What is the status of women in the global wind energy industry?
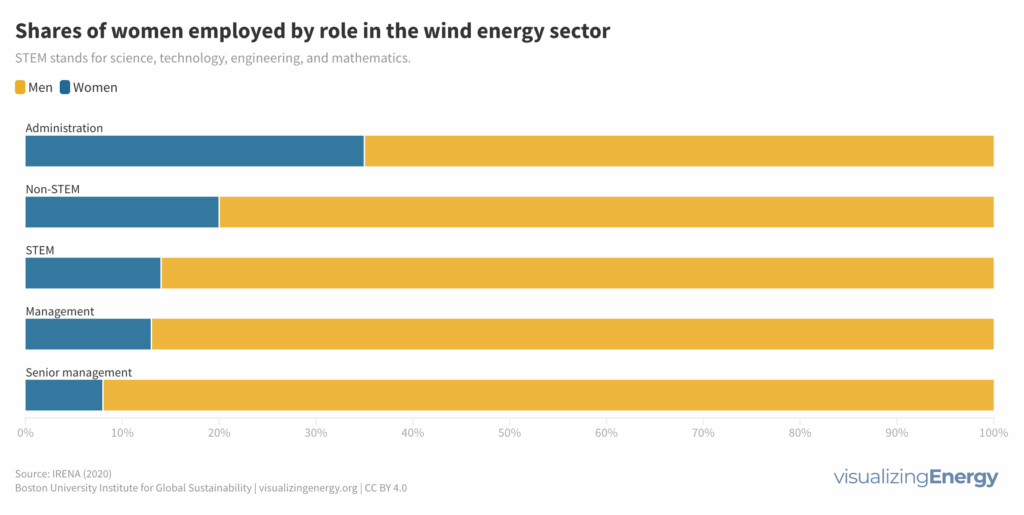
The global wind energy industry has seen substantial growth, but women make up only 21% of its workforce, lagging behind other renewable energy sectors. Barriers to gender equity include cultural norms, limited awareness of opportunities, and lack of support policies. Companies can promote change by prioritizing fairness, transparency, and work-life balance.
United States electricity history in four charts
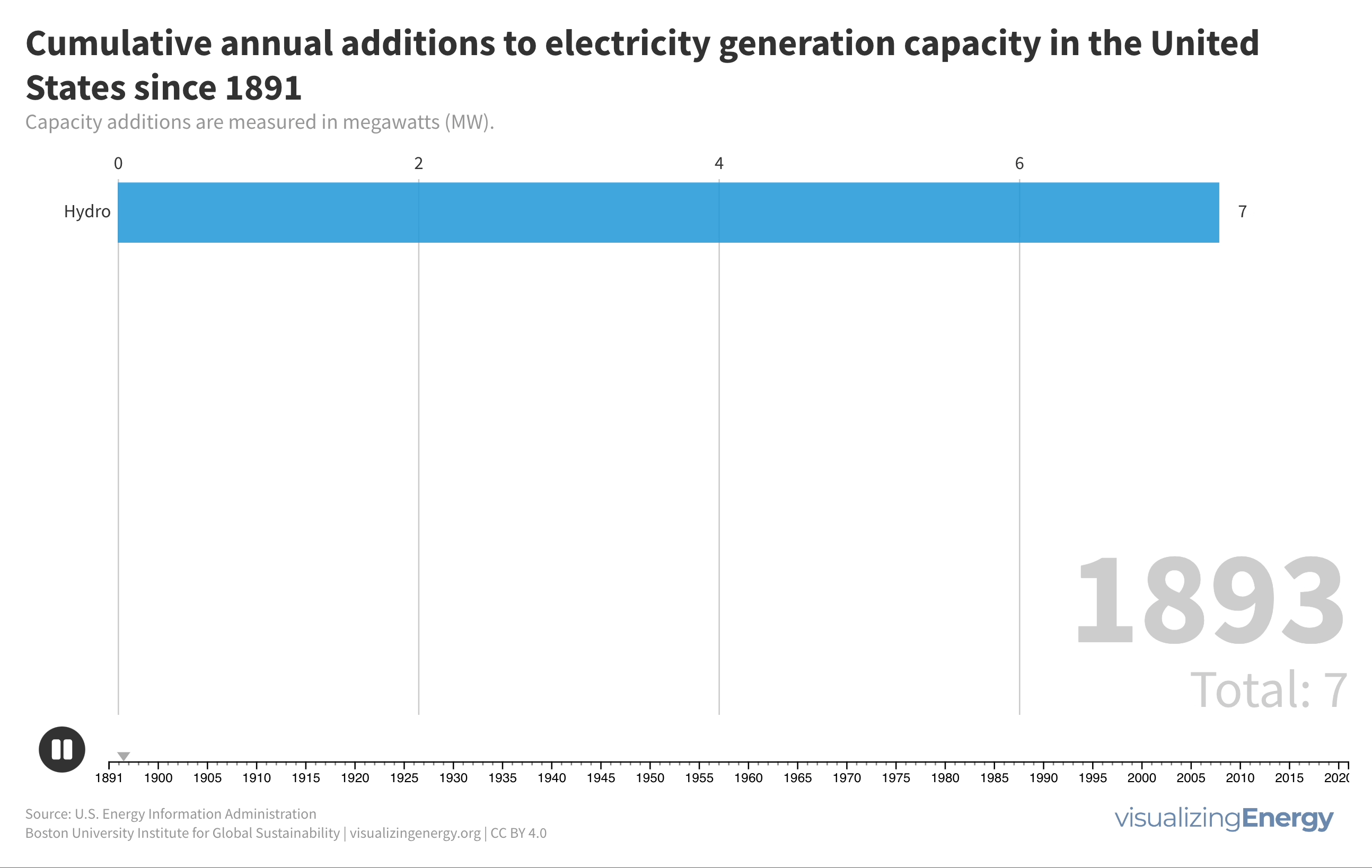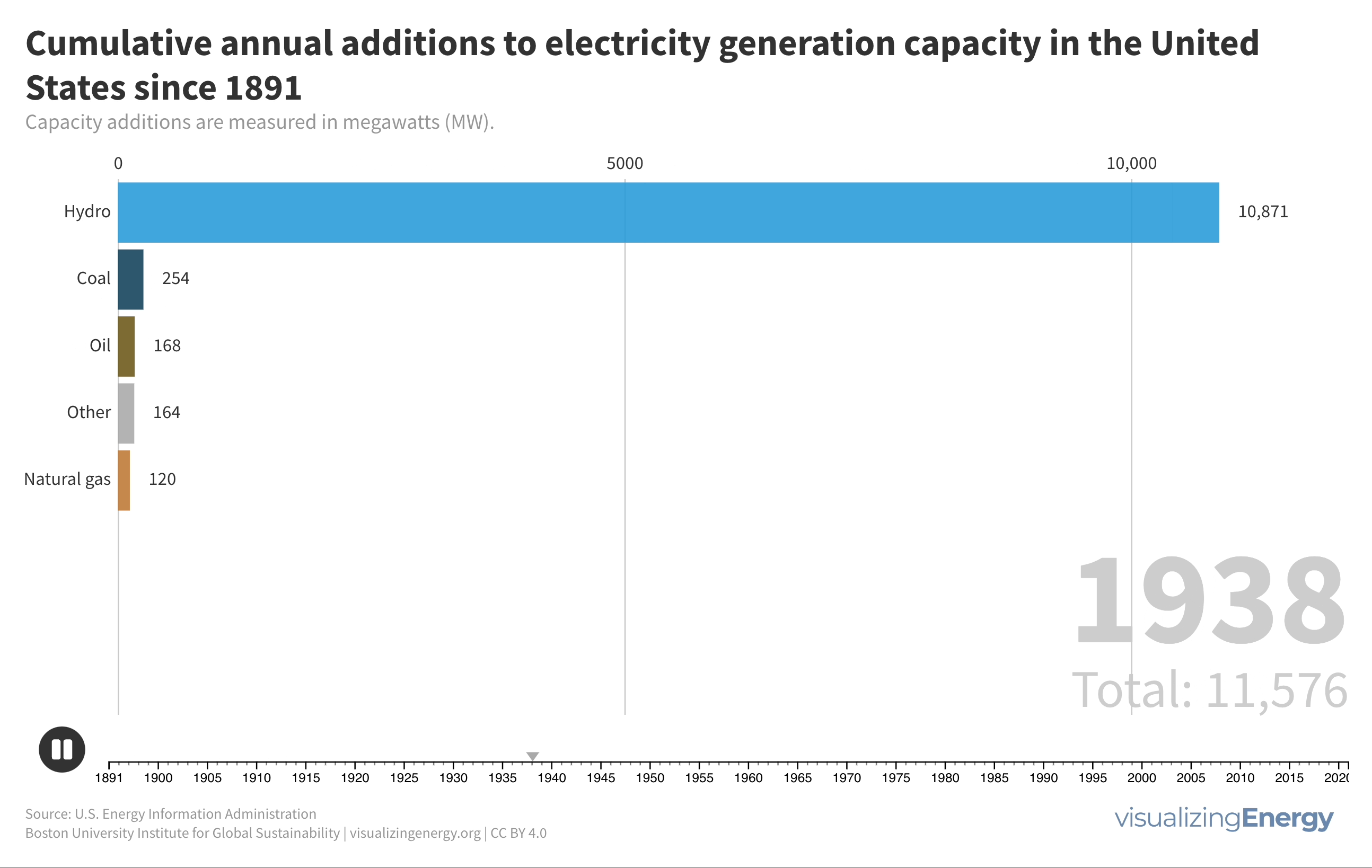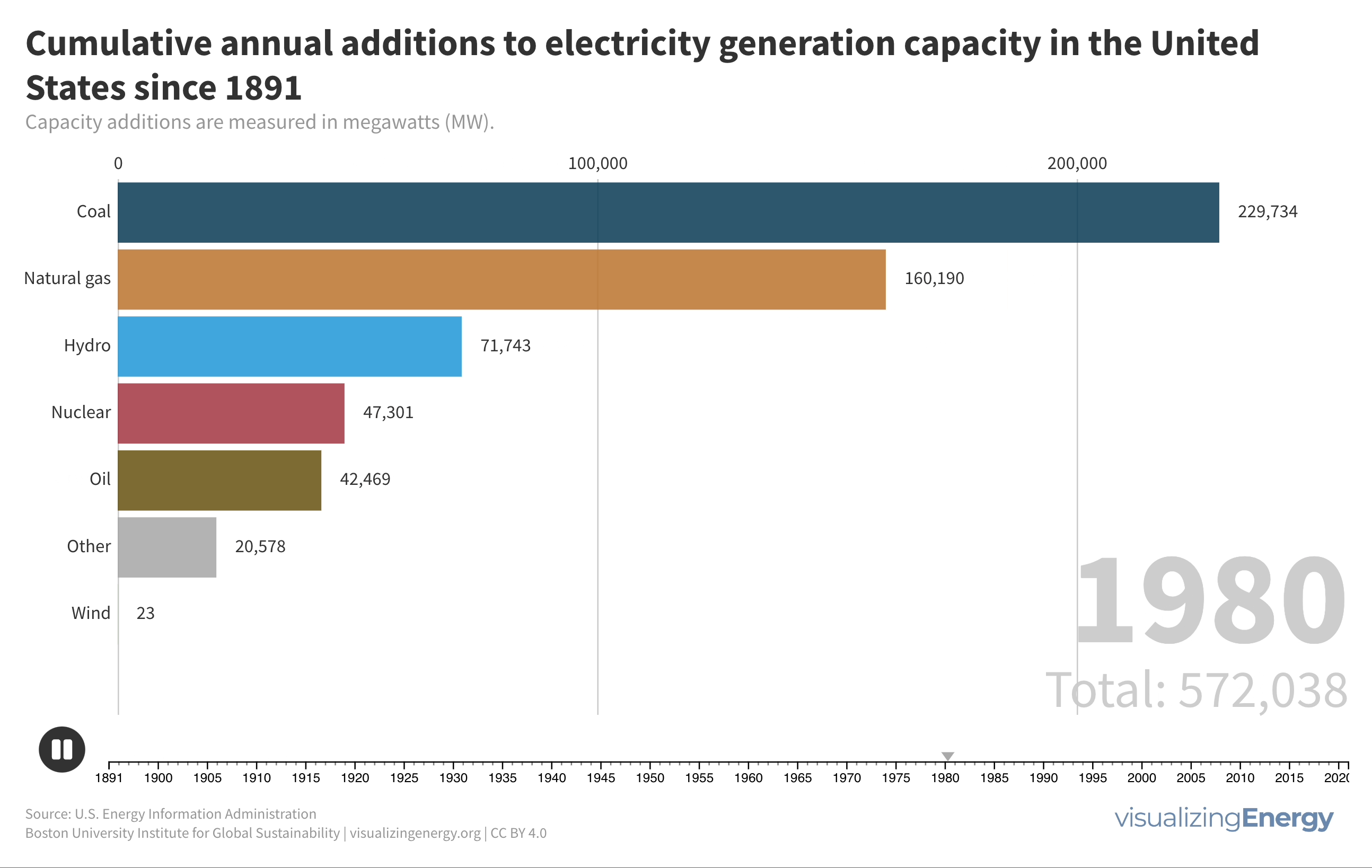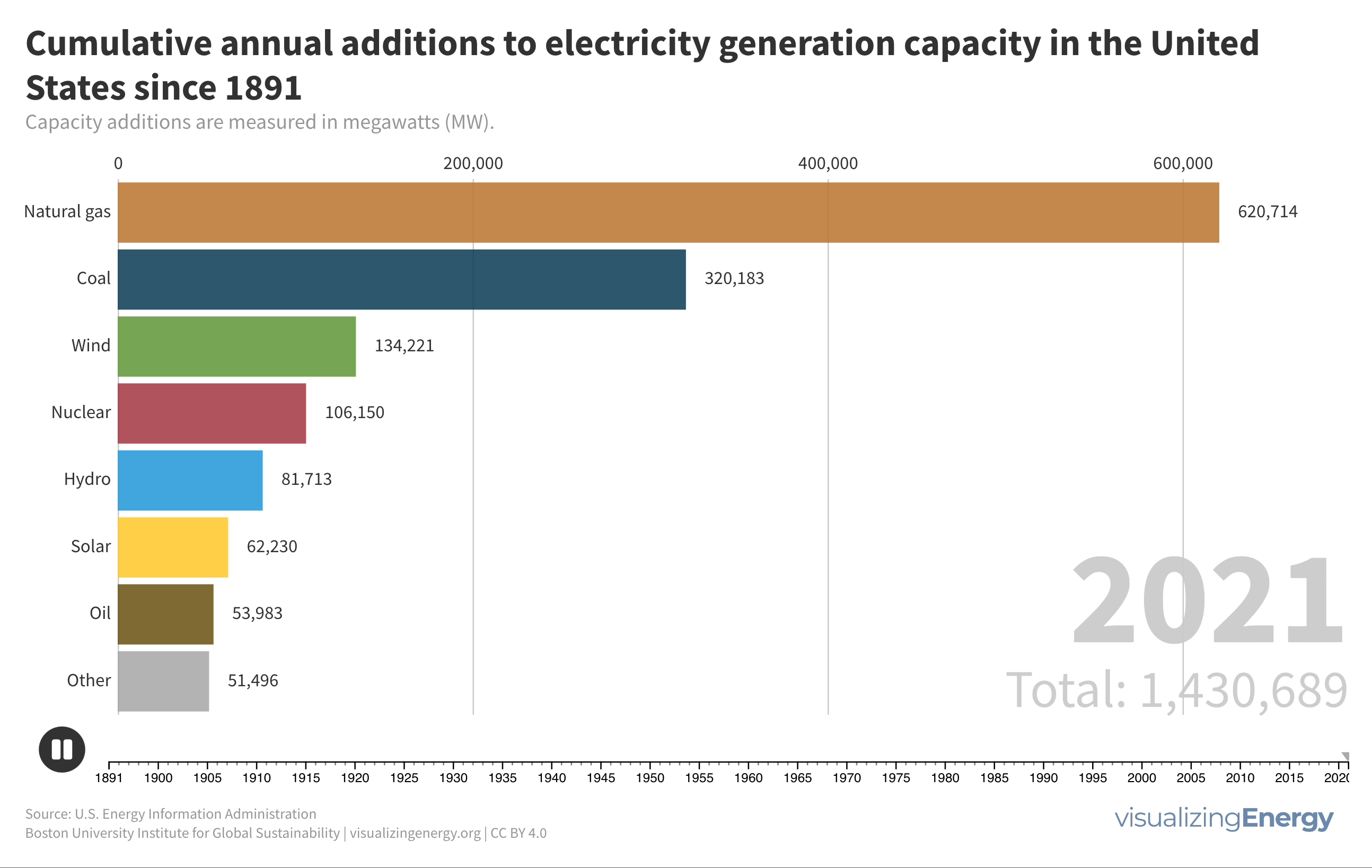
