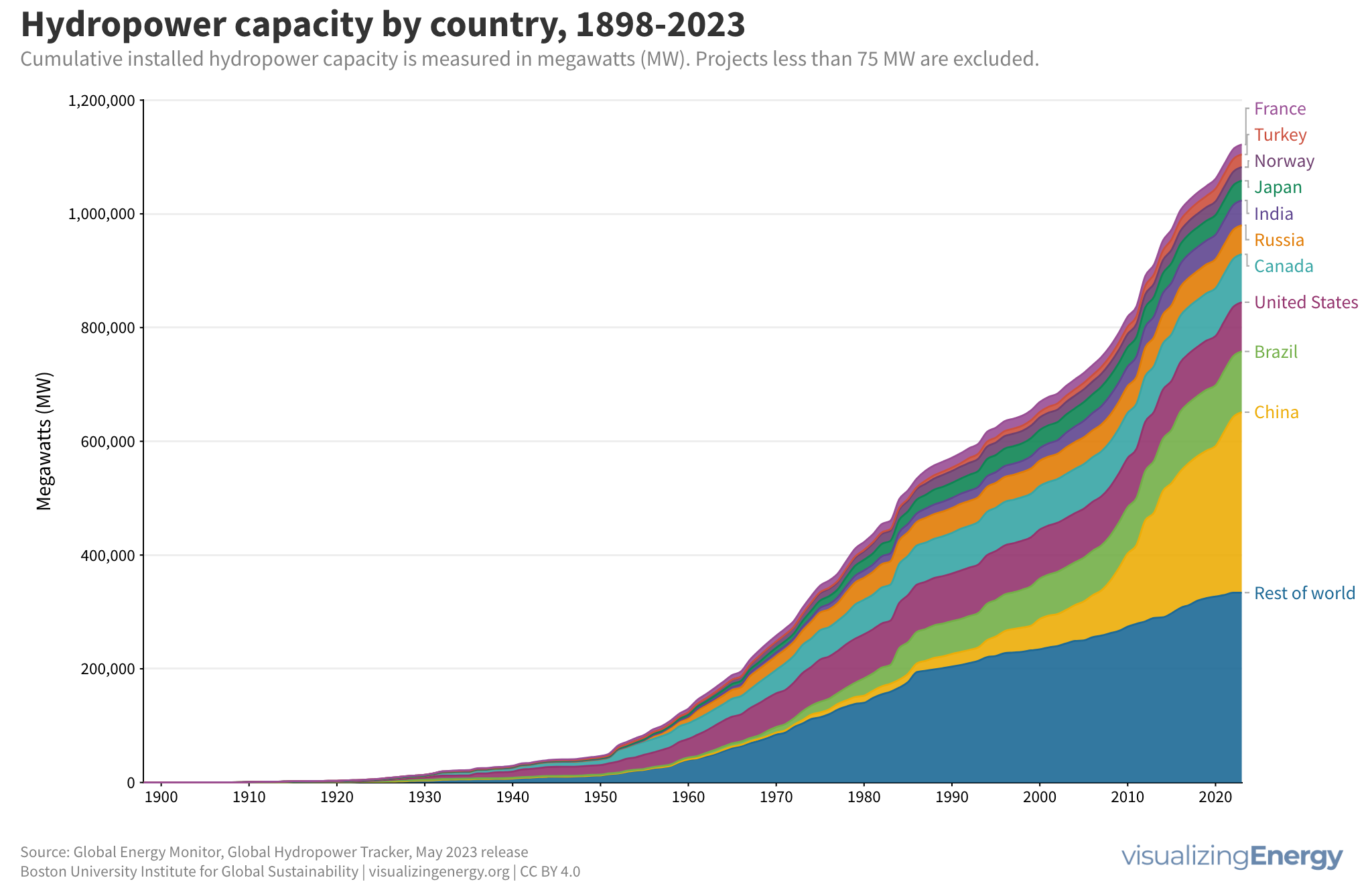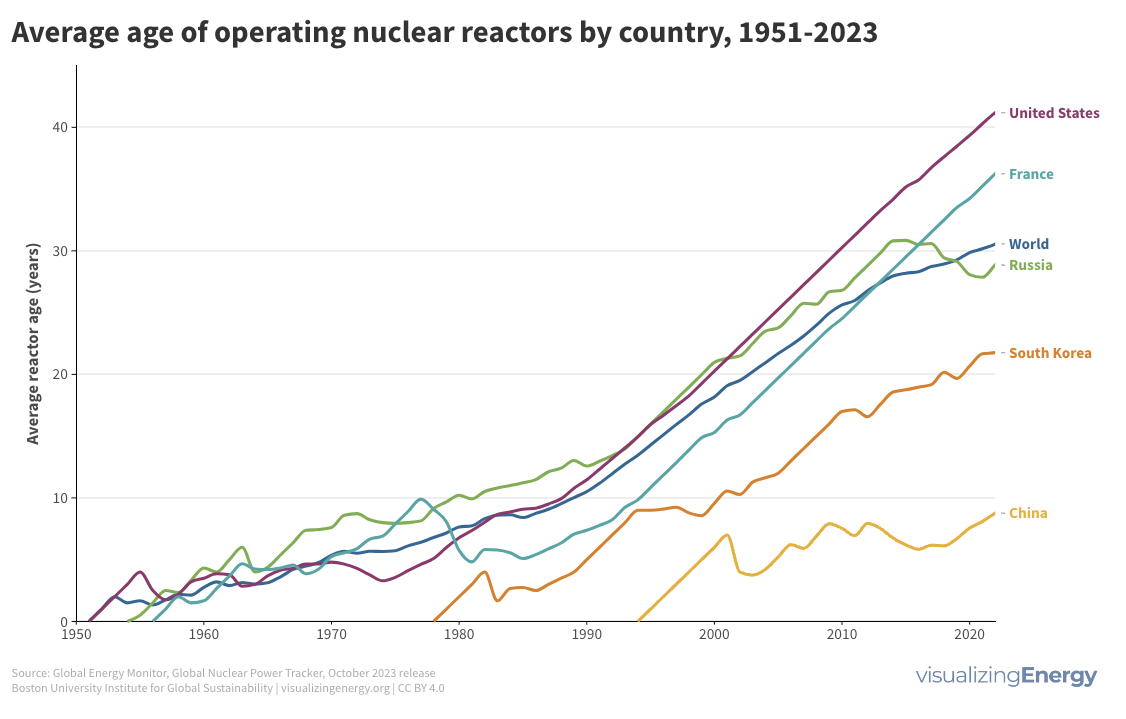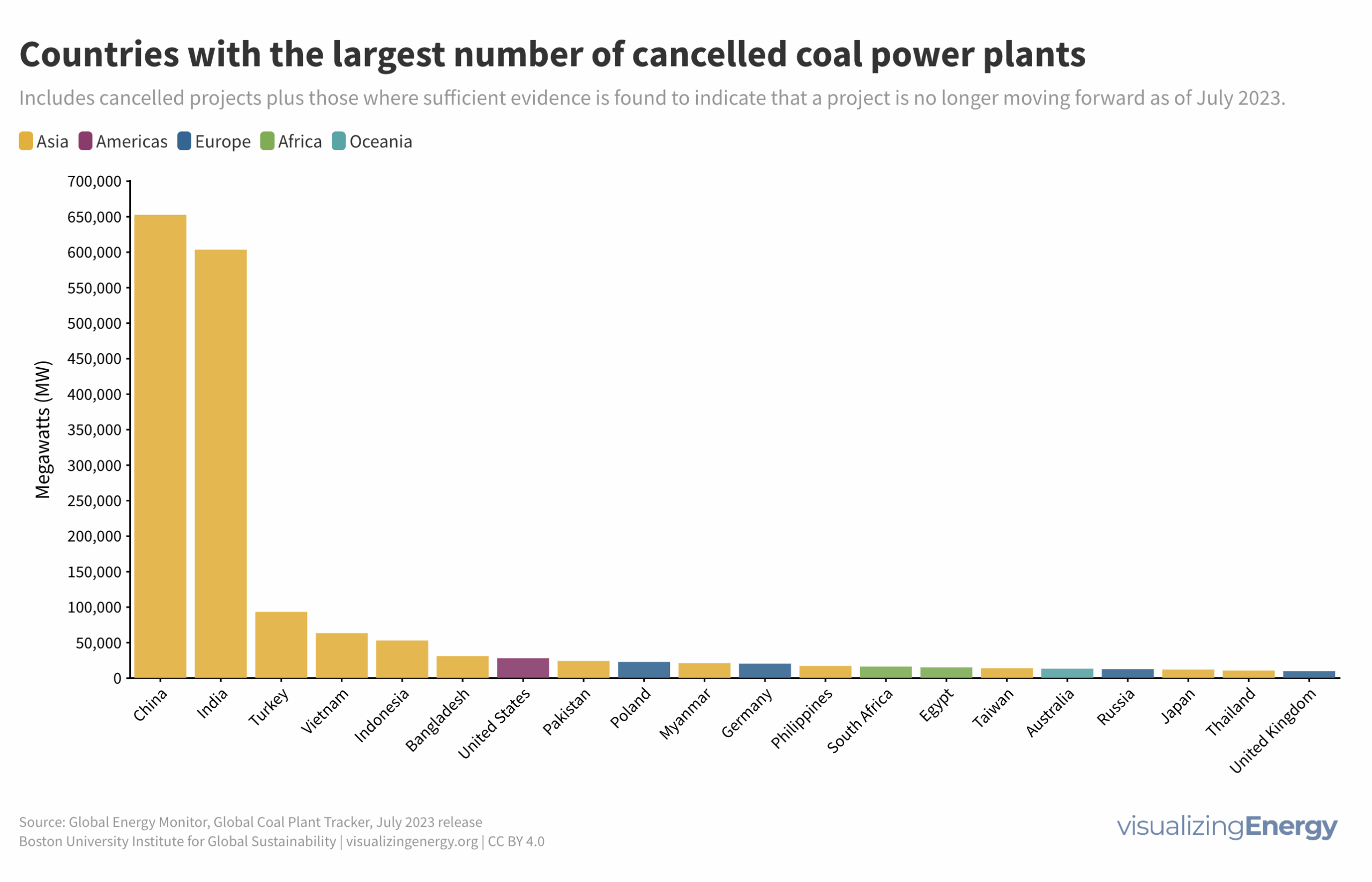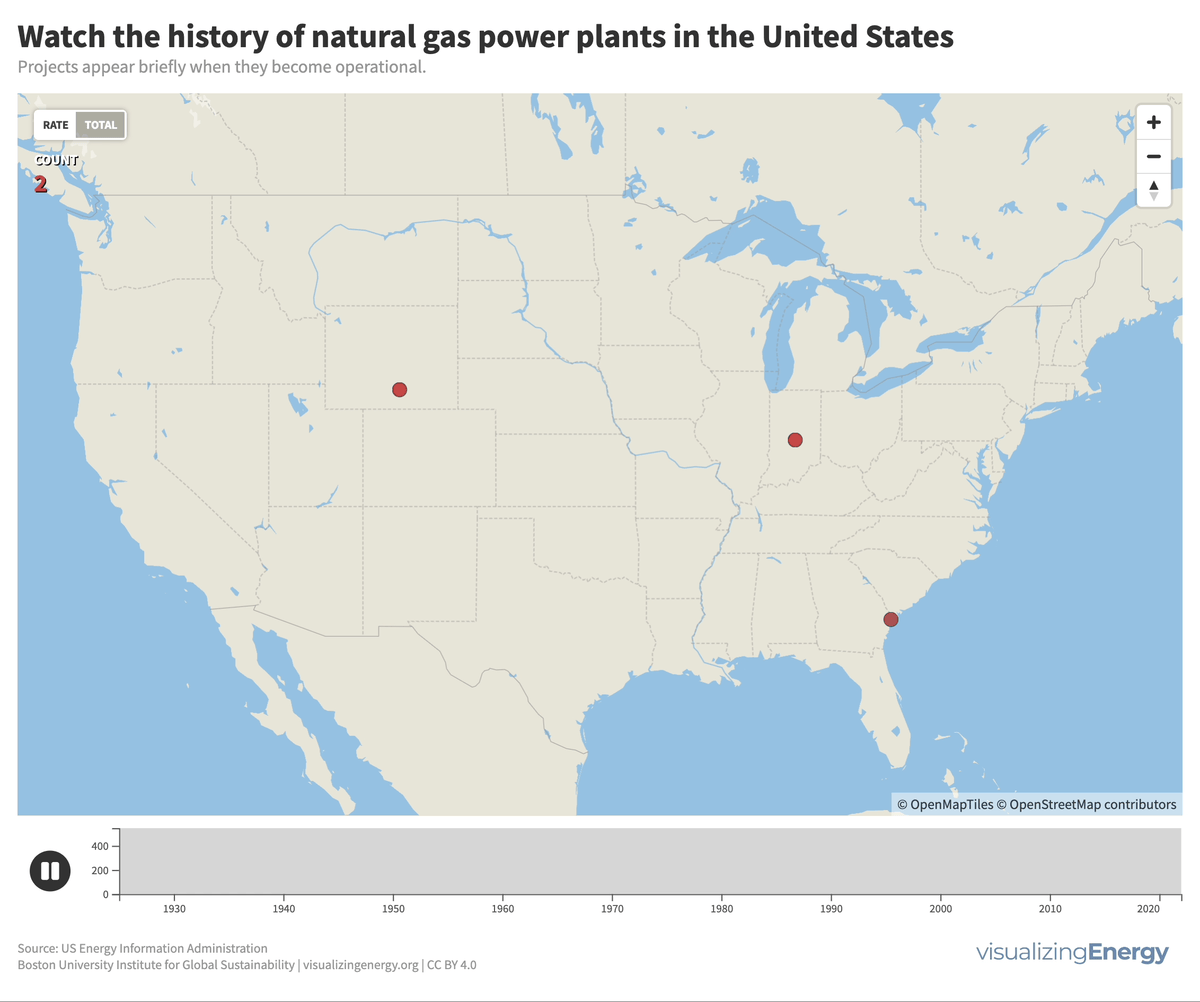