Underground natural gas storage in the United States
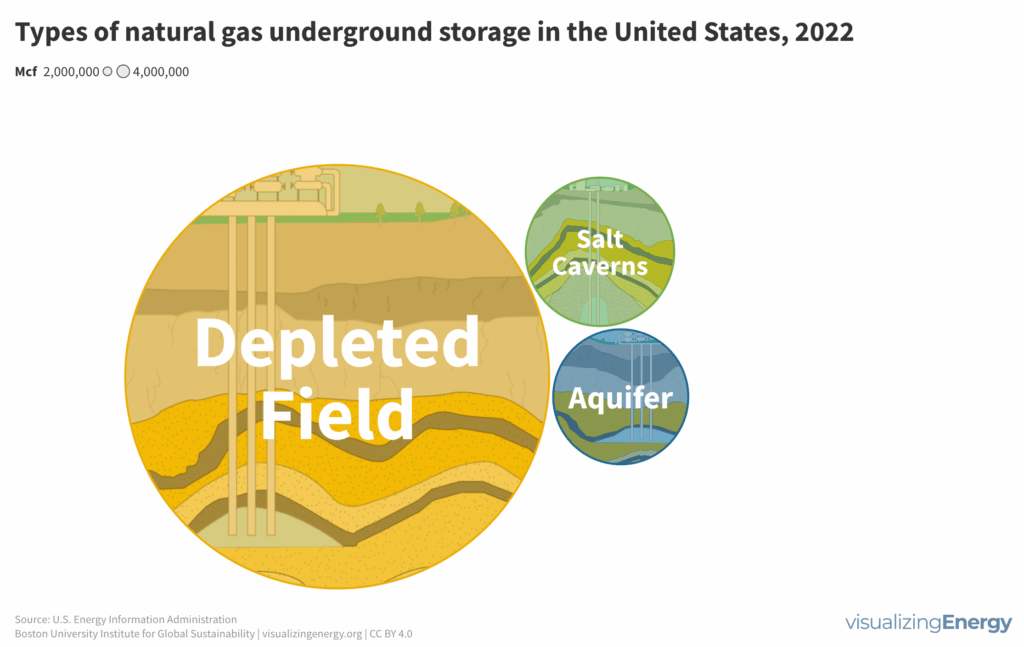
Natural gas demand in the U.S. varies seasonally, with higher consumption during colder months