Electricity in the United States has seen remarkable growth, with a significant shift from coal to renewable energy sources. Government policies and technological advancements have played a crucial role in shaping the energy landscape. President Biden’s goal of achieving 100% carbon-free electricity by 2035 highlights the need for continued progress in policy, technology, and public perception.
United States energy history in two charts
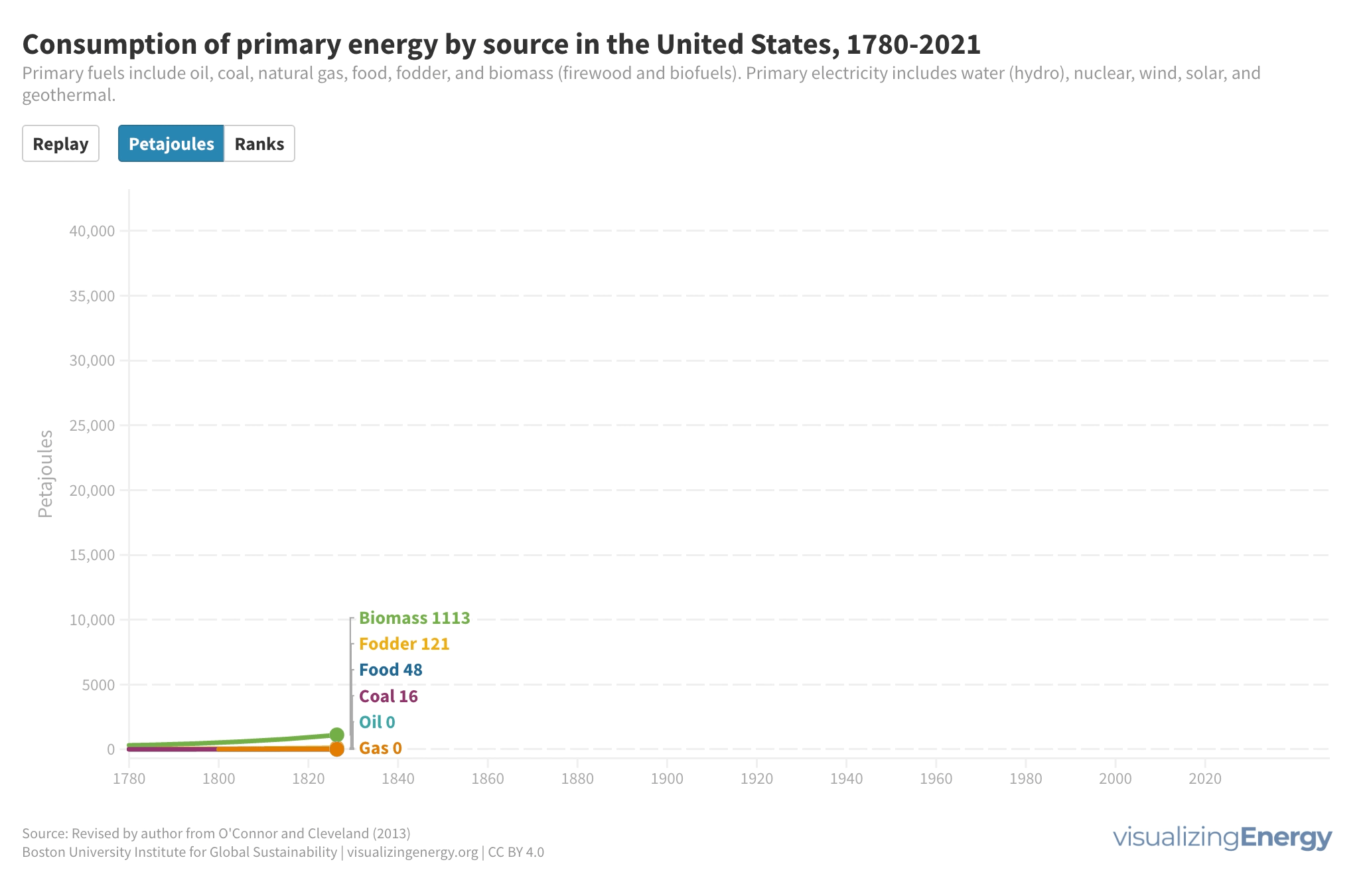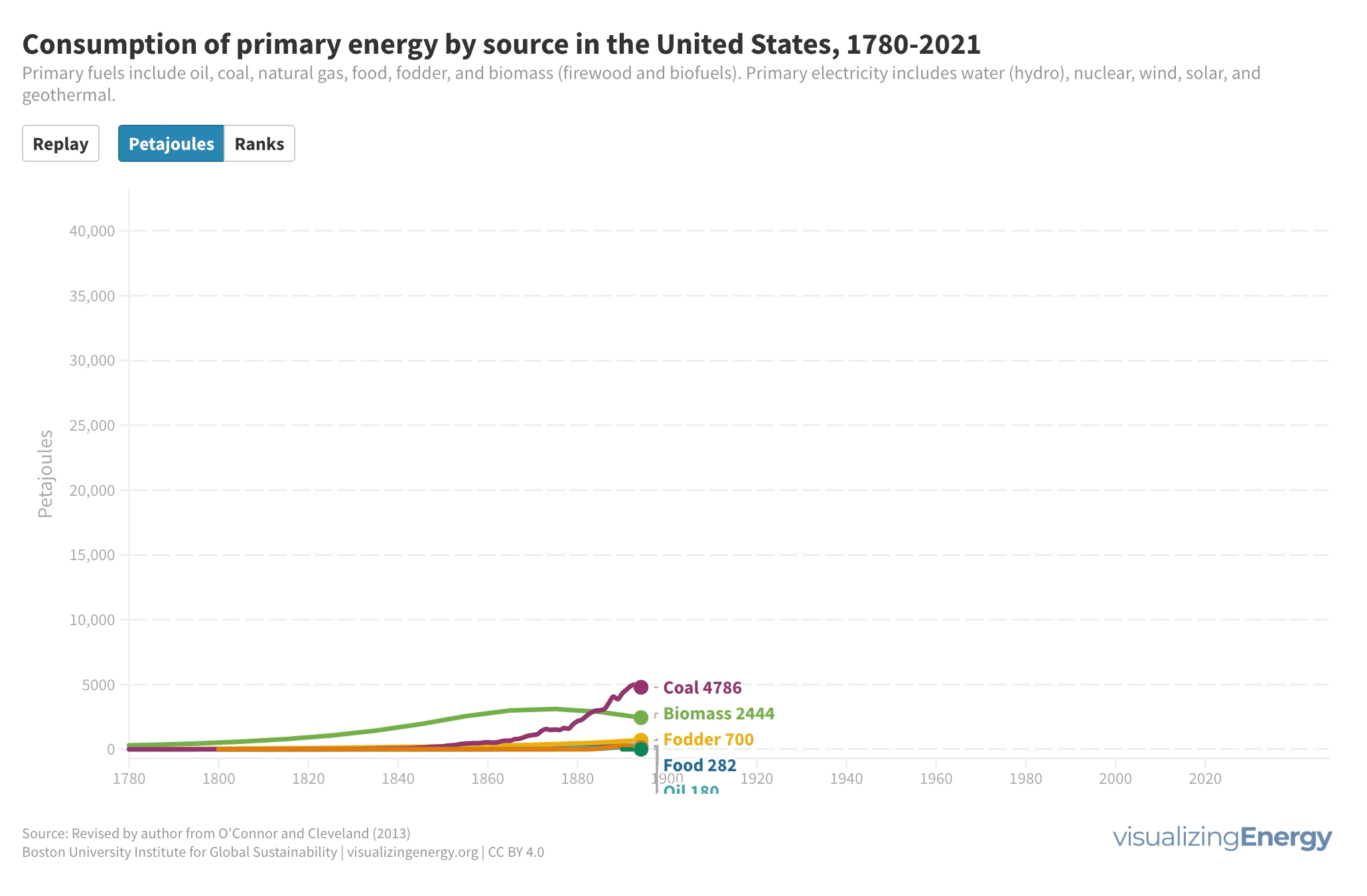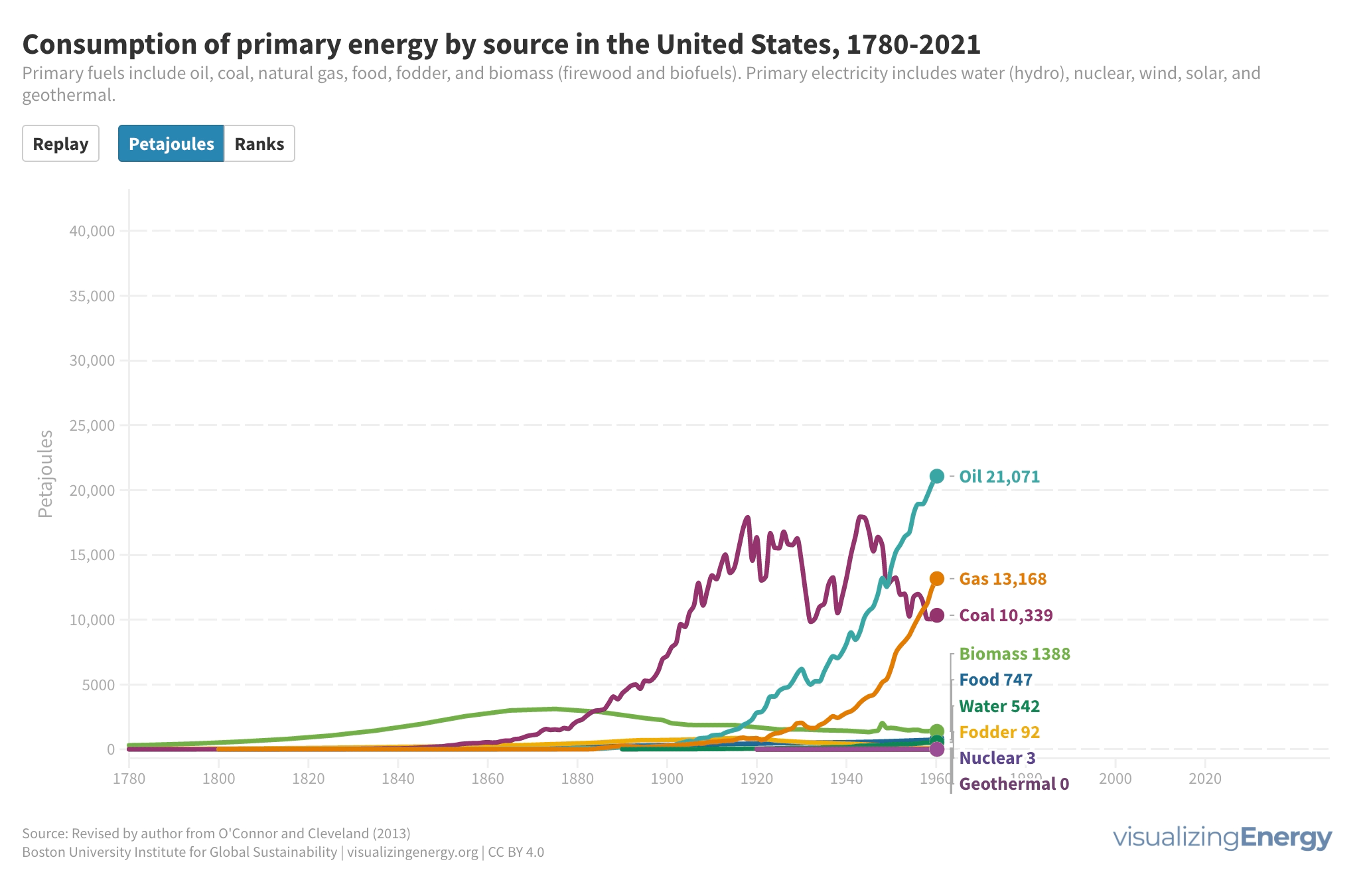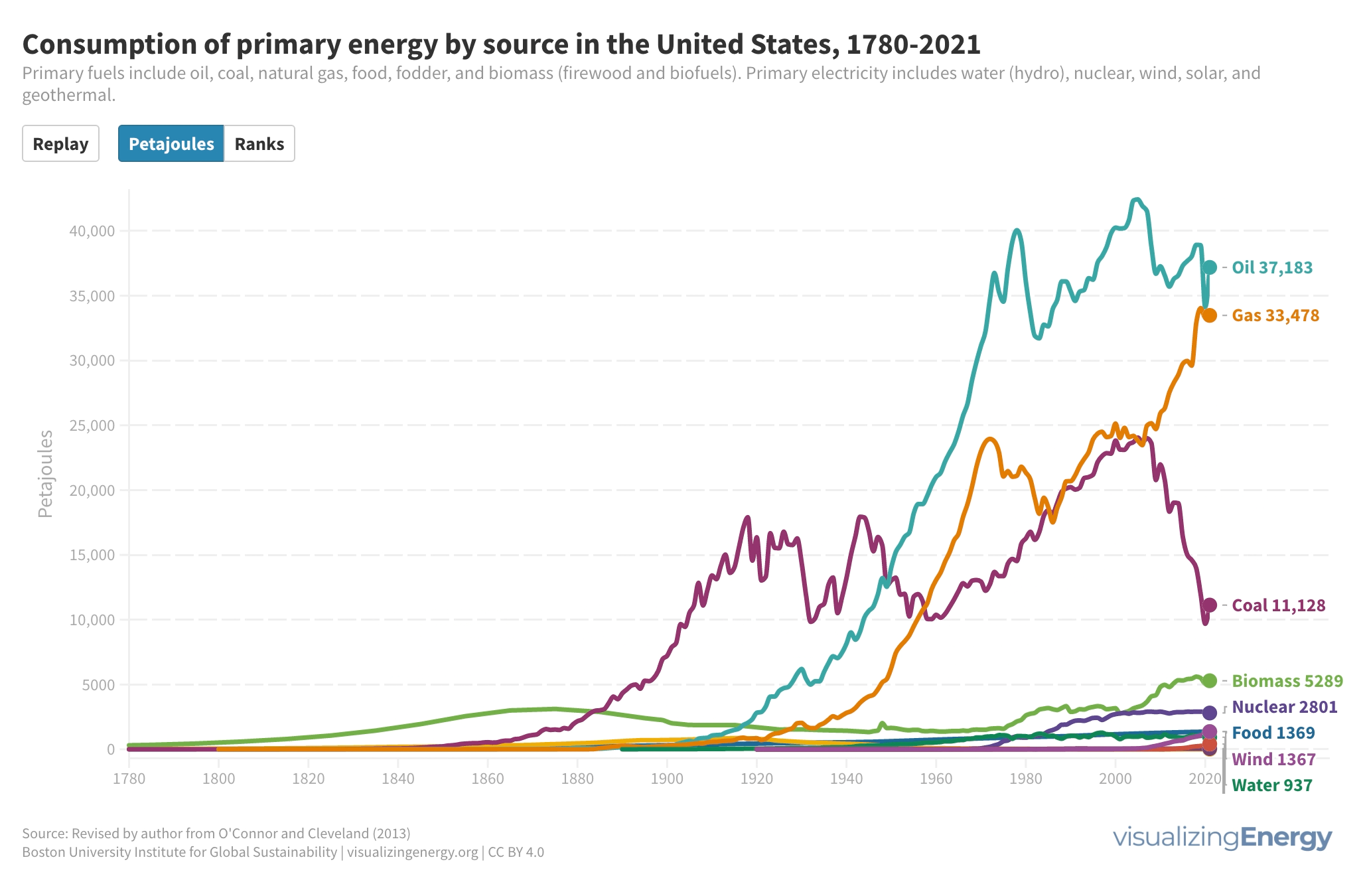
The United States has experienced a substantial increase in energy consumption over time, driven by factors like population growth and technological advancements. The transition from forests to coal, followed by oil and natural gas, has shaped the