Global anthropogenic sulfur dioxide emissions, 1750-2022
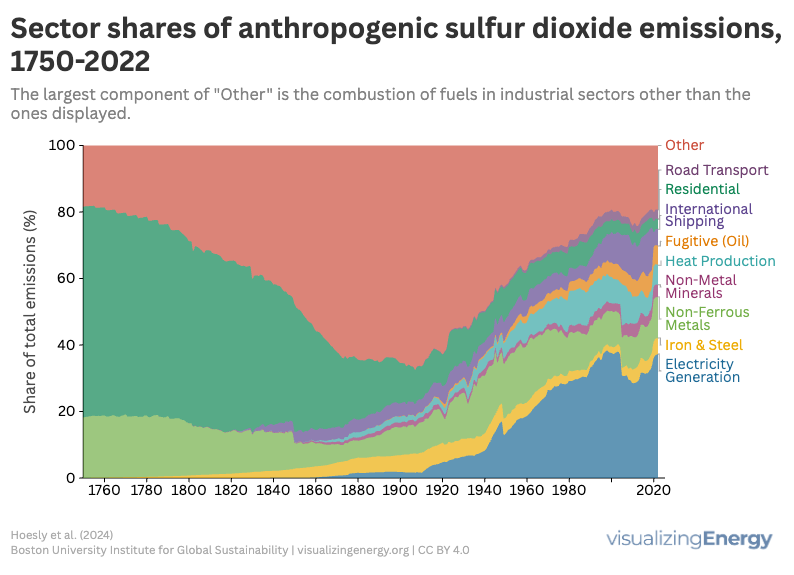
Sulfur dioxide (SO₂) is a major air pollutant produced from burning sulfur-containing fuels. It poses health risks, including respiratory issues and links to heart disease, while harming the environment by contributing to acid rain. Emissions have significantly decreased due to regulations and technology, but global reliance on fossil fuels continues to impact levels.
Underground natural gas storage in the United States
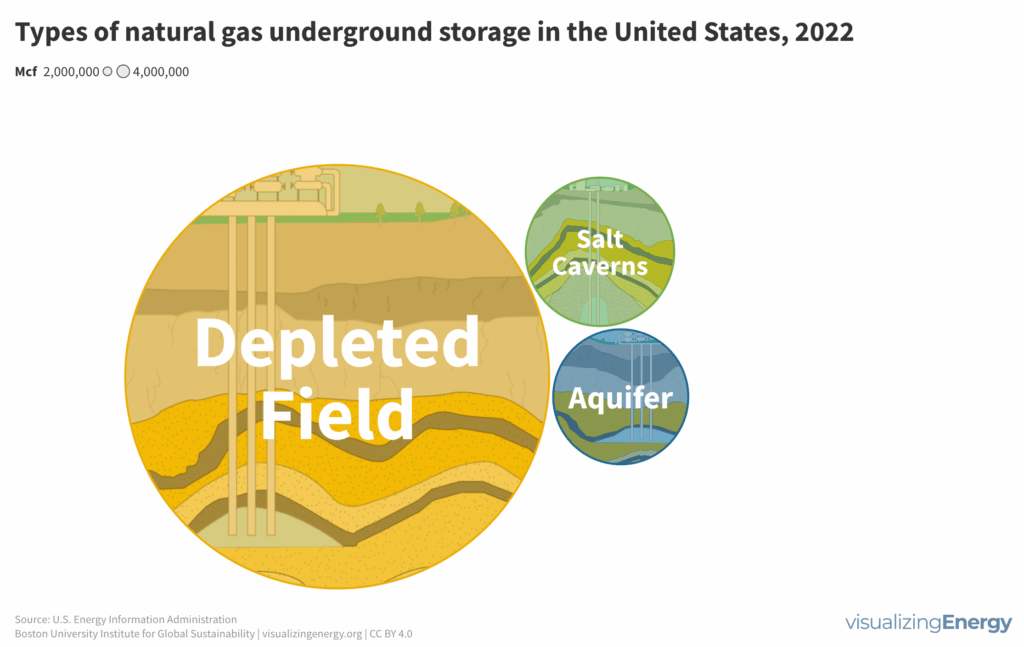
Natural gas demand in the U.S. varies seasonally, with higher consumption during colder months potentially causing price increases due to supply shortages. Underground storage, primarily in depleted reservoirs, salt caverns, and aquifers, helps balance supply and demand year-round. Storage levels drop significantly during colder winters, affecting overall availability.
