Where do energy taxes have the largest macroeconomic impact?
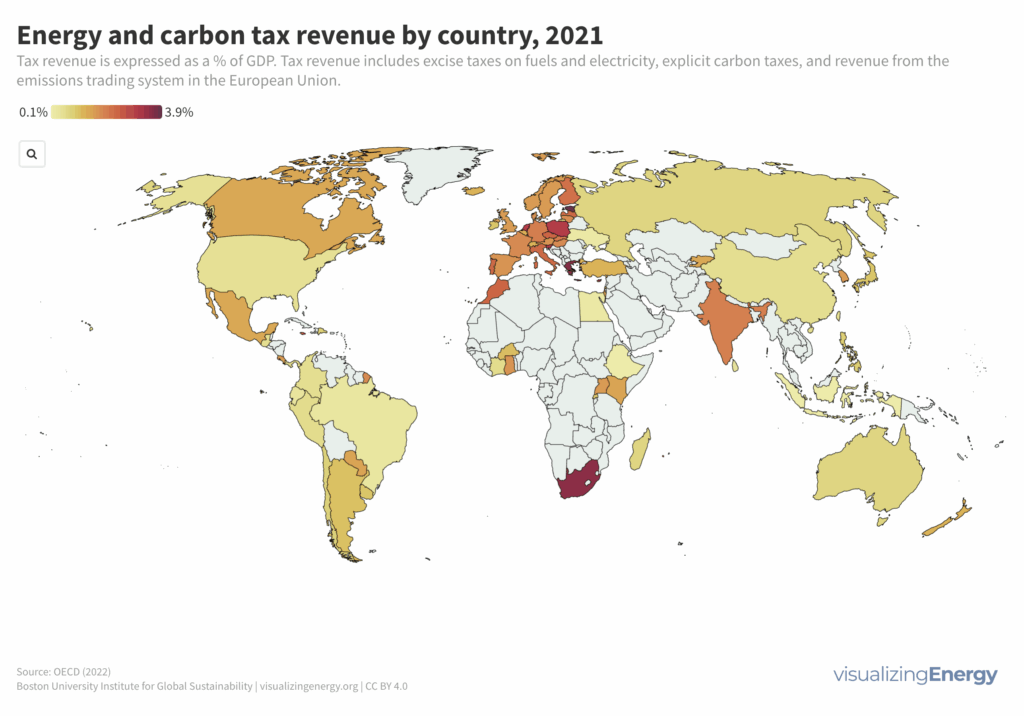
Economic policies impact the volume and nature of energy use and pollutants, including greenhouse gases. Government interventions typically include emissions trading, carbon taxes, and excise taxes. The OECD found that tax and subsidy policies influence GHG emissions and energy consumption globally. Current energy tax policies, however, do not align with GHG reduction goals.
What is the ‘diesel discount’ and does it matter?
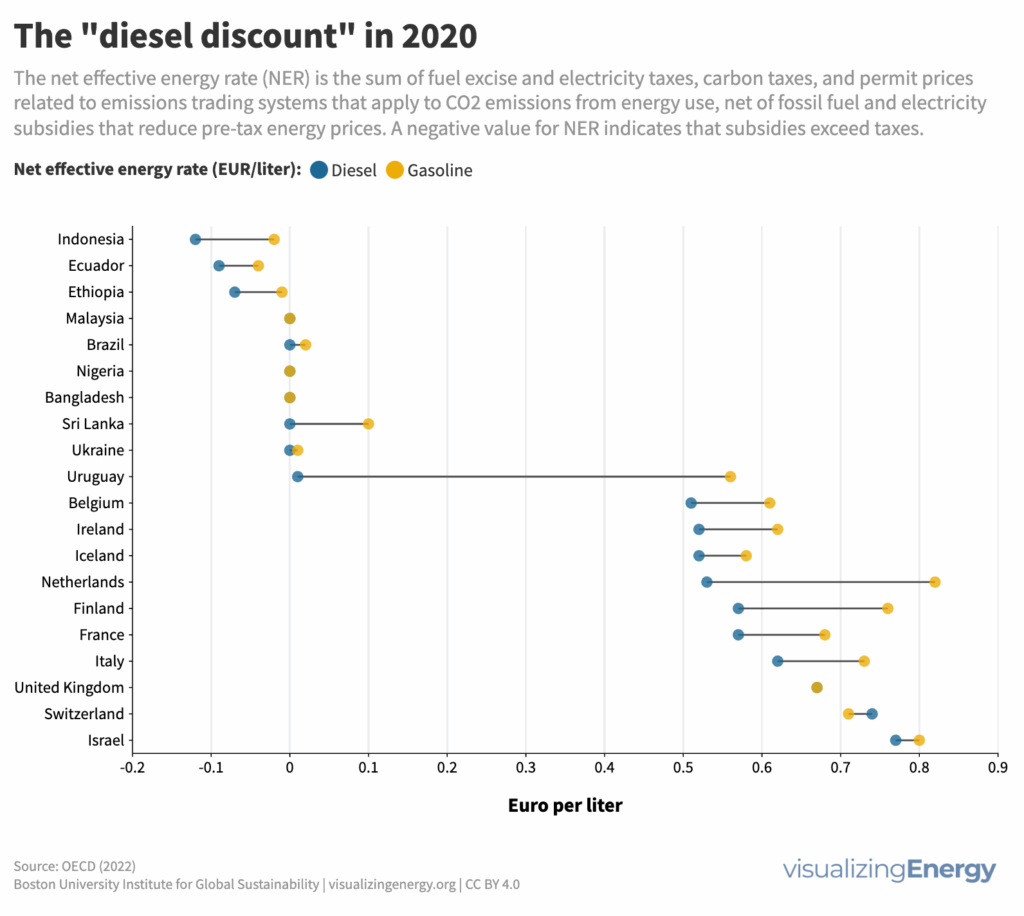
Road transport relies heavily on gasoline and diesel, influenced by government policies that often favor diesel for its efficiency. However, diesel produces more pollution, and the tax revenues it generates complicate change. The debate now centers on speeding up the transition to electric transportation to combat greenhouse gas emissions while balancing historical preferences with environmental concerns.
What countries have the greatest bioenergy power capacity?
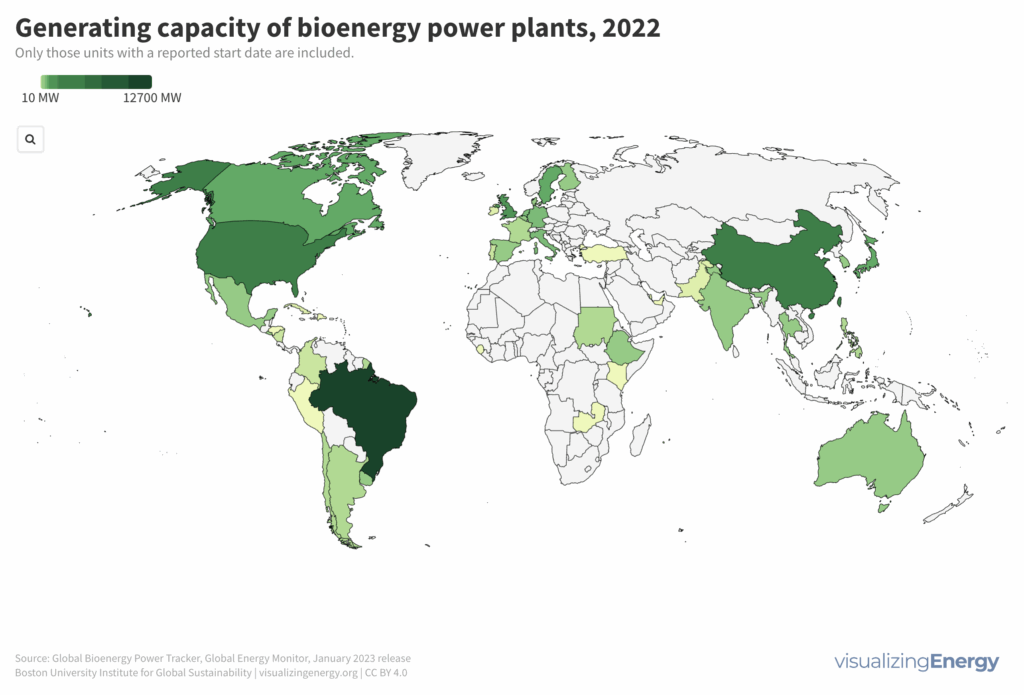
As of January 2023, 575 utility-scale biopower plants were operational globally, with a total capacity of over 29,000 MW, less than 0.5% of worldwide power generation. An additional 6,000 MW are under construction. China is believed to significantly underreport its true biopower capacity, perhaps as high as 22,000 MW, primarily from agricultural residues and waste-to-energy facilities. Brazil, another major player, relies largely on sugarcane byproducts.
Where are new biopower plants being built?