country’s energy sources. However, fossil fuels still dominate energy use, highlighting the need for a rapid shift towards renewable and low-carbon alternatives.
What are the connections among fuel poverty, time poverty, and gender equity?
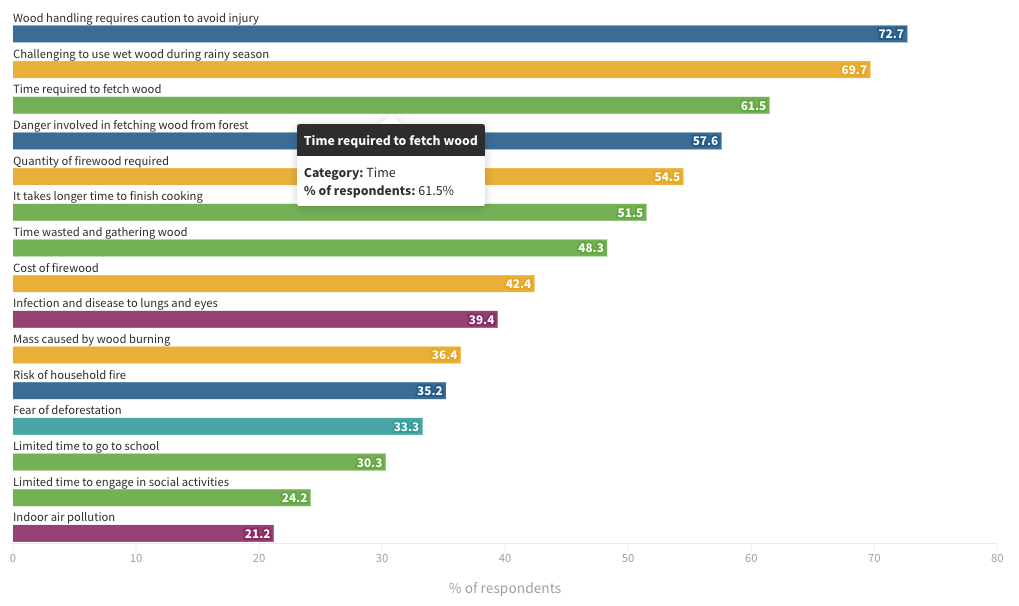
Access to clean cooking fuels is crucial for gender equity and poverty alleviation. Currently, billions of people lack safe and affordable energy sources for cooking. Women and girls bear a disproportionate burden in collecting and processing polluting fuels, affecting their well-being and opportunities. Clean cooking energy reduces cooking time, allowing women to engage in other activities like childcare, work, and household chores.
Where is new wind power in the world being built?
