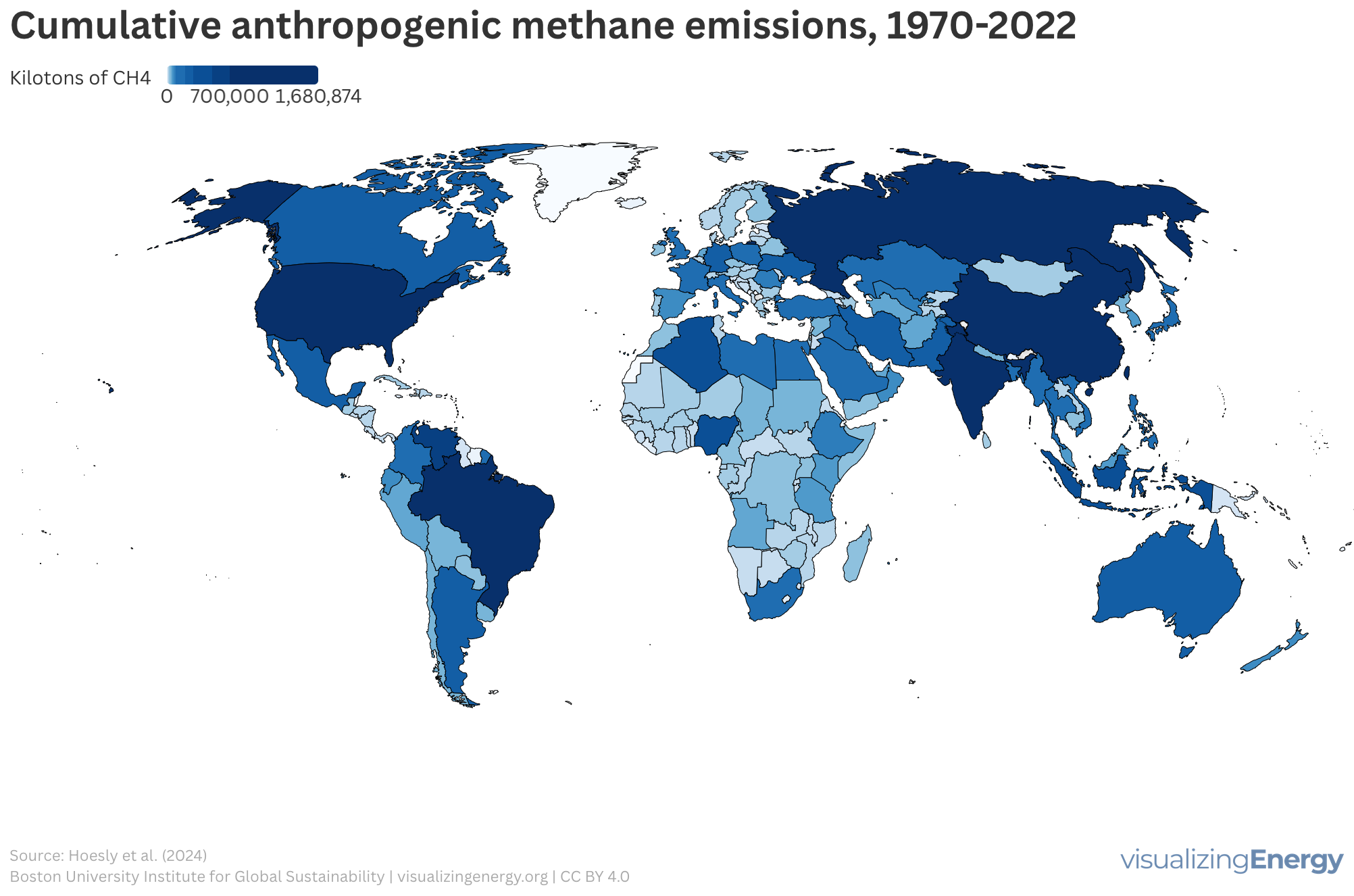
Global anthropogenic methane emissions, 1970-2022
Methane (CH4) is a hydrocarbon and a major component of natural gas. It is a potent greenhouse gas (GHG), so its presence in the atmosphere

Methane (CH4) is a hydrocarbon and a major component of natural gas. It is a potent greenhouse gas (GHG), so its presence in the atmosphere