potentially causing price increases due to supply shortages. Underground storage, primarily in depleted reservoirs, salt caverns, and aquifers, helps balance supply and demand year-round. Storage levels drop significantly during colder winters, affecting overall availability.
Watch the history of pumped storage hydropower in the United States
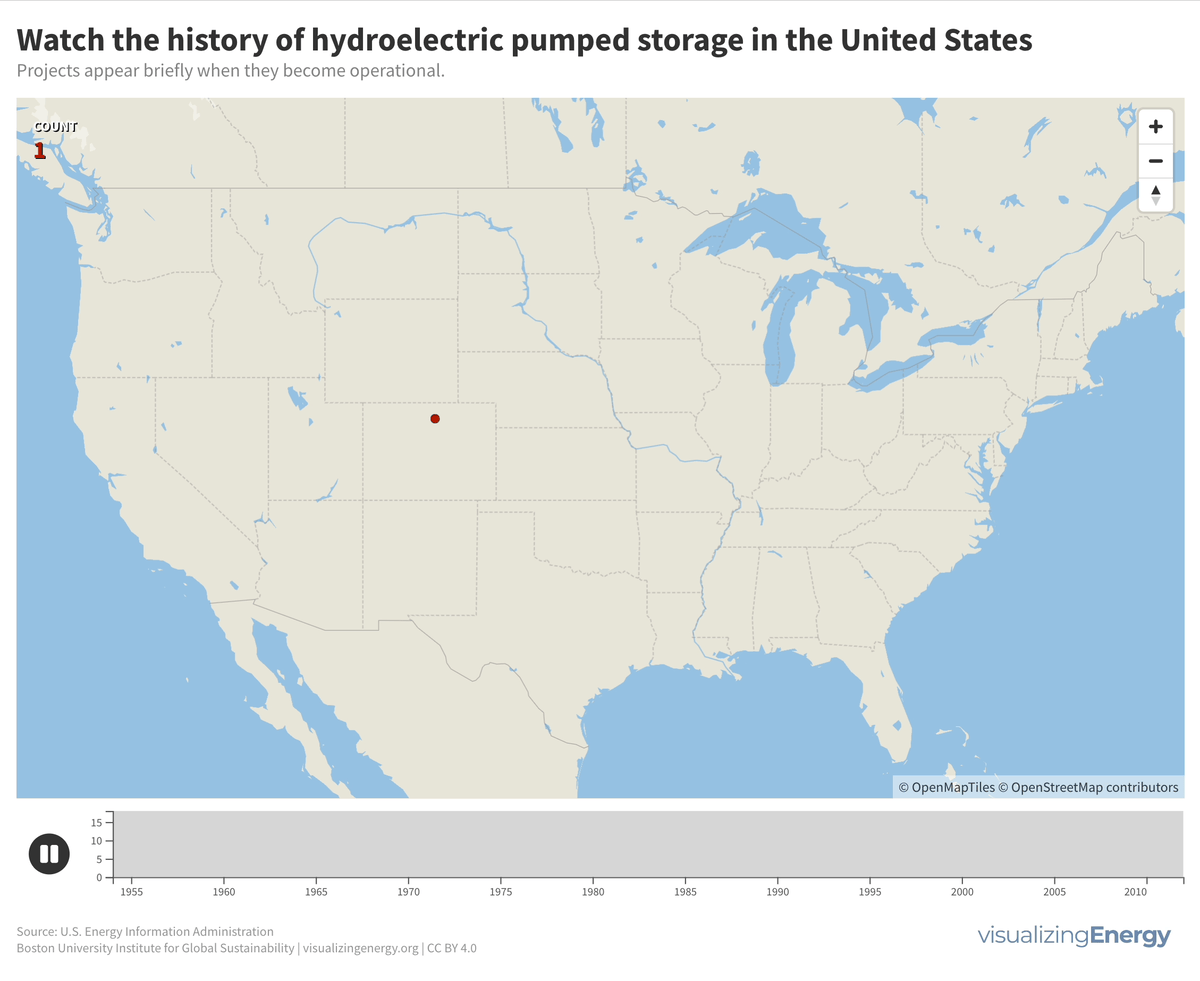