Explore the world history of nuclear reactors, 1951-2022
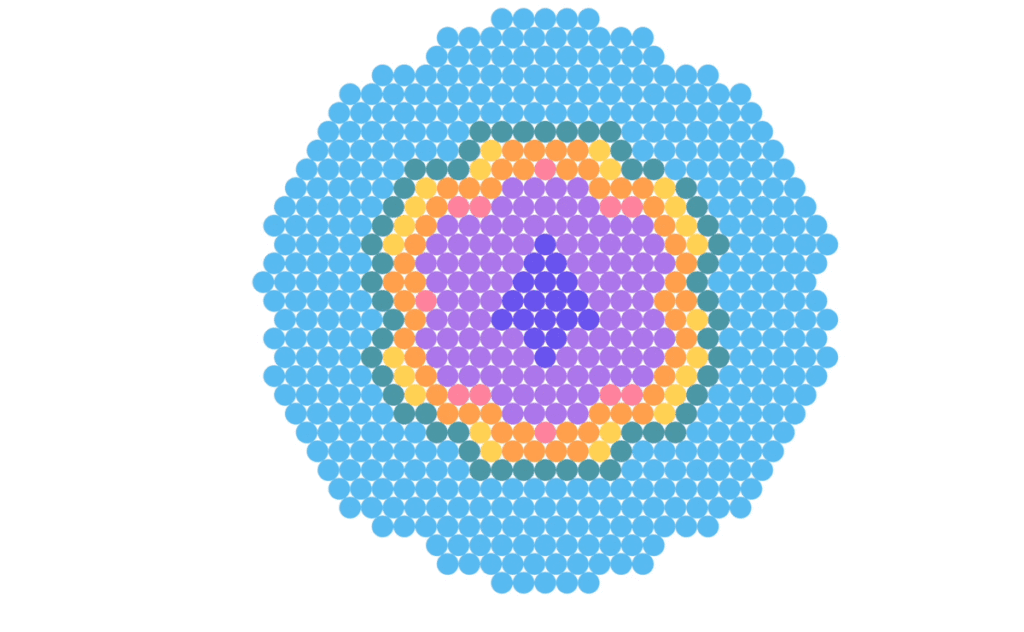
Explore the global history of nuclear reactors from 1951 to 2022. This visualization showcases 626 operational reactors, highlighting the dominance of pressurized light water reactors (PWRs). Different reactor types exhibit geographic patterns, with retired reactors and ongoing upgrades observed in various countries. The average age of reactors in the United States was 41 years in 2021.
Who benefits from energy booms? The case of fracking in Texas
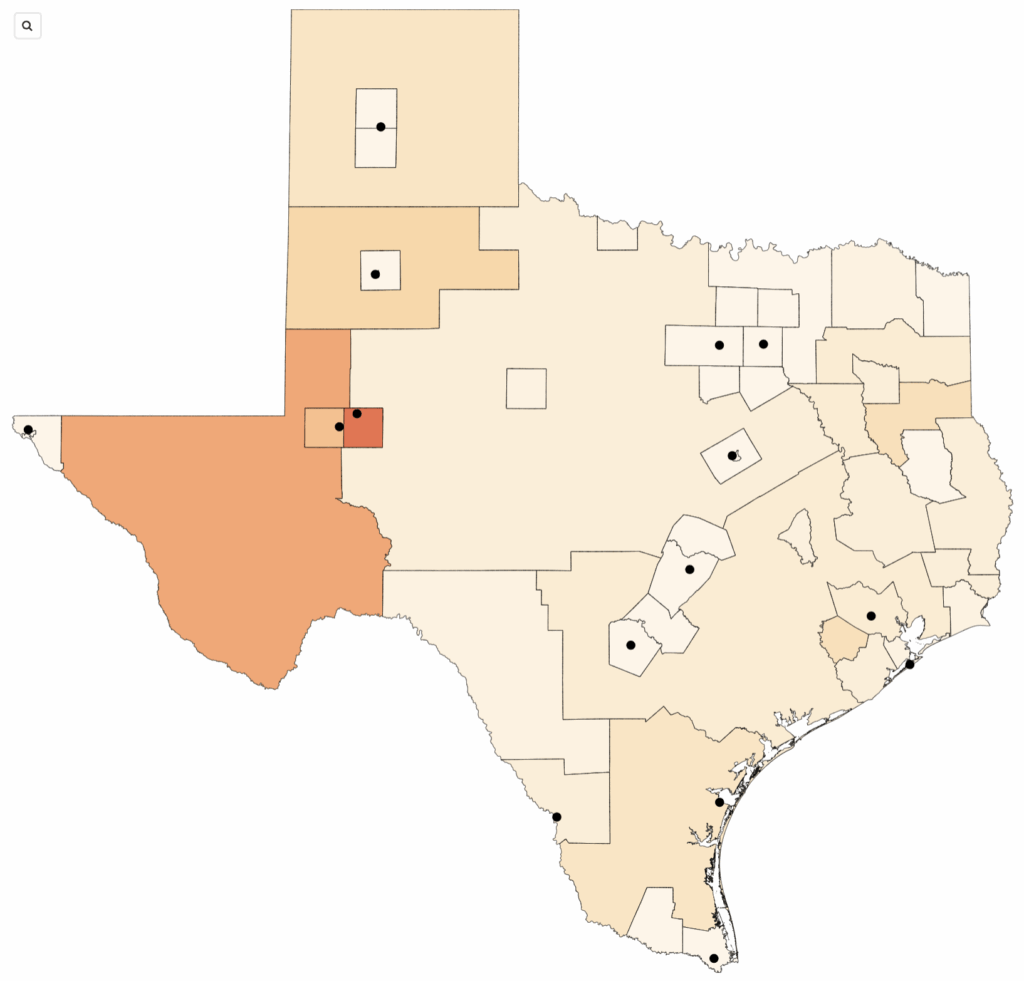
Texas has emerged as a prominent oil and gas producer, ranking as the fifth largest oil producer globally if it were its own country. The development of fracking technology and a surge in oil prices led to a significant increase in oil and gas production in Texas from 2000 to 2014. However, the distribution of employment gains during this boom varied across gender, race, and ethnicity. The Texas example underscores the importance of ensuring an equitable distribution of economic benefits in energy systems, especially as governments incentivize low carbon energy initiatives.
What prime movers have generated the most electricity since 1900?
