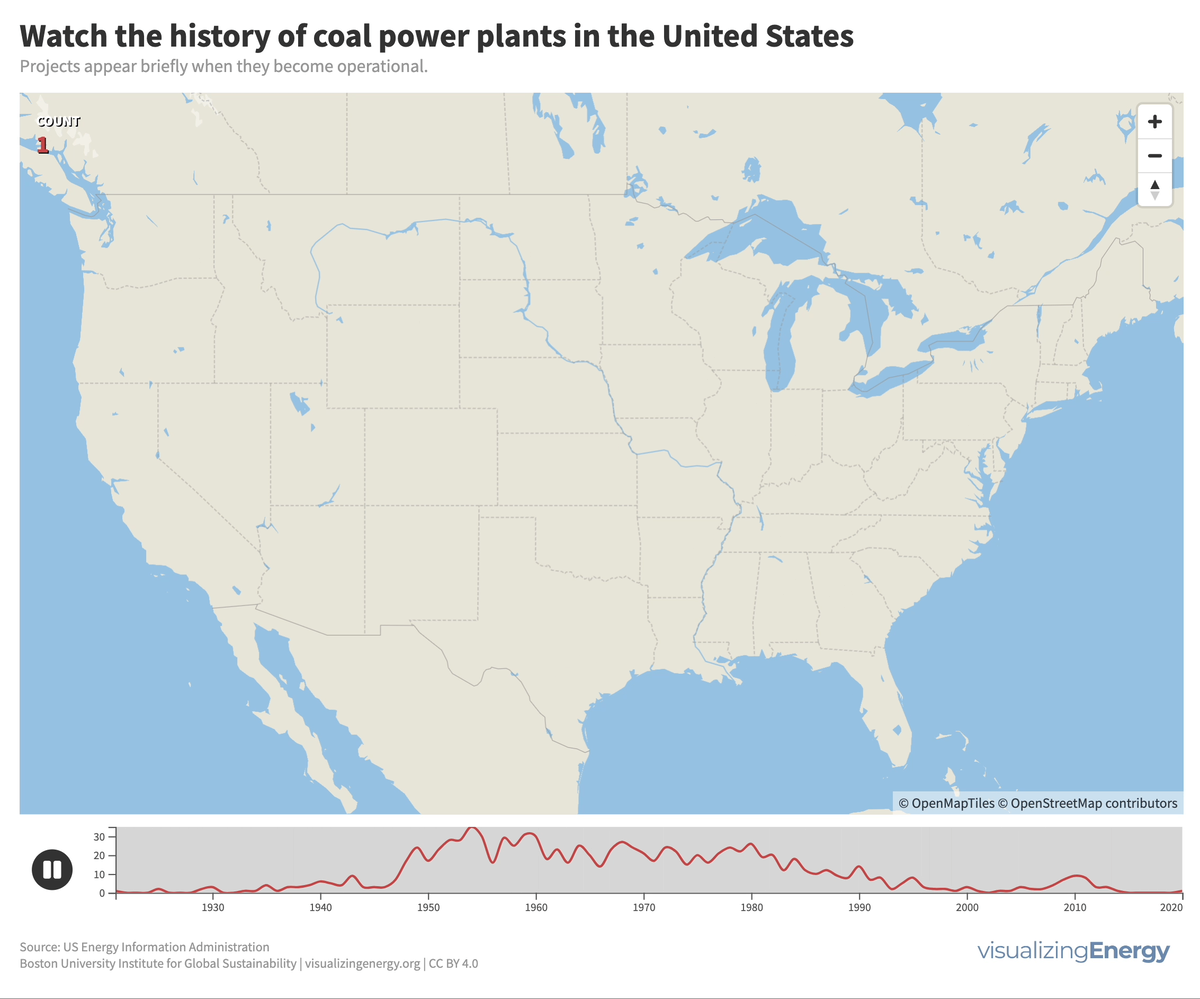
Coal played a significant role in the US, generating half of the nation’s electricity in 1920 and maintaining that share for decades. However, aging coal plants are being retired due to competition from efficient natural