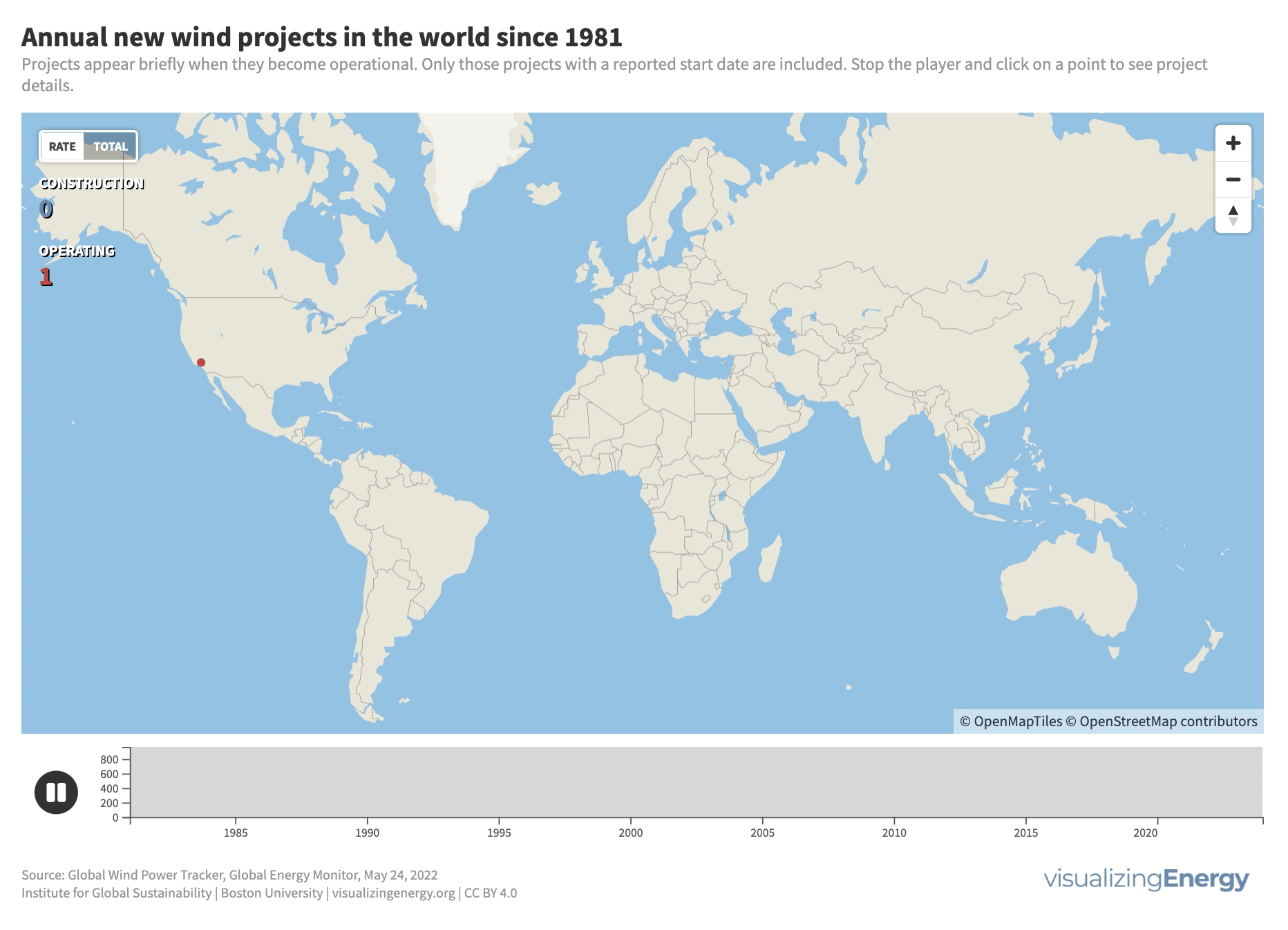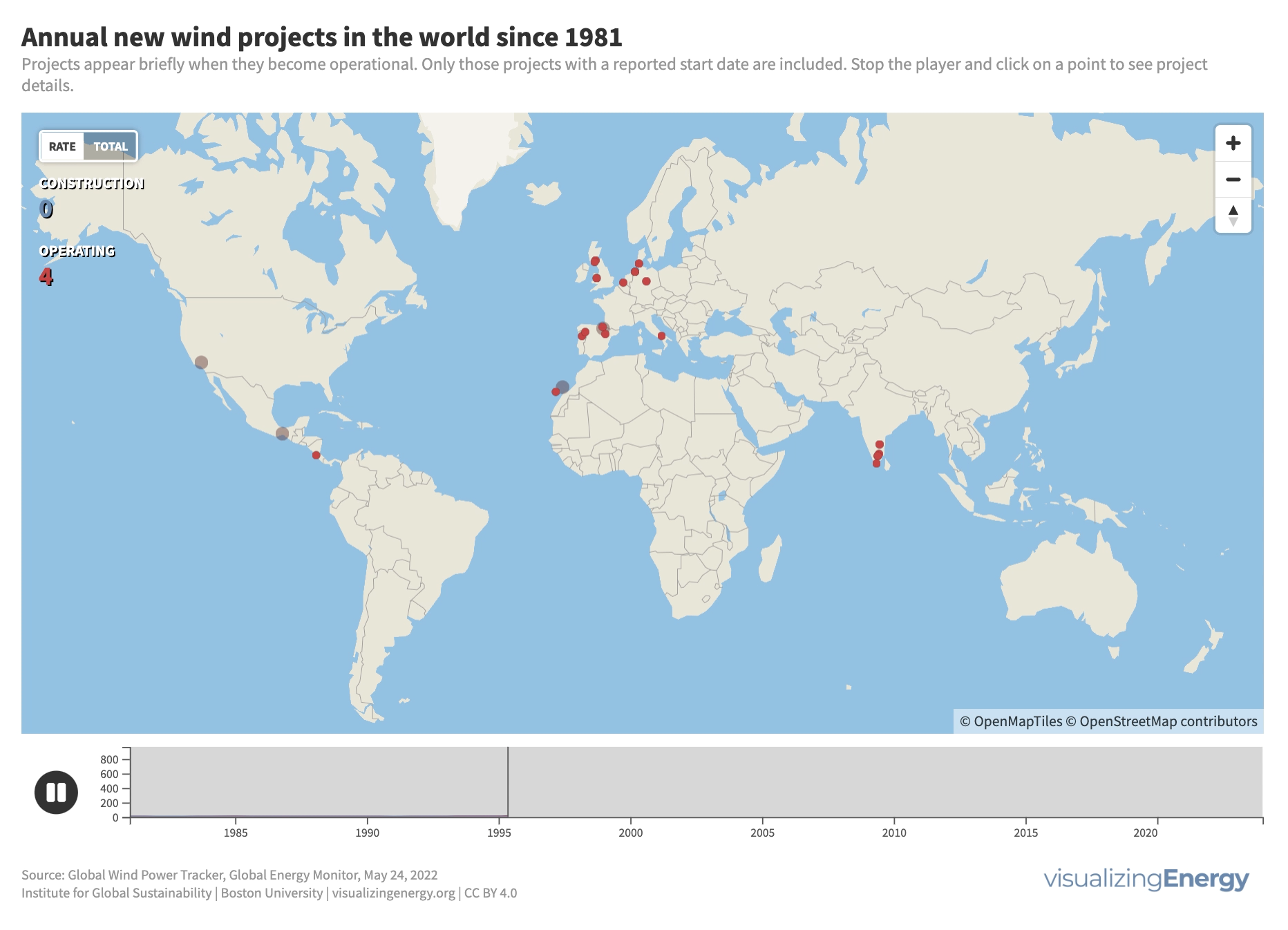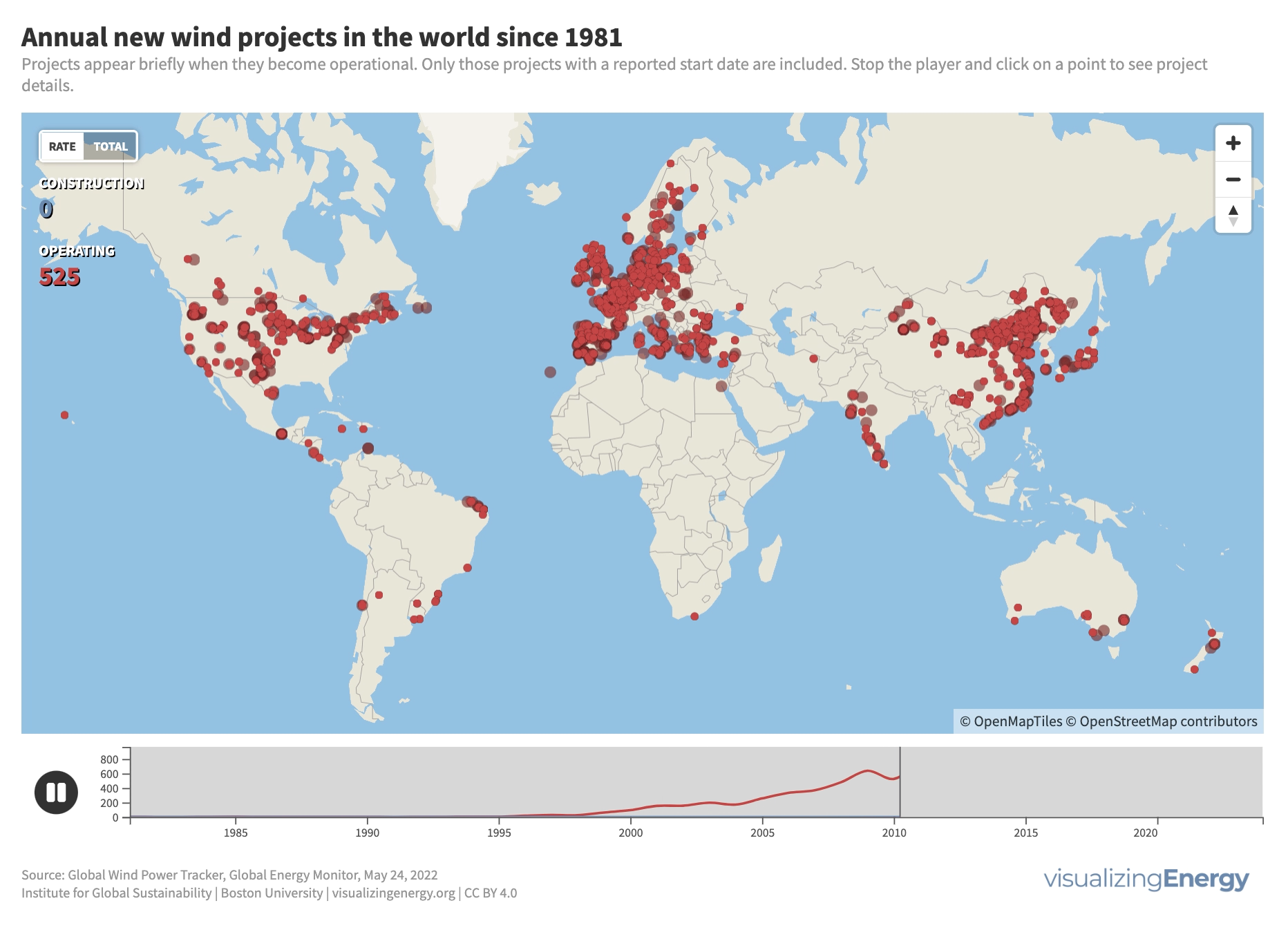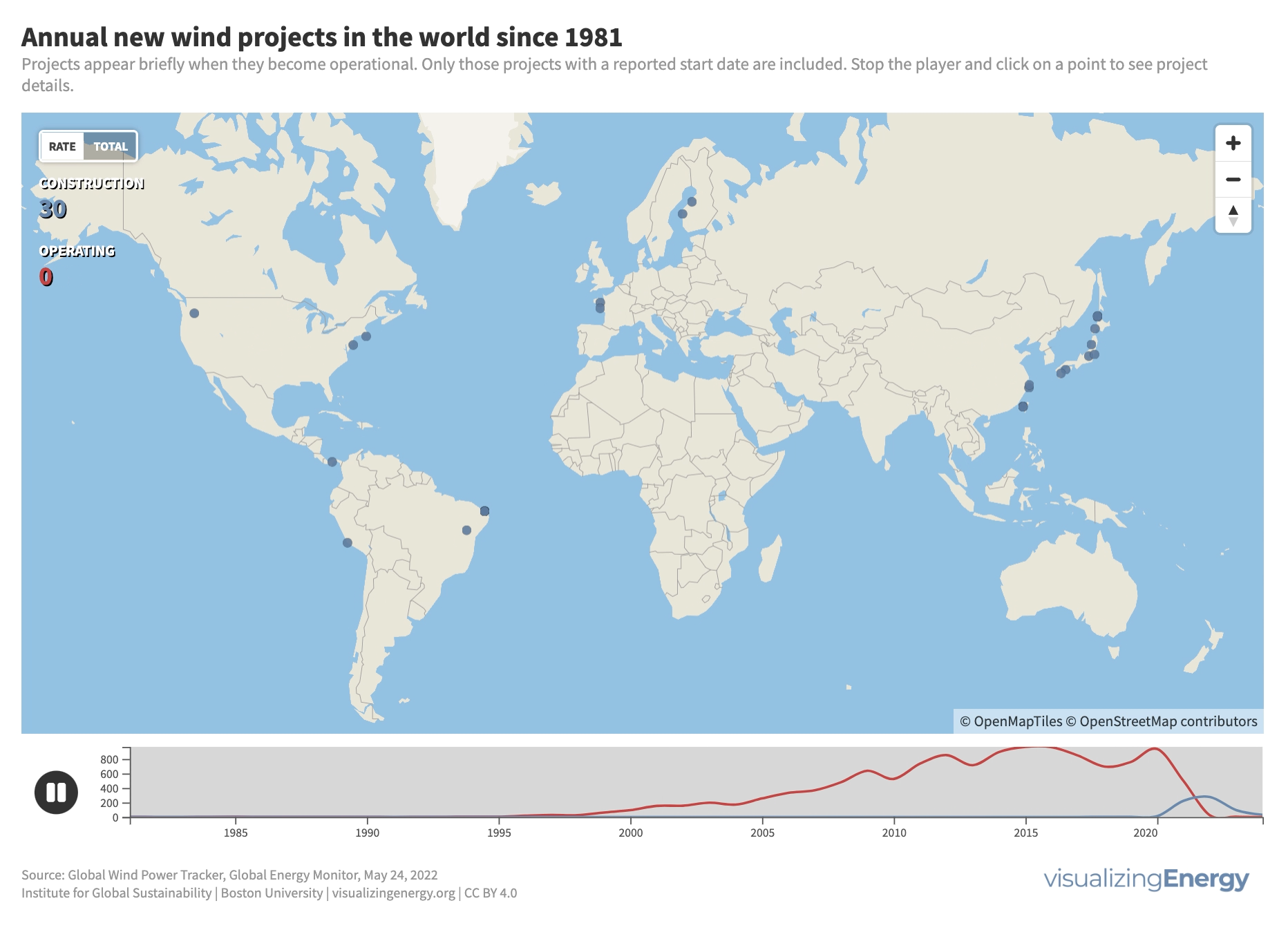
The wind energy industry started in the 1980s in Southern California and several European countries. Today, the United States, Europe, and countries like India, Australia, Japan, Canada, China, and Brazil lead in new wind power capacity. Currently, wind power generates around 7% of global electricity, with onshore systems dominating but offshore capacity expected to grow in the future.