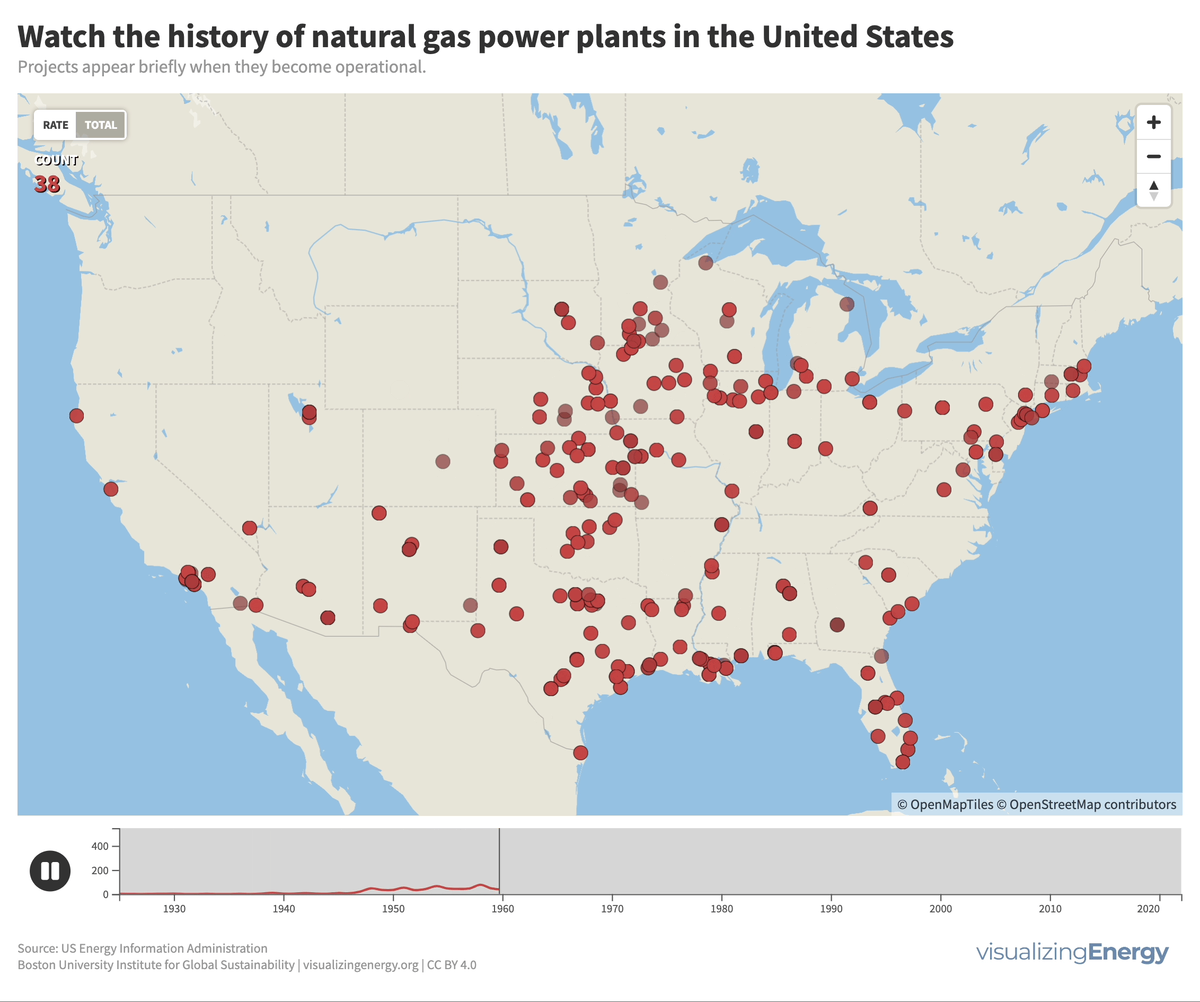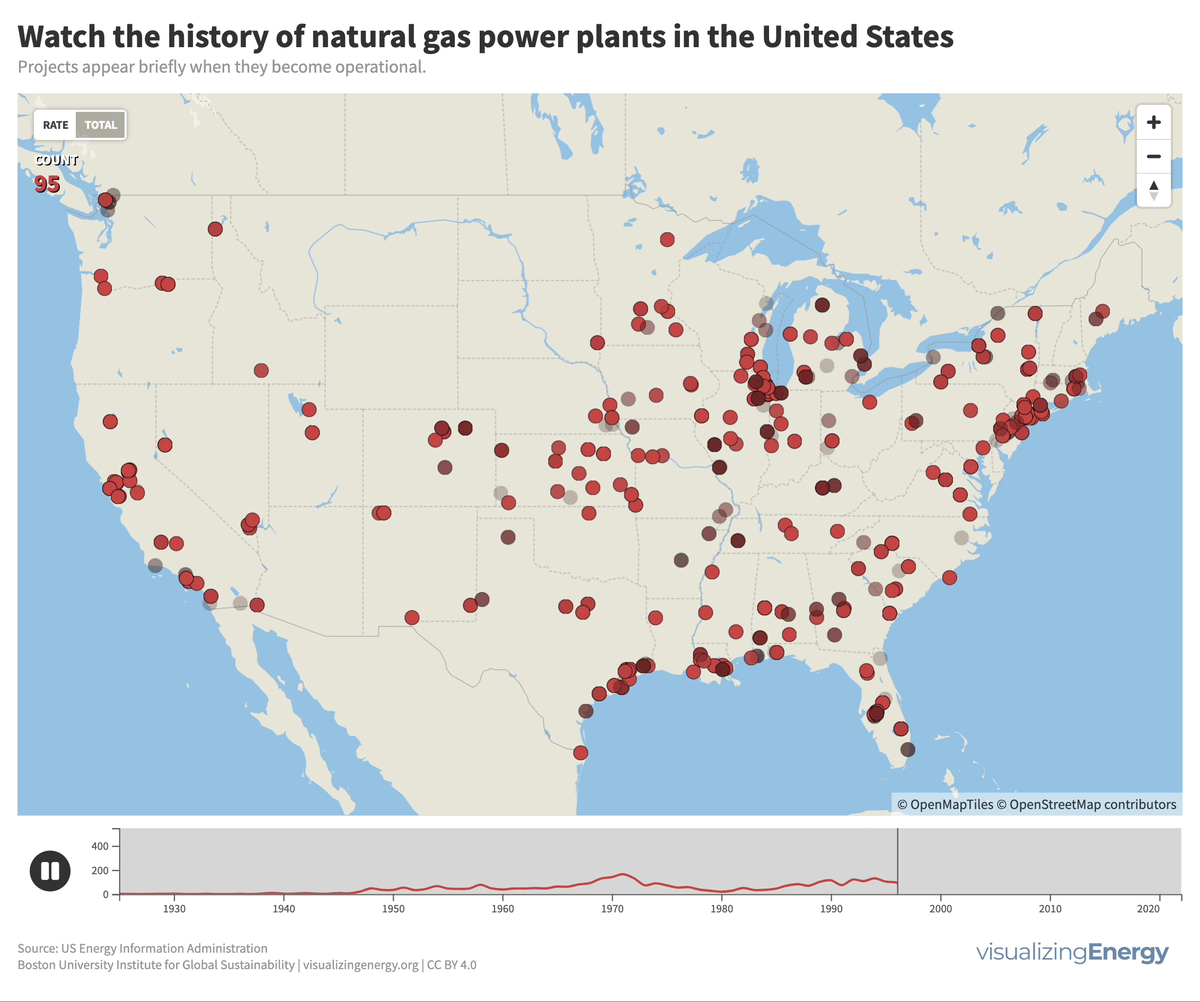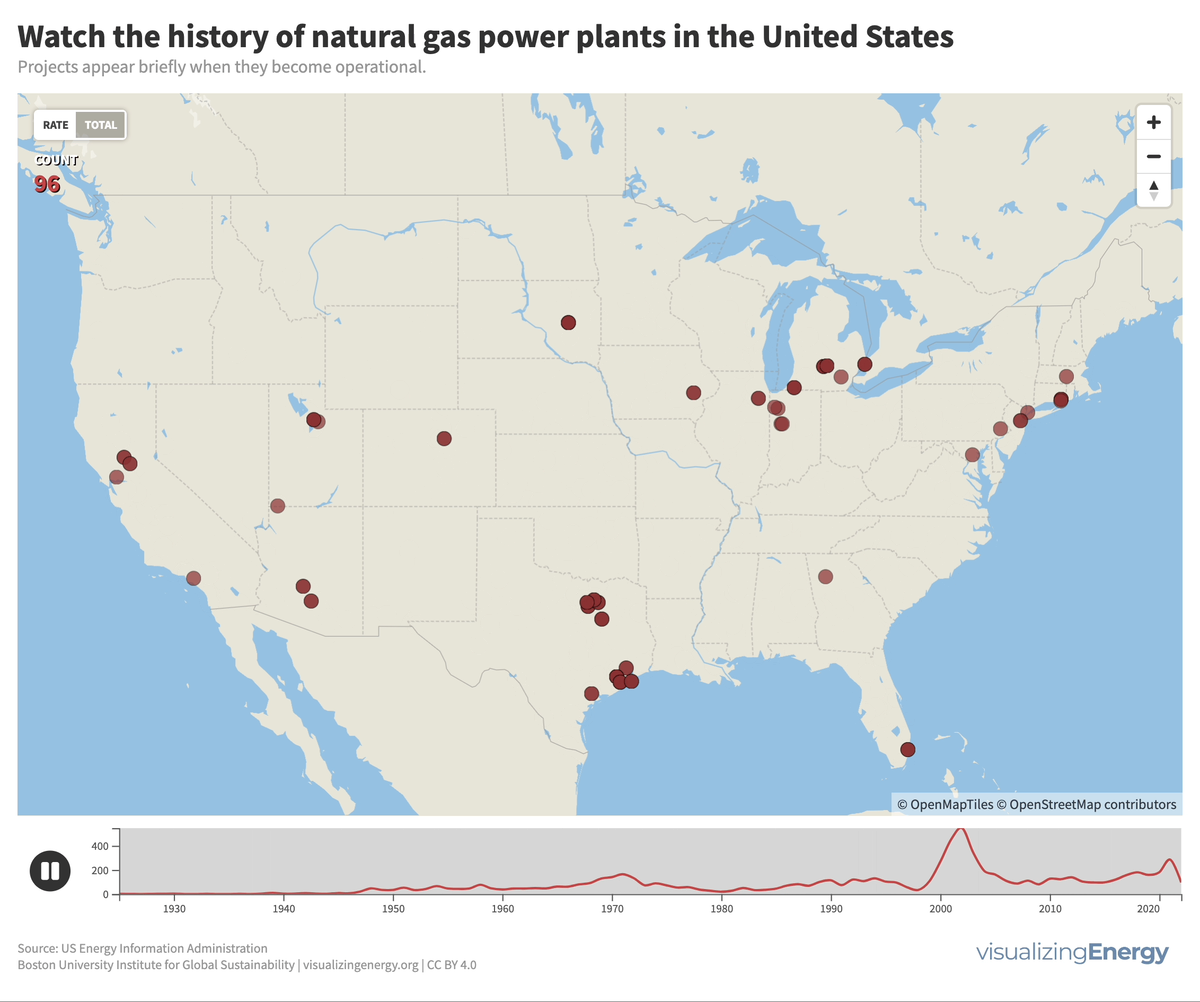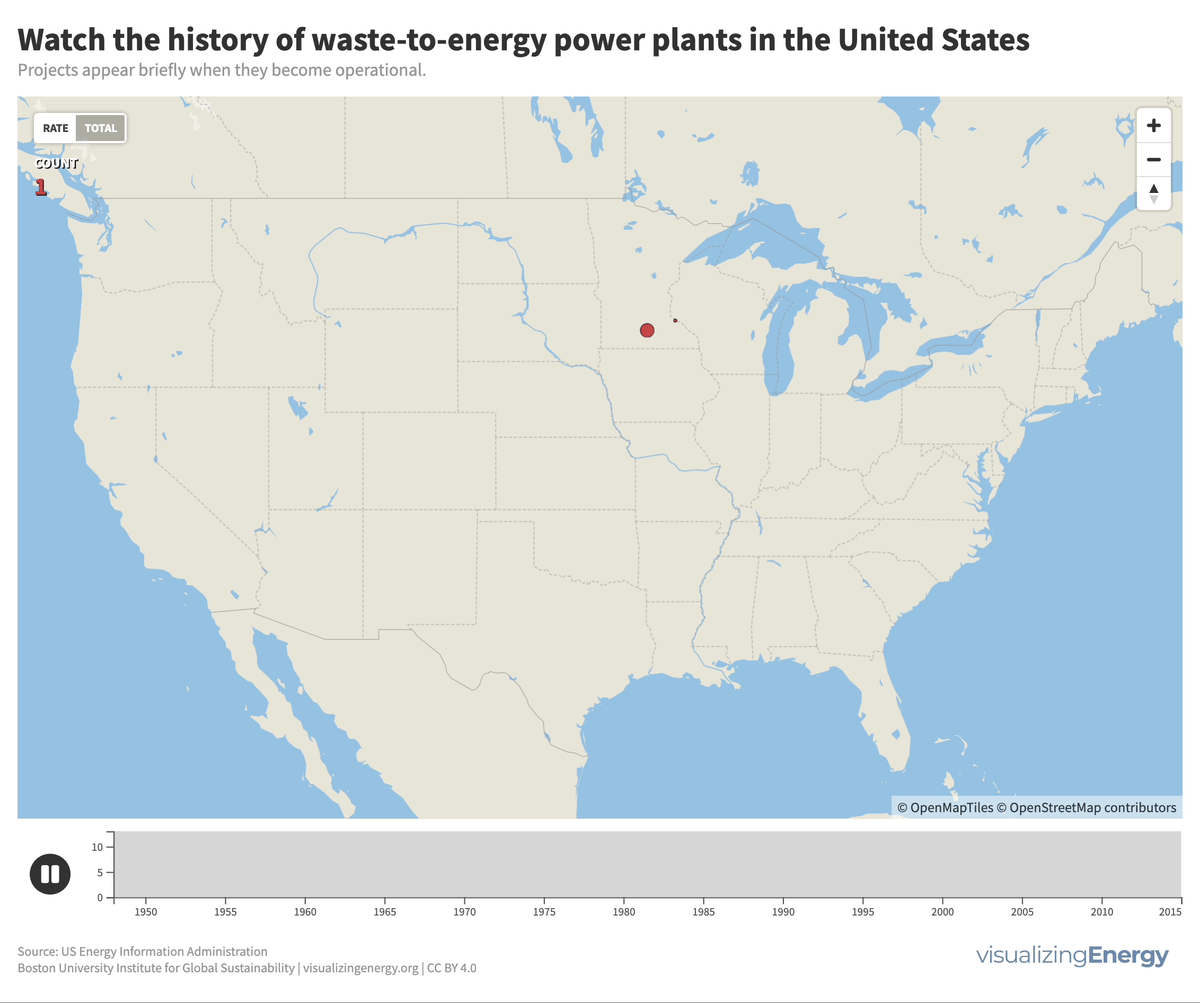