gas and renewable energy sources, as well as state climate policies. This shift reflects growing concerns about cost and carbon emissions.
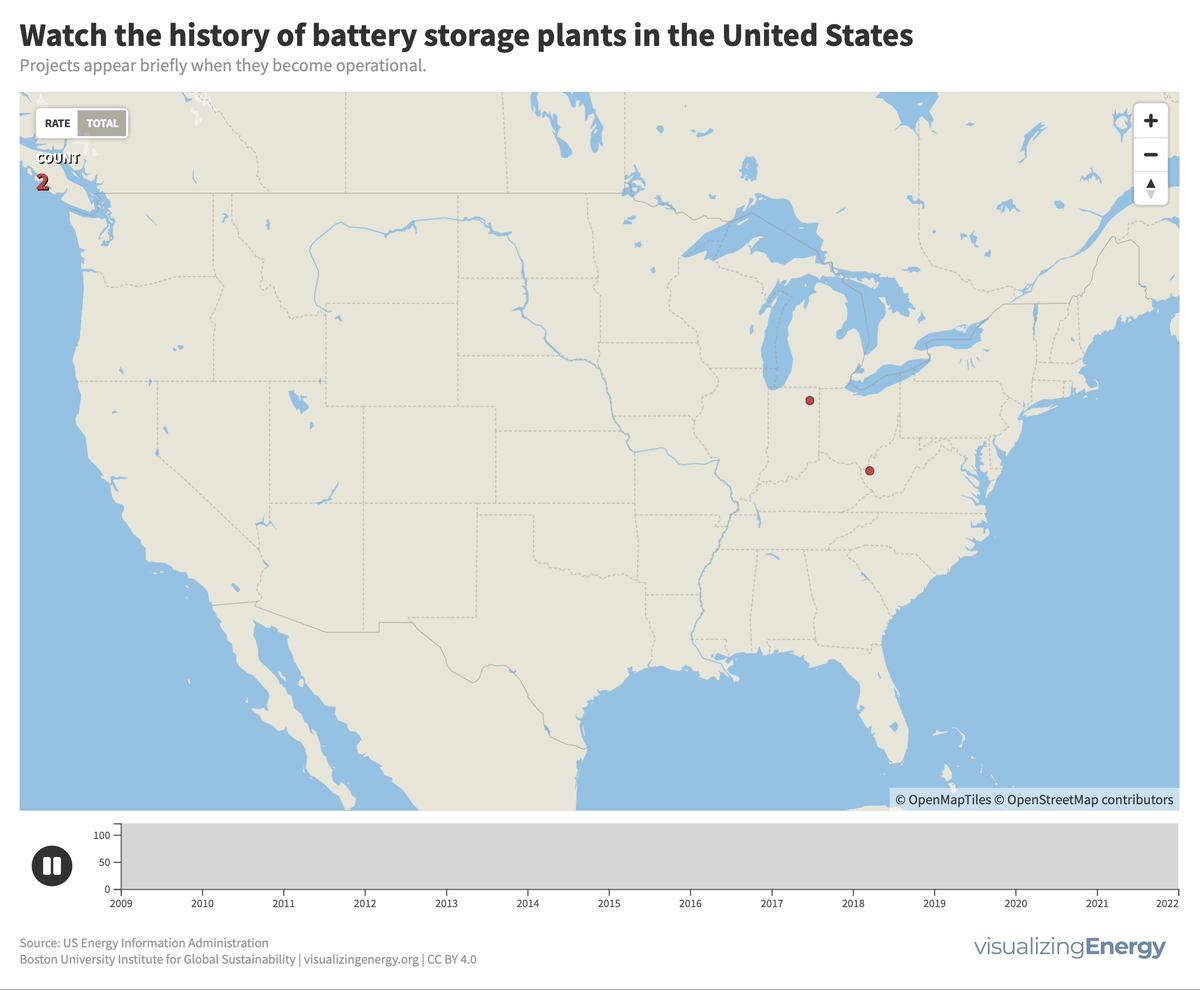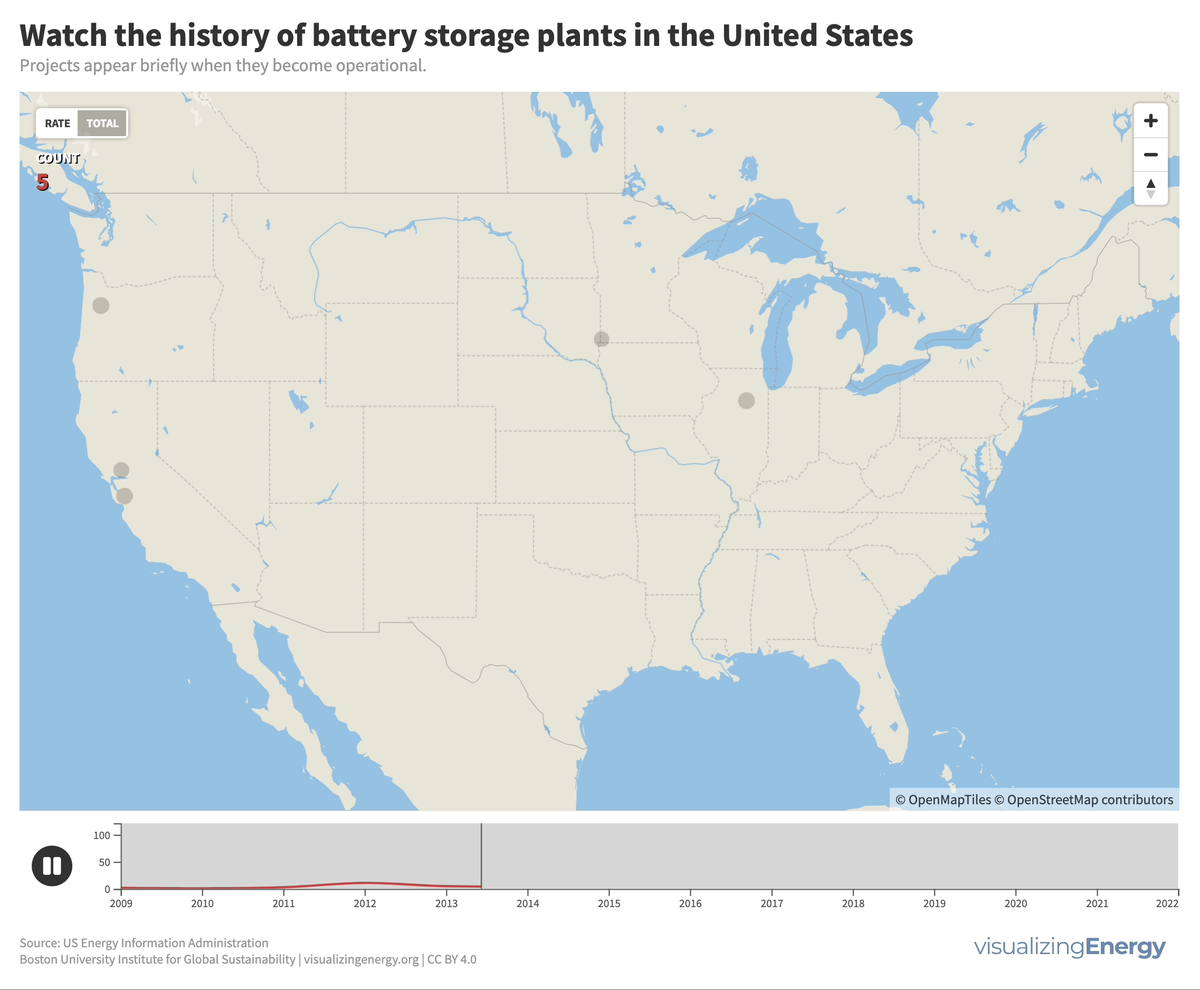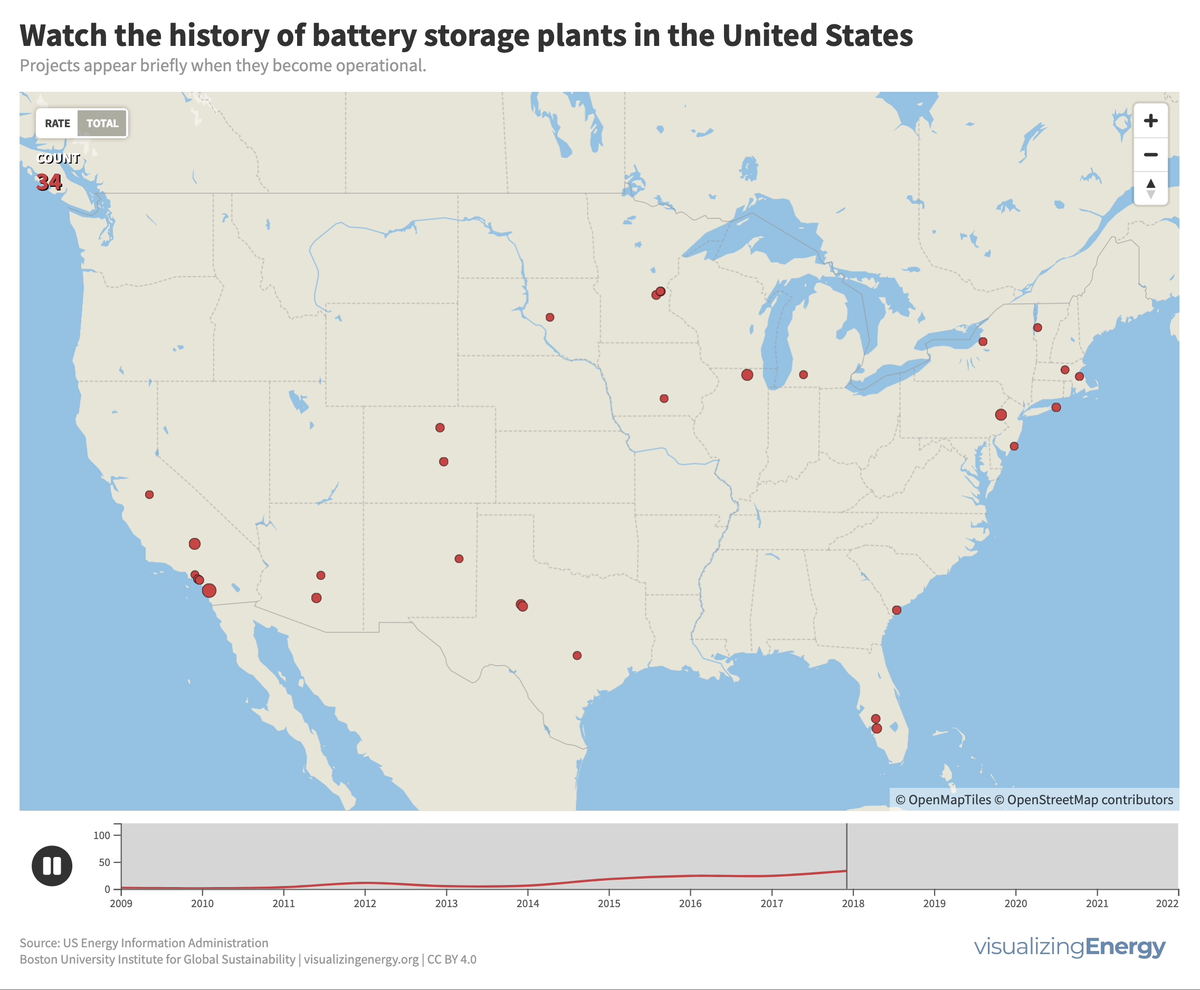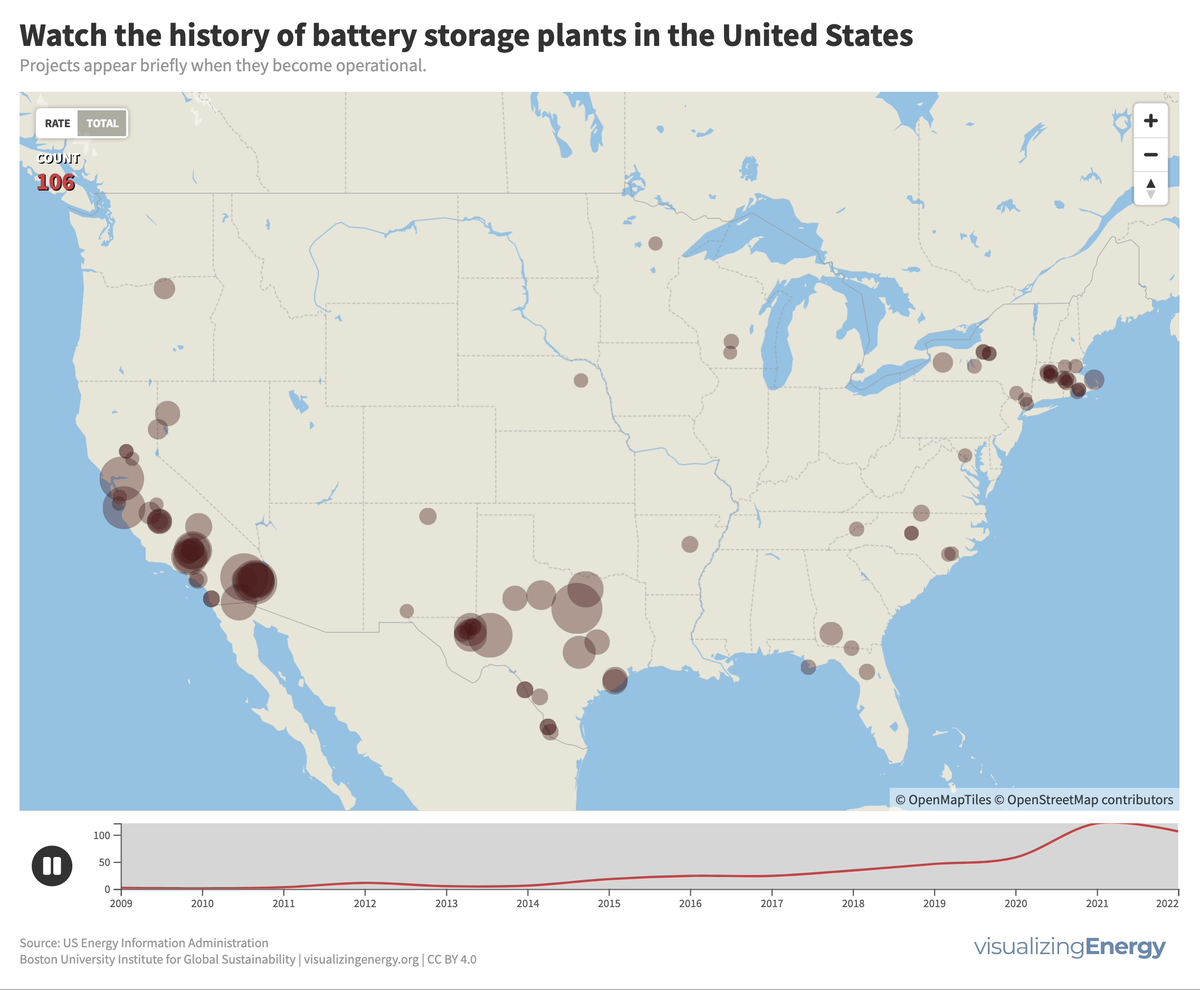