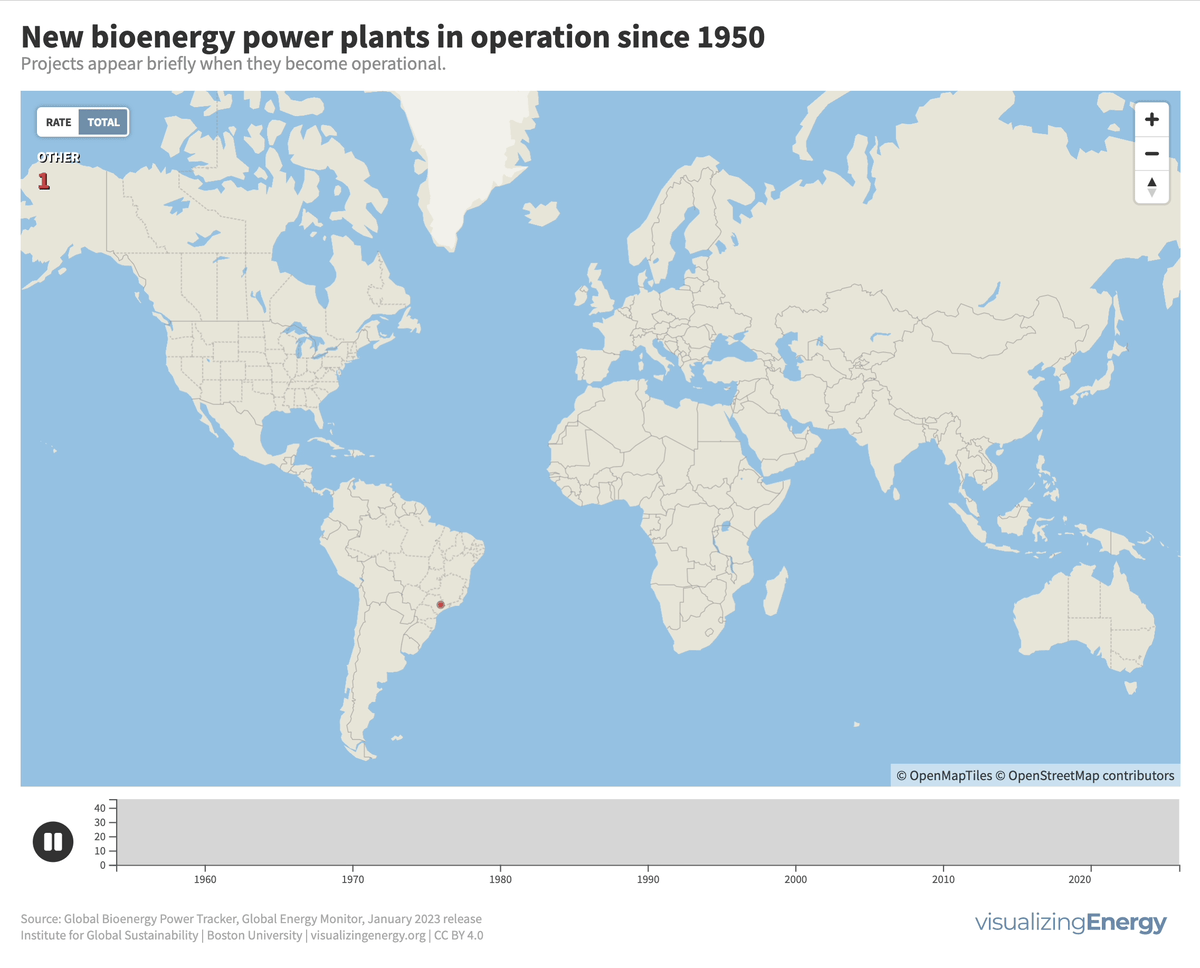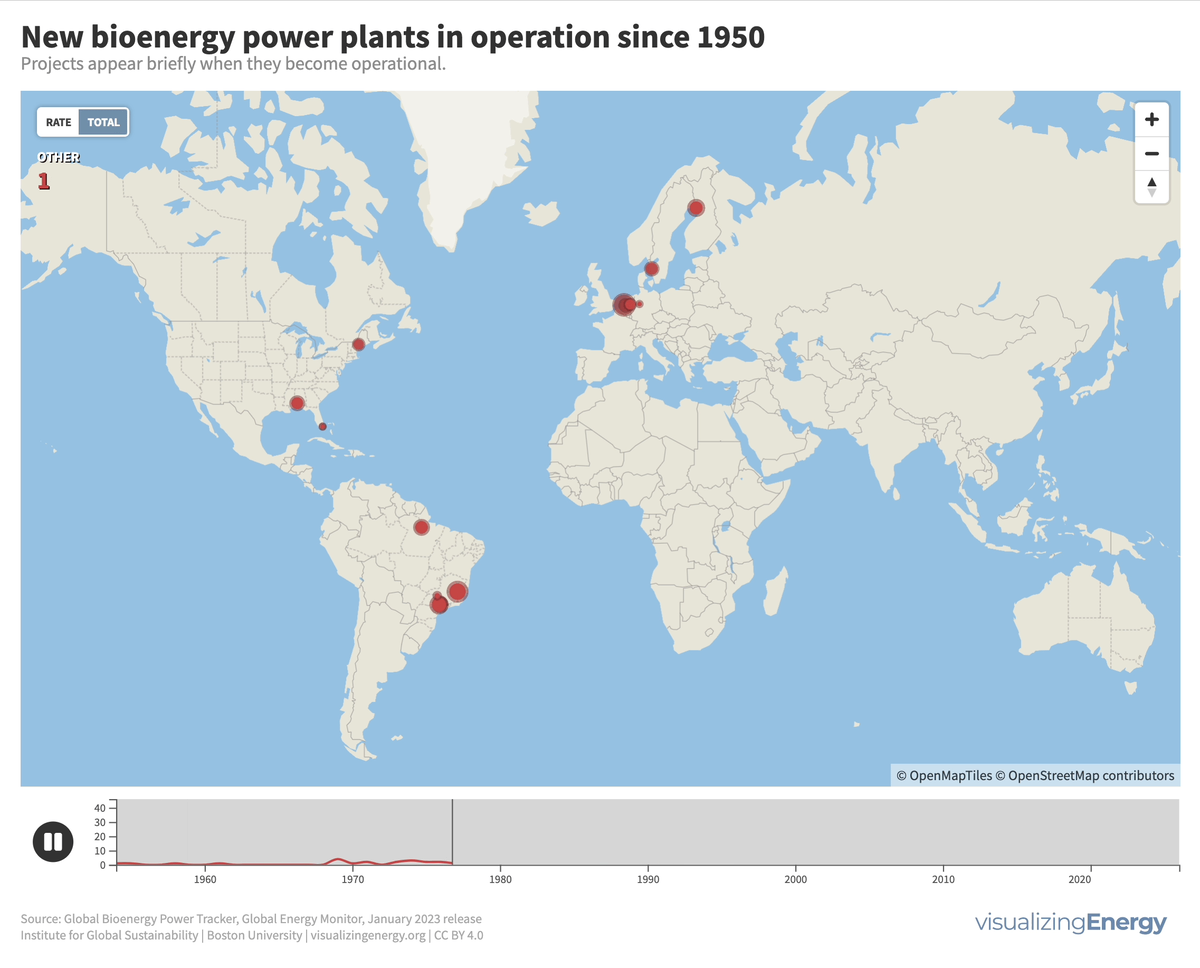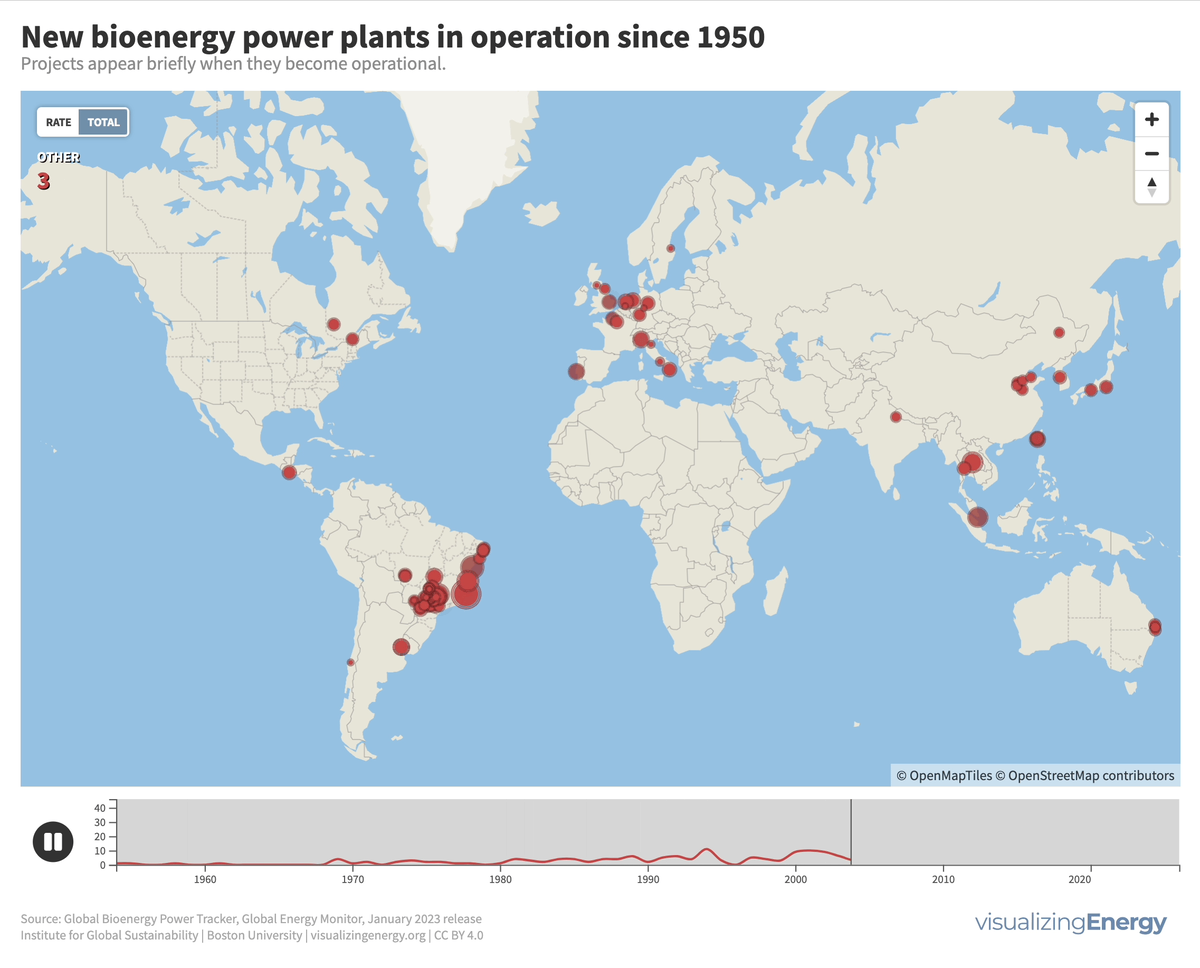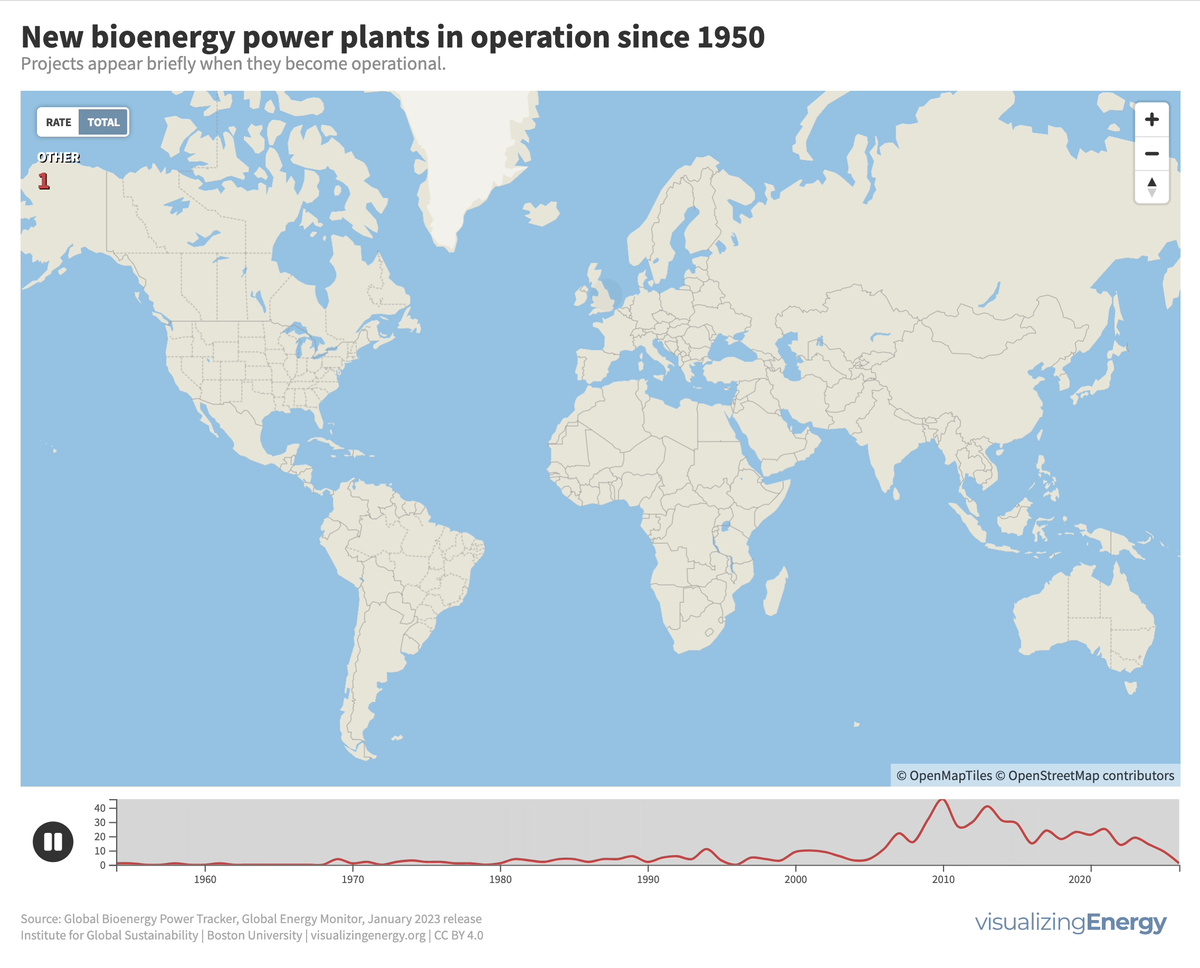
Biopower is the production of electricity from biomass-derived fuels, with significant growth in Brazil due to sugarcane-based ethanol byproducts, while in certain regions like the United States, Germany, and the United