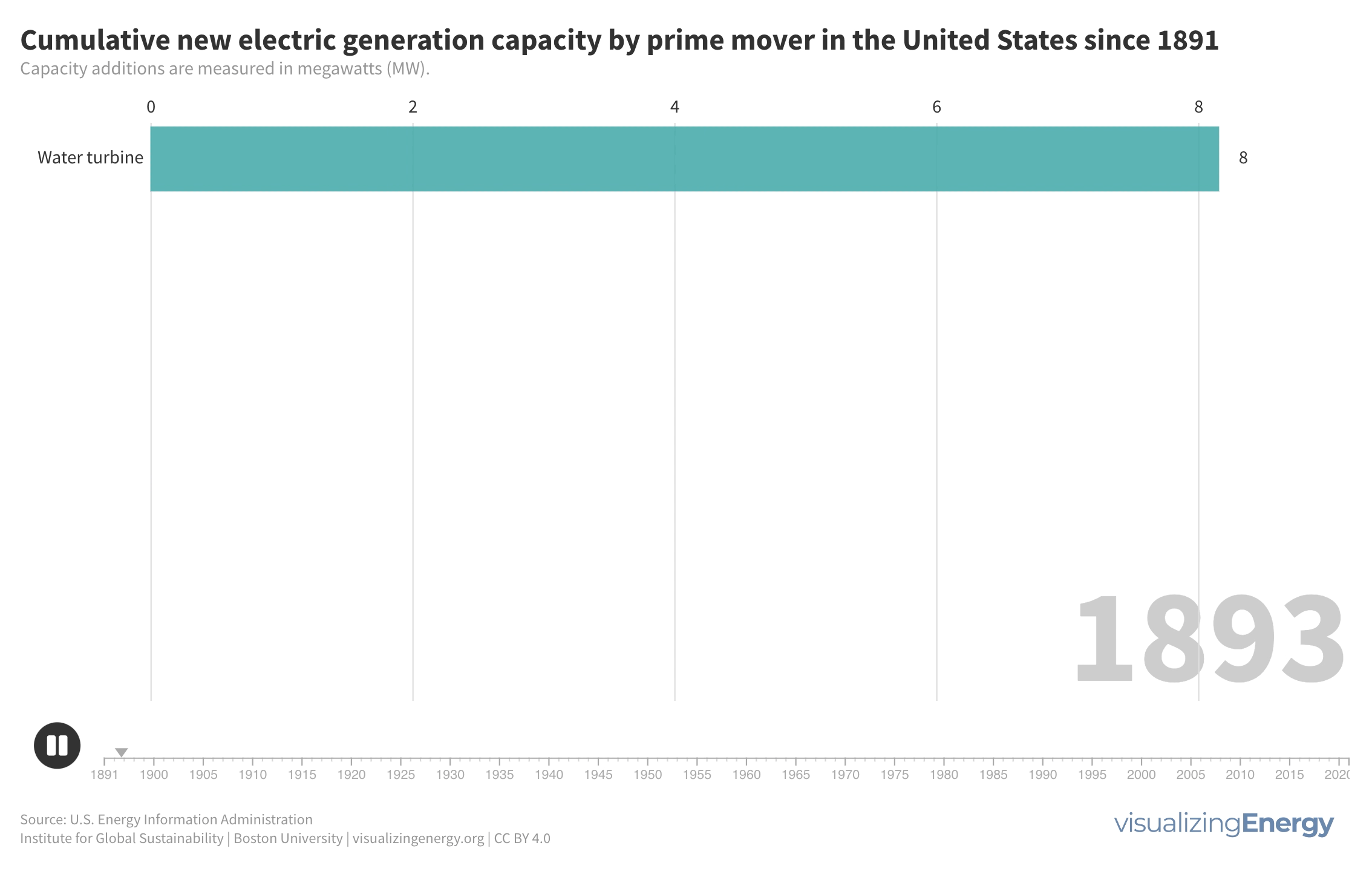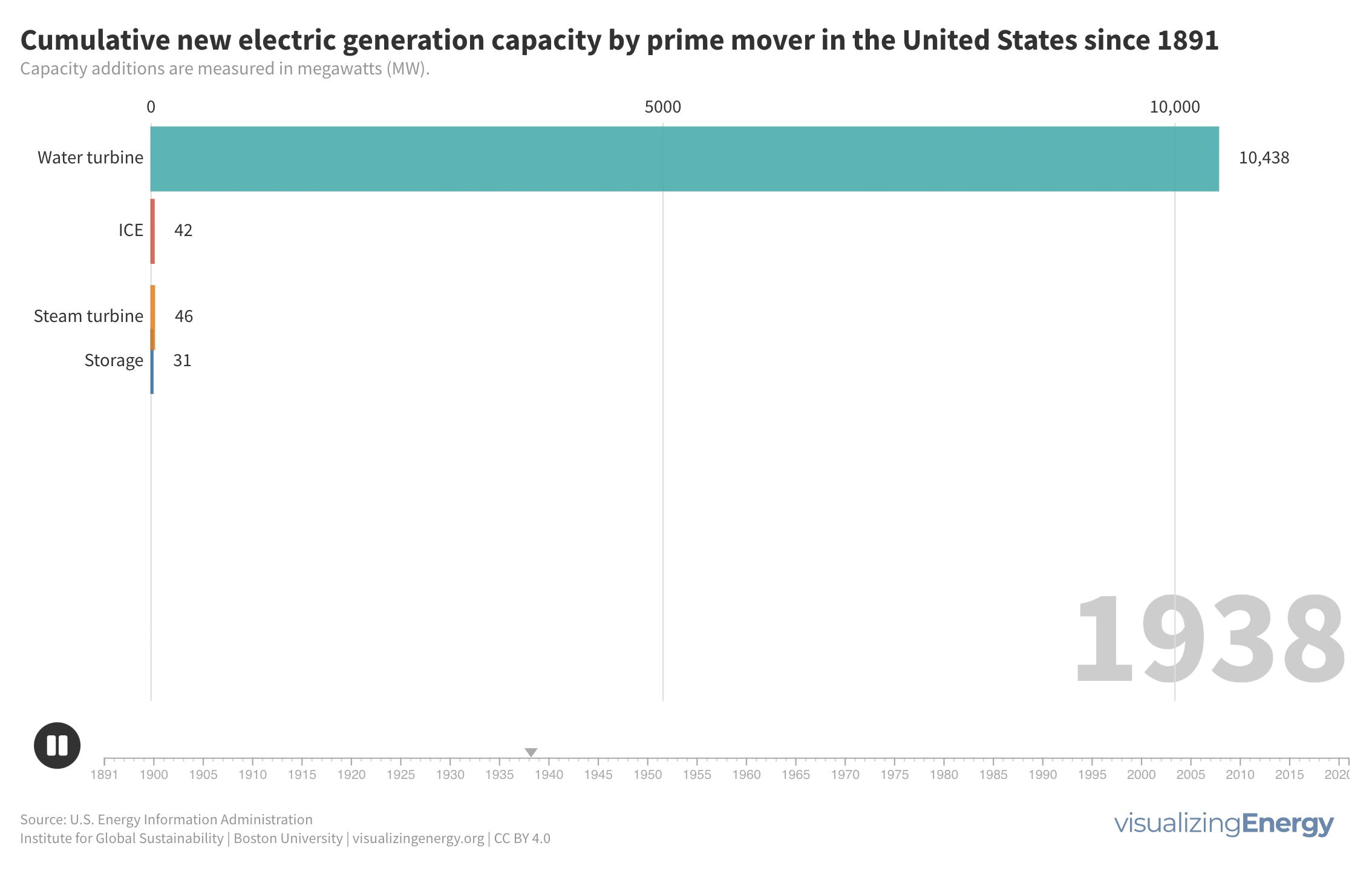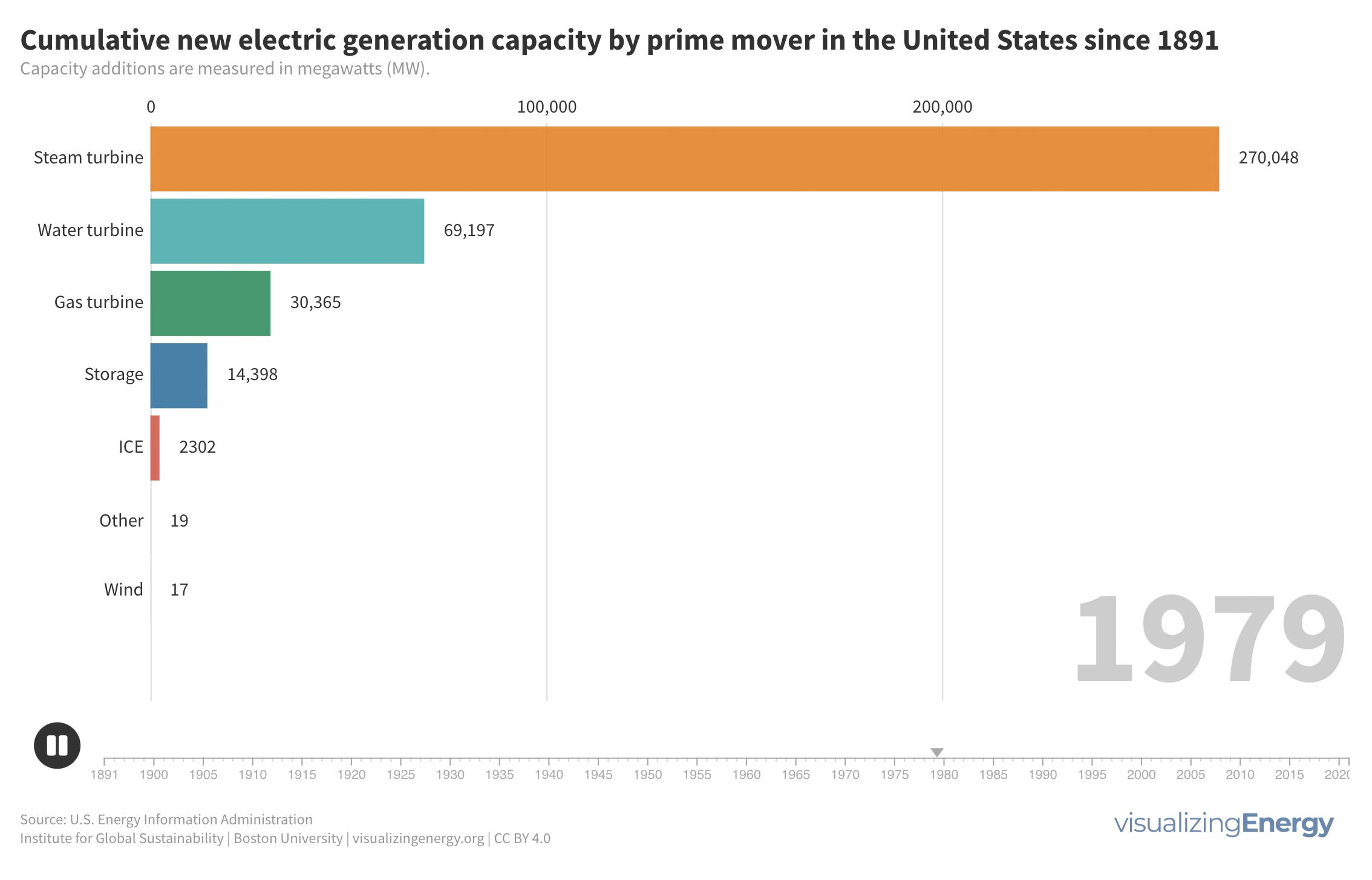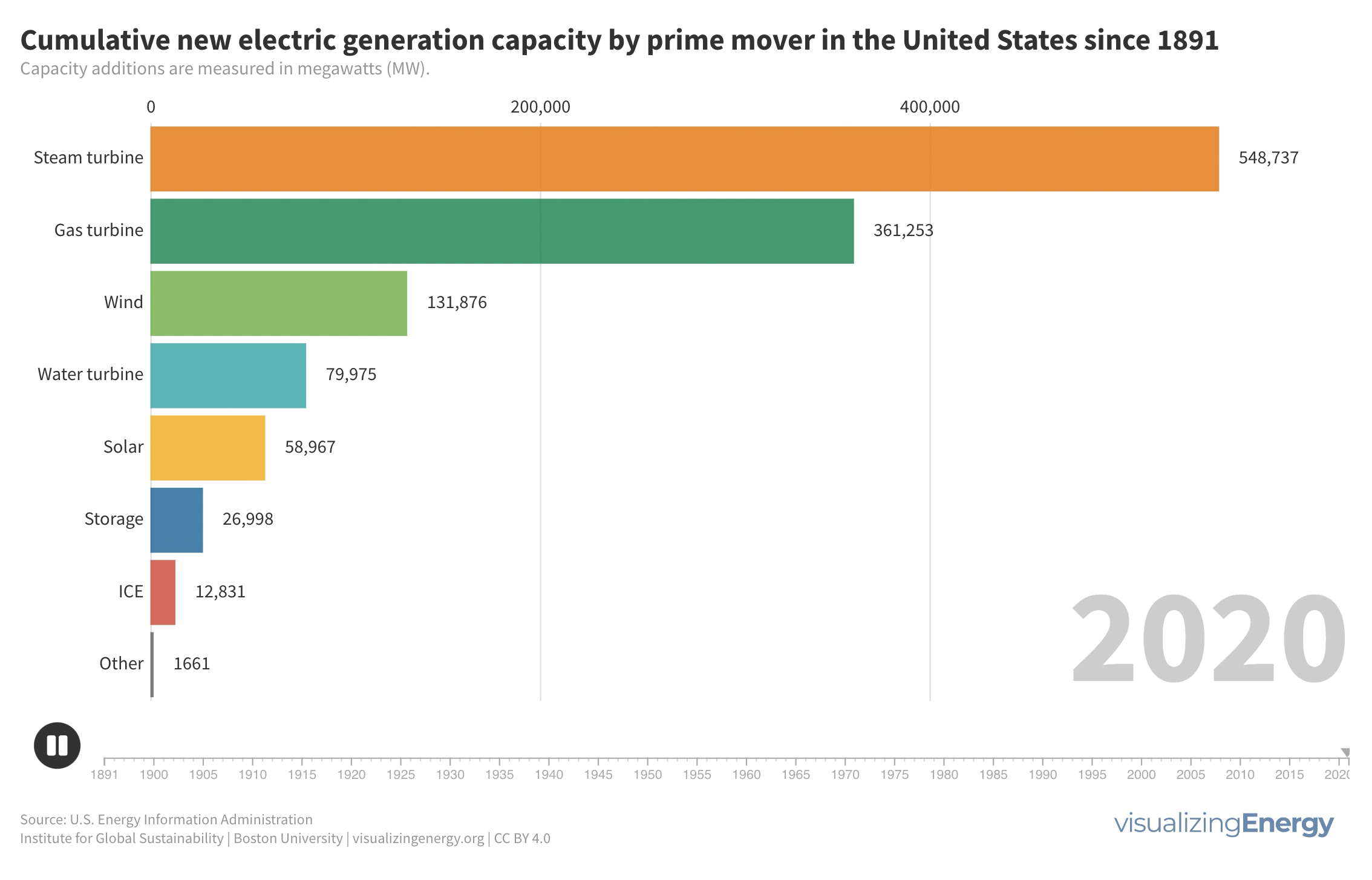
Prime movers are devices that convert natural sources of energy into mechanical energy to generate electricity. Historically, hydropower from water turbines and steam turbines played major roles. Gas turbines emerged as a more efficient and cost-effective option. In recent years, solar cells and wind turbines have made significant advancements, providing competitive and environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional energy sources.
Seventy-five years of world uranium production and resources
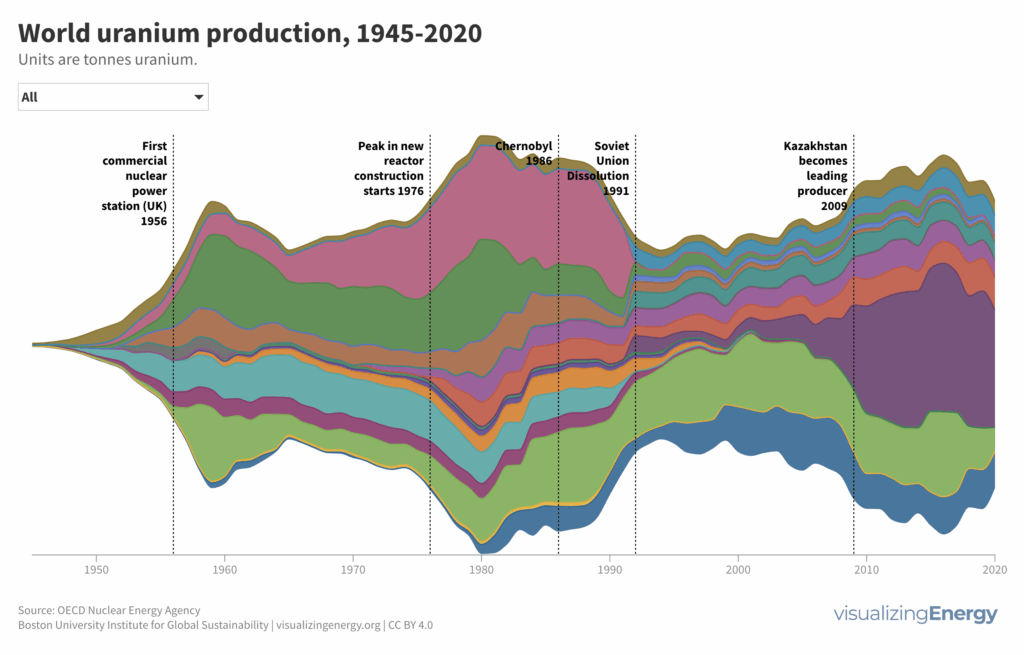
Uranium is crucial for nuclear power generation, supplying 10% of global electricity. The largest recoverable uranium resources are held by Australia, Kazakhstan, Canada, Russia, and Namibia. Major uranium consumers rely on imports due to limited domestic production, leading to significant international trade in uranium products.