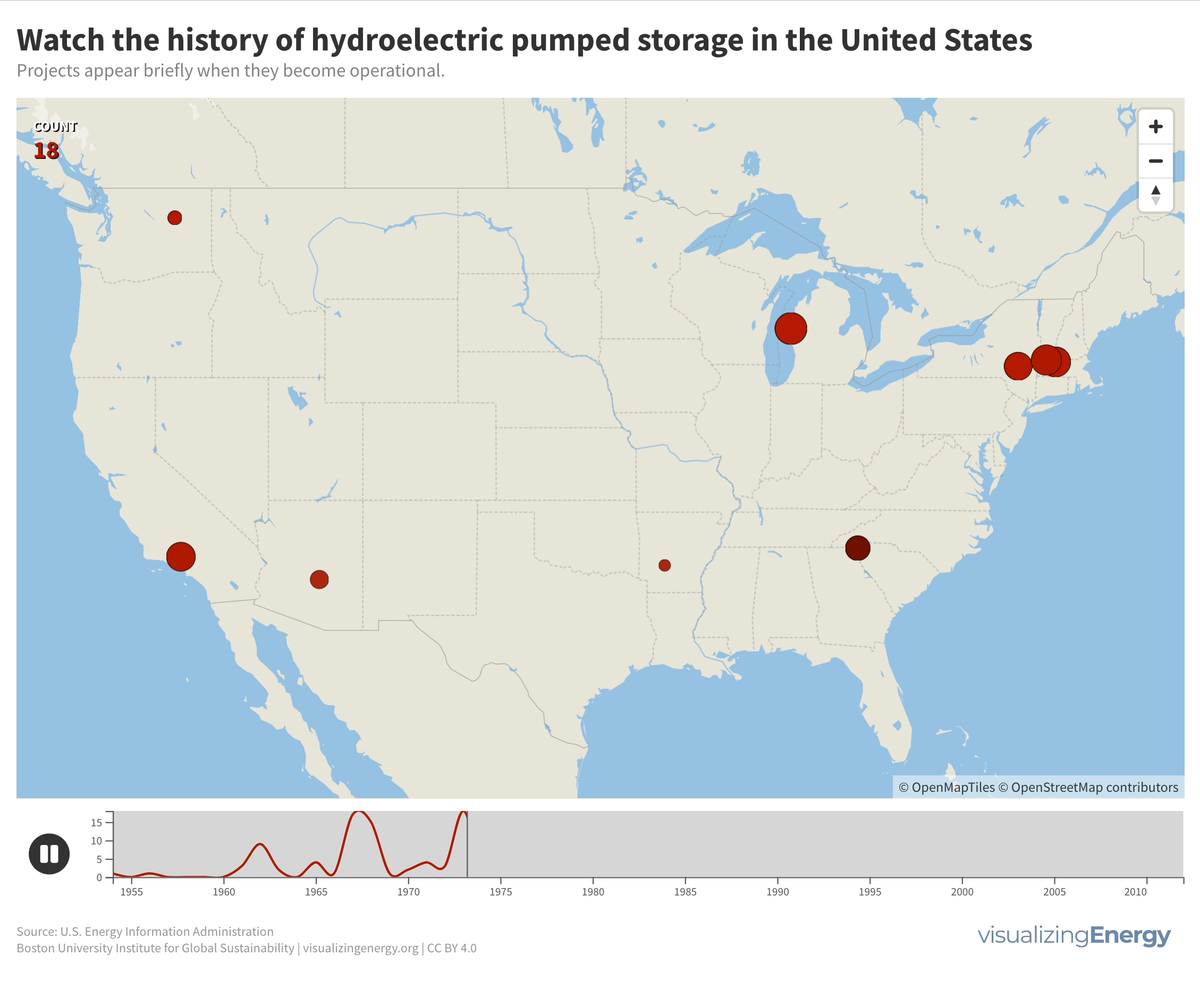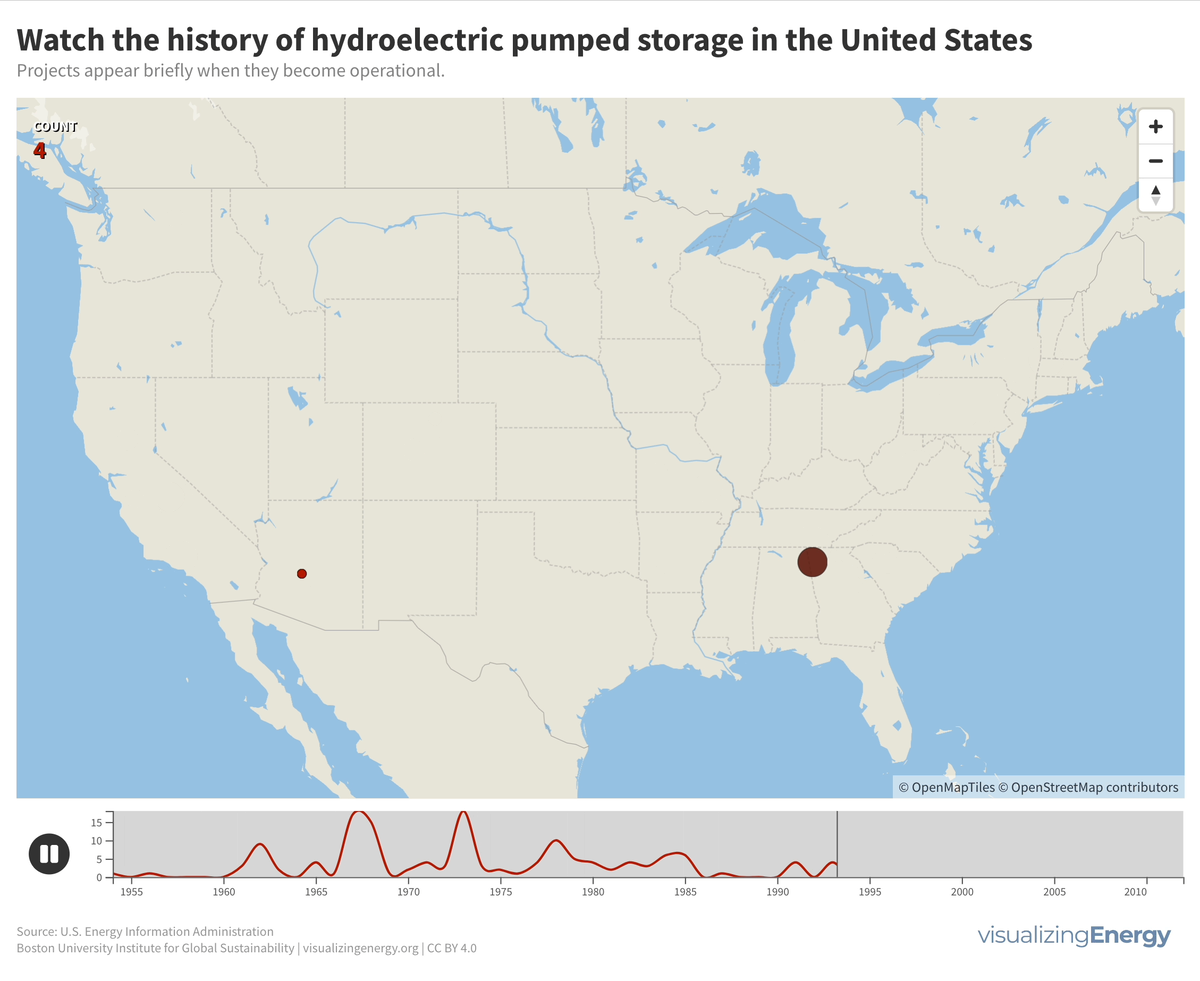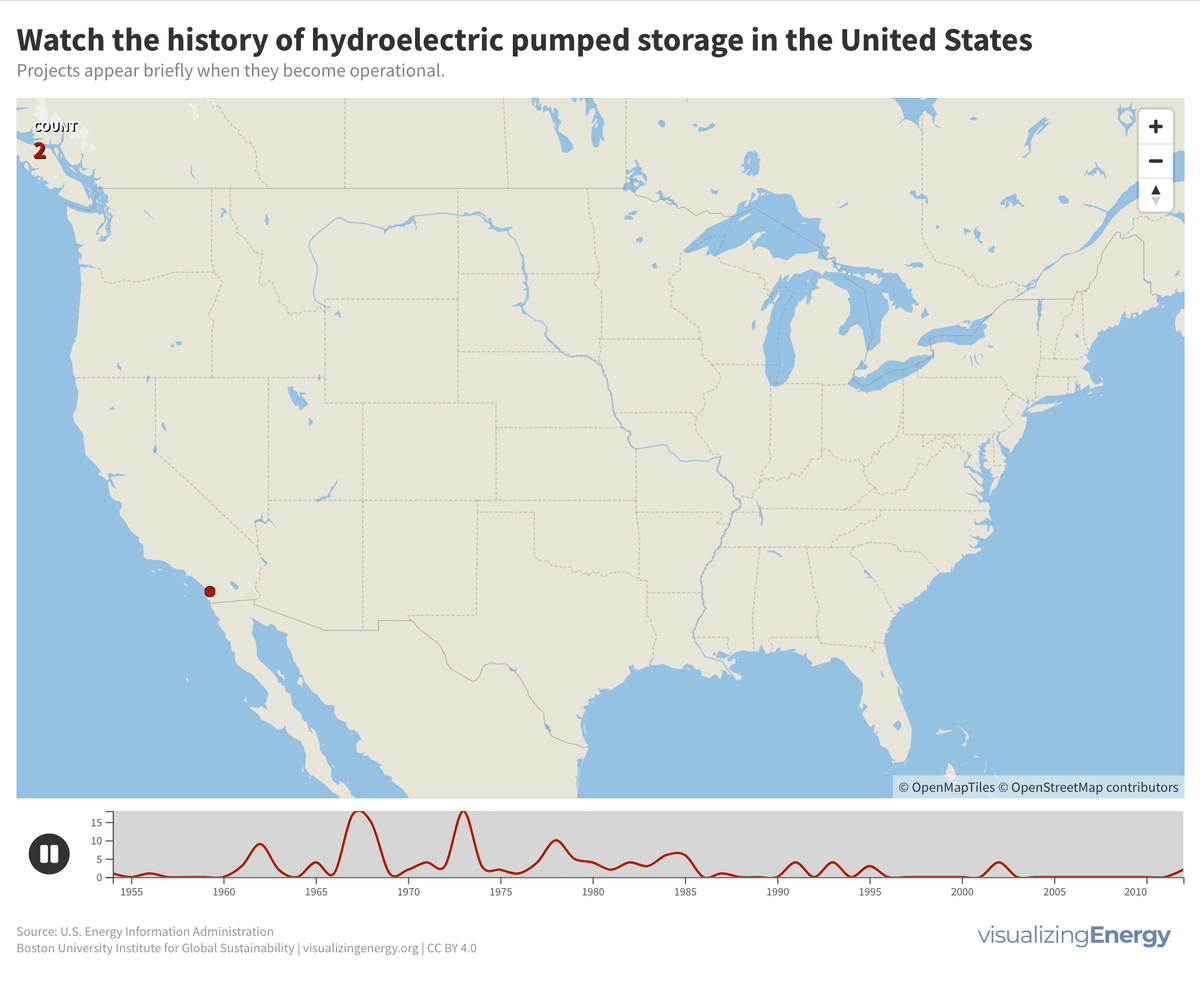
Pumped storage plants for hydroelectric power in the United States