Kingdom, waste-to-energy facilities are used due to land constraints and landfill opposition.
Watch the history of solar power in the United States
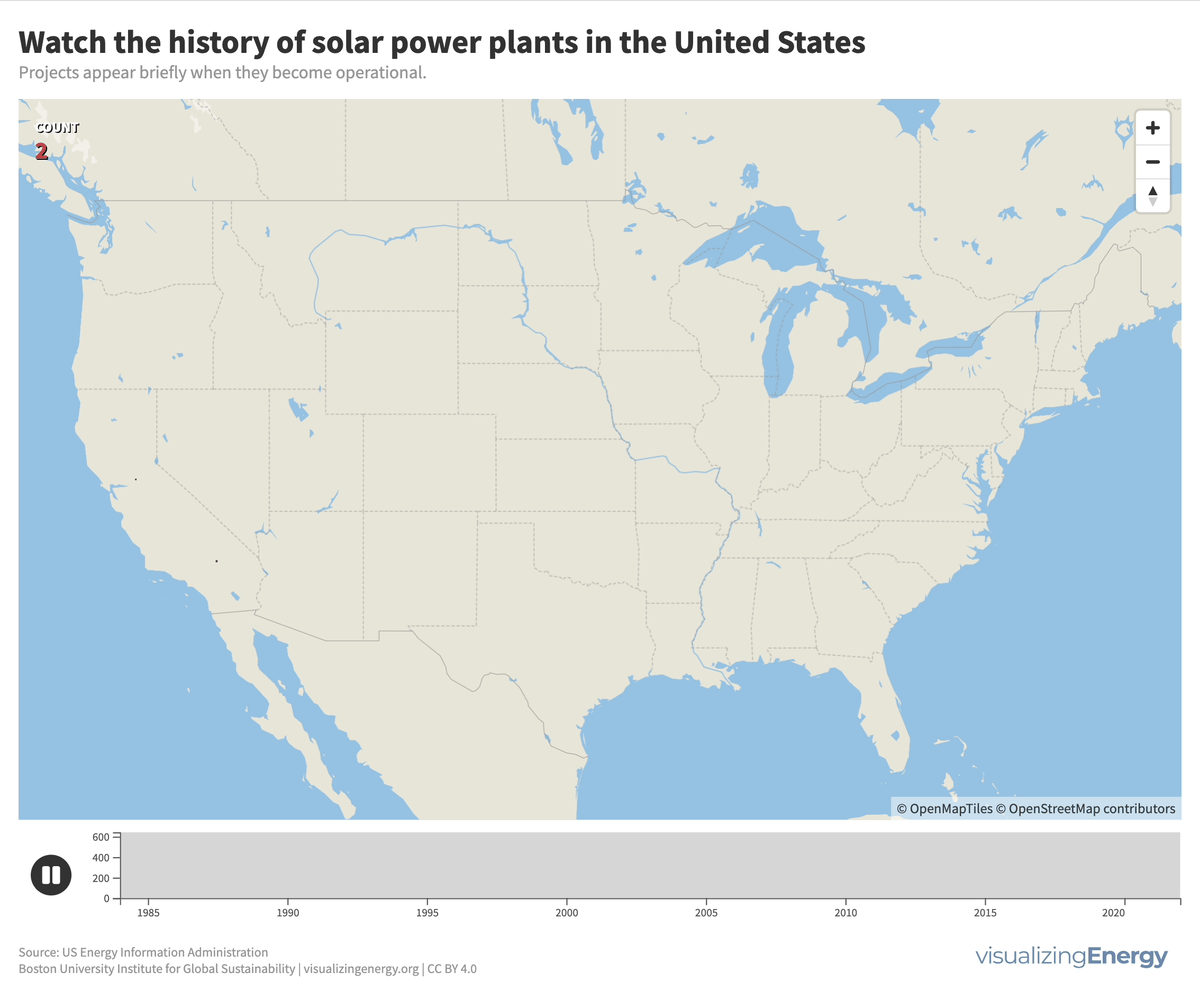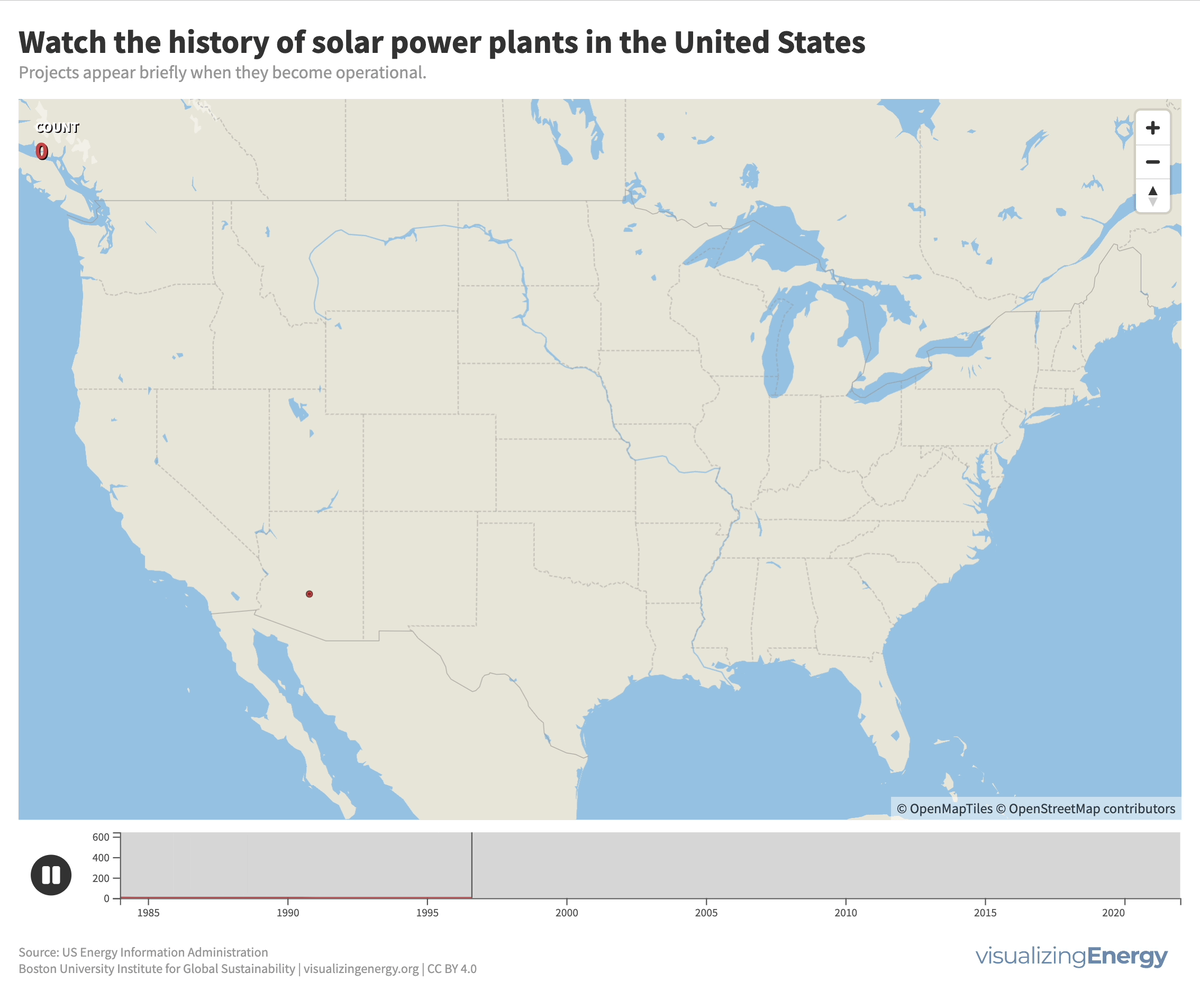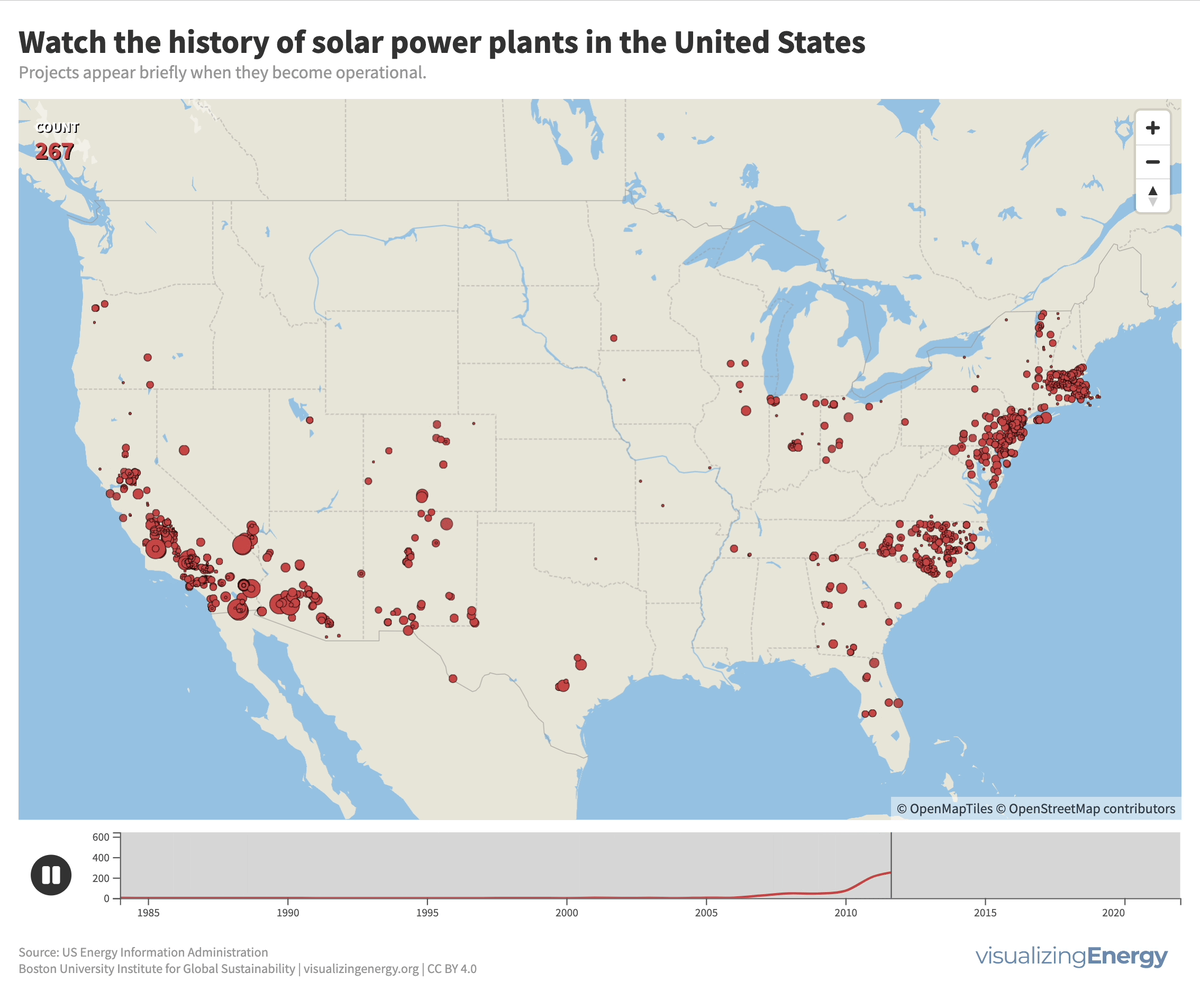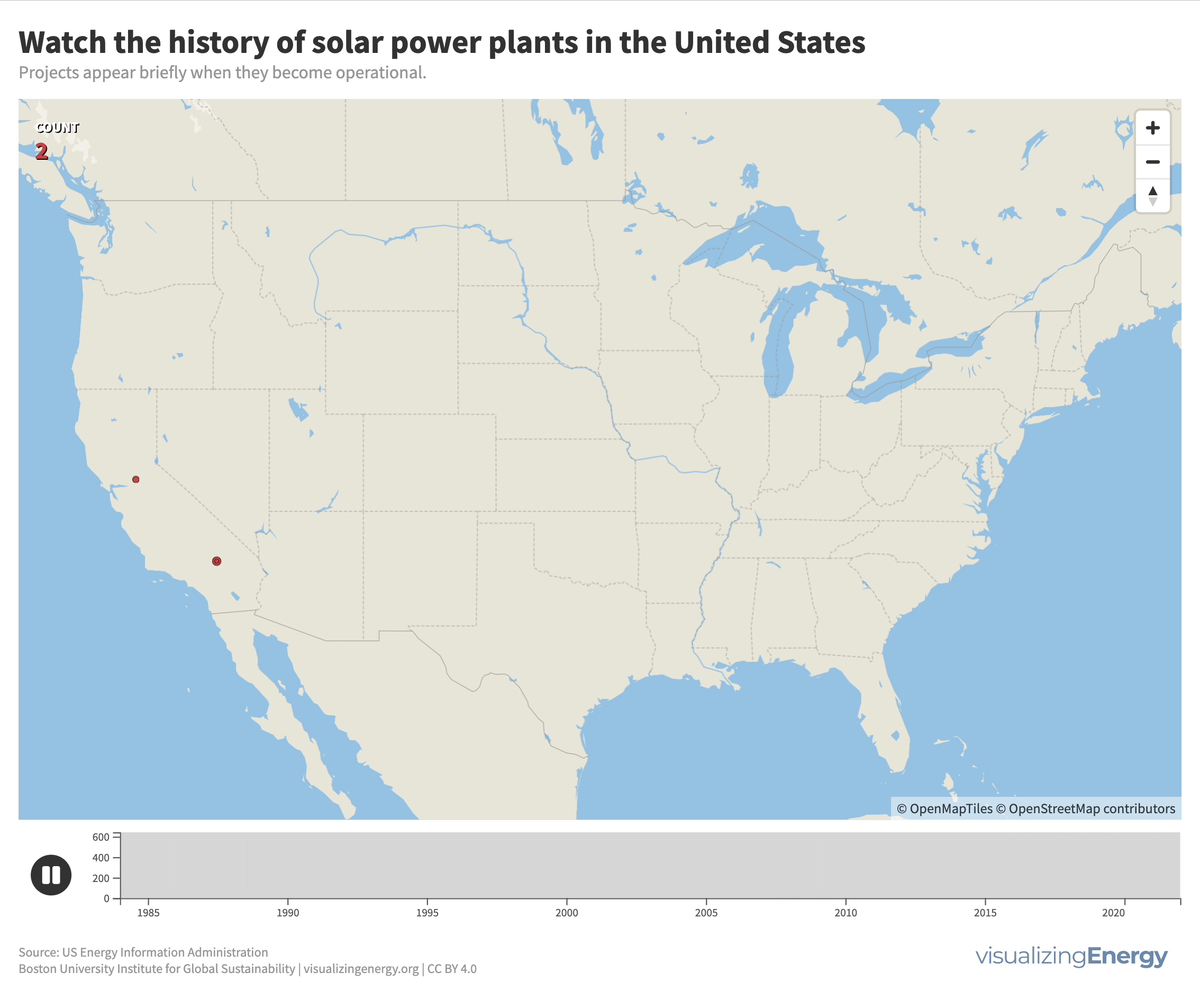
In 2022, the United States saw a significant rise in solar power generation, with 5730 utility-scale solar PV plants and 13 solar thermal plants producing 146 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity, equal to 3.4% of total utility-scale generation. This growth traces back to the 2000s, marked by falling solar system costs, enhanced efficiency, and government incentives like the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009.