Where in Europe do people struggle to stay warm?
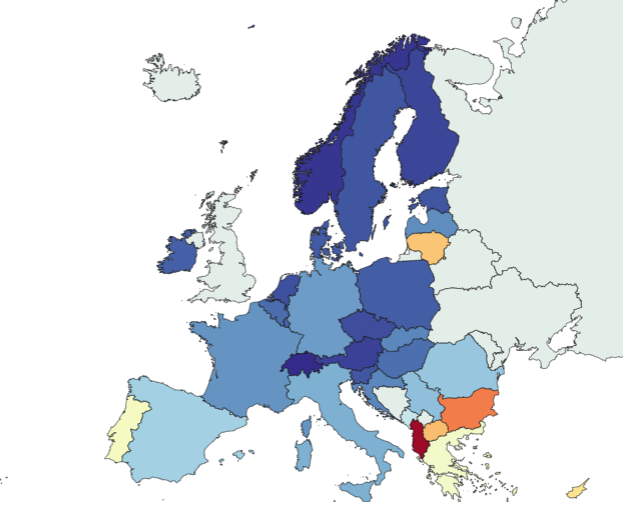
In Europe, energy insecurity affects 8% of the population, with some countries facing higher rates of thermal discomfort. Milder winters due to climate change have improved overall energy security, but about 35 million people still struggle to stay warm. Germany, Spain, Italy, and France have a significant number of individuals affected.
What is the relationship between energy use and level of education?
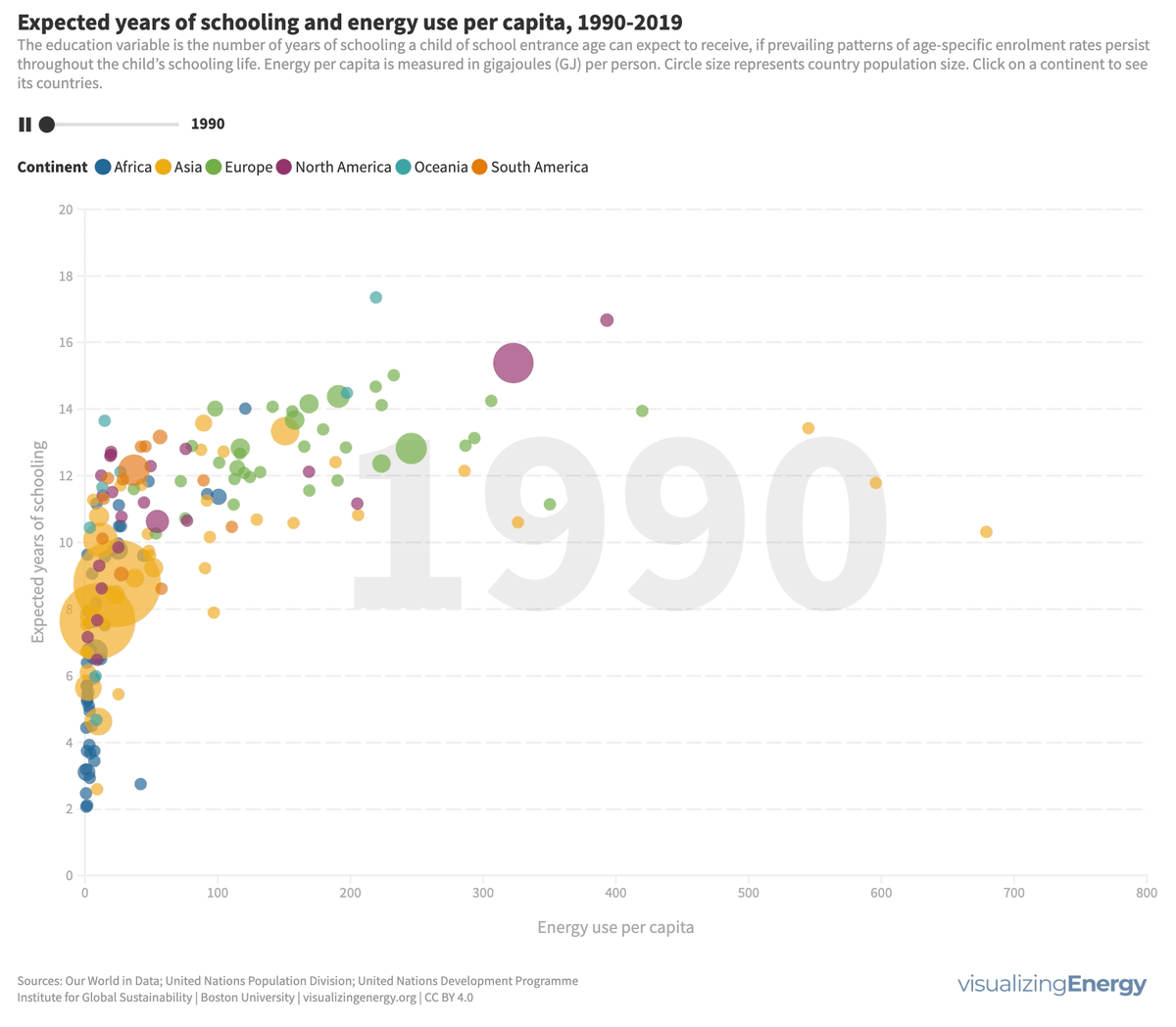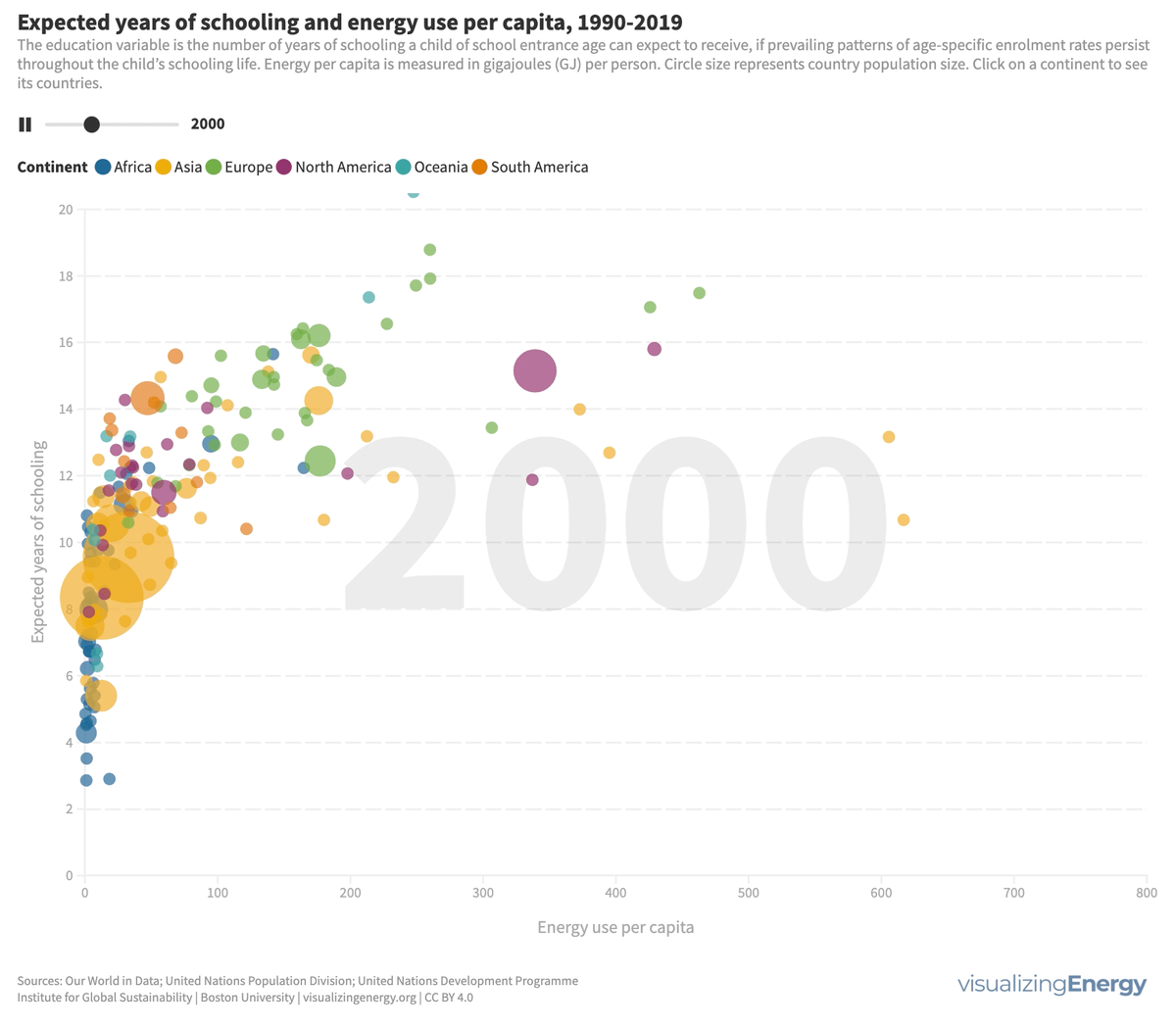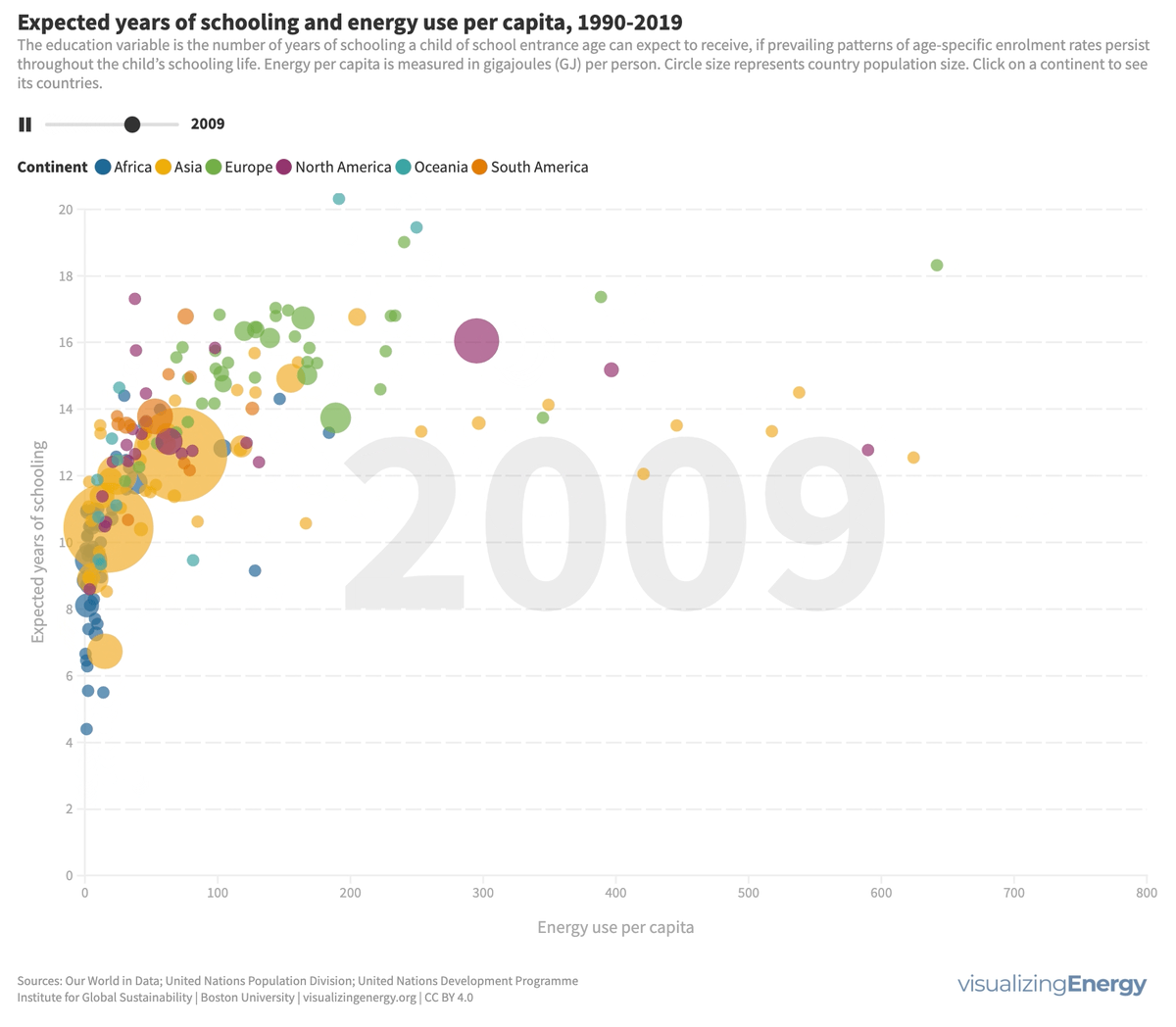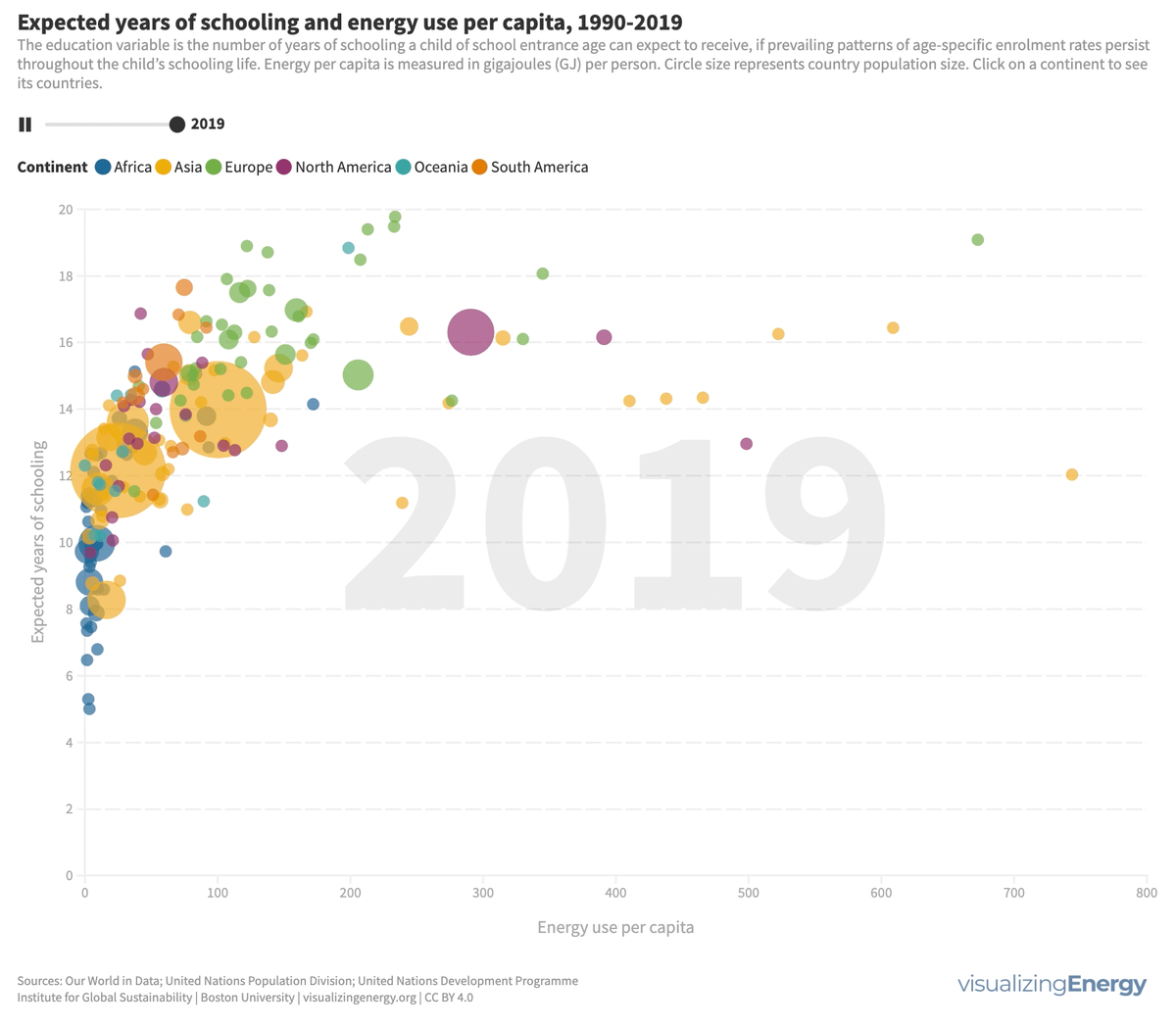