What happens to low level nuclear waste in the United States?
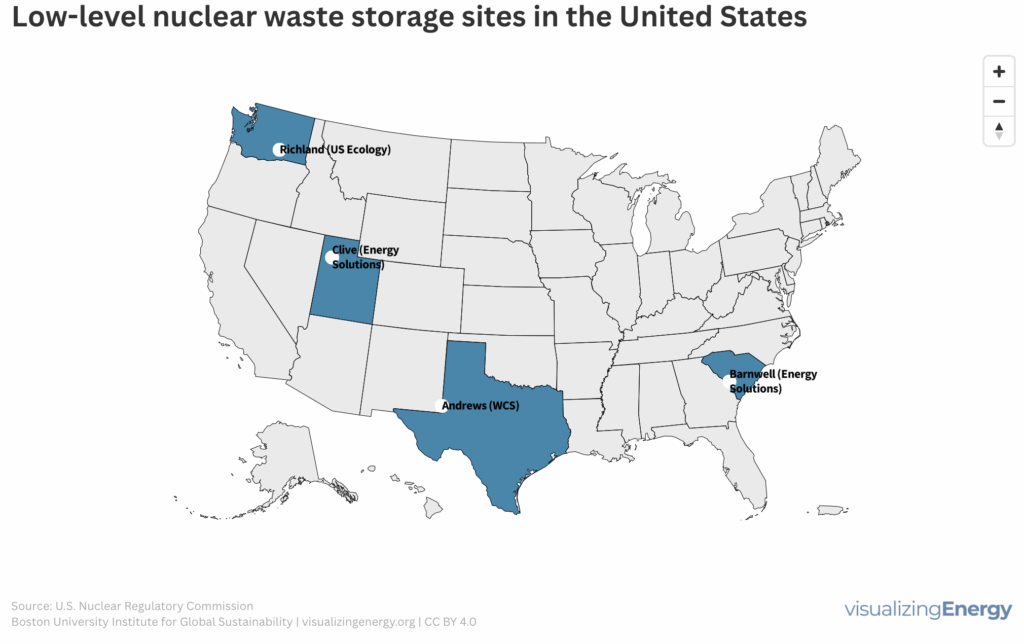
Low-level radioactive waste (LLW) is produced by various commercial operations and the U.S. Department of Energy. It includes contaminated materials like clothes, tools, and medical supplies. LLW is typically stored on-site until it decays or is shipped to disposal sites, regulated under the Low-Level Radioactive Waste Policy Act of 1980.
Sankey diagrams for national energy systems
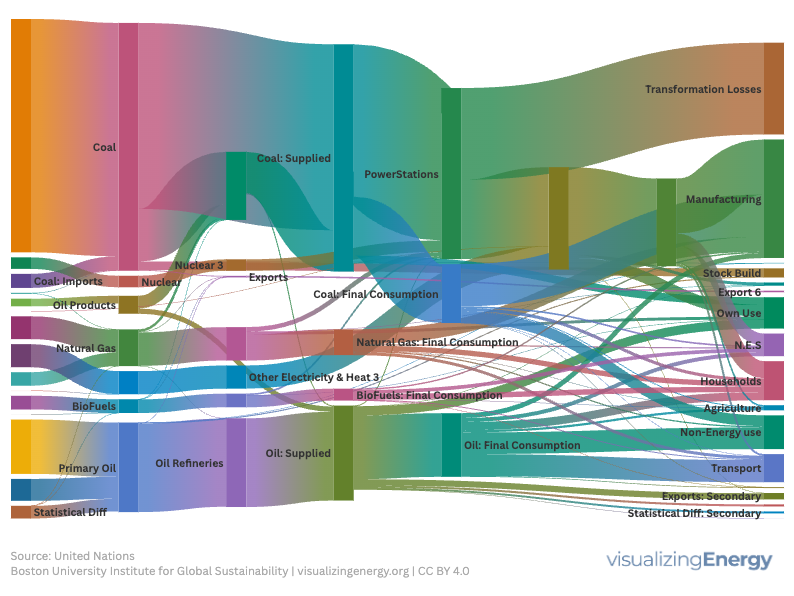
In 1898, H. Riall Sankey developed a diagram illustrating steam engine efficiency, leading to the widespread use of Sankey diagrams for visualizing energy flows in various systems. They effectively display energy extraction, transformation, consumption, and losses while mapping the roles of primary and secondary energy sources across different usage sectors.