Is wind energy a major threat to birds?
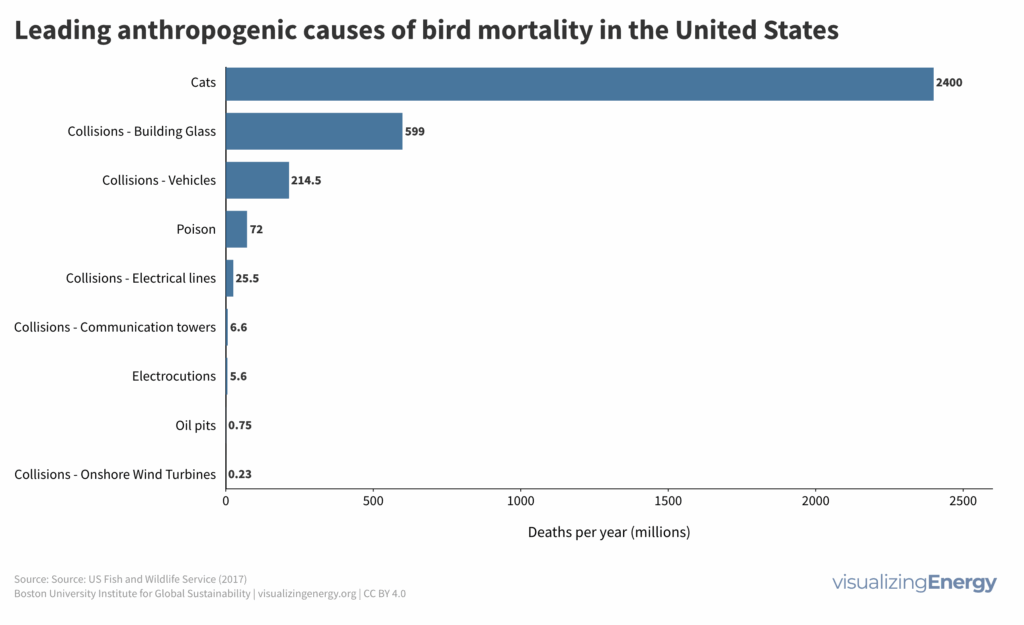
Concerns about wind turbines causing bird deaths are often exaggerated. Data shows that bird fatalities from wind turbines are relatively low compared to other causes like domestic cats and building collisions. When assessing the relative impact on bird mortality, wind energy appears less harmful than many other forms of electricity generation.
How did people benefit from energy transitions in the United Kingdom?
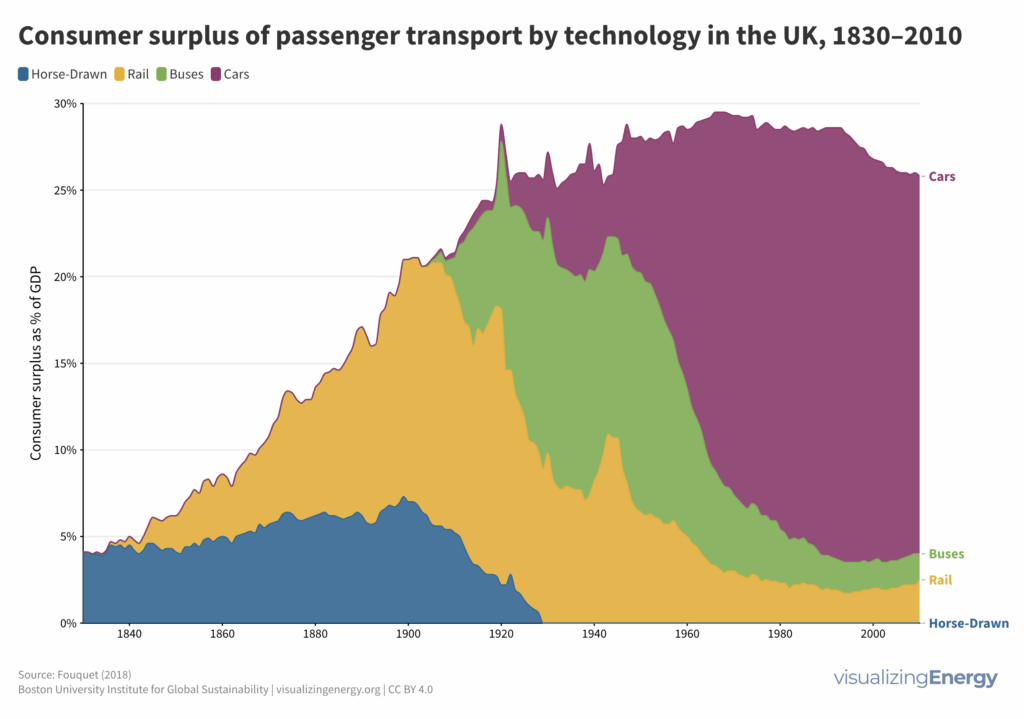
Historic energy transitions, primarily driven by fossil fuels, significantly improved human well-being, measured through consumer surplus. In the UK, transitions from stagecoaches to railways to cars, and from candles to gaslight to electric lighting, substantially increased consumer surplus. However, these benefits diminish as societies reach high well-being levels.