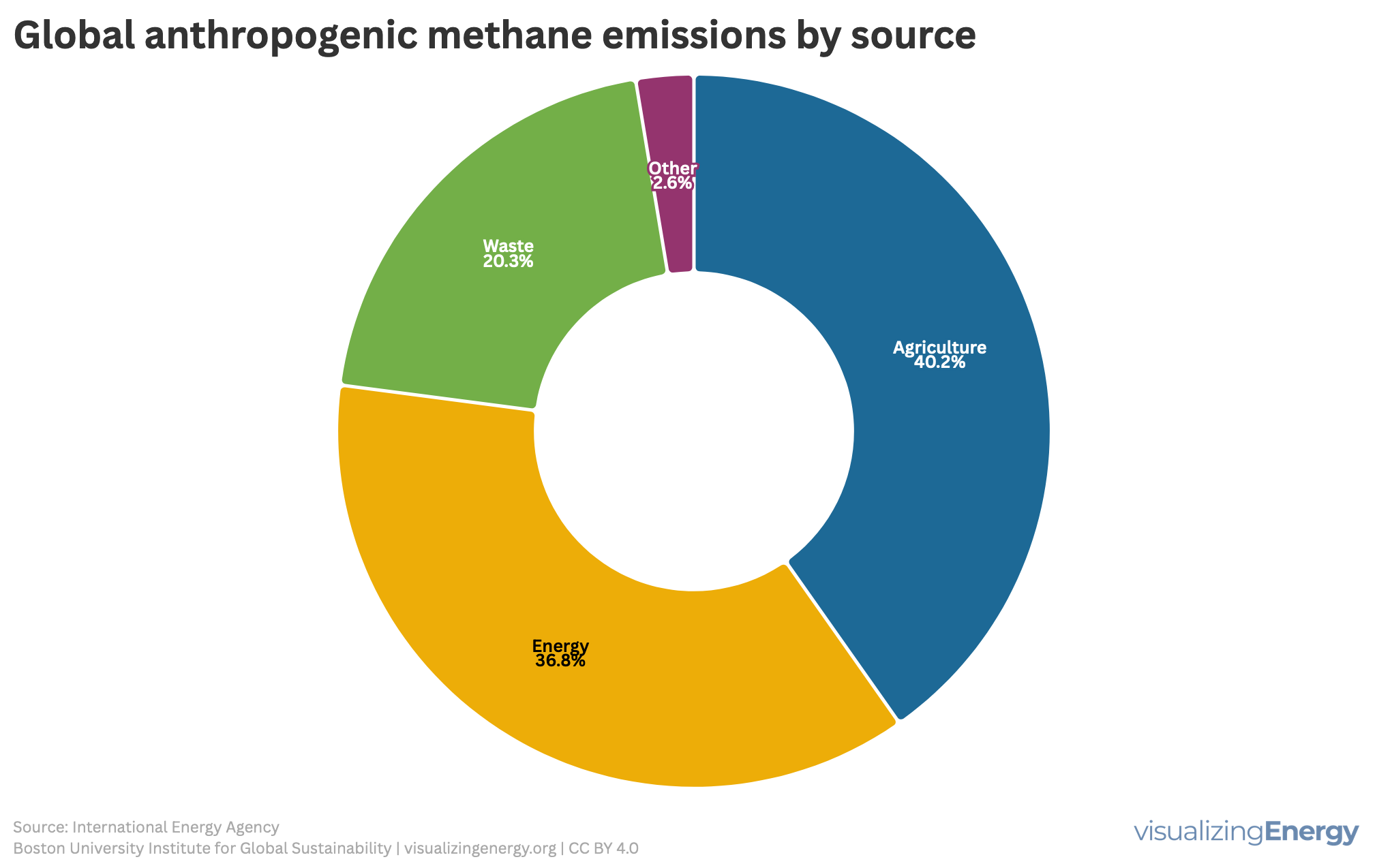
Methane belongs to a class of so-called “super pollutants” that simultaneously contribute to climate change and degrade the health of people and ecosystems. It has
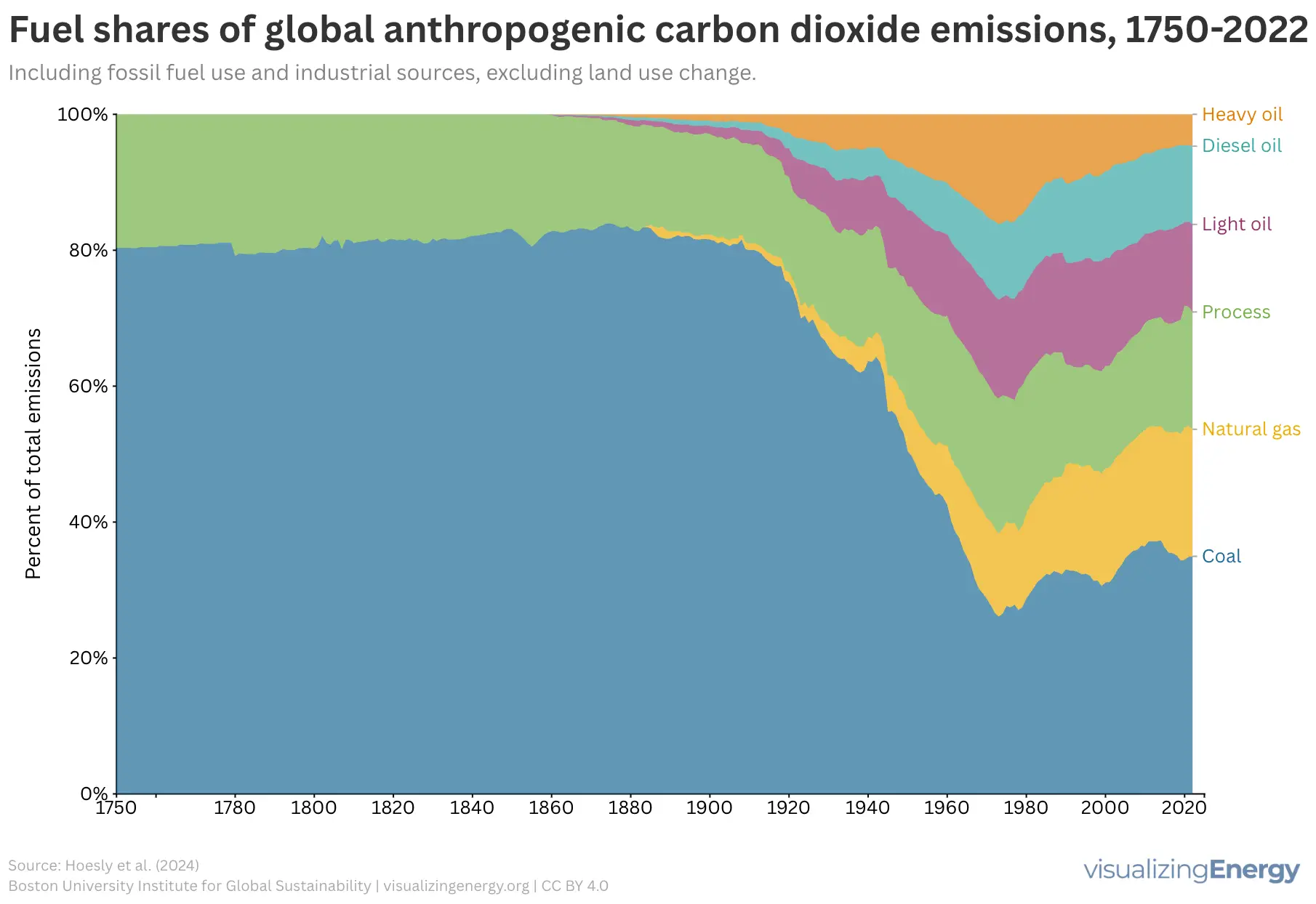
Anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions increased from about 9,000 kilotons in 1750 to approximately 36 million tons in 2022—a 4,000-fold increase. Economic growth and the shift to fossil fuels that accompanied the Industrial Revolution drove this rise in emissions. Between 1850 and 1900, there were only two years in which emissions did not increase from the previous year.