were primarily built between 1960 and 1990. There have been no new projects since 2012, but three new ones have been proposed, potentially adding 2.6 GW to the existing 22 GW capacity. The largest facility is the Bath County Pumped Storage Station in Virginia, with 2.9 GW.
Watch the history of battery storage in the United States
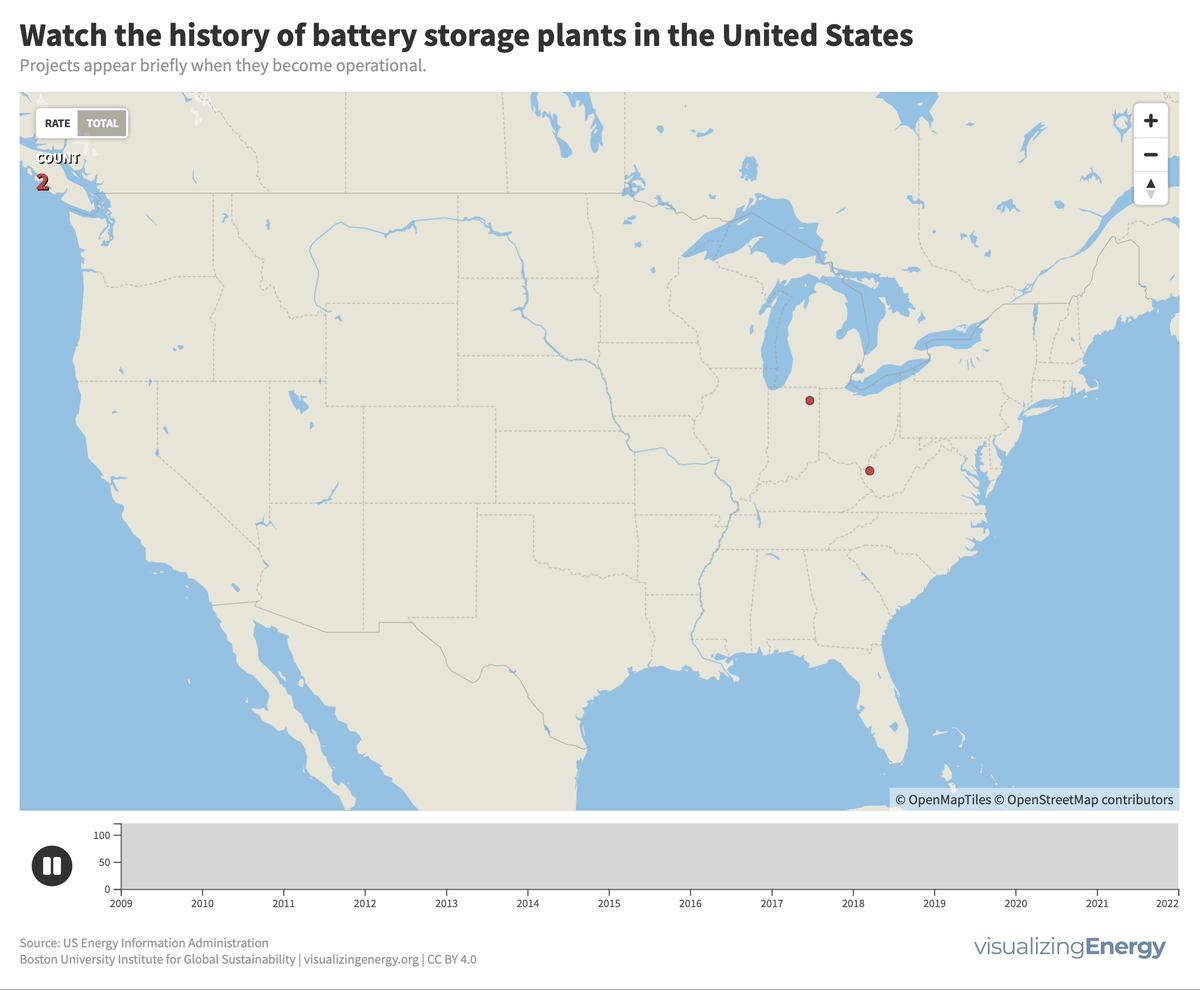