What do these charts say about the safety of nuclear reactors?
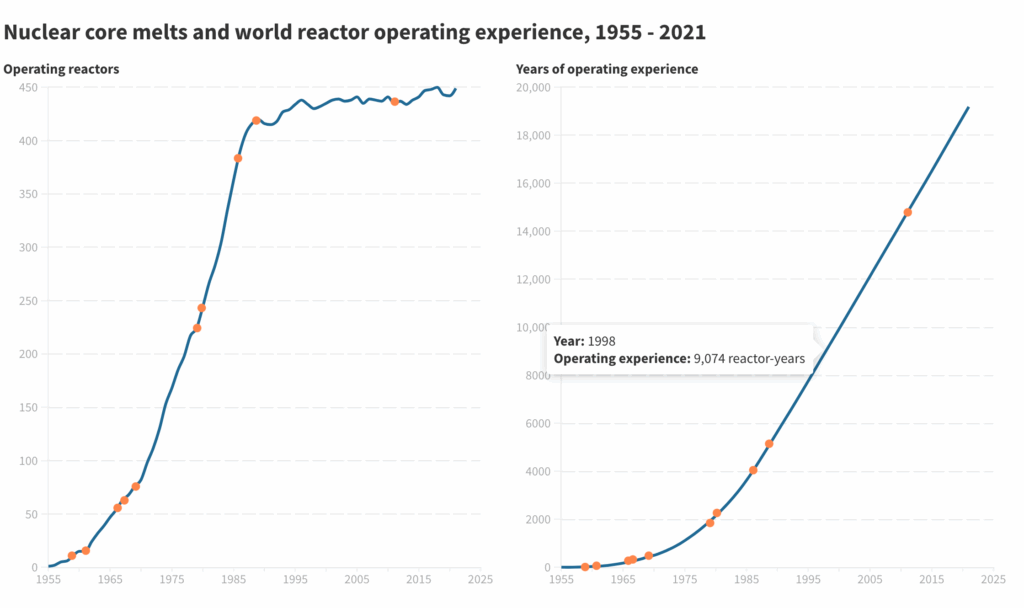
The safety of nuclear reactors is a subject of debate. While incidents like Three Mile Island, Chernobyl, and Fukushima have had impacts on human health and the environment, the overall risks of radiation exposure are considered small. Advancements in technology and regulations have significantly reduced the frequency of core damage incidents. Nuclear power is an important low-carbon energy source, but opinions differ on its safety compared to fossil fuels and renewables.