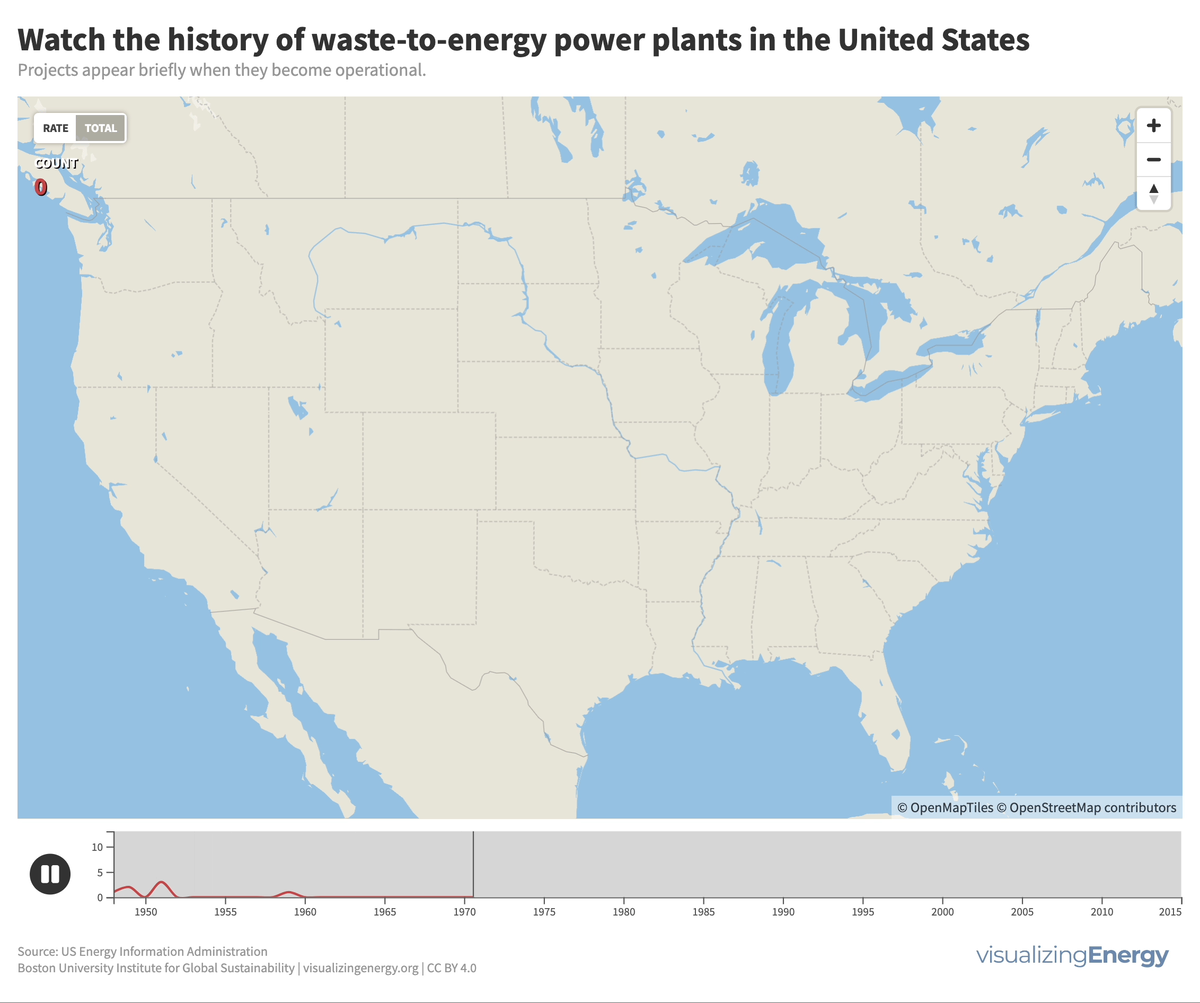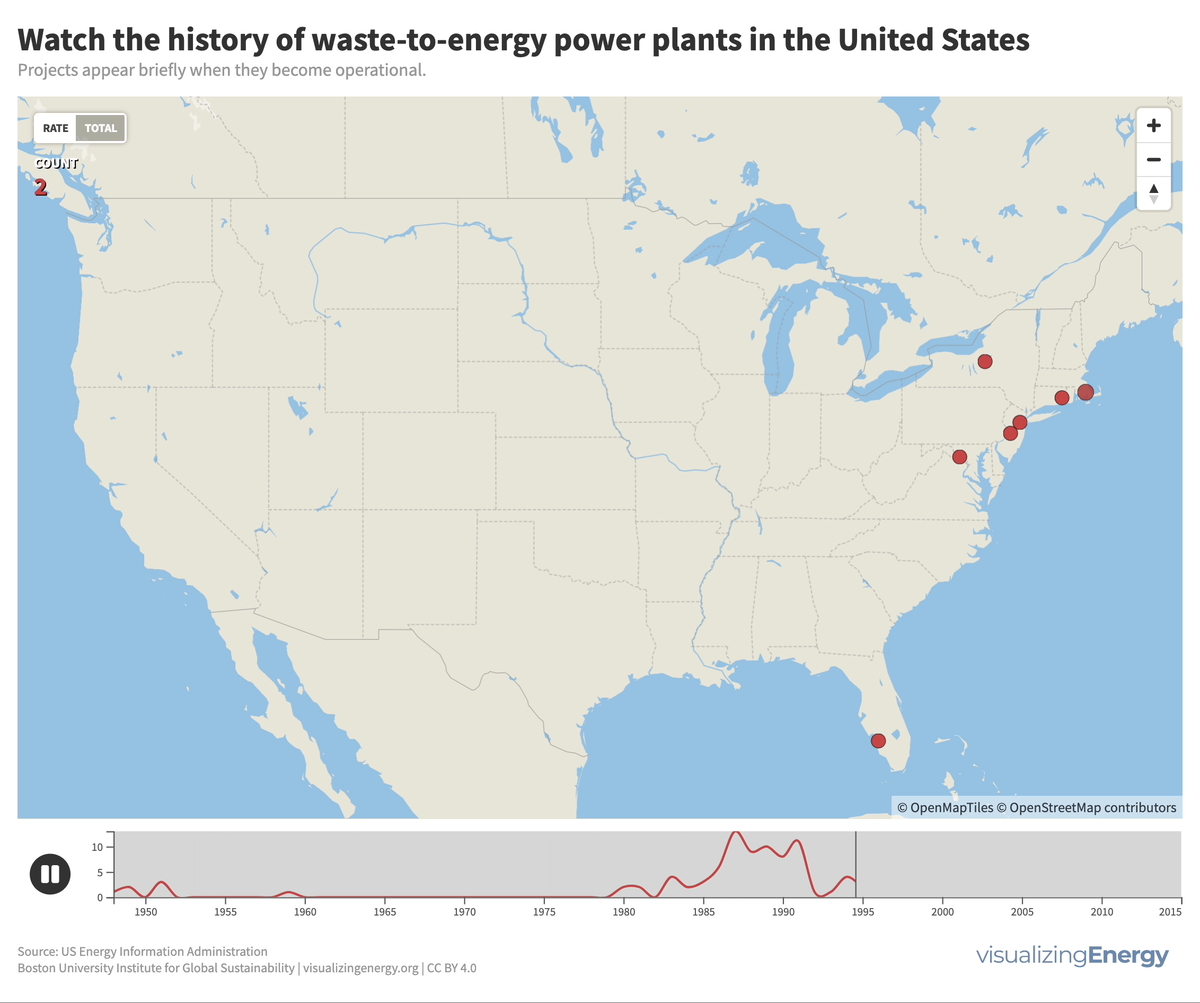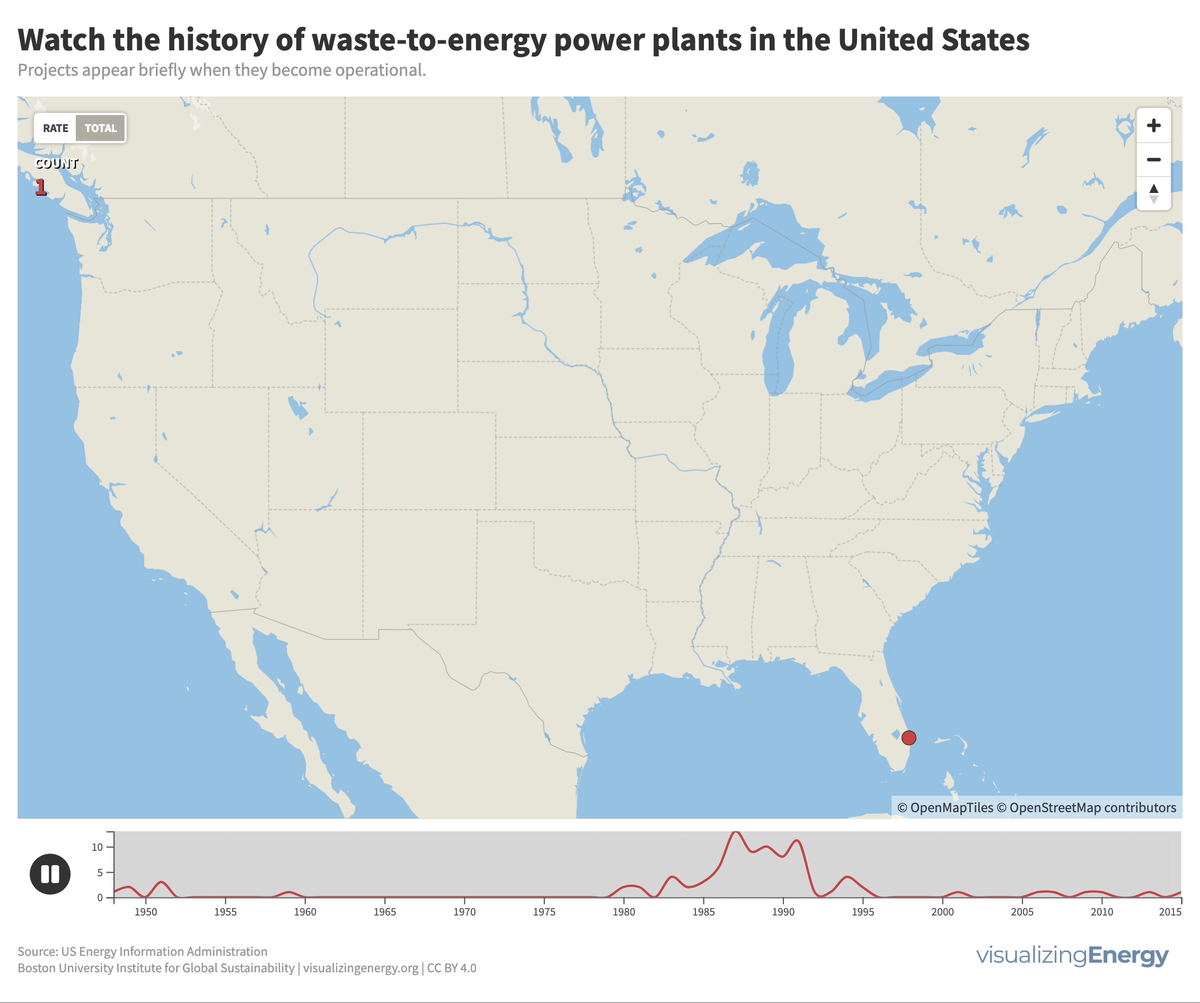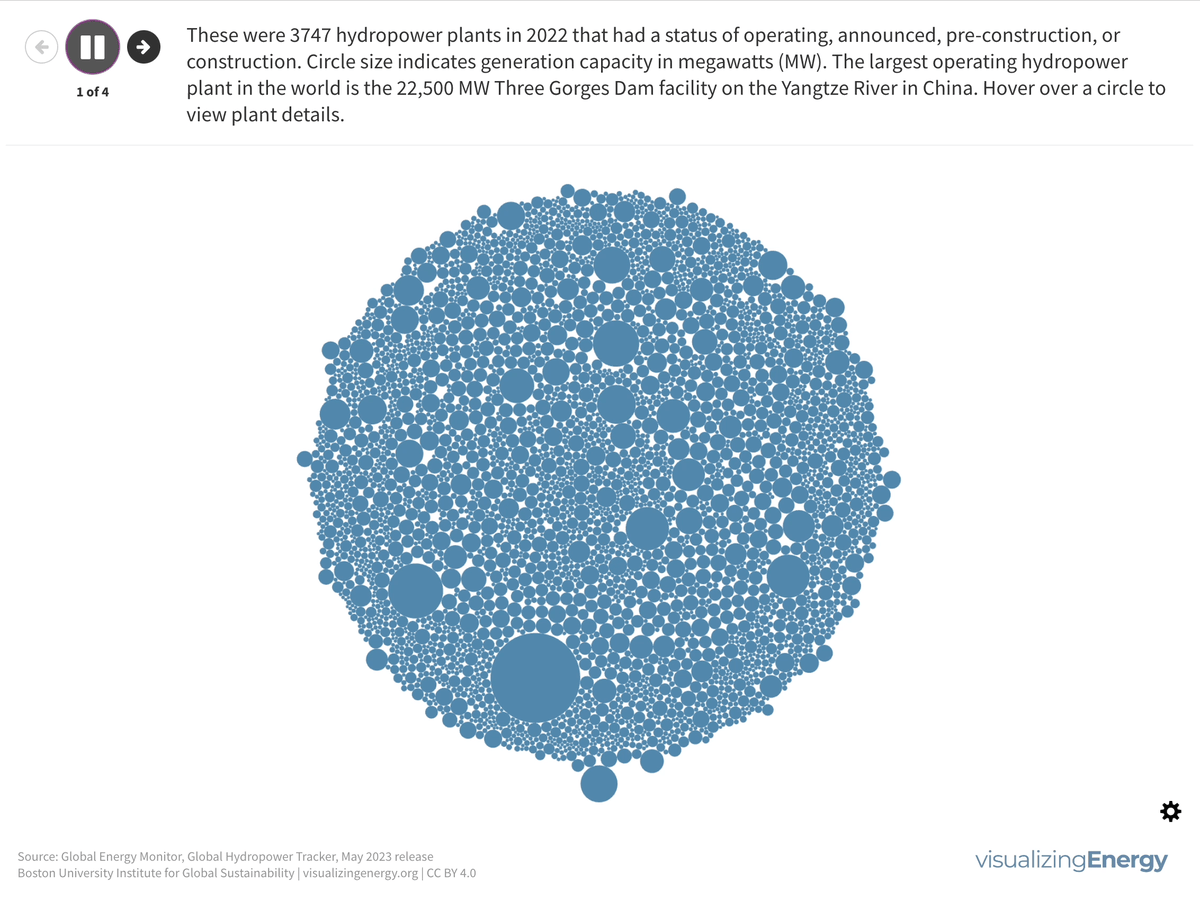