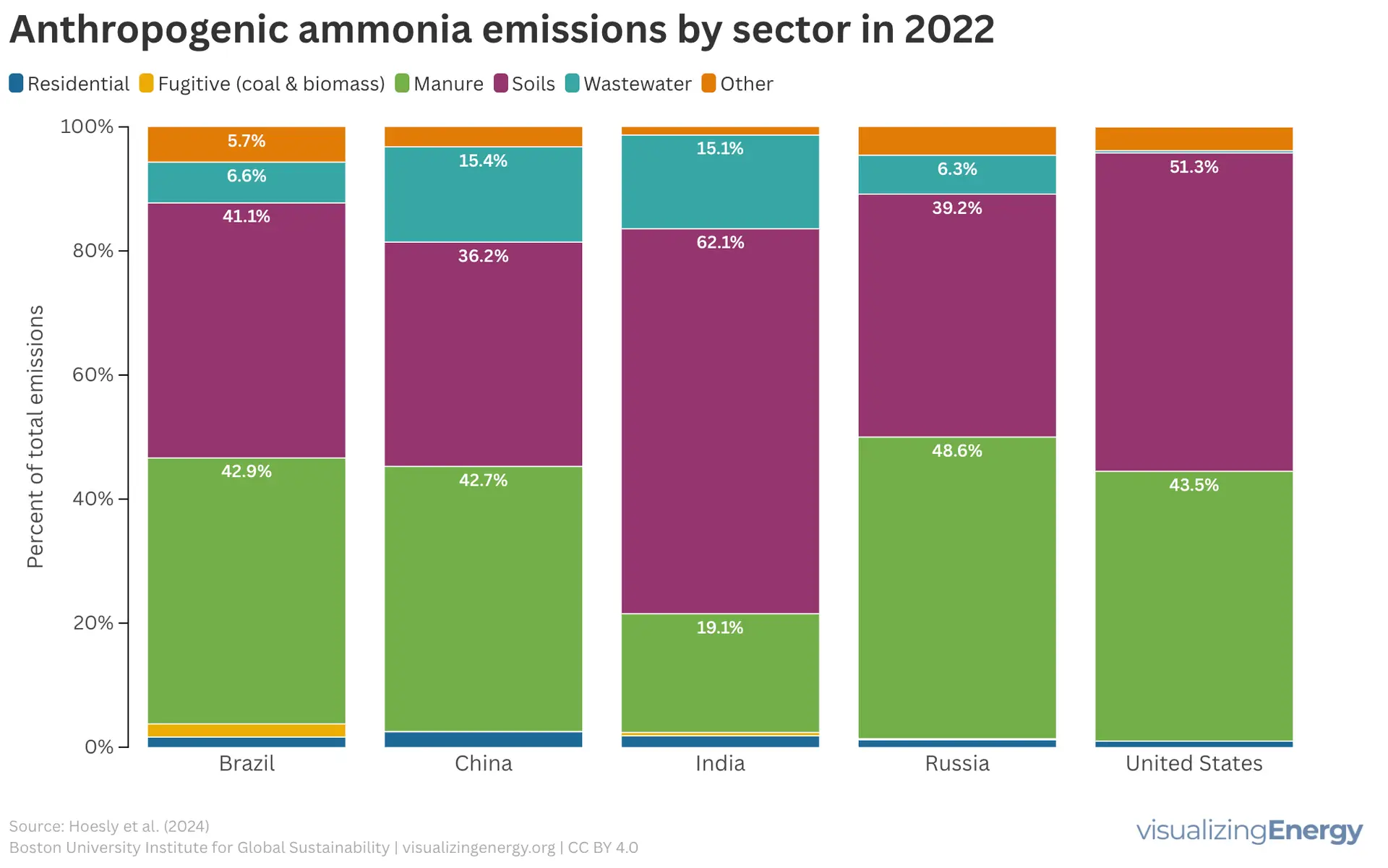
Ammonia (NH3) feeds and pollutes the world.1 The synthesis of ammonia underpins all nitrogen fertilizers, and without their applications it would be impossible to feed,
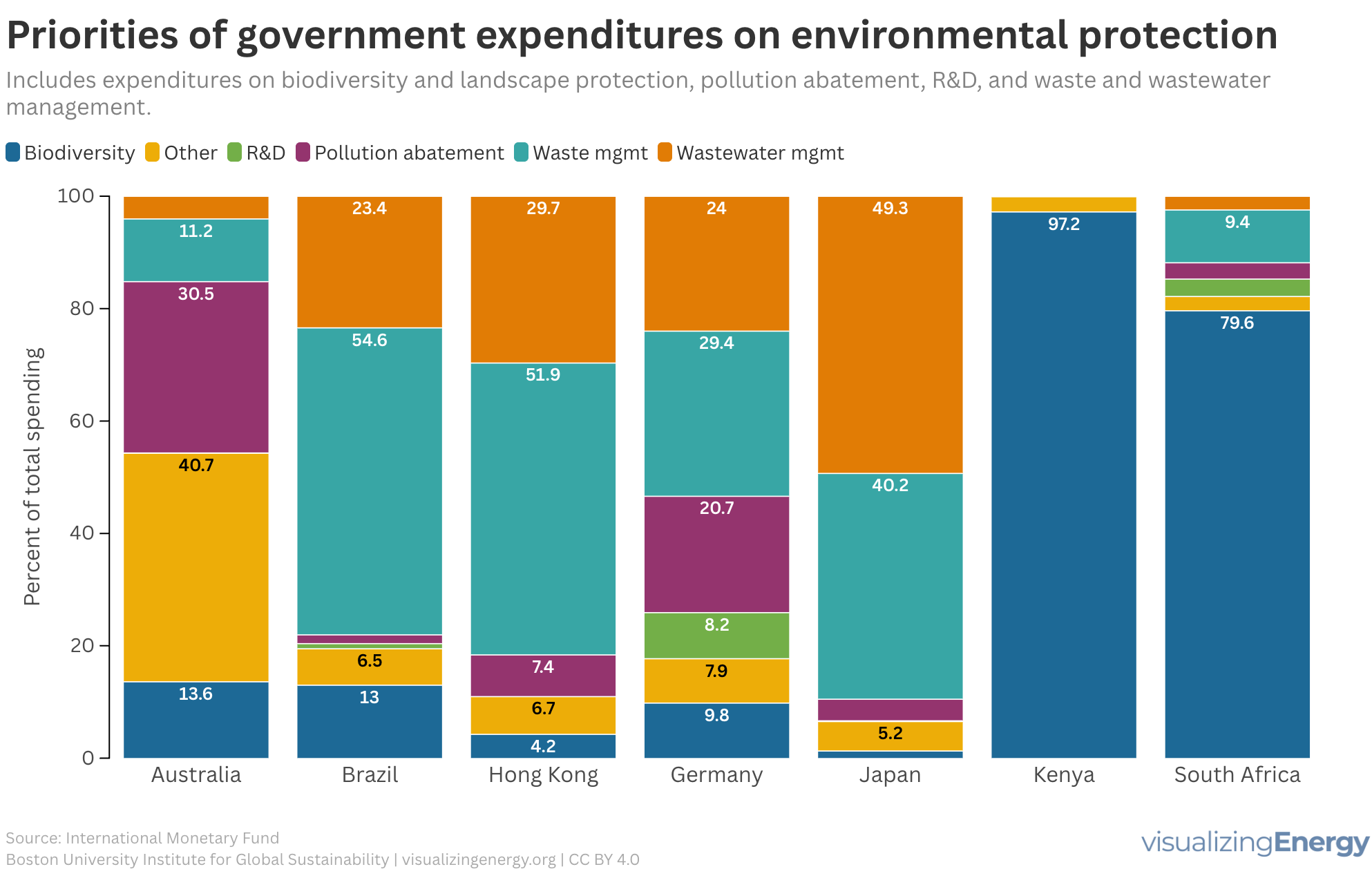
National governments began spending on environmental protection in the late 19th century, escalating after World War