Where is new nuclear power in the world being built?
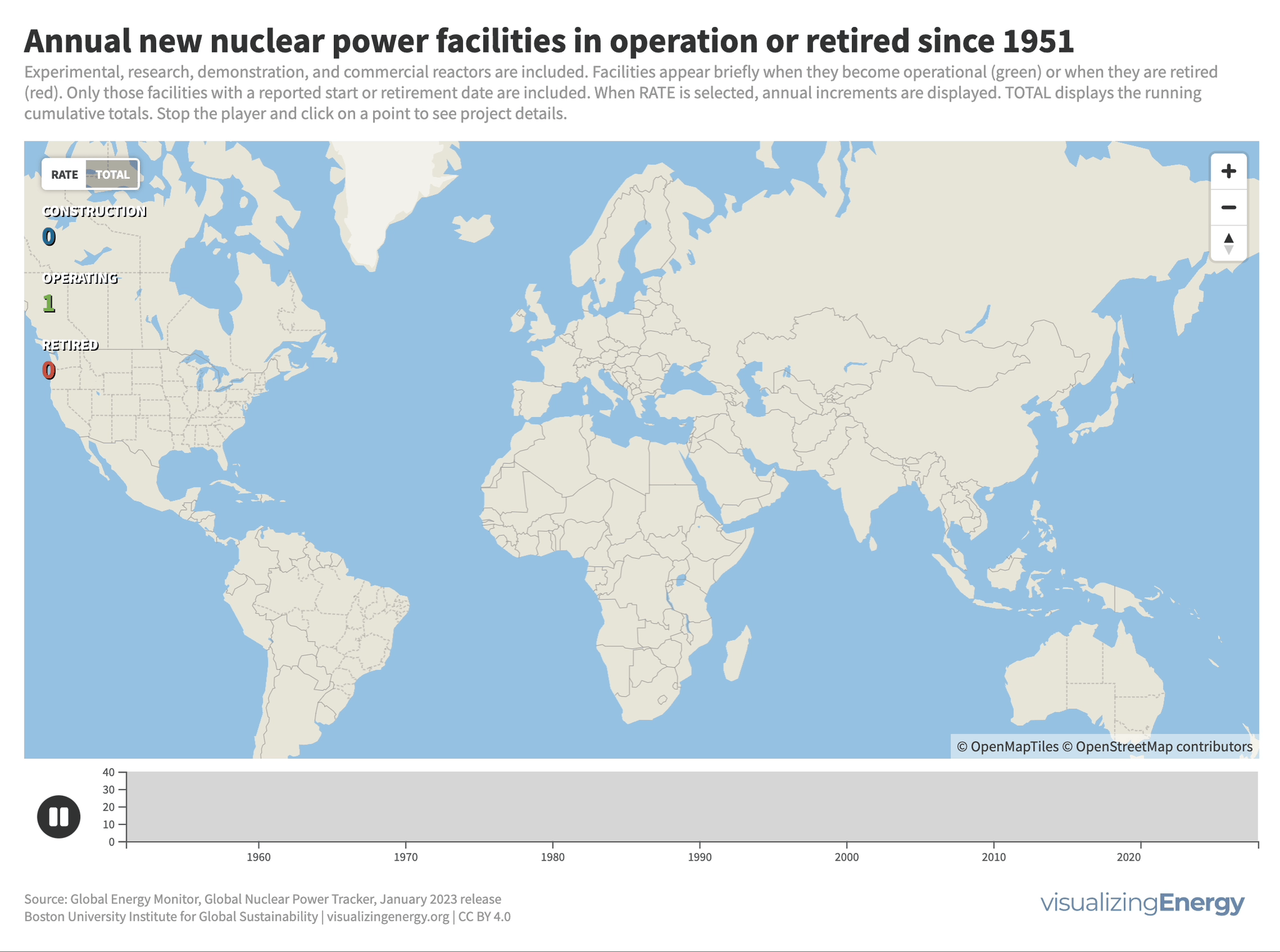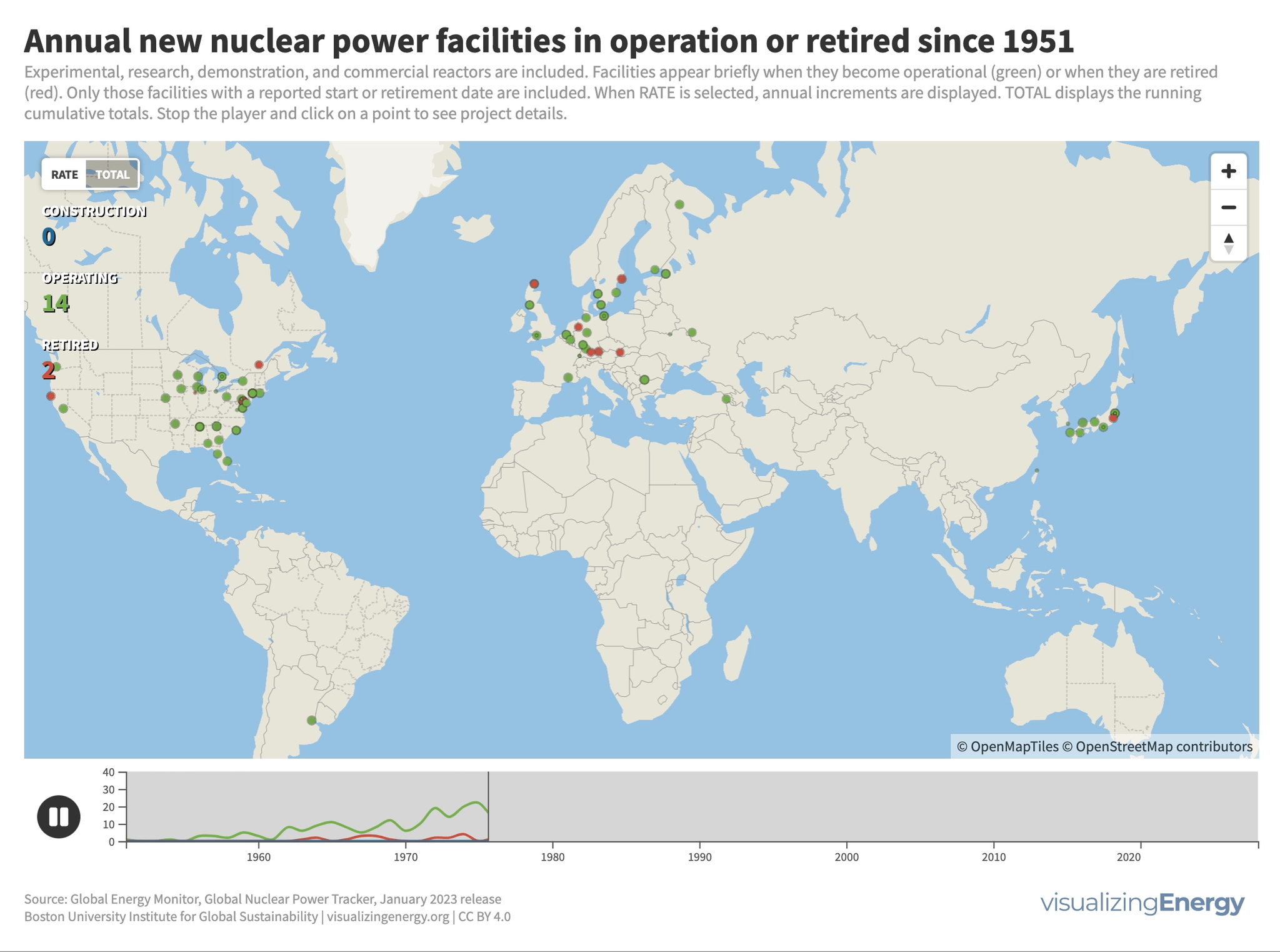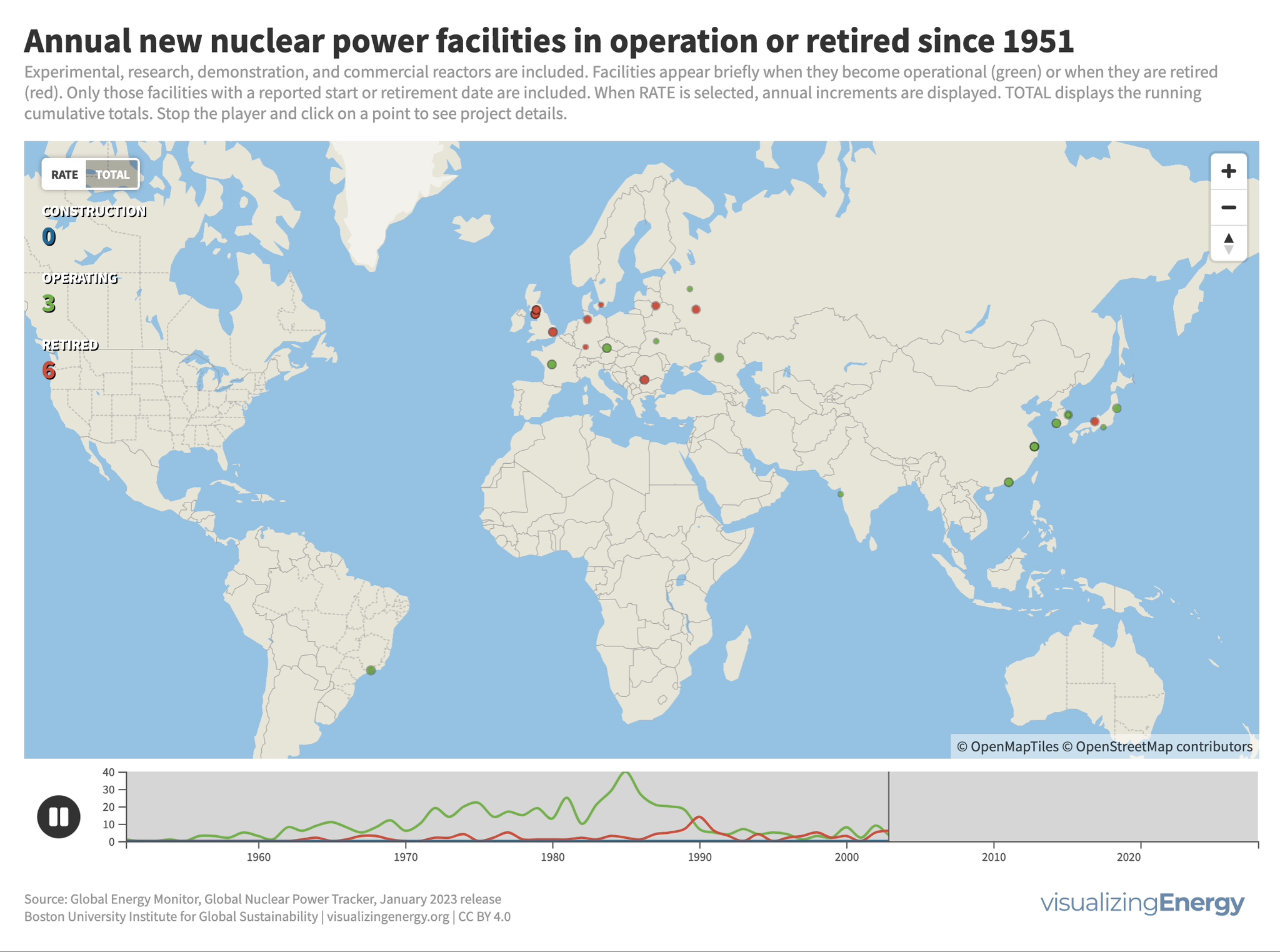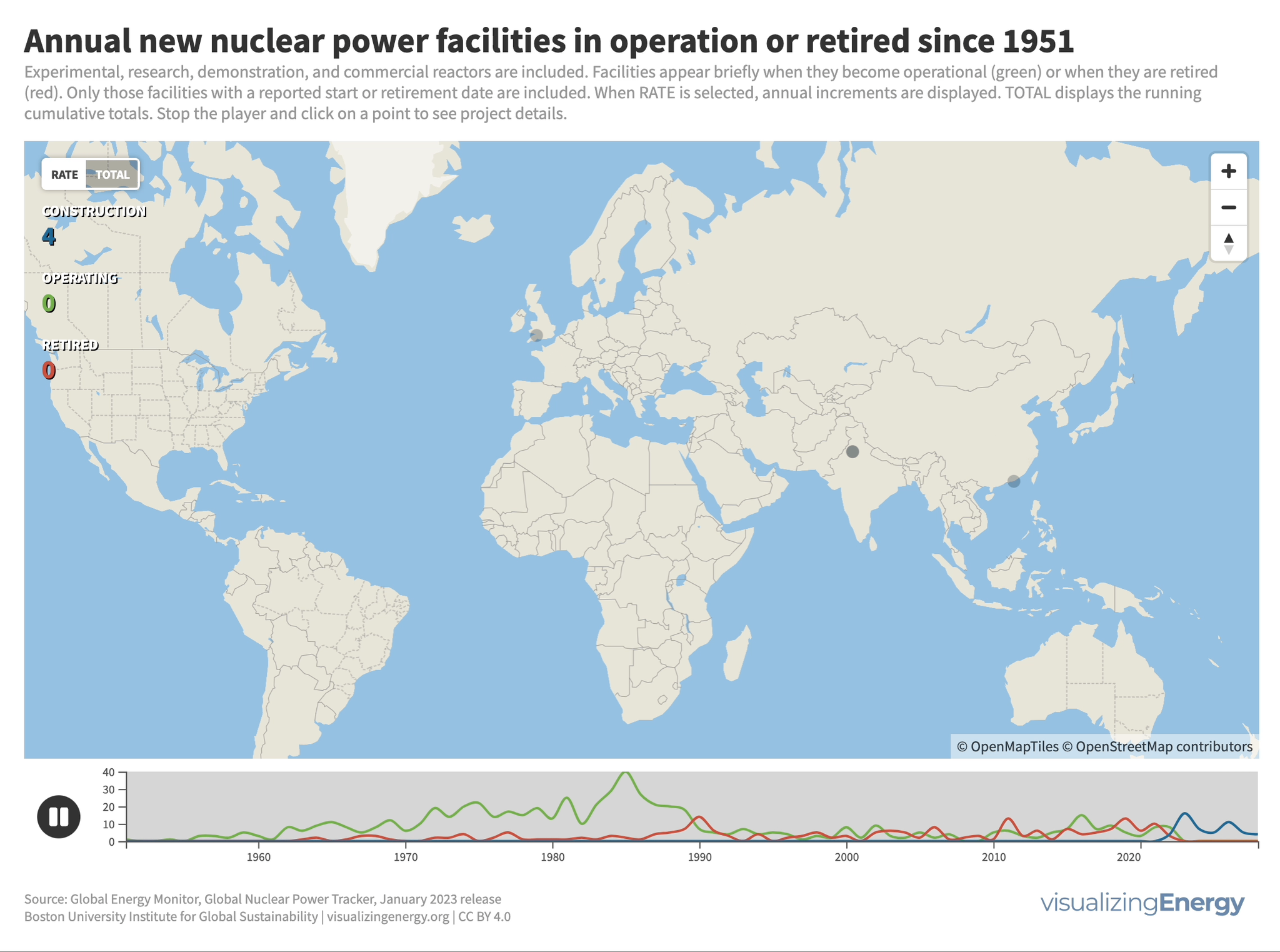
Nuclear power plant construction has shifted to countries like China, India, Russia, and South Korea. Around 64 GW of new nuclear capacity is currently under construction, with China leading the way. An additional 177 GW has been announced globally. Some countries see nuclear power as a low-carbon option to meet climate goals. Factors such as economics and geopolitical considerations will determine how much new nuclear capacity actually gets built.