Watch the history of oil power plants in the United States
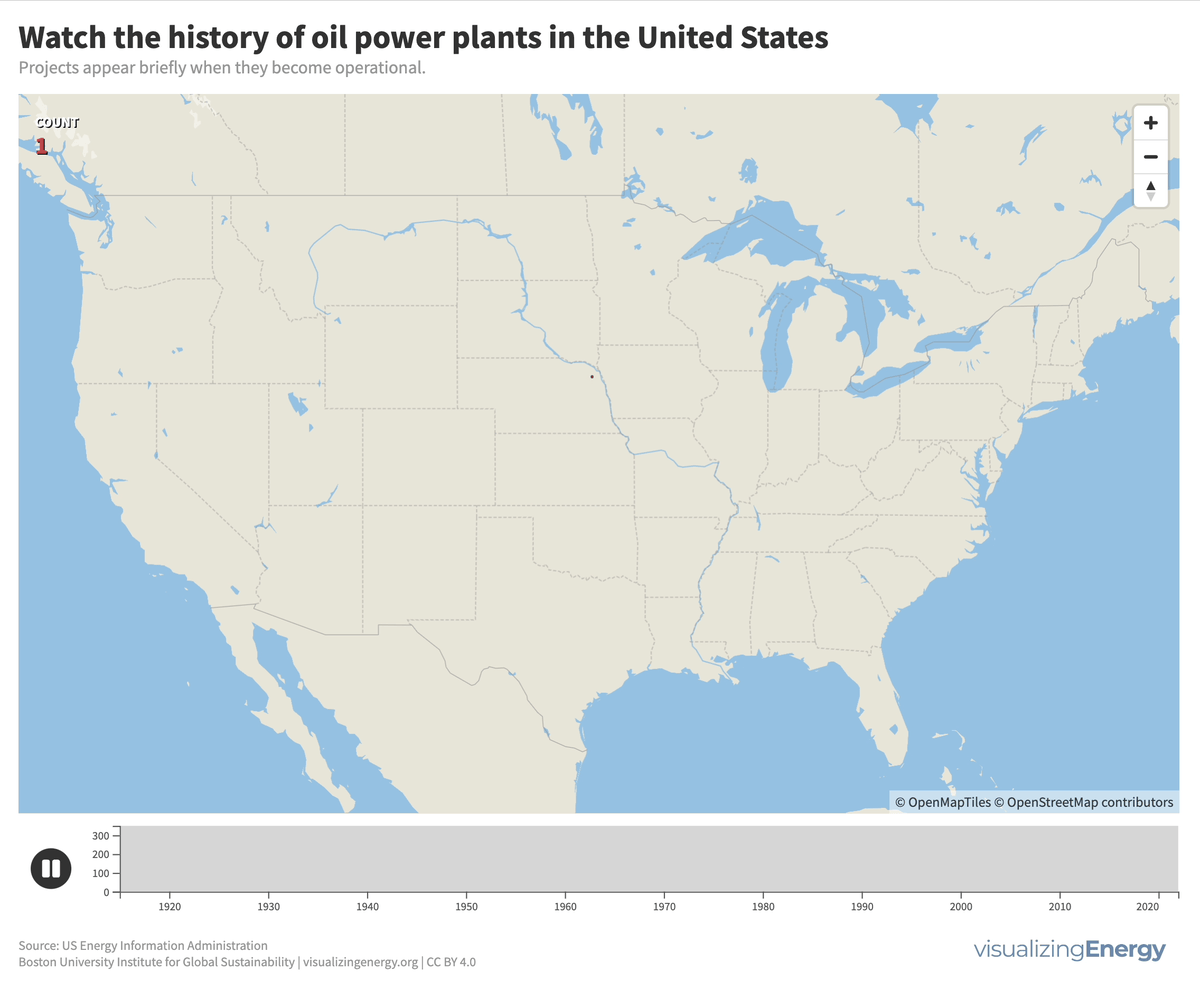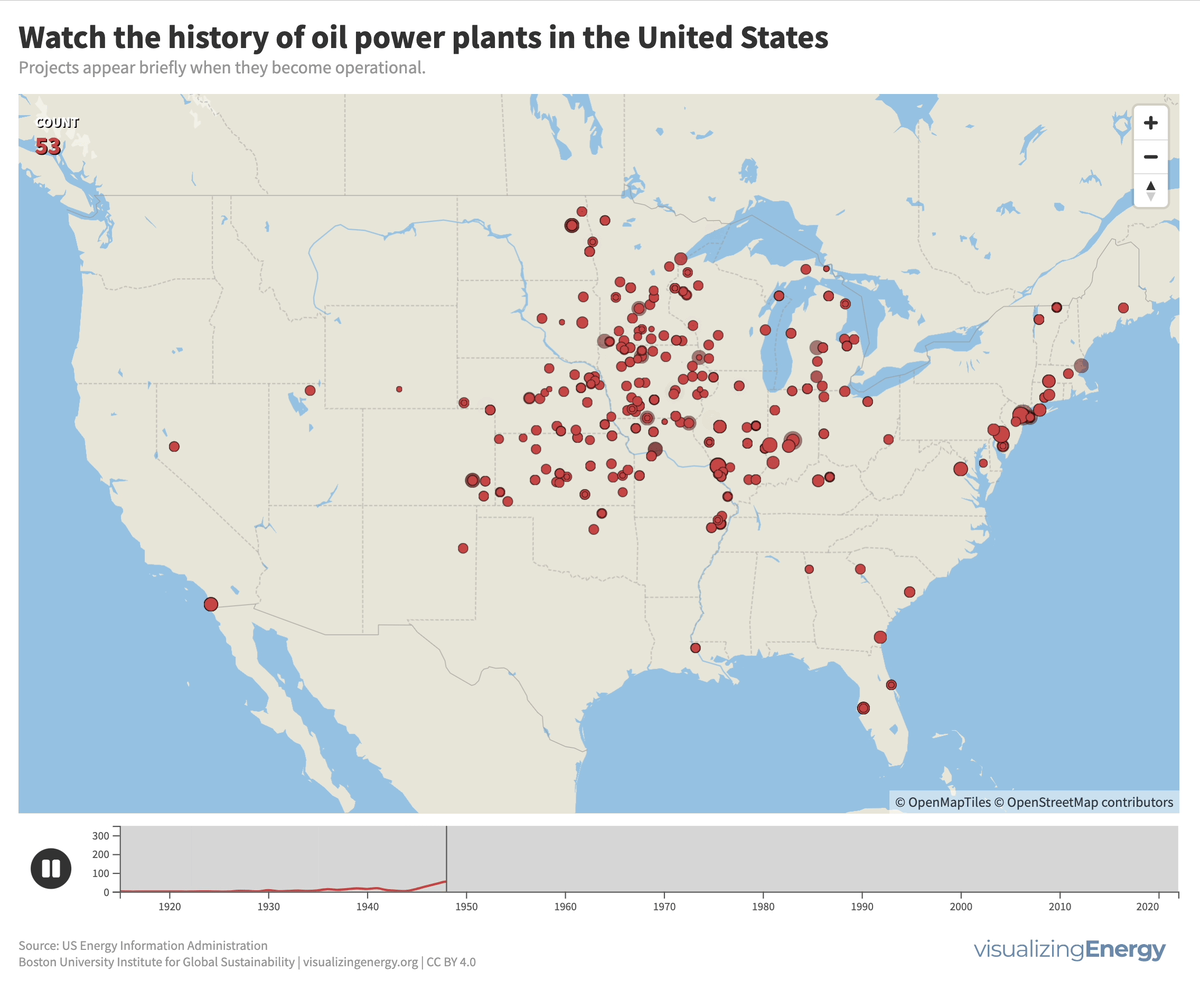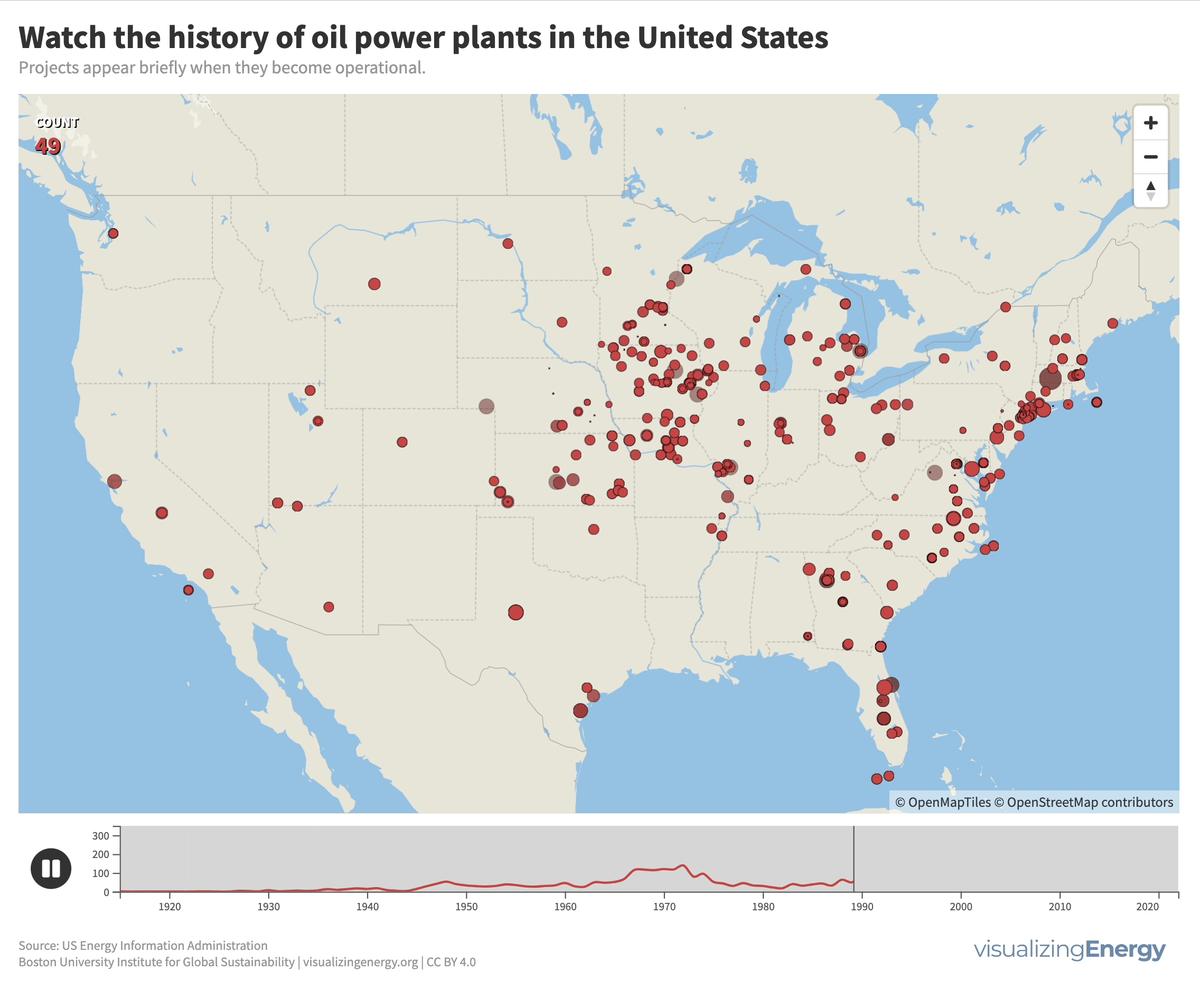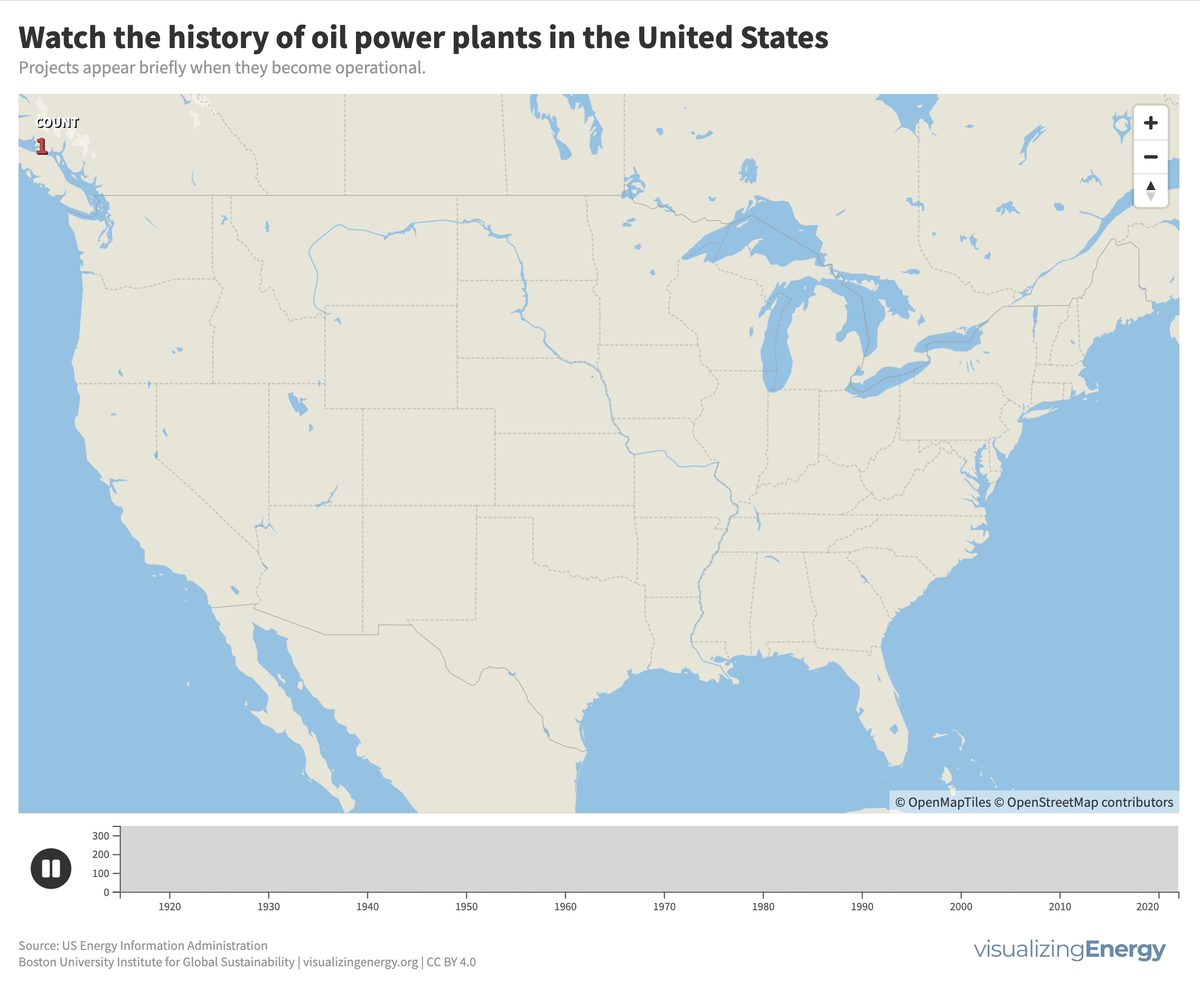
In 2022, the US had about 4,000 petroleum-burning generators, providing only 0.6% of the nation’s electricity due to lower efficiency and higher costs than alternatives. These smaller generators are mainly used for peak power and emergency backup, with policies since 1978 discouraging their use to reduce oil dependence for national security.