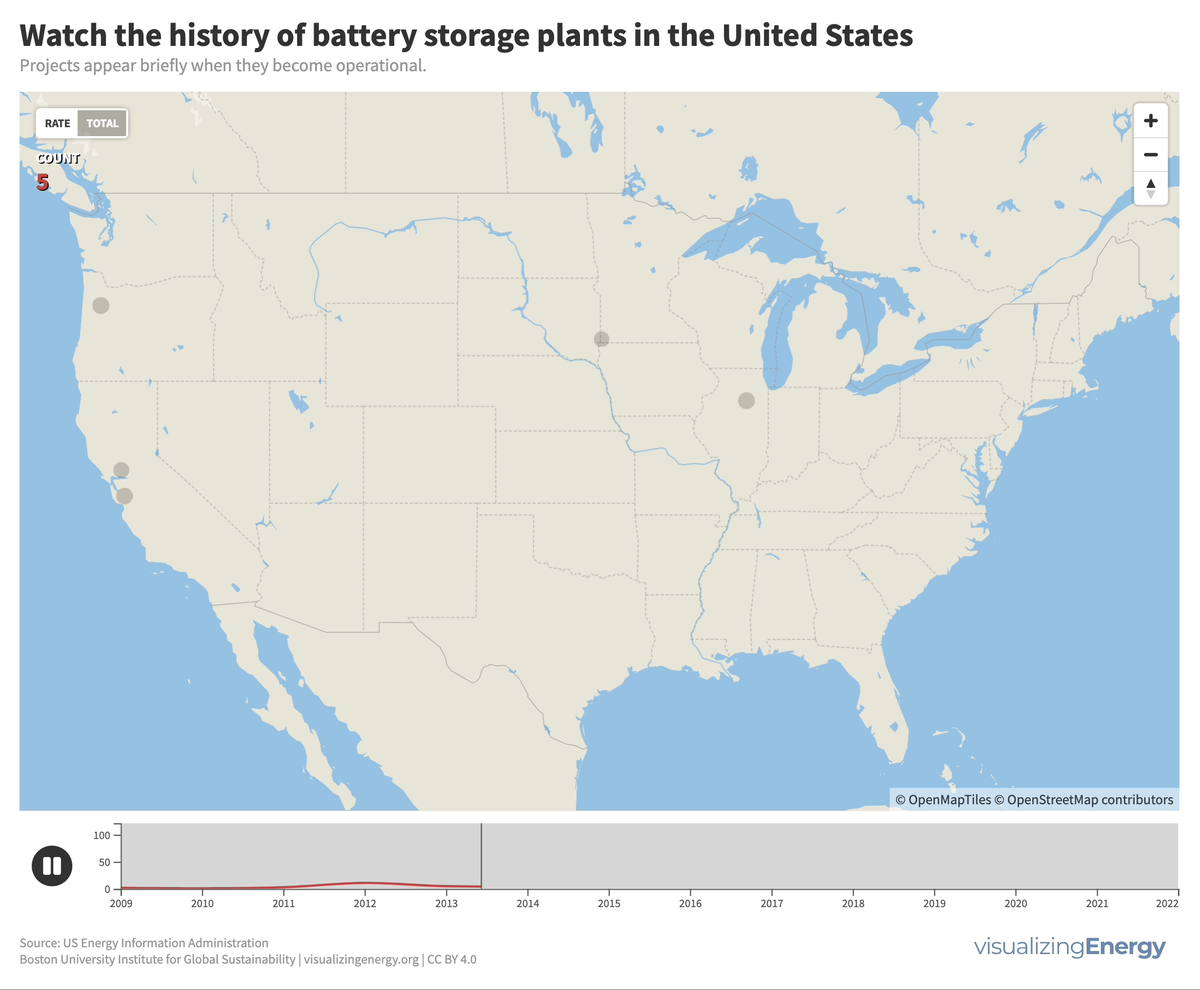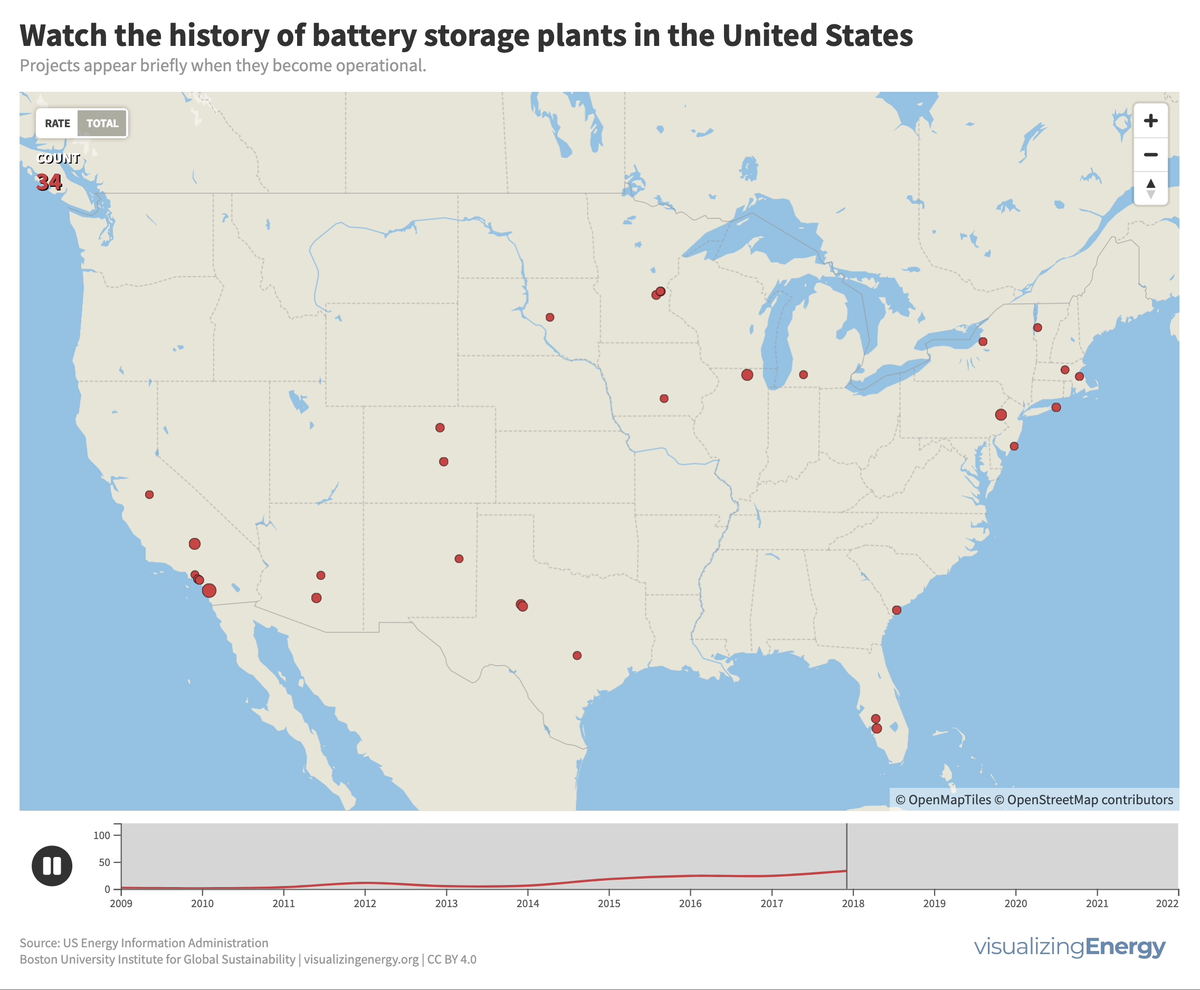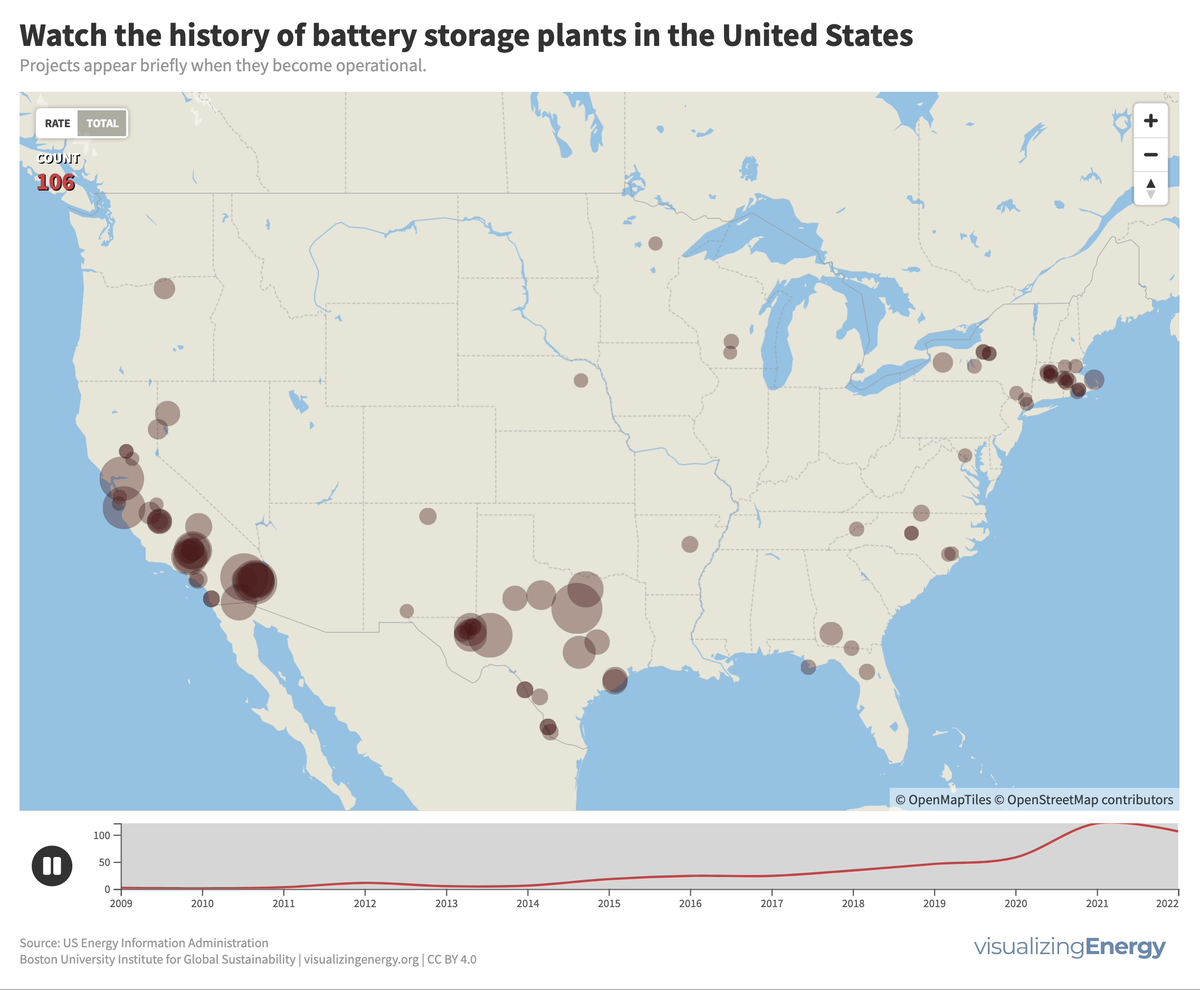
Utility-scale battery storage (BESS) systems store and distribute large-scale electricity and are crucial for renewable energy integration. Since the mid-2000s, about 460 such systems were built in the U.S., the largest being the 409 MW Manatee Energy Storage Center.