Explore the geography and technology of new electricity generation in the United States in 2021
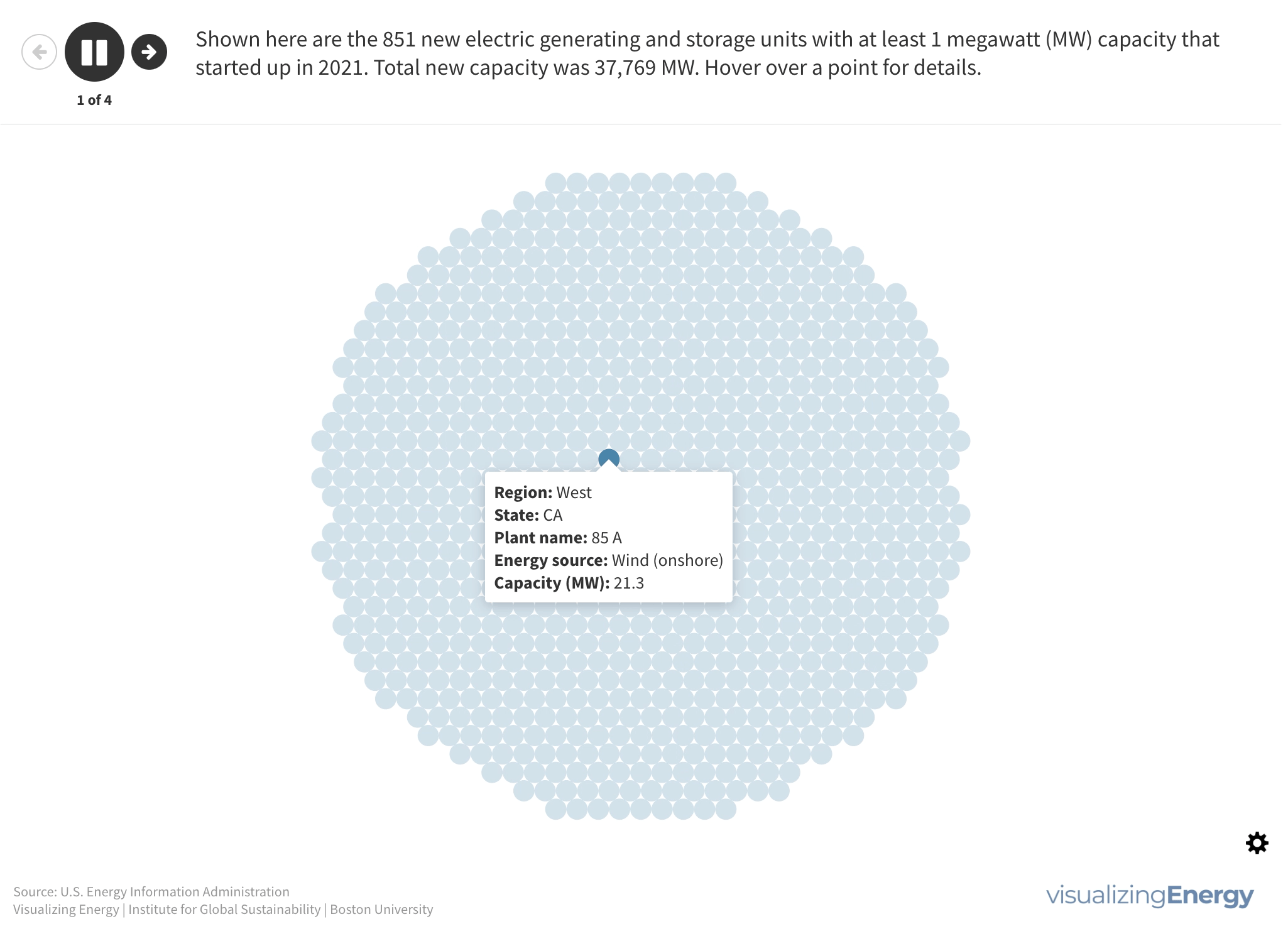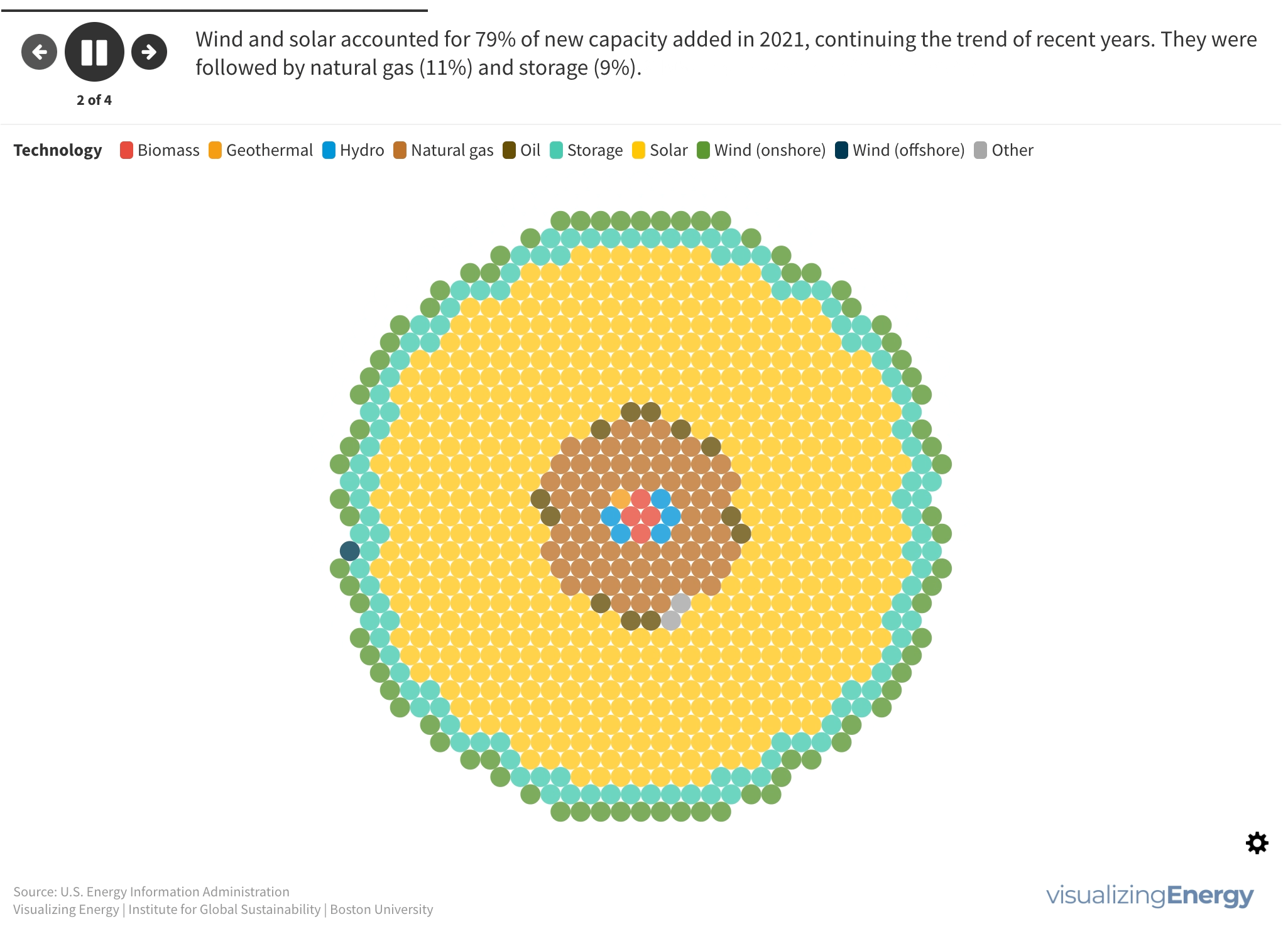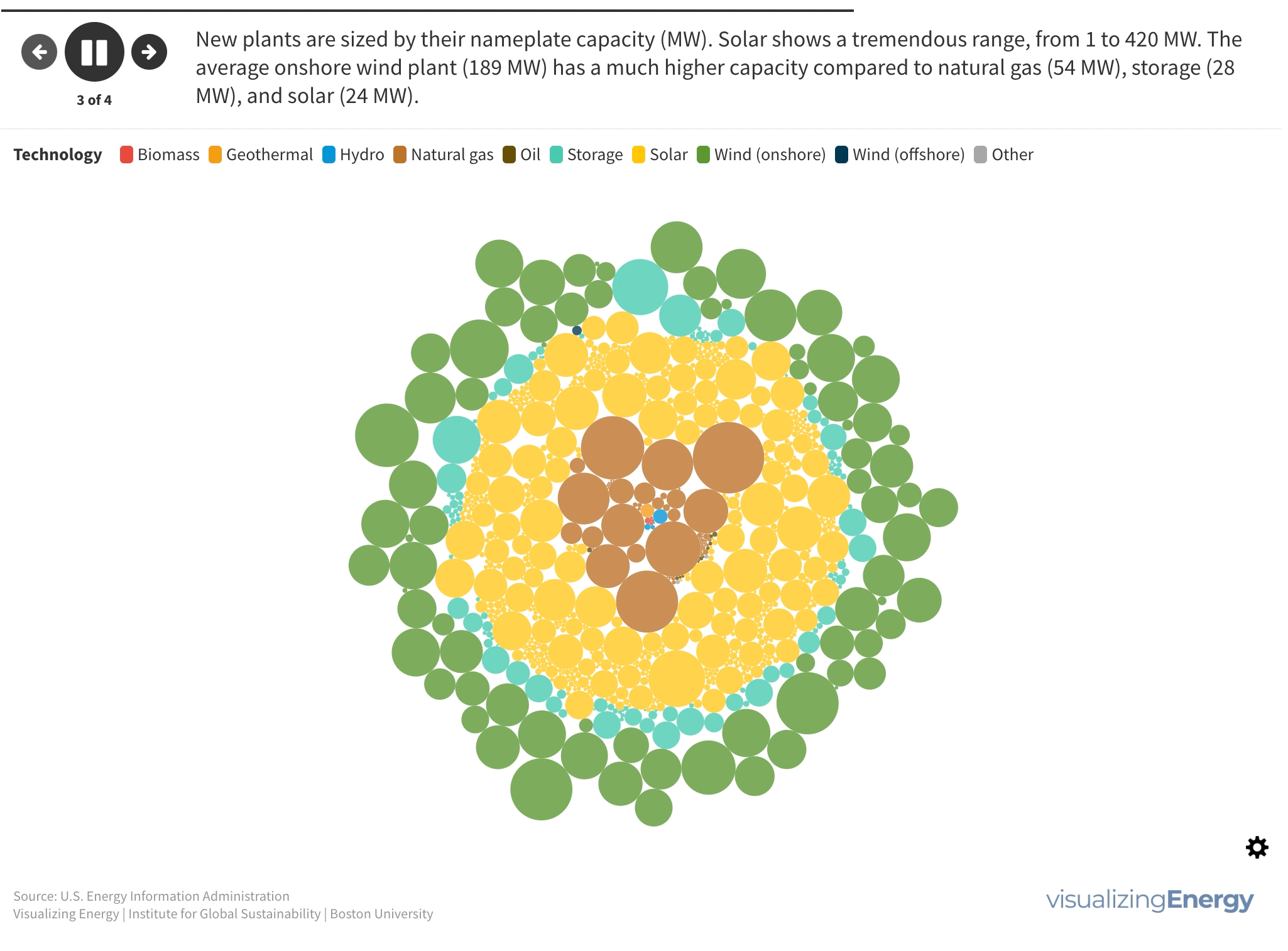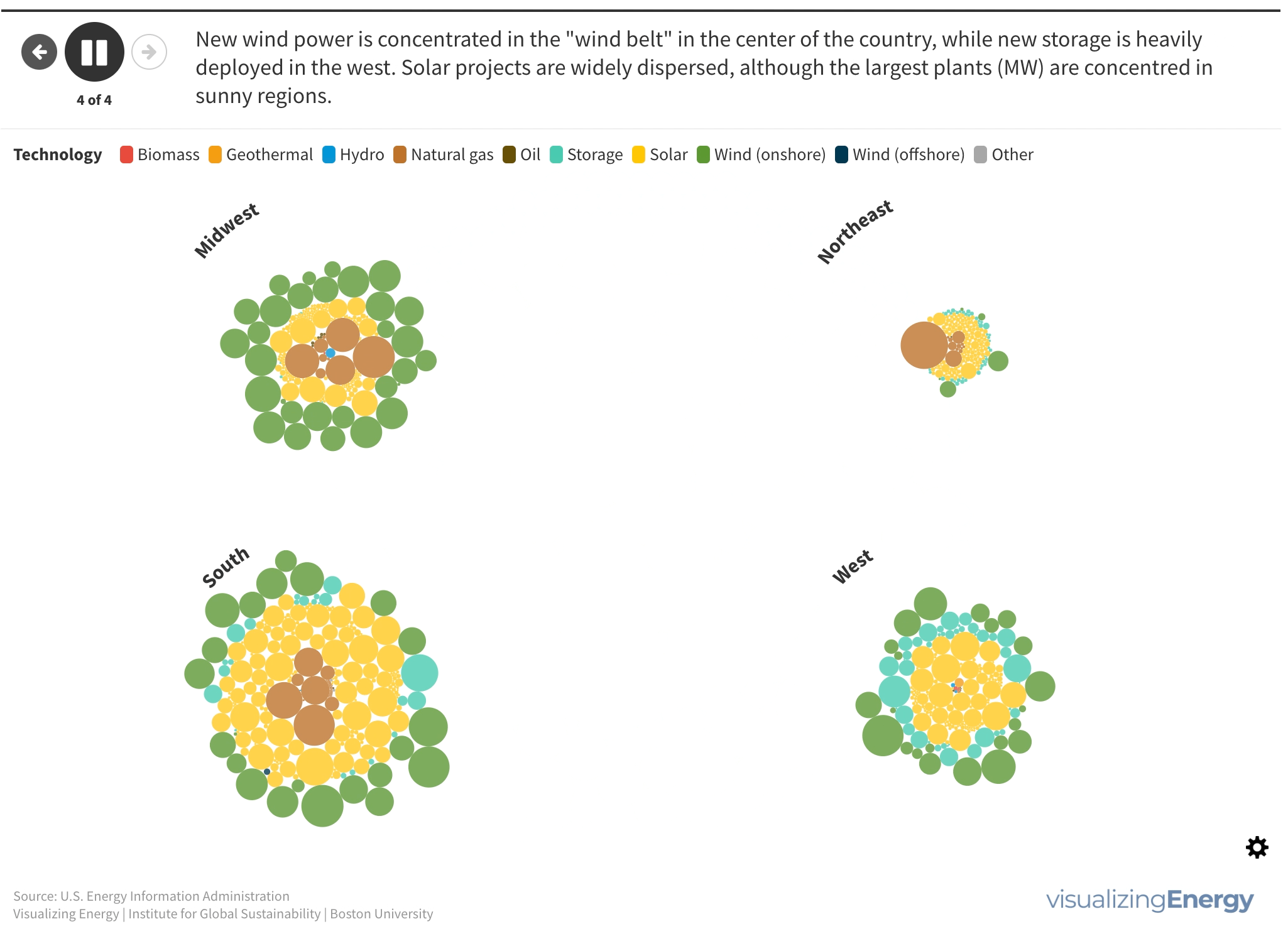
In 2021, the United States saw the addition of 851 new electric generating and storage units with at least 1 MW capacity, totaling 37,769 MW of new capacity. Wind and solar accounted for 79% of this new capacity, followed by natural gas (11%) and storage (9%).
What is the status of women in the global solar PV industry?