Utility-scale battery storage (BESS) systems store and distribute large-scale electricity and are crucial for renewable energy integration. Since the mid-2000s, about 460 such systems were built in the U.S., the largest being the 409 MW Manatee Energy Storage Center.
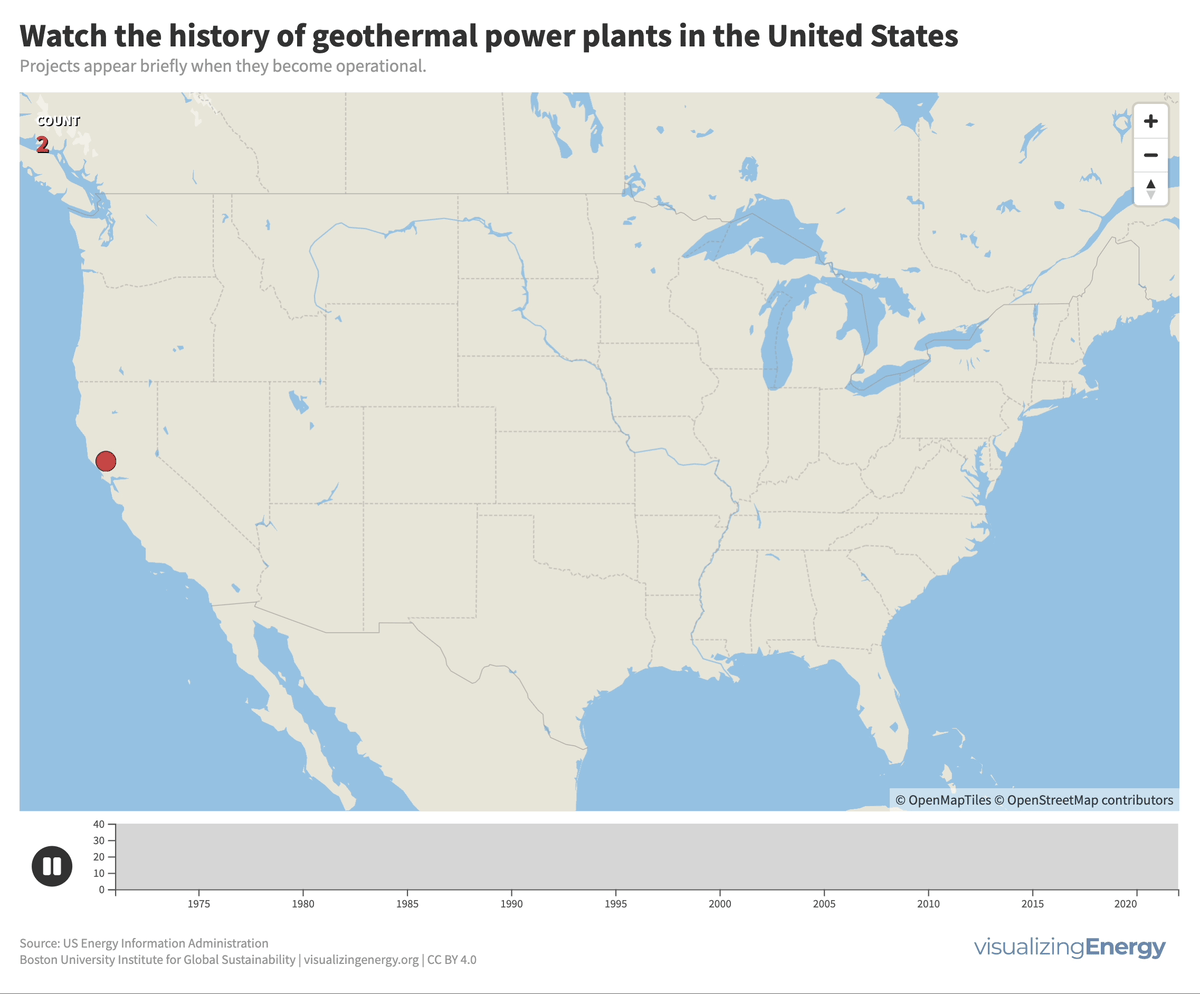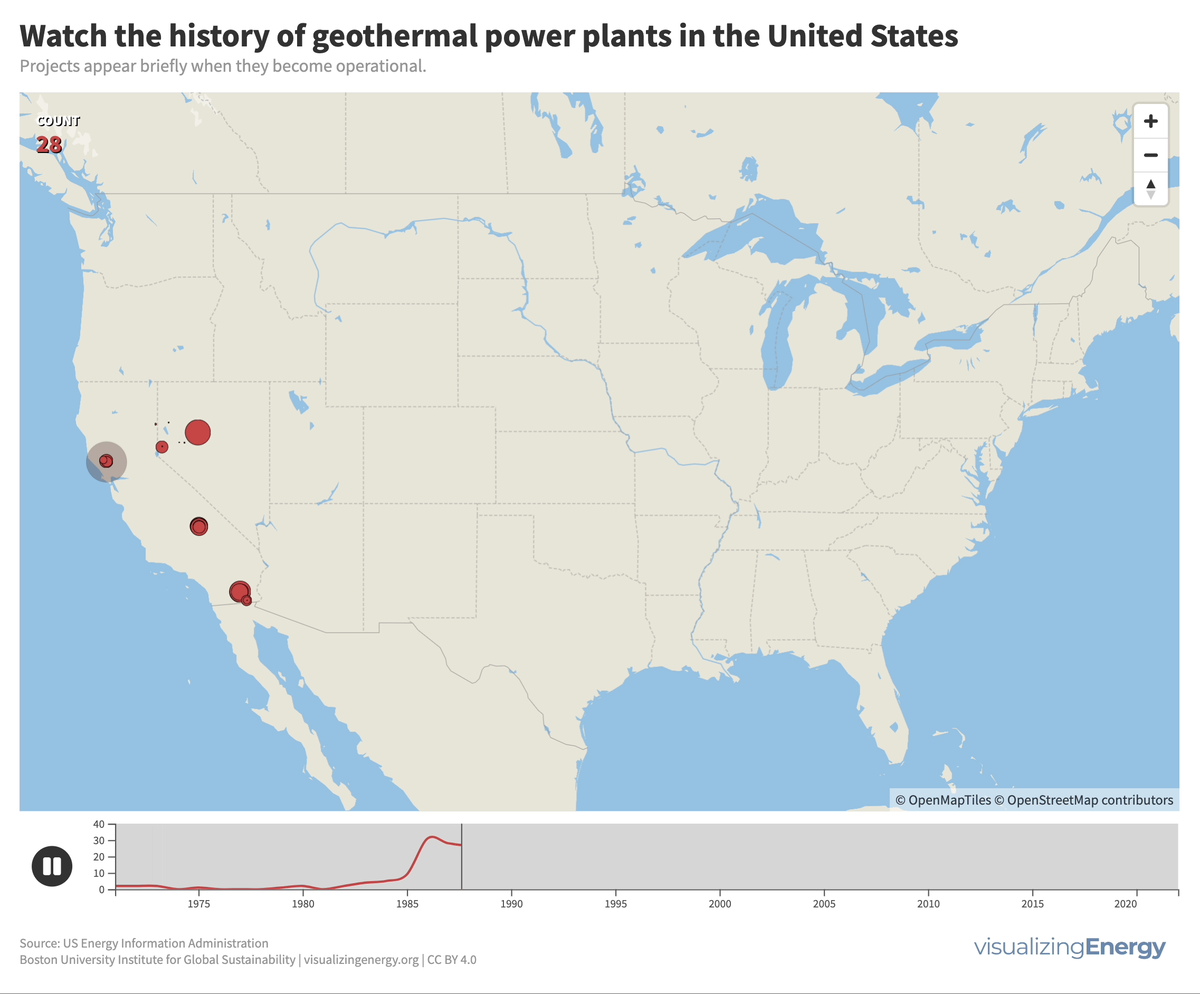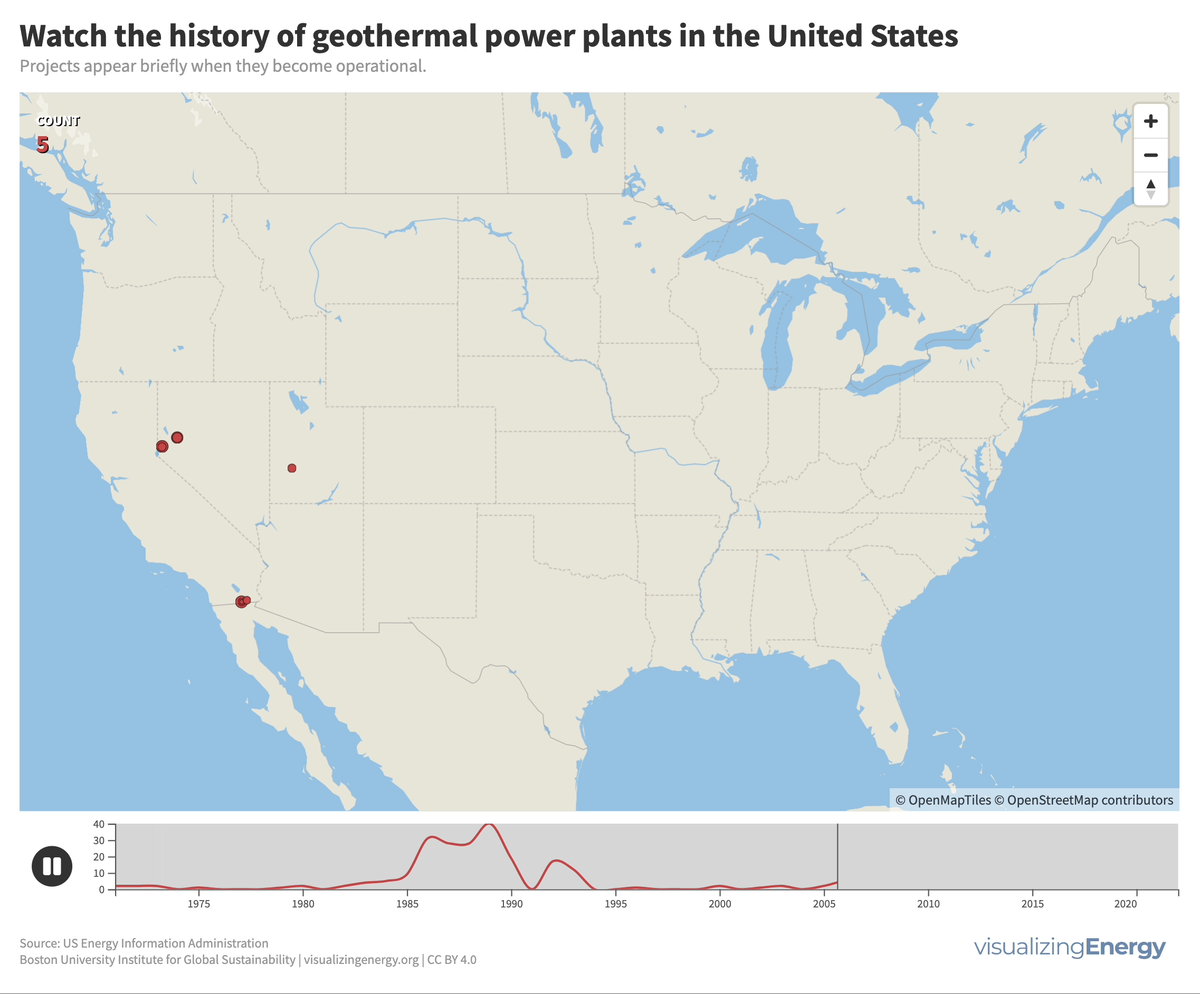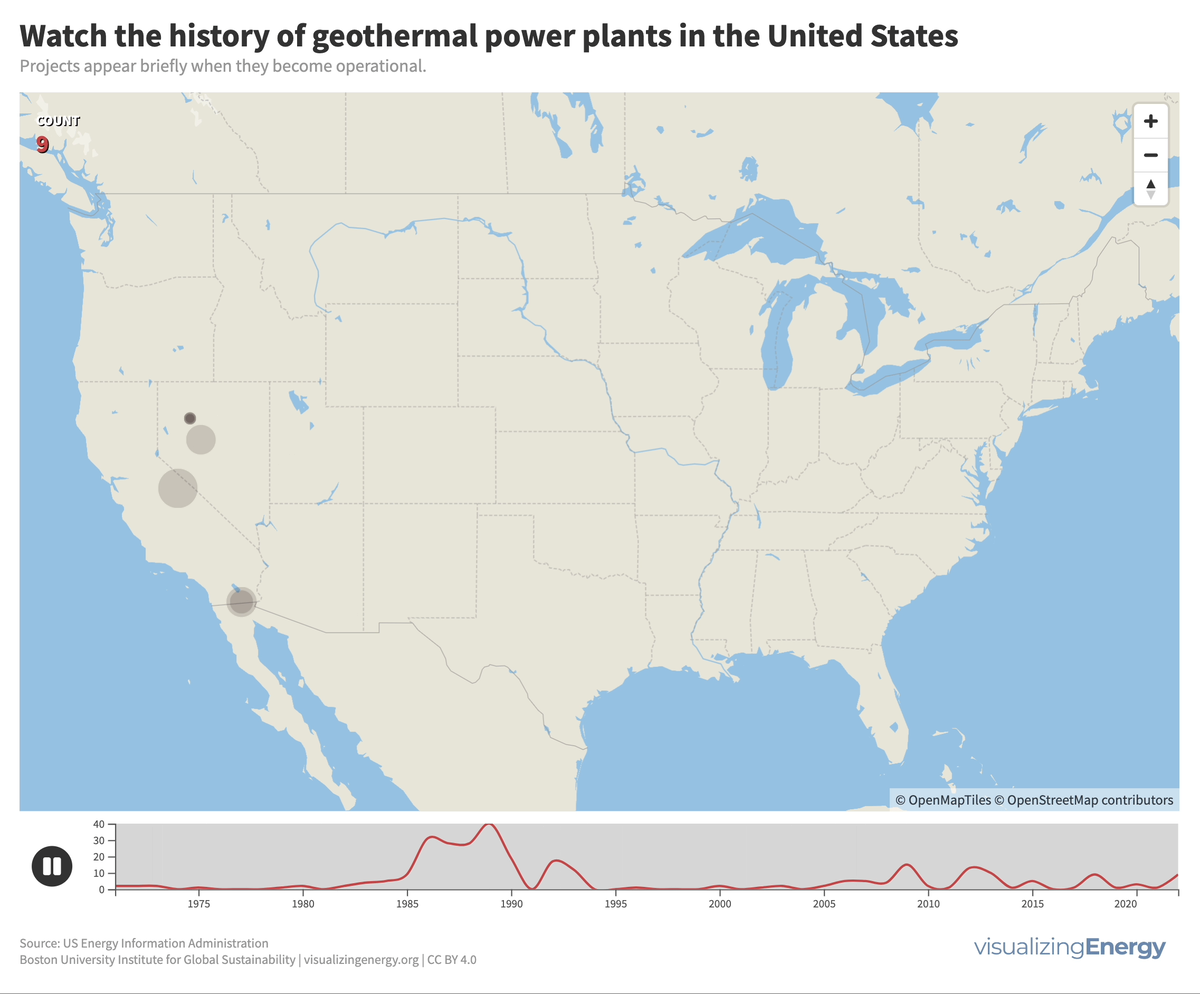
In the United States, geothermal power plants are predominantly located in six western states due to significant tectonic activity. In 2022, California housed 72% of this capacity, generating 6% of its electricity from geothermal power. The Geysers project in northern California is the world’s largest geothermal array.