II due to pollution concerns. Key legislation emerged worldwide, including Japan’s 1967 law and the U.S. Endangered Species Act. In 2023, EU spending on environmental protection totaled €142 billion, highlighting diverse national priorities in tackling environmental issues.
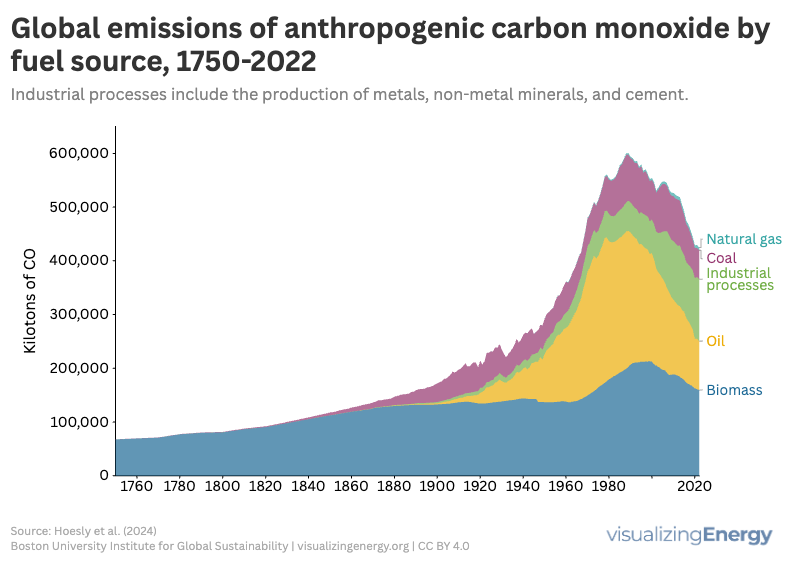
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a toxic, colorless gas from incomplete combustion of fuels, leading to potential health hazards like headaches and confusion. Residential sources produce significant CO emissions, impacting 2.4 billion people reliant on biomass. Globally, emissions peaked in 1989, but have since declined due to regulations and technological advancements in combustion efficiency.