The history of coal production in the United States
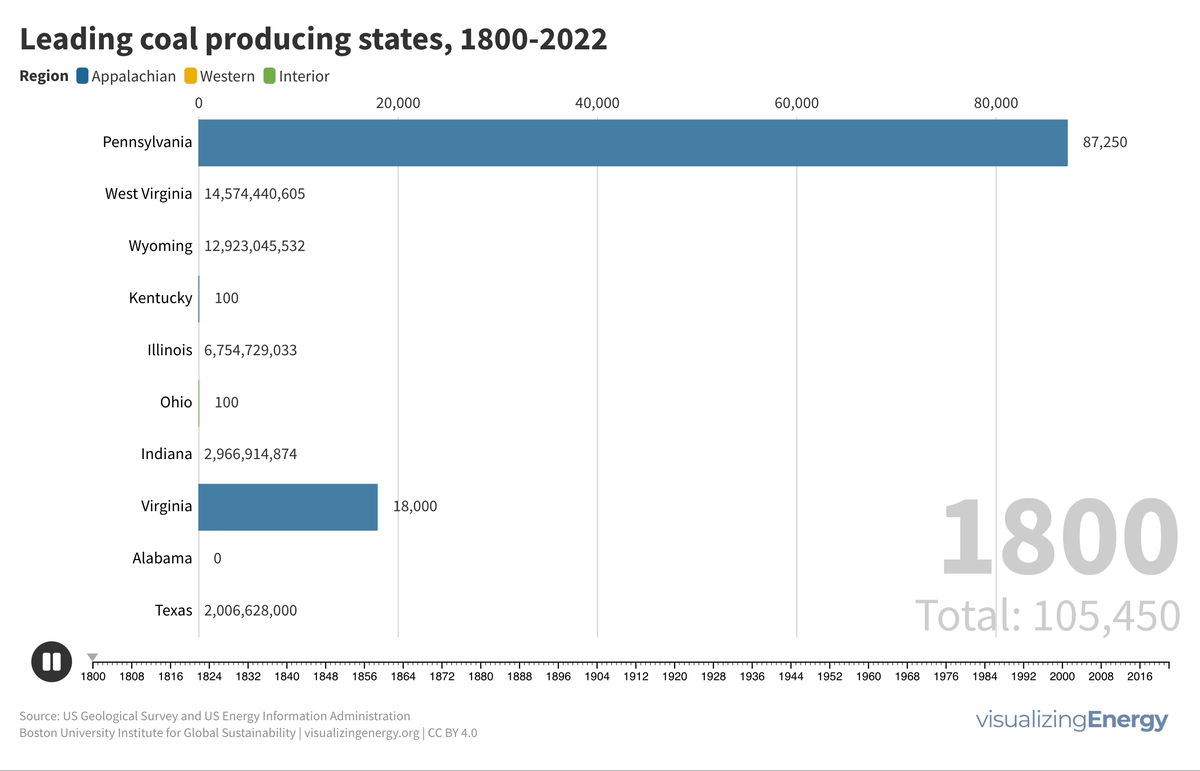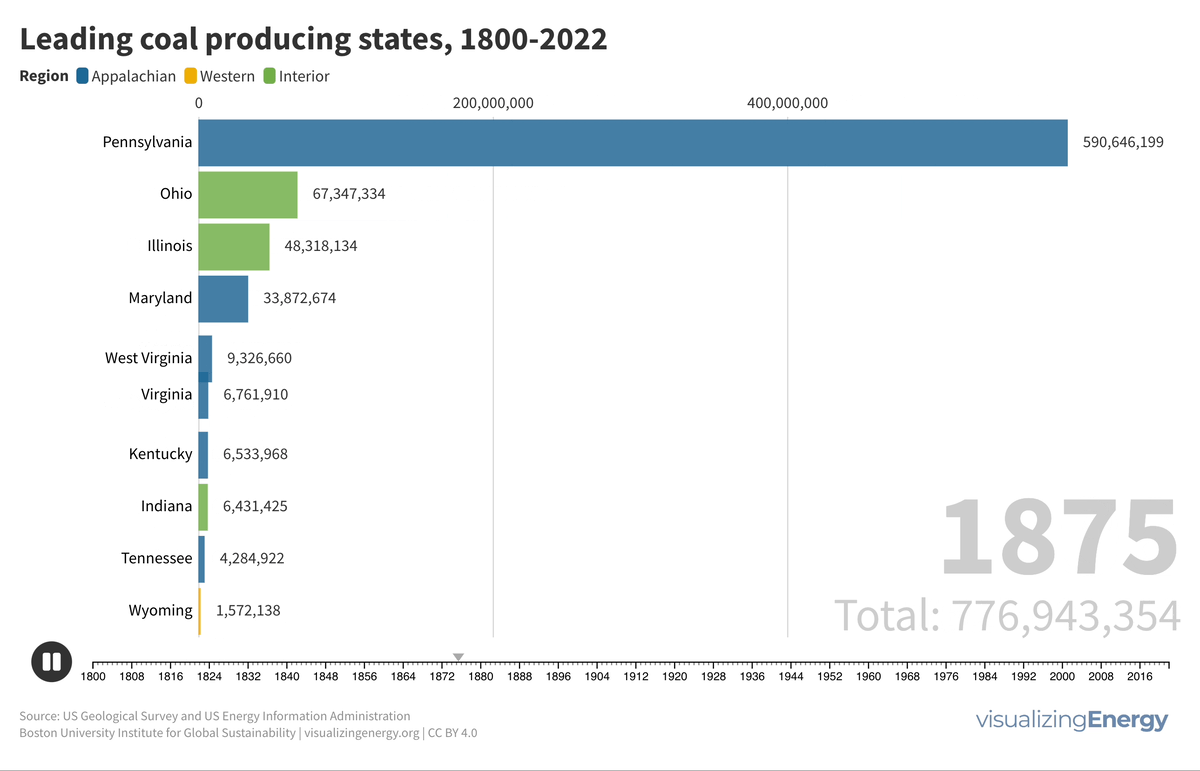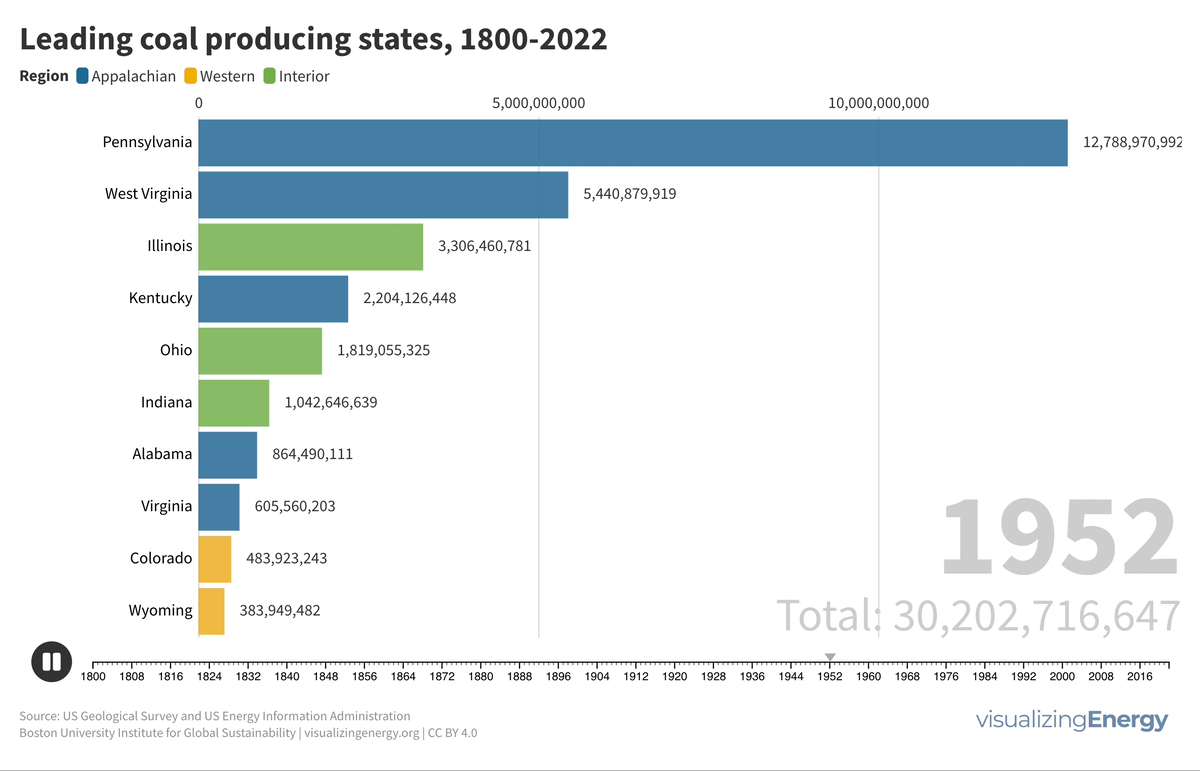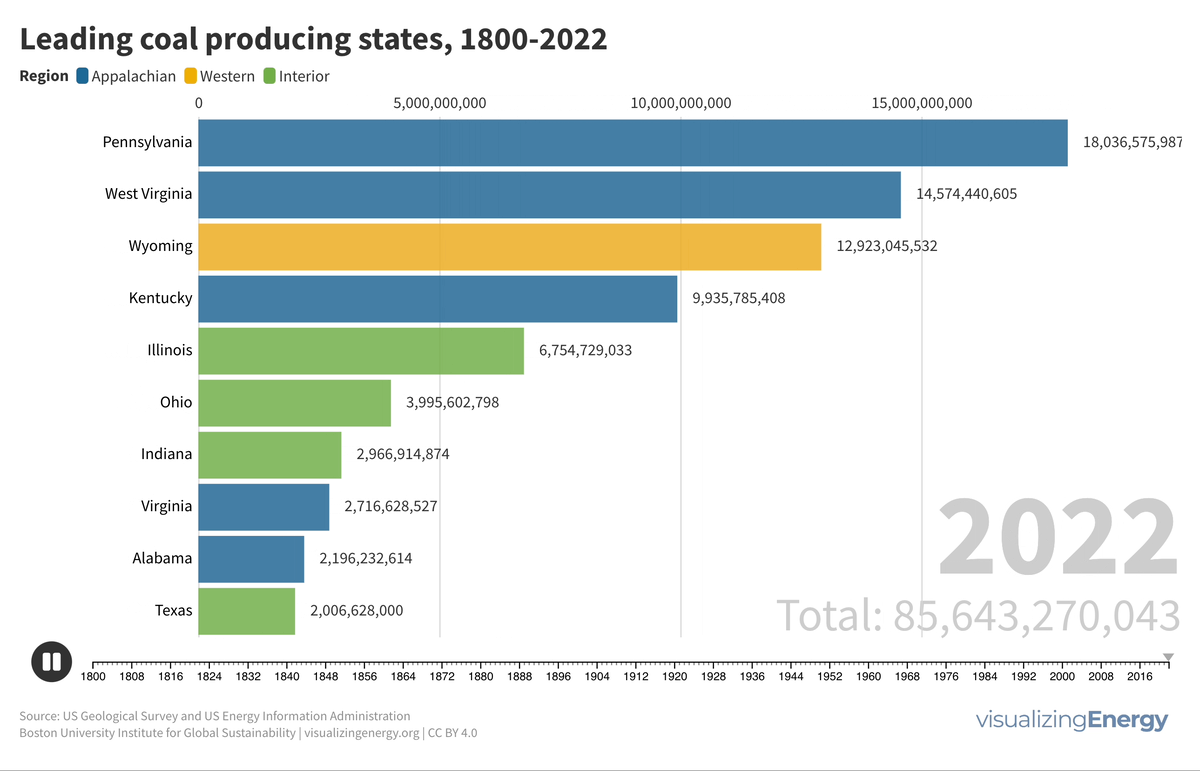
Coal has played a pivotal role in the United States’ industrial history, fueling steel production, electricity generation, and economic growth in the early 20th century. However, this legacy also comes with significant environmental and health issues, including miner health problems, landscape degradation, abandoned mines, and pollution.