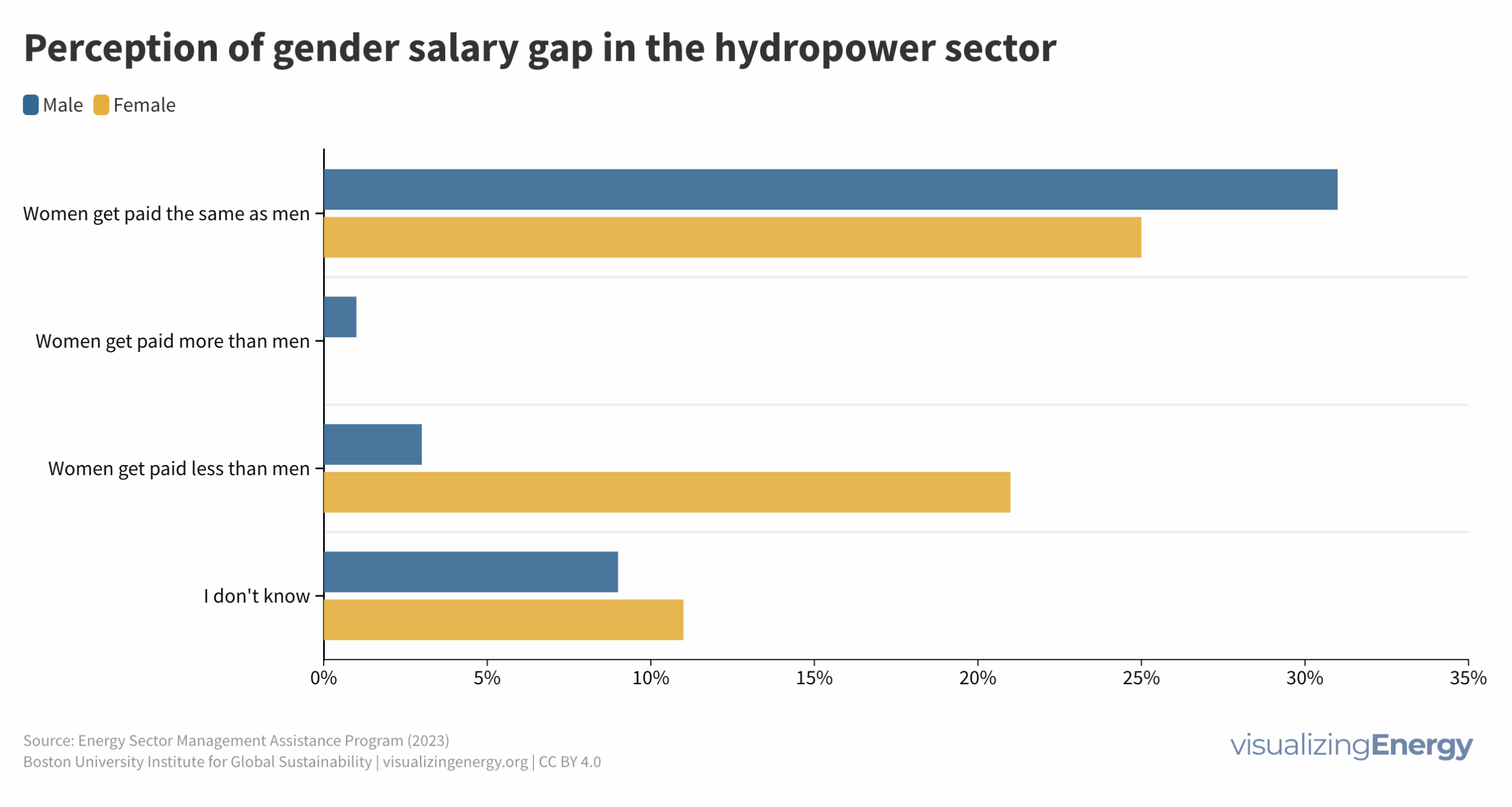
Hydropower, the world’s largest source of renewable, low-carbon electricity, faces a significant gender gap. Women hold only a quarter of jobs globally, mainly in non-technical roles. Factors hindering women include a lack of STEM skills, limited awareness, inadequate female role models, and managerial bias. Improved family-friendly policies and female inclusion in policymaking are required for industry advancement.