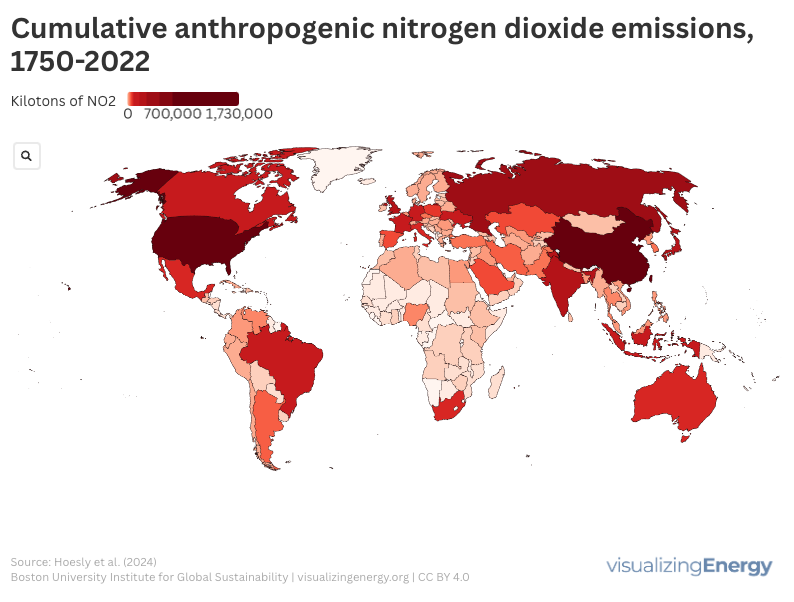
NOx, comprising nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide, significantly impacts air pollution and health, causing respiratory issues and contributing to harmful pollutants. Mainly emitted from transportation and industrial activities, NOx levels vary globally. Efforts to reduce emissions include regulatory policies and technology advancements, along with a shift towards cleaner energy sources.
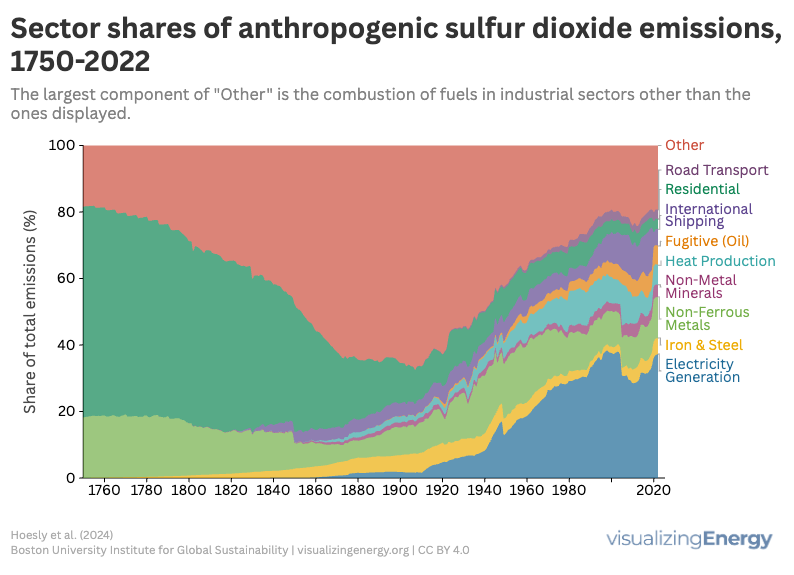
Sulfur dioxide (SO₂) is a major air pollutant produced from burning sulfur-containing fuels. It poses health risks, including respiratory issues and links to heart disease, while harming the environment by contributing to acid rain. Emissions have significantly decreased due to regulations and technology, but global reliance on fossil fuels continues to impact levels.

Satellites significantly enhance our understanding of methane emissions, responsible for about 30% of anthropogenic global warming. The United Nations Environment Programme’s Methane Alert and Response System detects plumes from waste, oil, gas, and coal, identifying super emitters to improve emissions accountability. Methane from waste facilities is particularly concerning due to inefficient capture methods.