Satellite detection of methane plumes, 2022-2024

Satellites significantly enhance our understanding of methane emissions, responsible for about 30% of anthropogenic global warming. The United Nations Environment Programme’s Methane Alert and Response System detects plumes from waste, oil, gas, and coal, identifying super emitters to improve emissions accountability. Methane from waste facilities is particularly concerning due to inefficient capture methods.
Global natural gas flaring, 2012-2023
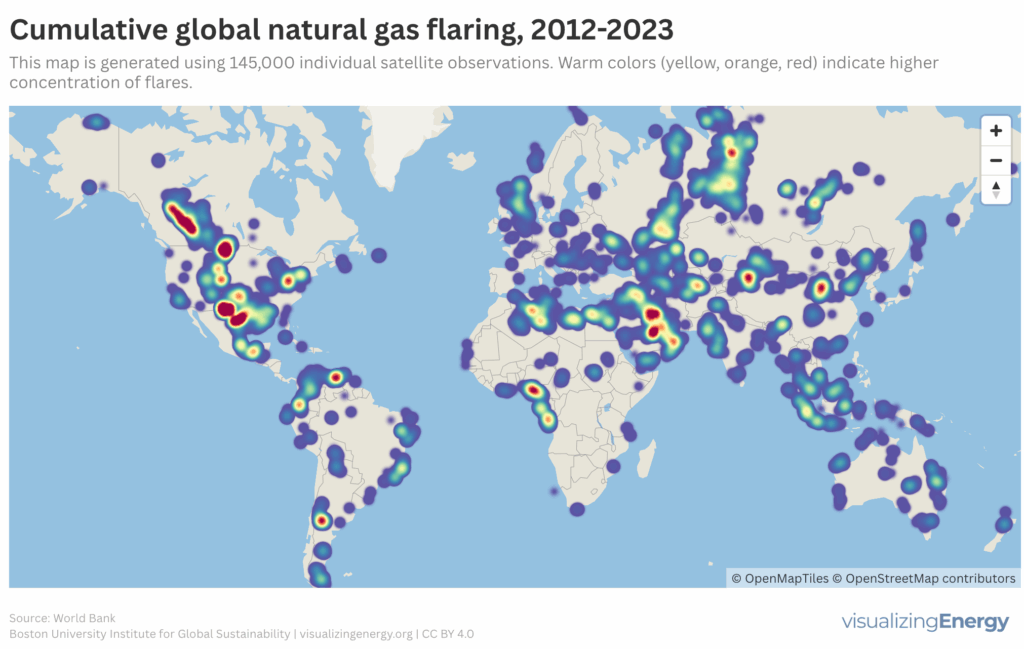
Crude oil and natural gas often coexist in reservoirs, leading to natural gas flaring when oil is extracted. This process not only wastes energy but also contributes significantly to global methane emissions. Despite initiatives like the Zero Routine Flaring by 2030, flaring volumes remain high, particularly in nine major countries responsible for the majority.
Peak shaving facilities in the United States
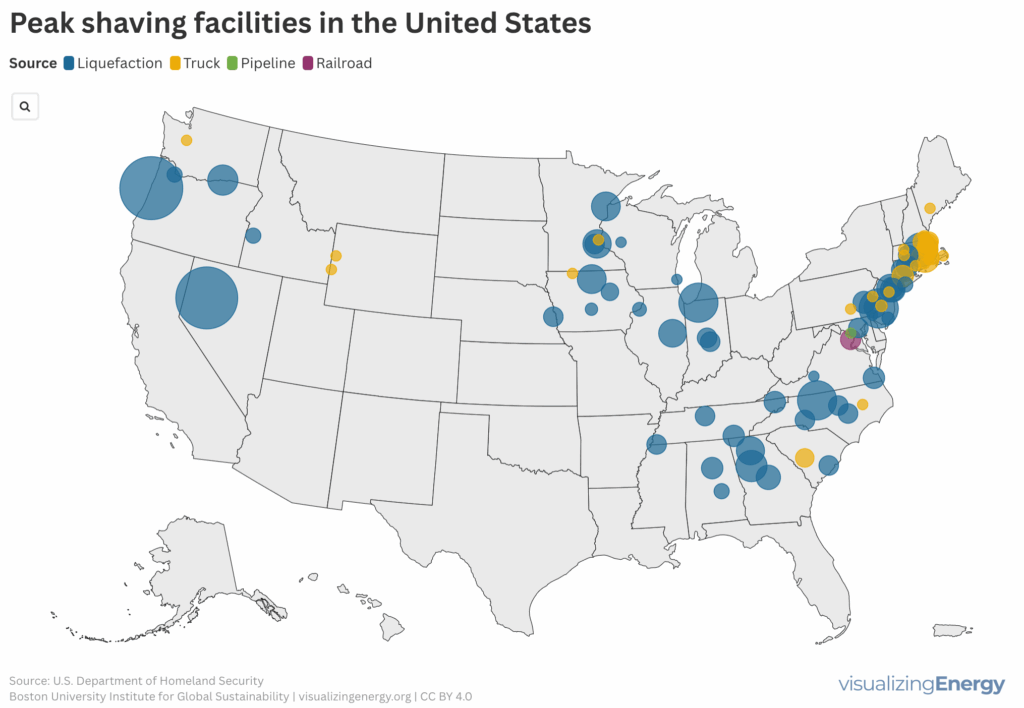
A peak shaving facility is an energy system that balances fuel demand fluctuations, particularly for natural gas during peak usage times. It stores liquefied natural gas (LNG) at low demand and releases it when needed. Commonly found in metropolitan areas and regions with pipeline limitations, these facilities aid in preventing shortages and price spikes.