Four million wells and counting: the history of oil and gas drilling in the U.S.
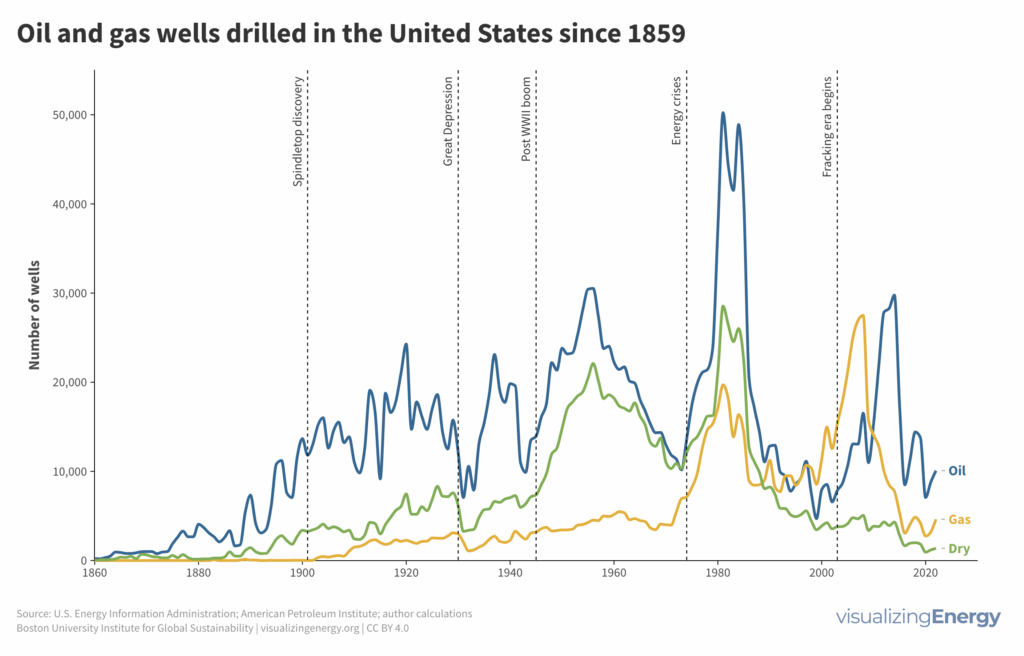
Since the first successful oil well in 1859, the U.S. has drilled millions of wells for oil and gas. Drilling surged with demand, technology, and geopolitics, with notable periods like the post-WWII boom and the fracking-driven increase in natural gas wells. This progress has brought economic benefits and energy shifts, yet also raised environmental and social concerns.