Energy is essential for education, enabling longer study hours, technological advancements, and improved outcomes. While access to education has improved globally, certain regions still face challenges. Increasing energy access, particularly electricity, positively impacts education.
What is the relationship between energy use and access to safe water?
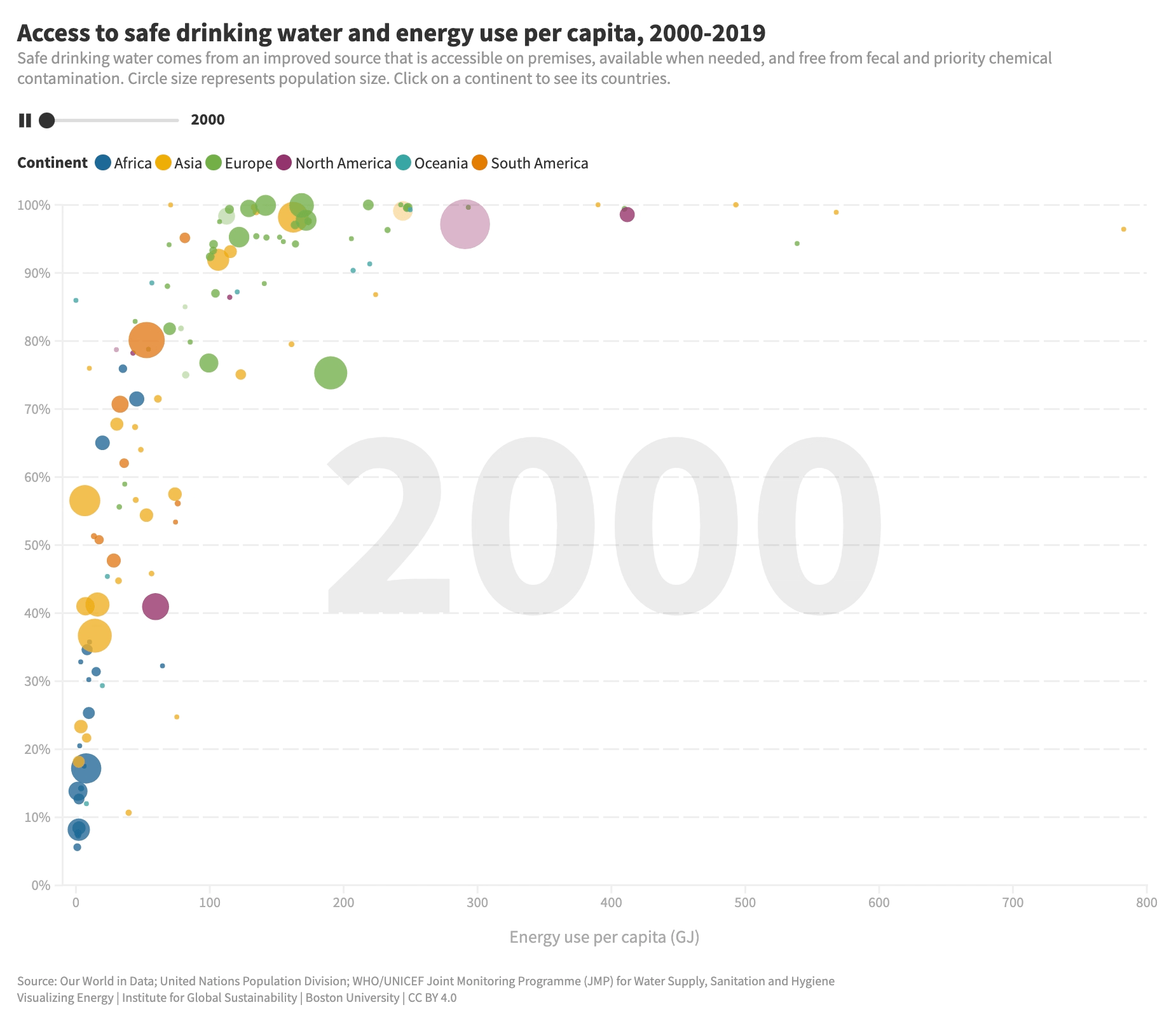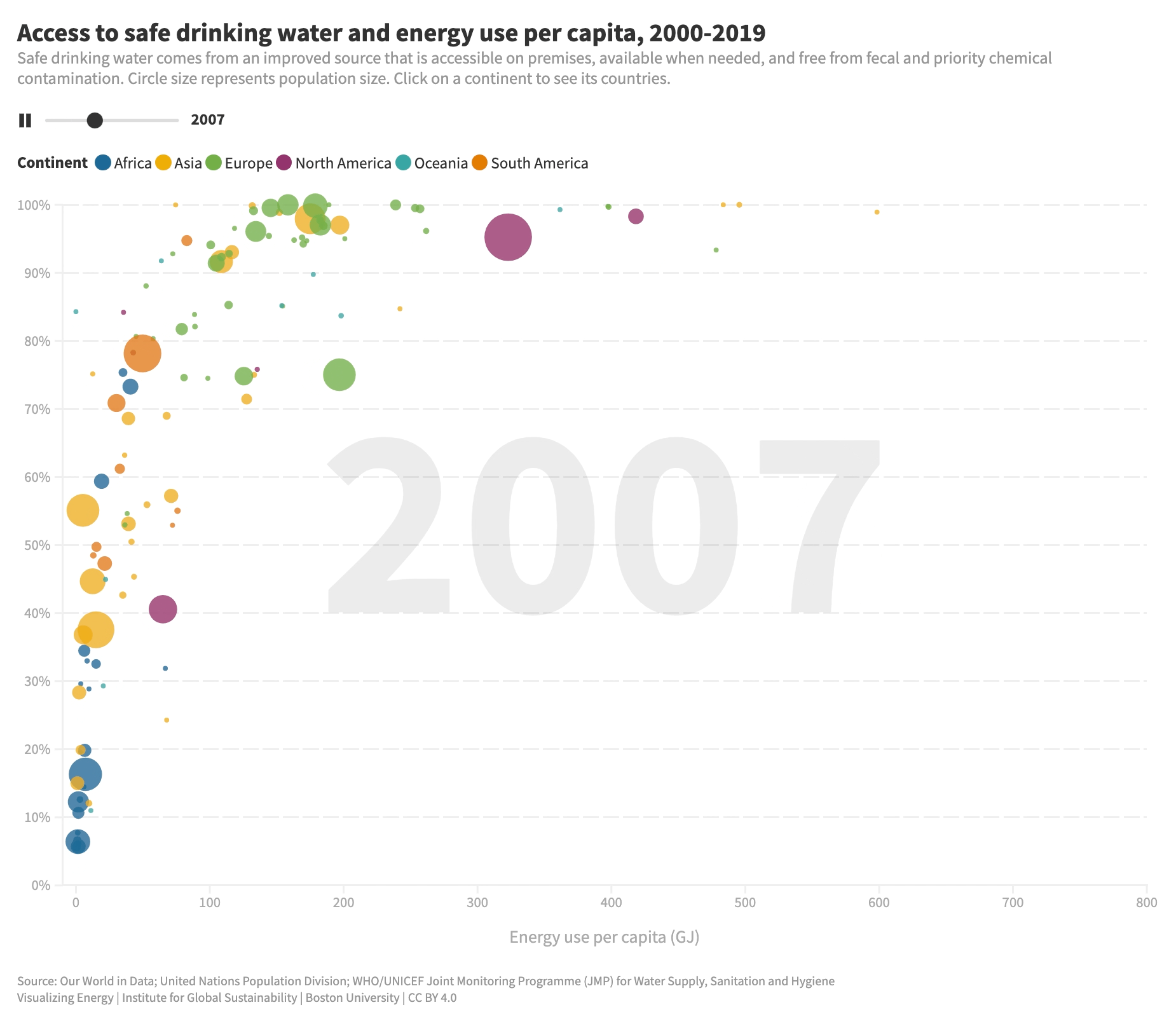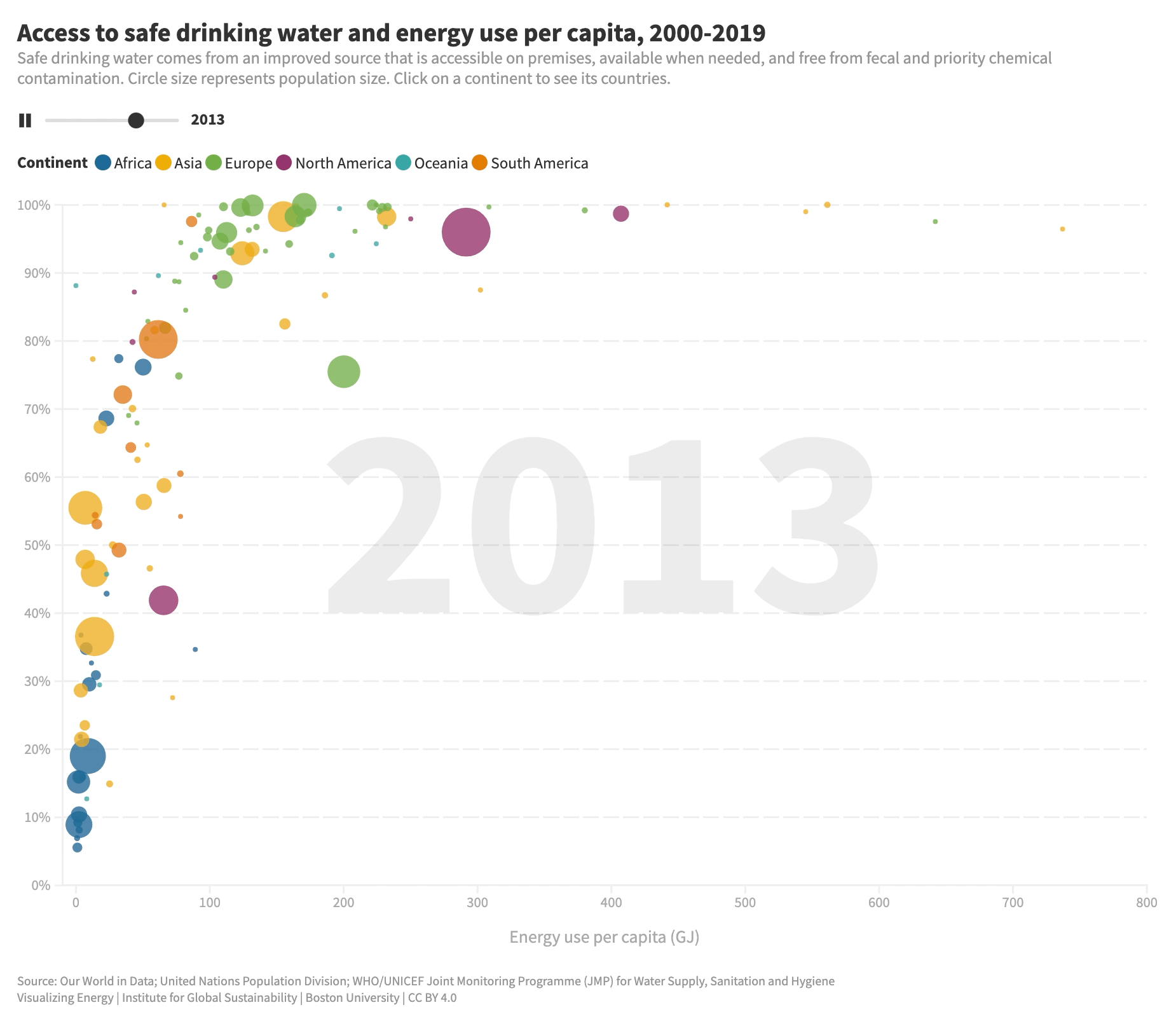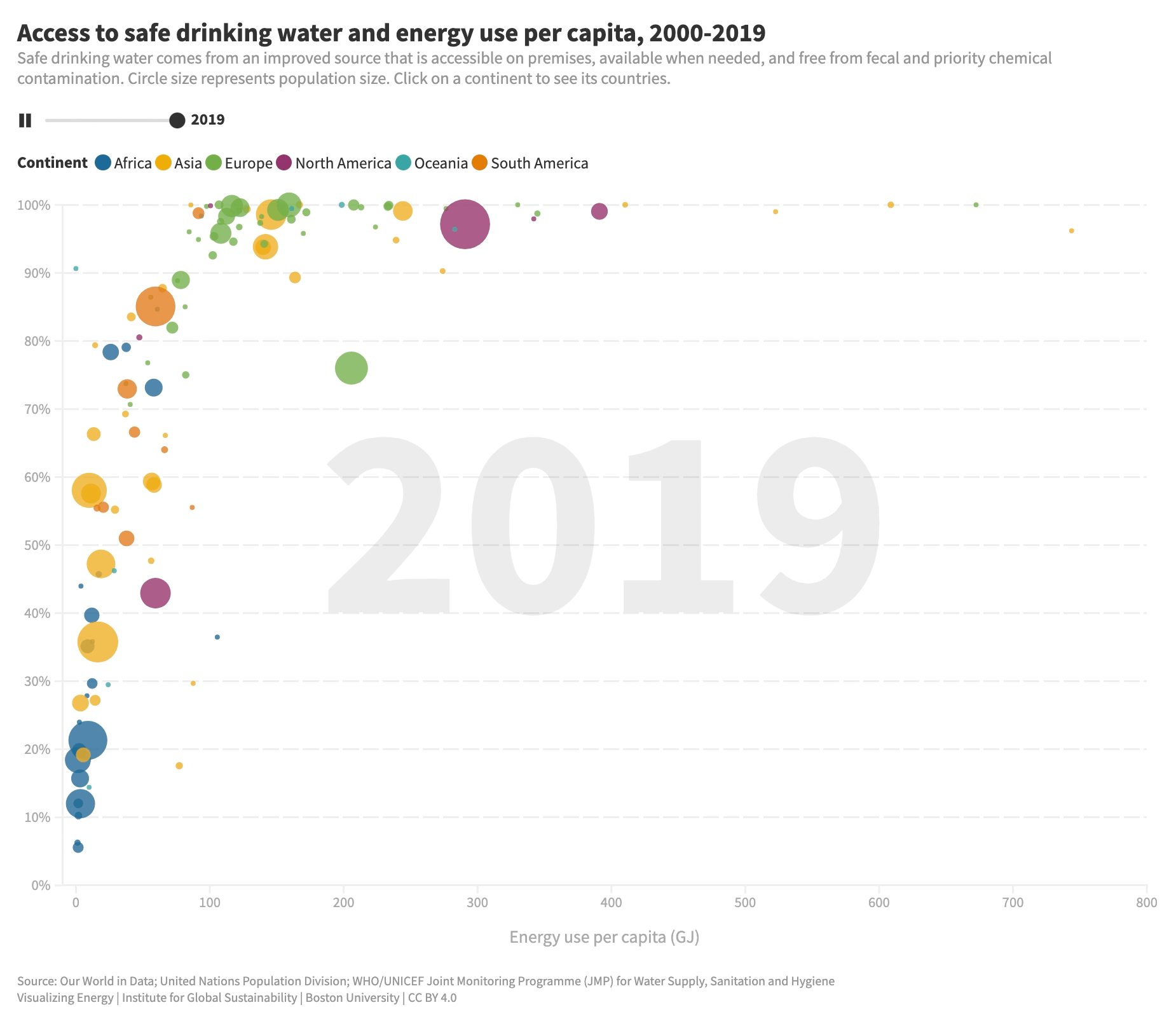
Access to safe water is vital for human well-being. While progress has been made, millions still lack basic water services. Energy plays a key role in expanding water