Where are people most exposed to particulate matter?
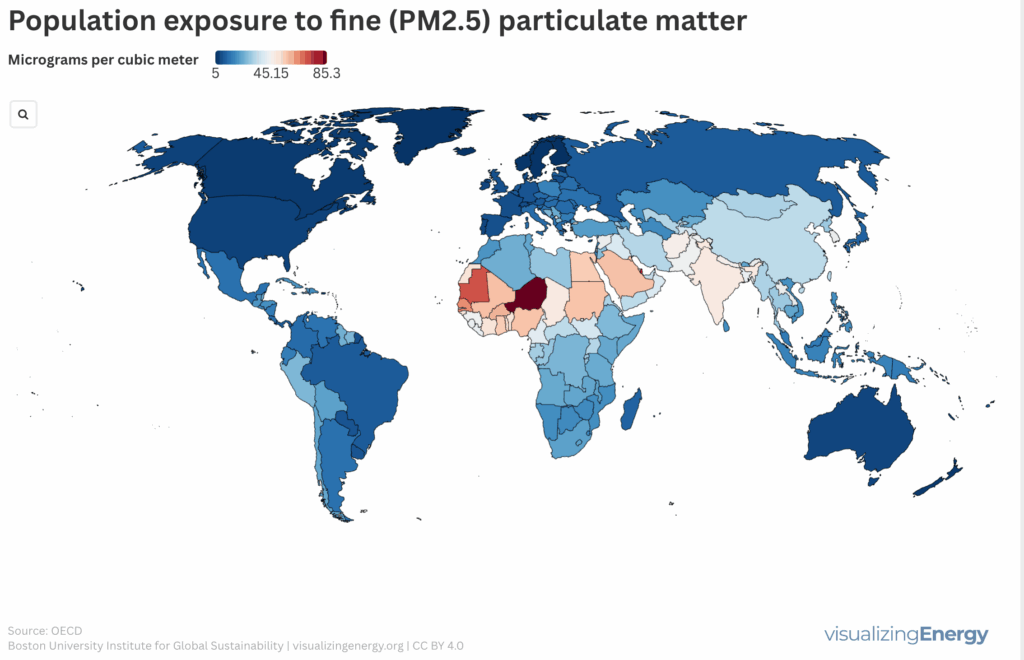
Airborne particulate matter (PM2.5) comprises tiny particles that pose significant health risks, including heart disease and lung cancer. Major sources include natural events and human activities, with notable geographic variations. Reductions in PM2.5 levels have been observed in affluent regions, but exposure remains high in countries like China and India, impacting public health.