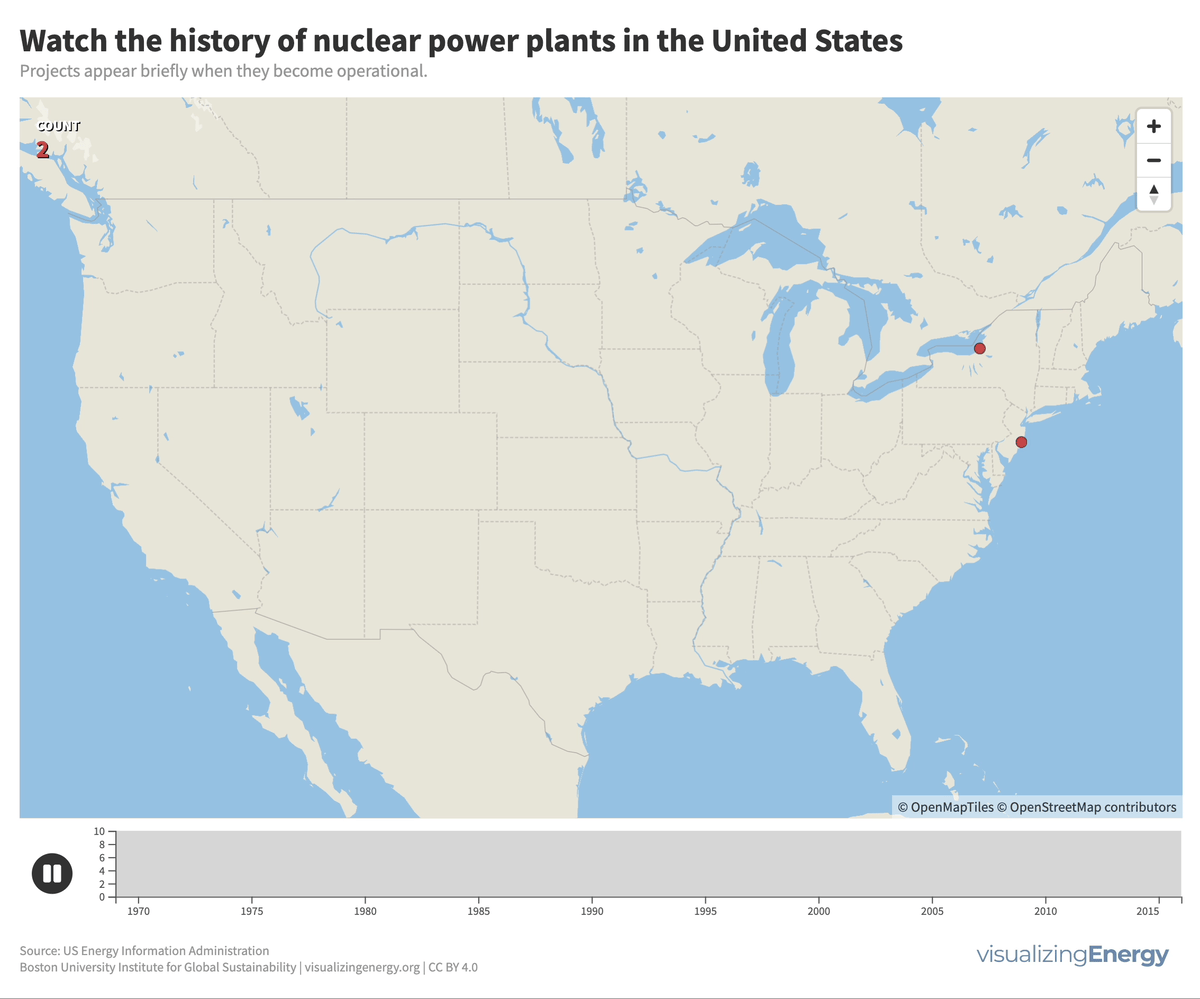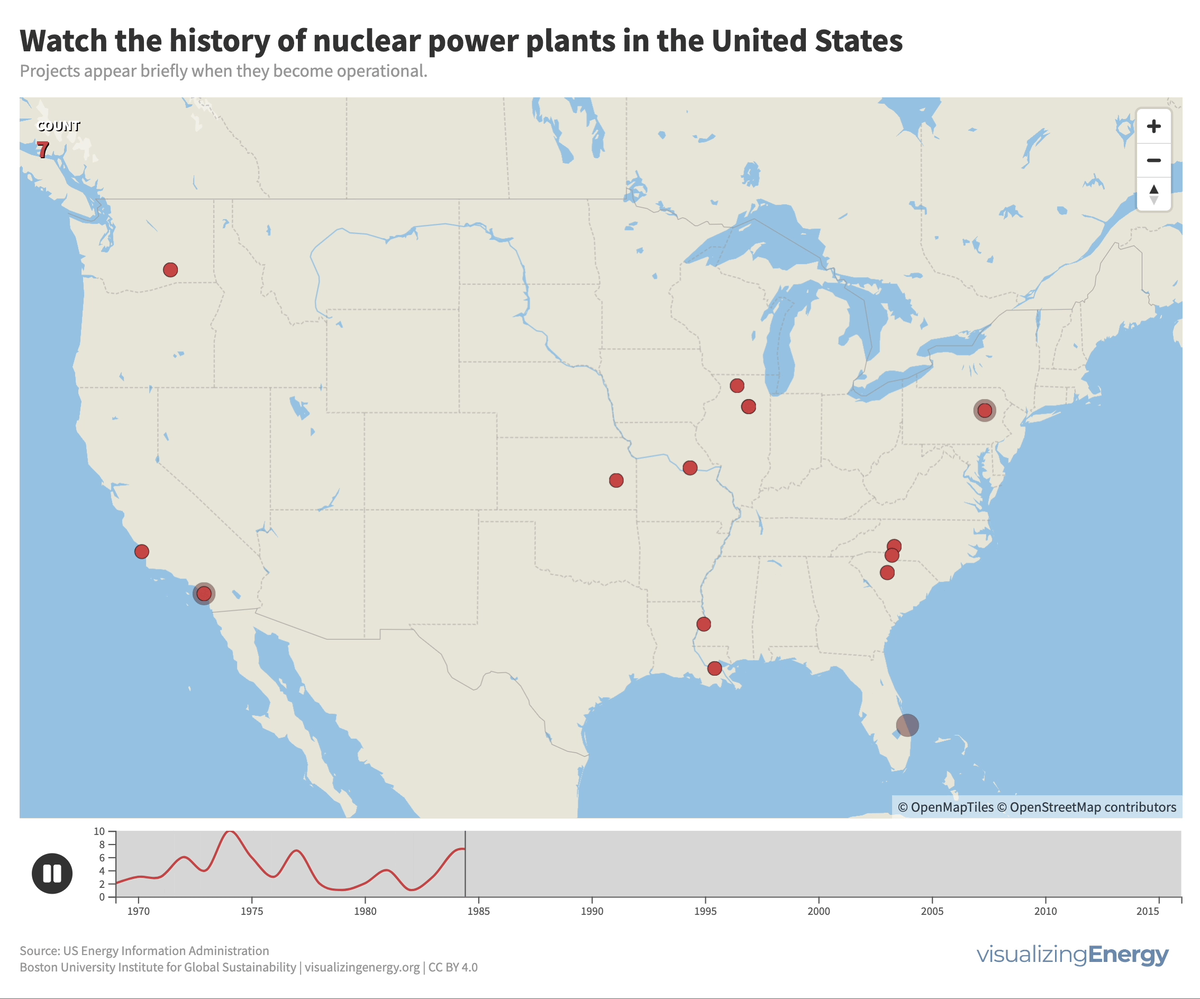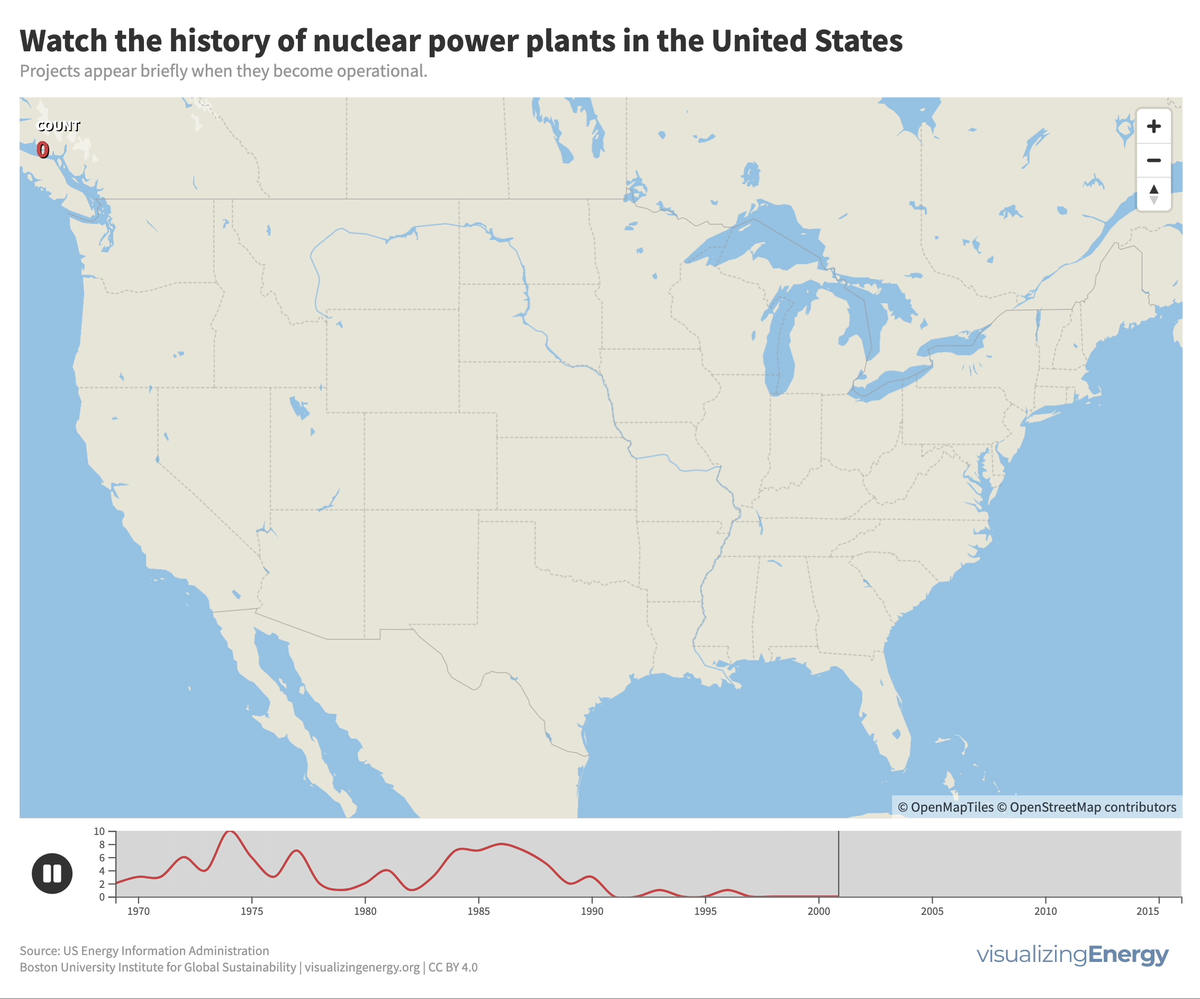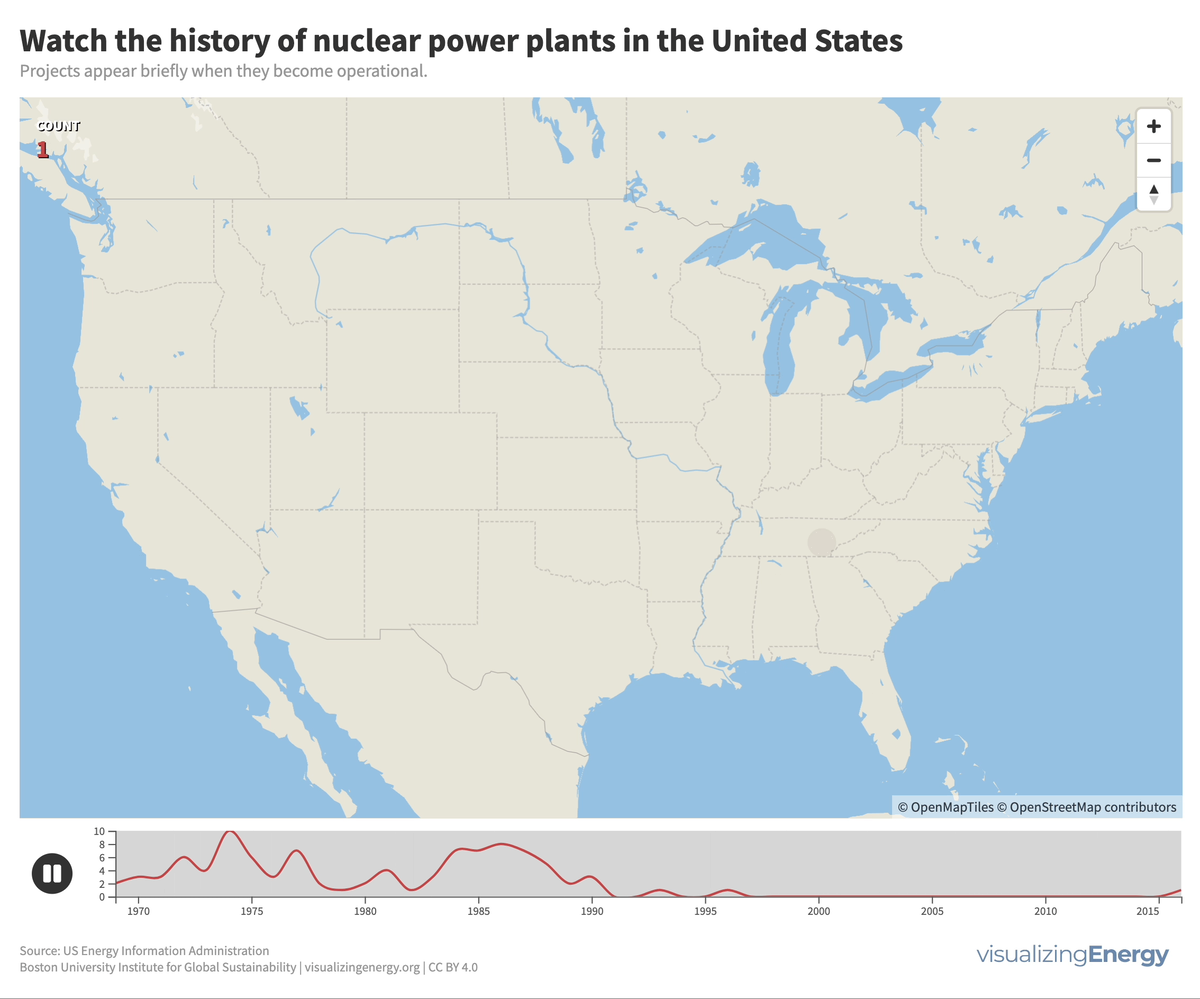
In 2022, the U.S. had 92 nuclear power plants generating 18% of total electricity. The industry, once a major player, declined due to high costs, long construction timelines, decreased demand, accidents, regulations, and market deregulation. There’s renewed interest in nuclear power to combat climate change, with the first new plant in 30 years, though debates continue on cost, safety, and alternative energy sources.