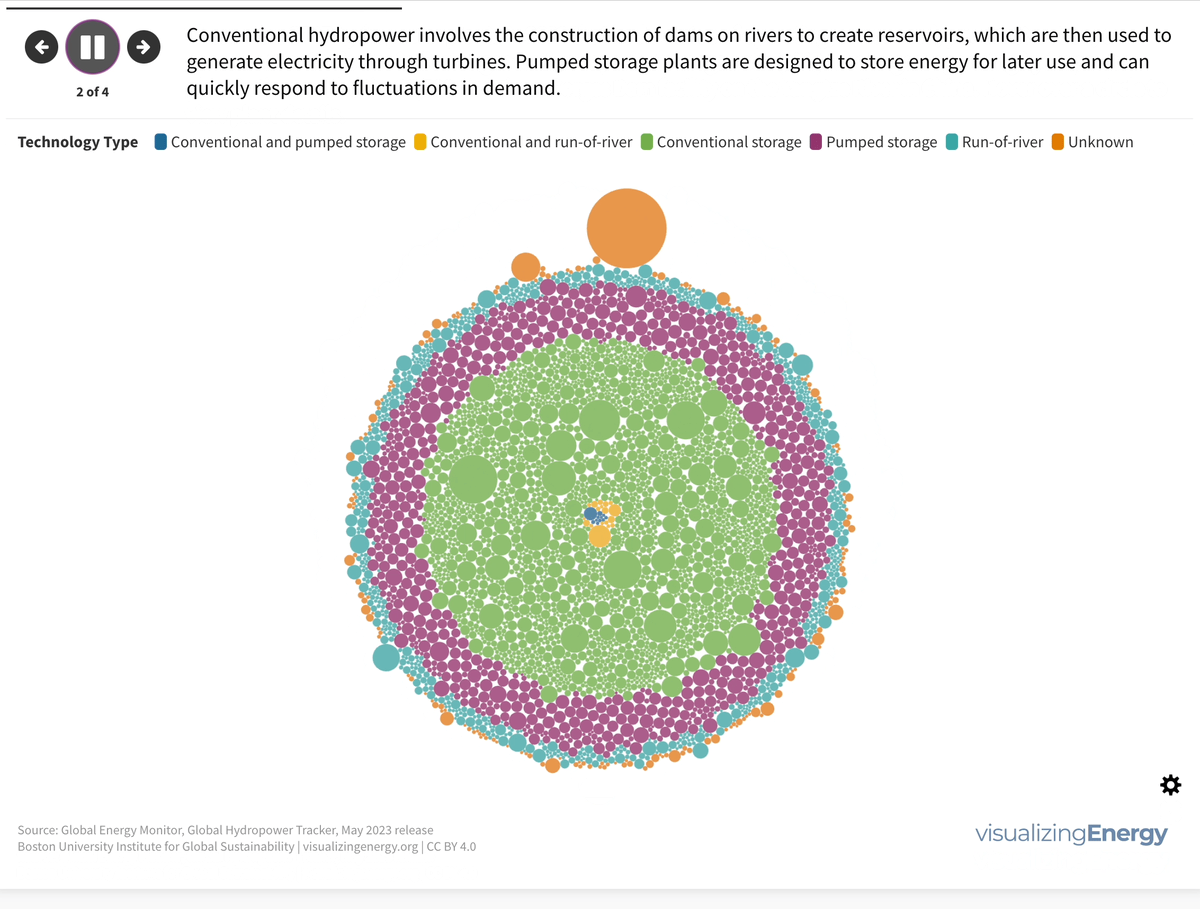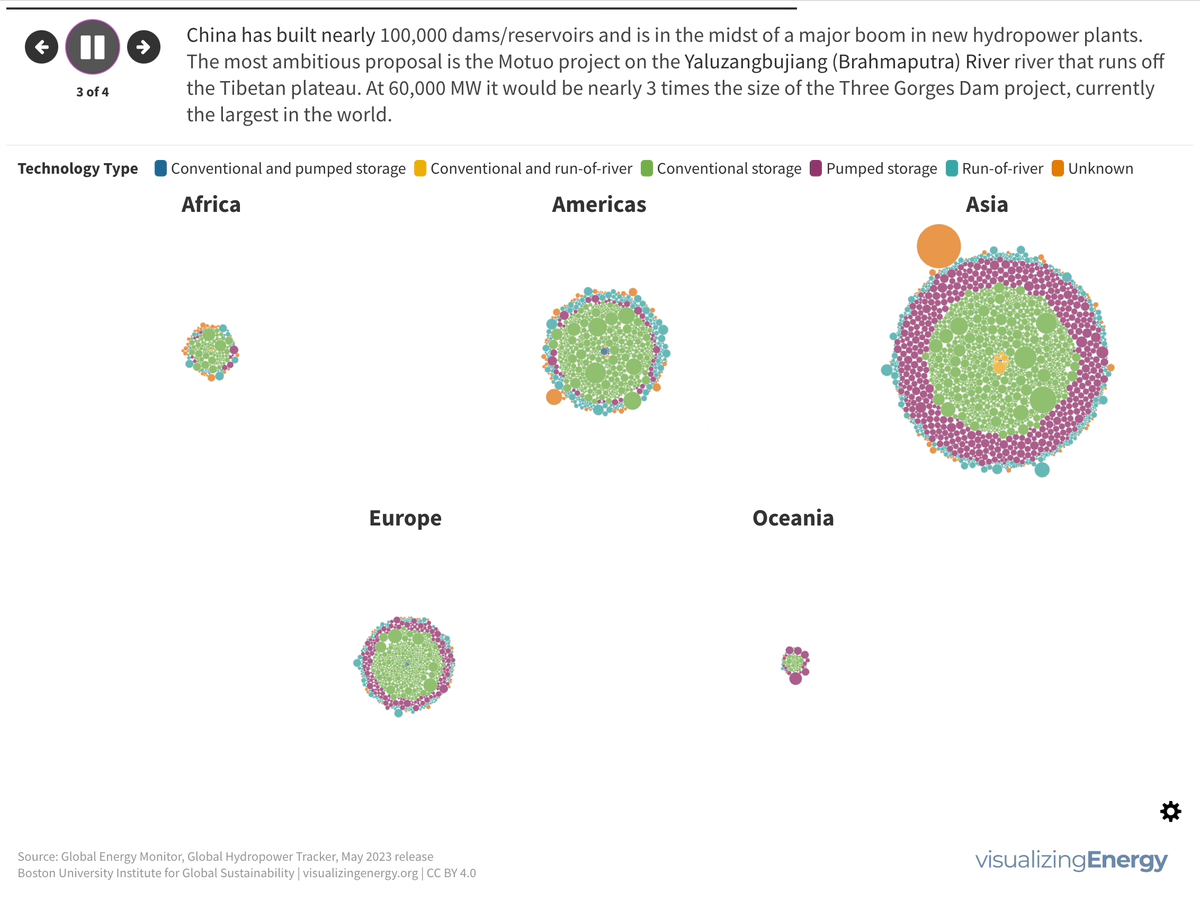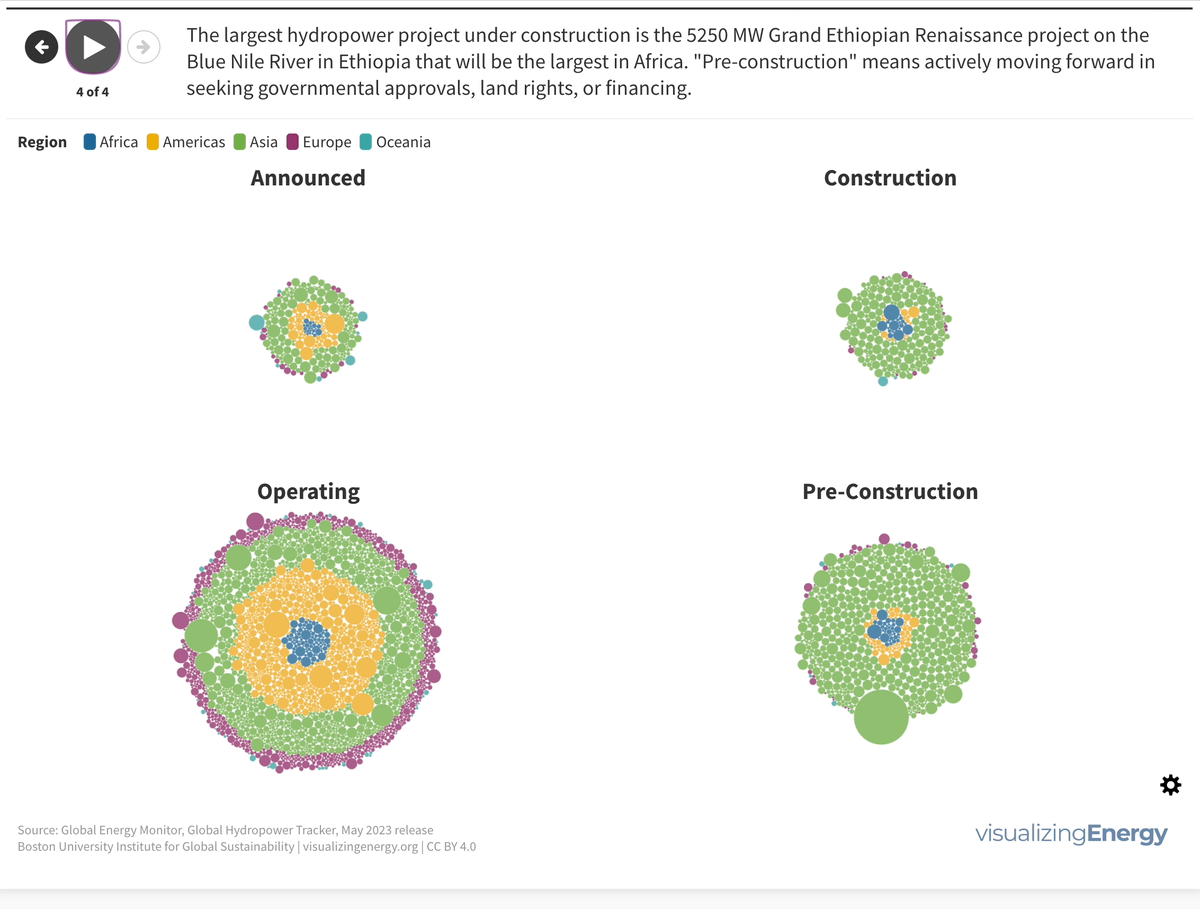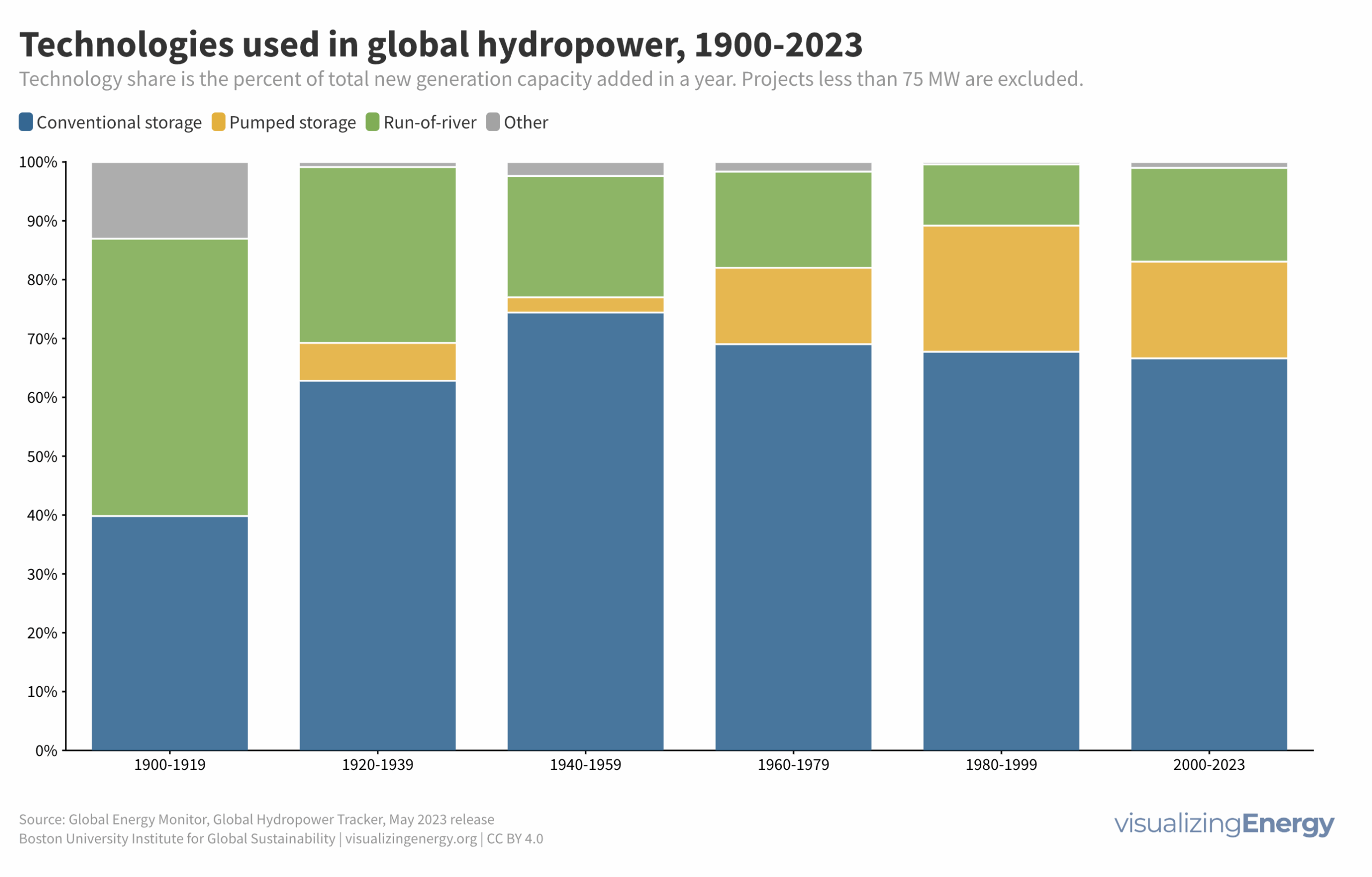