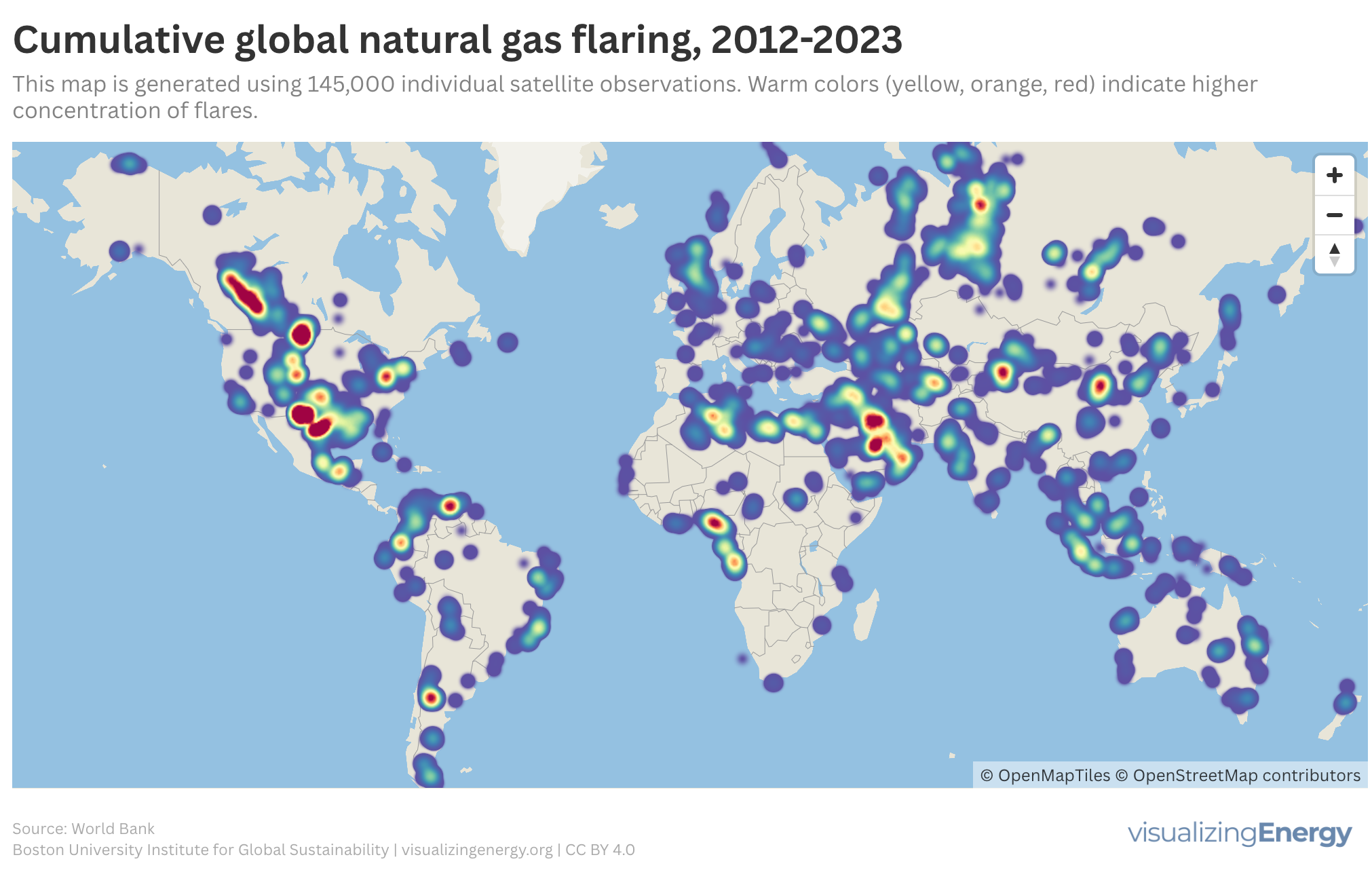
Crude oil and natural gas often coexist in reservoirs, leading to natural gas flaring when oil is extracted. This process not only wastes energy but also contributes significantly to global methane emissions. Despite initiatives like the Zero Routine Flaring by 2030, flaring volumes remain high, particularly in nine major countries responsible for the majority.