access, powering machinery, pumps, and purification systems. Increasing energy use per capita improves access to clean water, but the impact diminishes at higher energy levels.
Why do oil reserve estimates vary so widely?
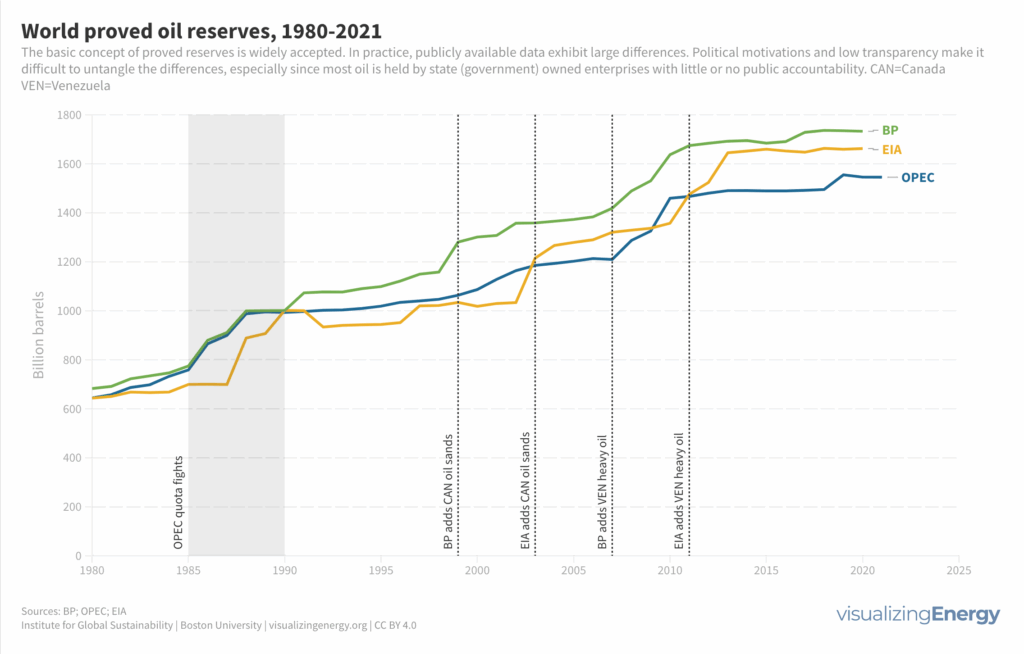
Oil reserve estimates vary widely due to the challenges of accurately assessing oil deposits deep underground. Factors such as limited transparency, varying methodologies, and political influences contribute to the disagreements. Efforts are needed to align reserve estimates with climate goals and ensure transparency in reporting.
Where are people dying due to indoor air pollution from cooking fuels?