Global anthropogenic nitrous oxide emissions, 1970-2022
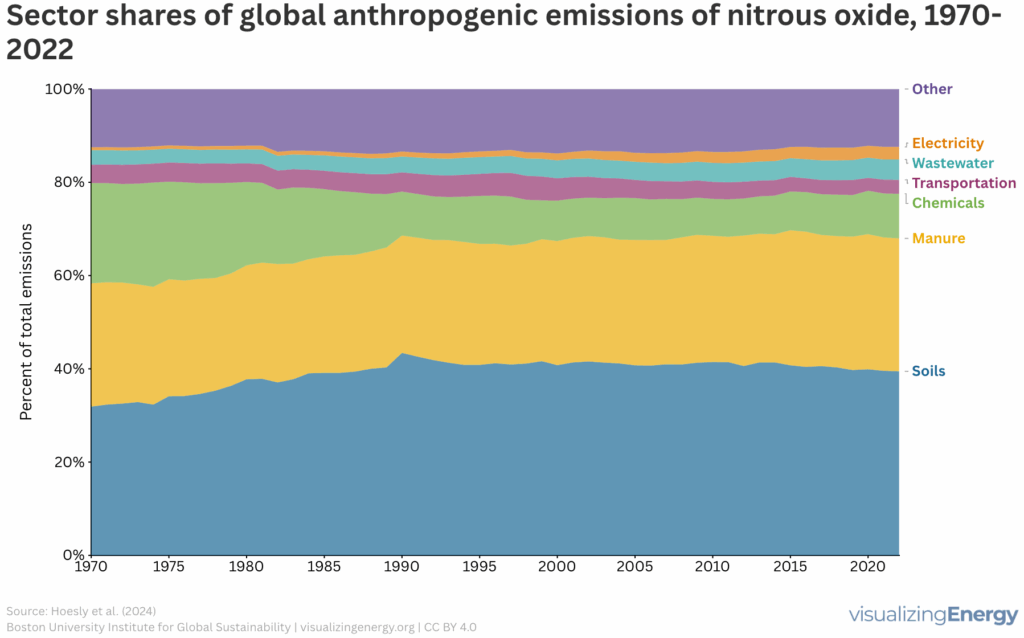
Nitrous oxide (N2O) is a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change and ozone depletion, with human activities significantly increasing its emissions since the 1970s. Key sources include agricultural practices, livestock manure, and industrial emissions. Action is necessary across sectors to mitigate N2O emissions and improve nutrient management strategies.
Why are gasoline prices lower in oil-exporting countries?
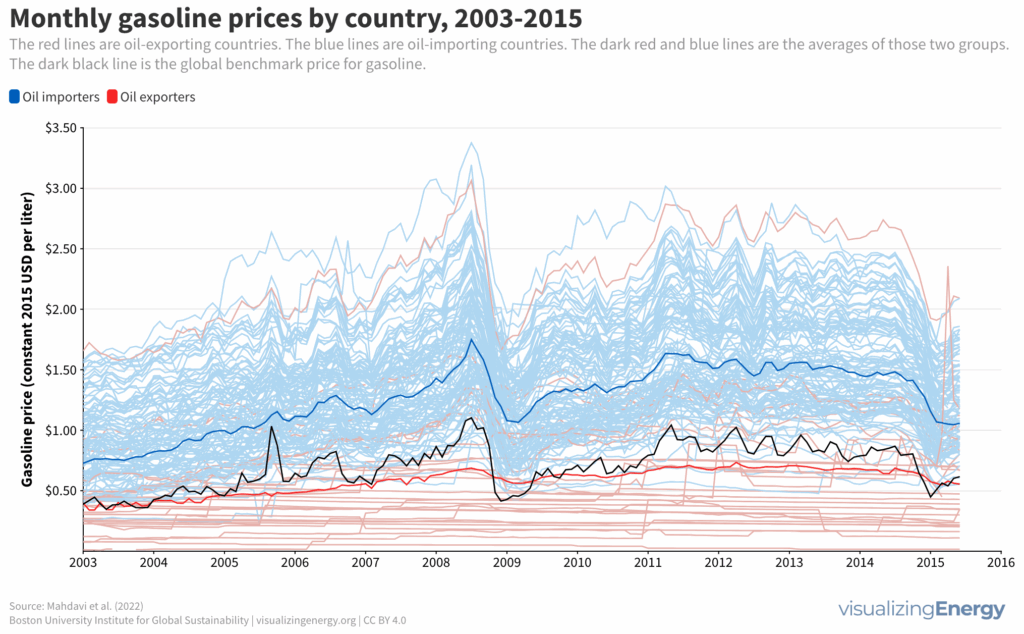
Government policies significantly influence gasoline prices, leading to disparities across countries. Most nations tax gasoline, while some subsidize it, especially oil exporters. Higher income countries typically impose steeper gasoline taxes to harness revenue. There’s a growing call to reduce fossil fuel subsidies to curtail greenhouse gas emissions, advocating for carbon pricing to promote clean technology.