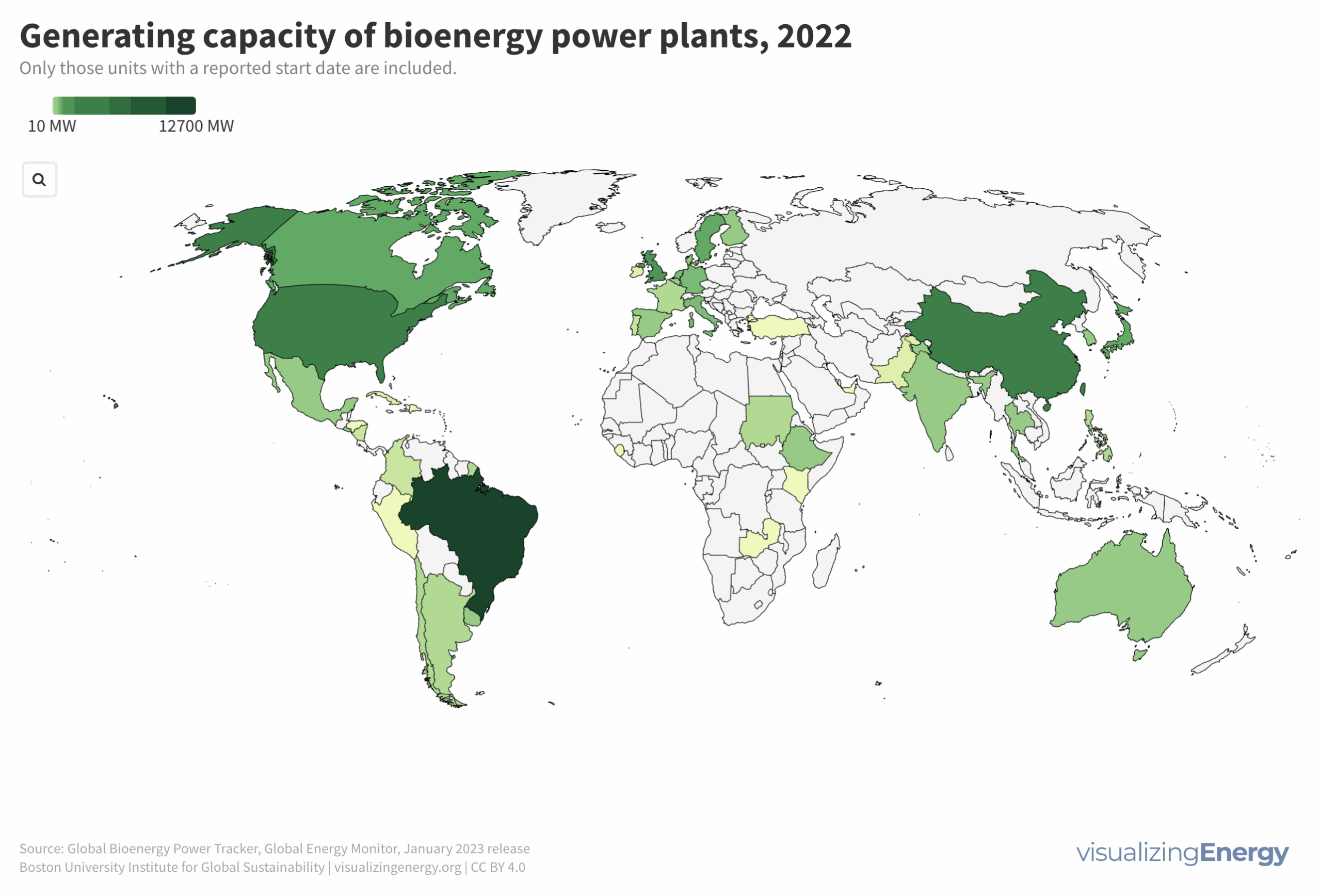
As of January 2023, 575 utility-scale biopower plants were operational globally, with a total capacity of over 29,000 MW, less than 0.5% of worldwide power generation. An additional 6,000 MW are under construction. China is believed to significantly underreport its true biopower capacity, perhaps as high as 22,000 MW, primarily from agricultural residues and waste-to-energy facilities. Brazil, another major player, relies largely on sugarcane byproducts.