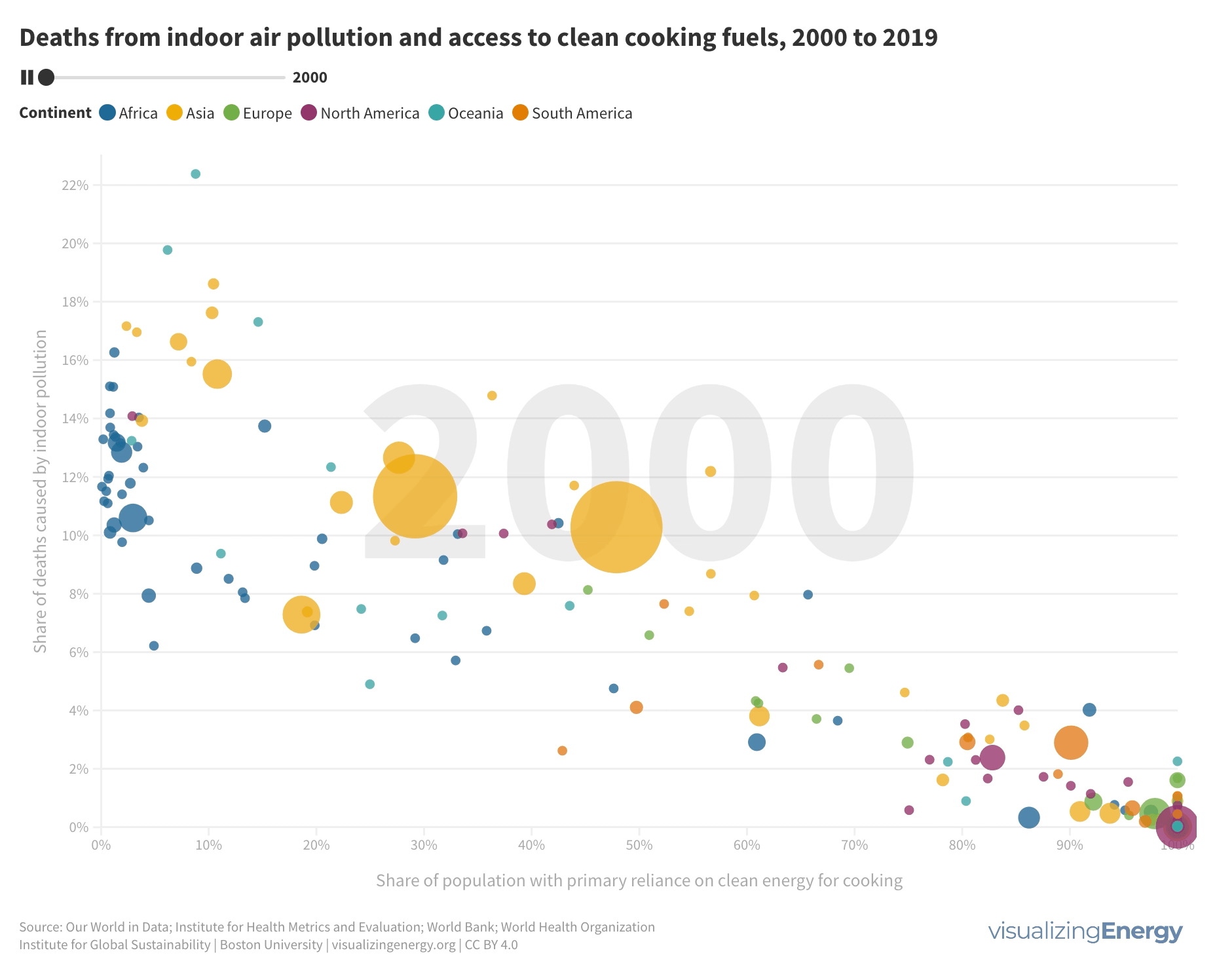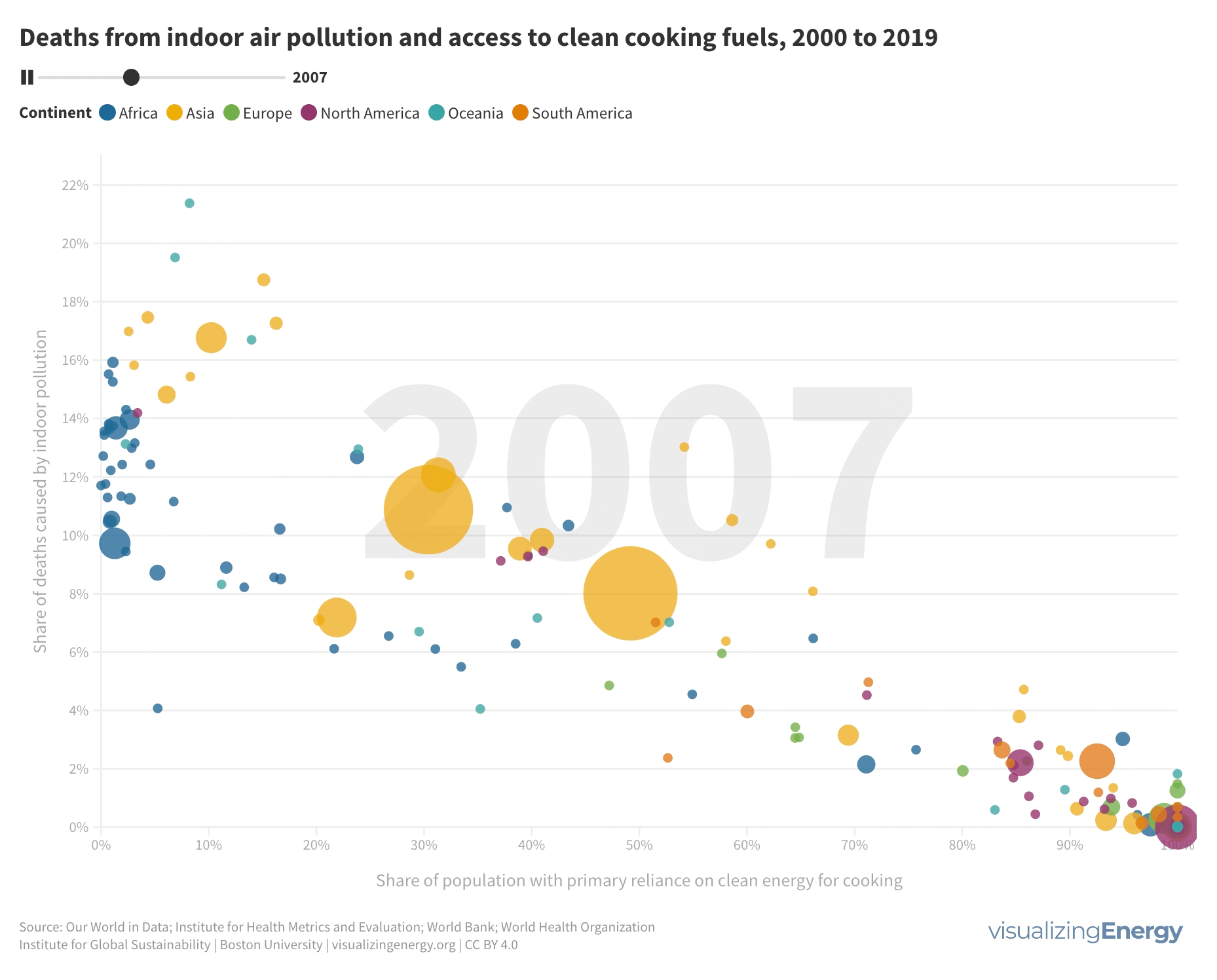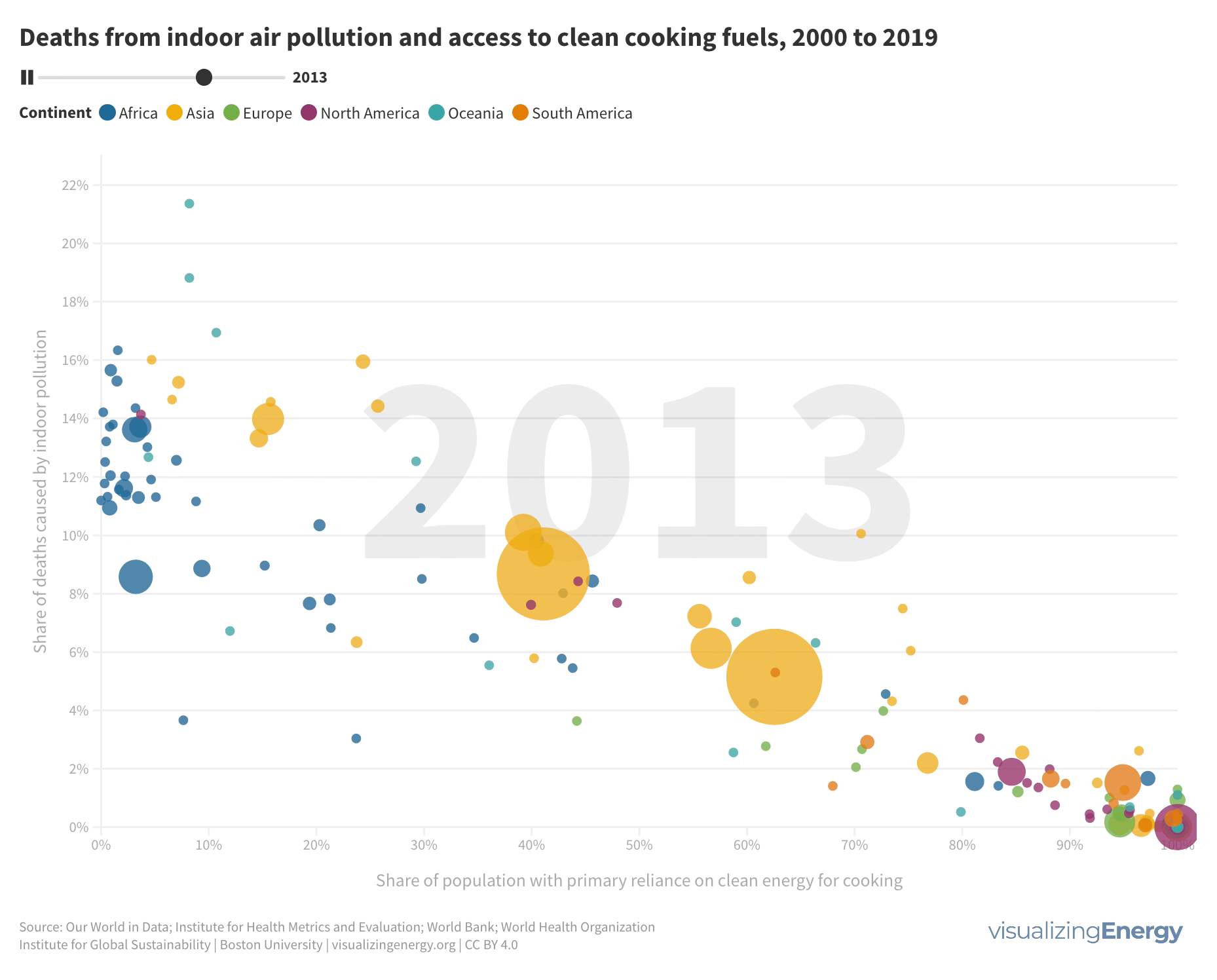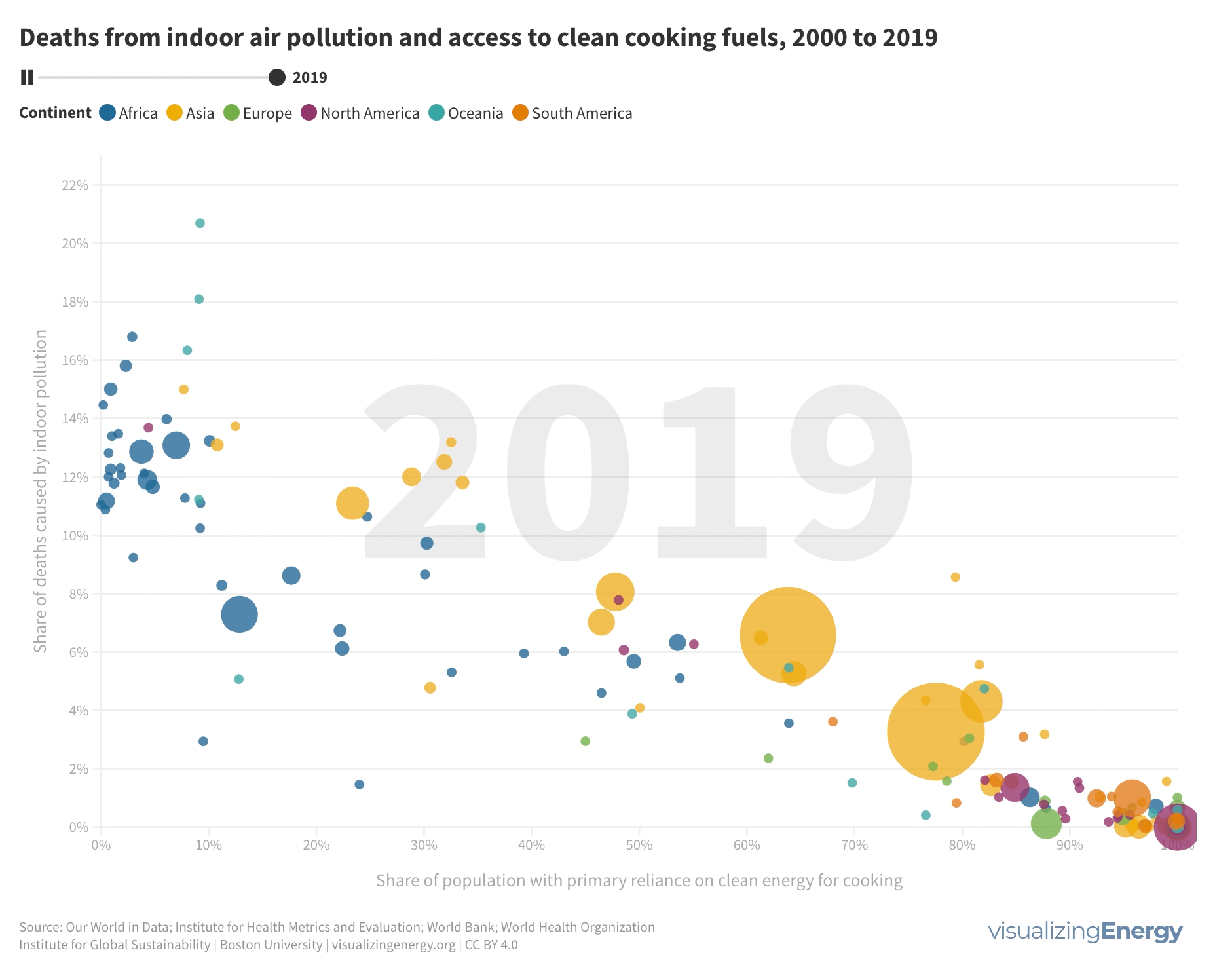
Millions of people die each year due to indoor air pollution caused by the combustion of solid fuels and kerosene in inefficient stoves. Heart disease, stroke, COPD, lung cancer, and other illnesses are major contributors to these deaths. Access to clean cooking fuels is closely linked to lower death rates, with countries having universal access showing the lowest rates.