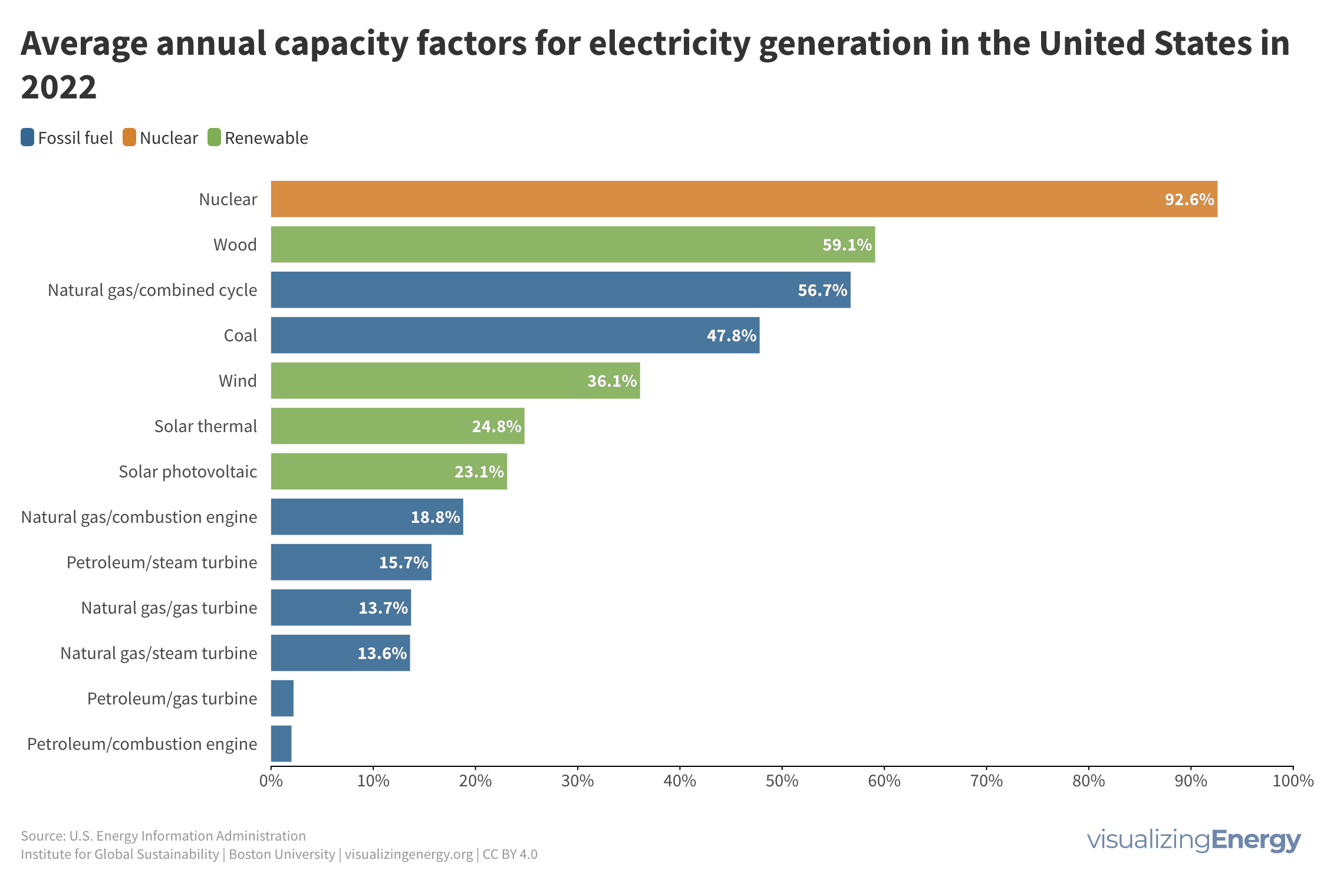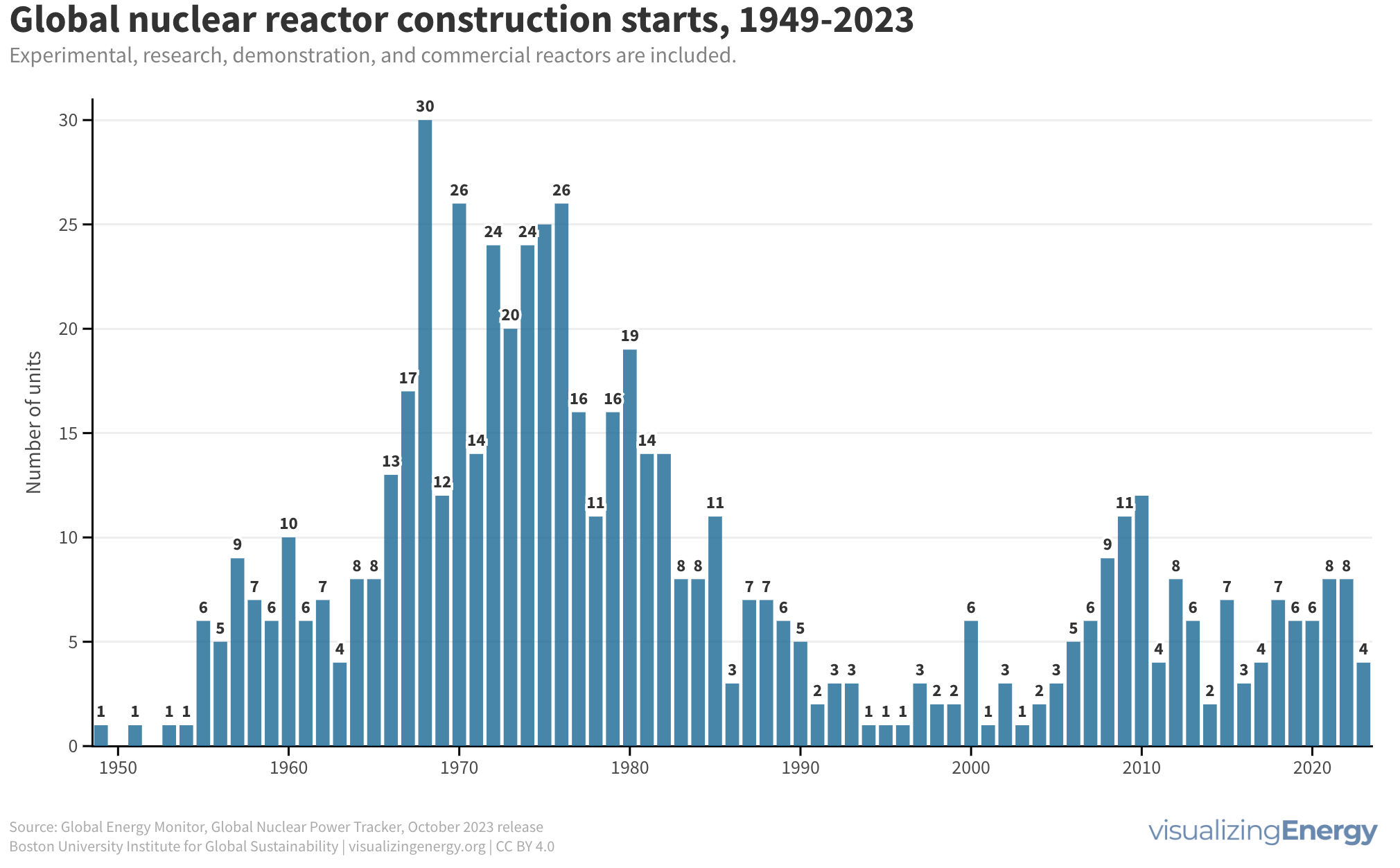
Global nuclear reactor construction starts and duration, 1949-2023
The construction of new nuclear power plants reflects changing electricity demand and technology competitiveness. Despite industry and government support, nuclear power faces challenges such as cost-competitiveness and safety concerns, leading to extended construction times. While some advocate for its expansion as vital for clean energy transition, others question its necessity due to declining global electricity share and the rise of cheaper renewables.