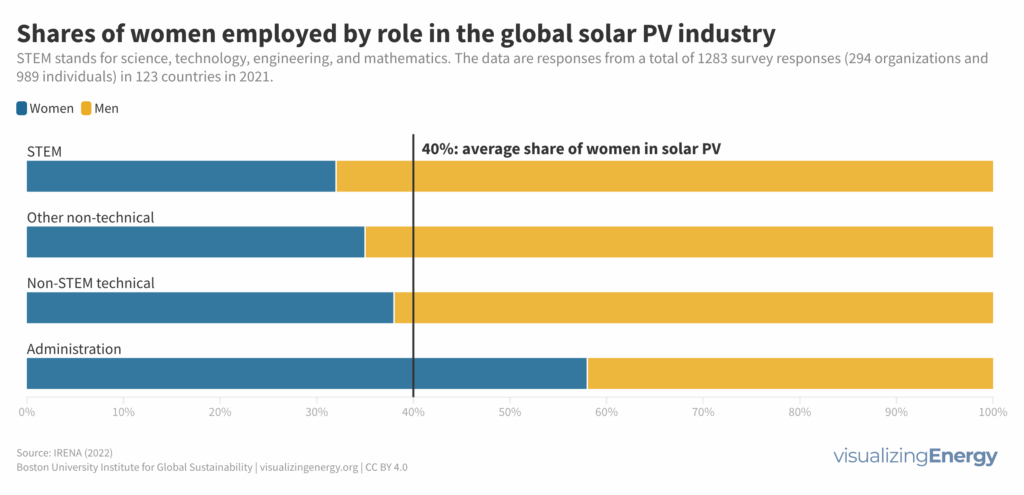
Women represent 40% of the global solar photovoltaic (PV) workforce, double the share in the wind industry and oil and gas sector. However, they are mainly in administrative and non-STEM technical positions, with underrepresentation in STEM and senior management roles. Gender bias and barriers to recruitment, advancement, and work-life balance exist in the industry, with women reporting higher perception of pay gaps and barriers.
Explore world wind power capacity added in 2020
In 2020, 938 new global wind projects added 75,812 MW, with the largest being the 1200 MW Hornsea offshore wind farm. Over 90% of new capacity came from onshore wind farms (76 MW average), while offshore farms averaged 283 MW.
Coal mine superemitters of methane
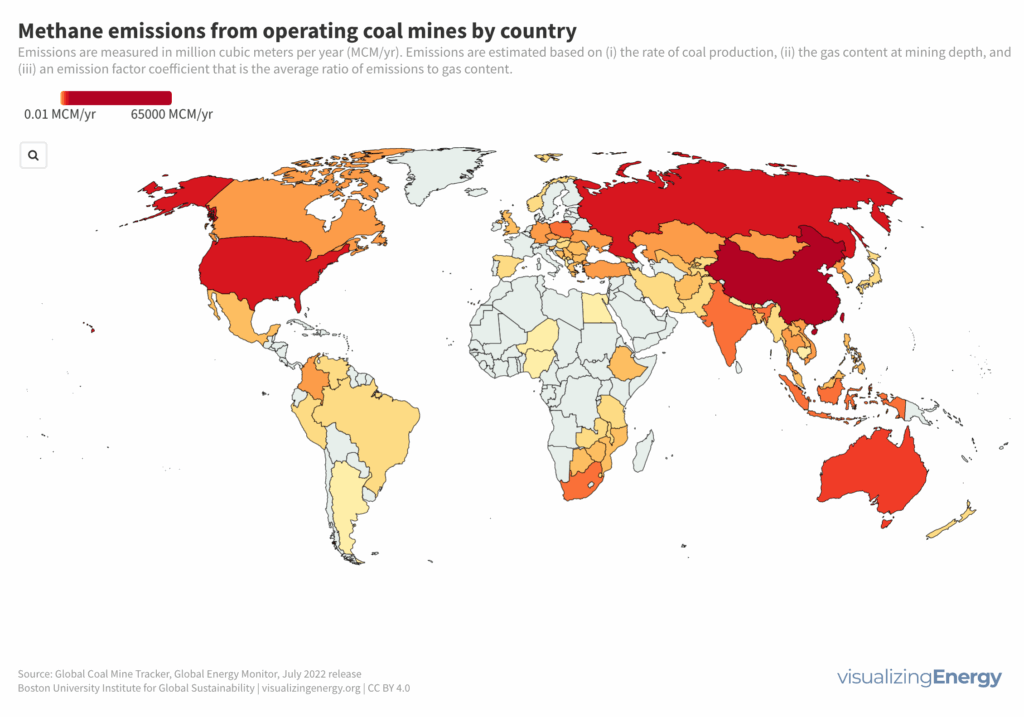
Methane emissions from coal mines are a significant concern for greenhouse gas reduction. Certain mines, known as “superemitters,” contribute a large proportion of global methane emissions. Factors like mine depth and coal rank affect methane content. While reducing coal use in electricity generation is important, mitigating methane emissions from mines needs greater attention.
