What are capacity factors and why are they important?
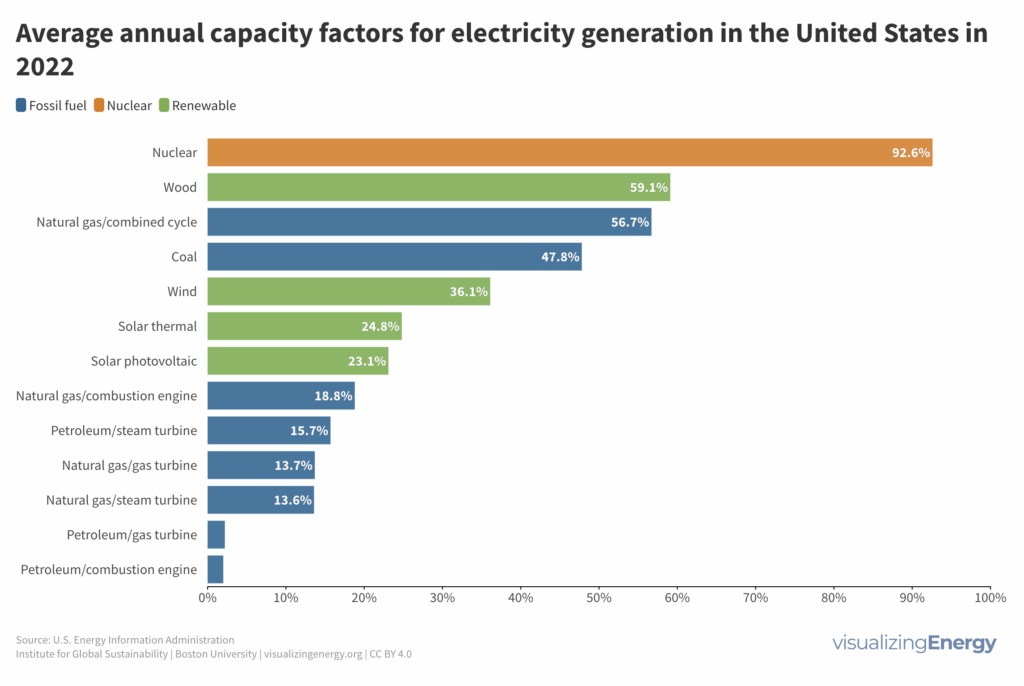
The capacity factor is a crucial measure for electricity generation. It represents the ratio of actual electrical energy production to the maximum possible output over a specific period. Nuclear plants lead with a 90%+ factor, while renewable sources like wind and solar struggle due to intermittency. New challenges arise with climate change impacting demand and production patterns.
Watch the history of biopower plants in the United States
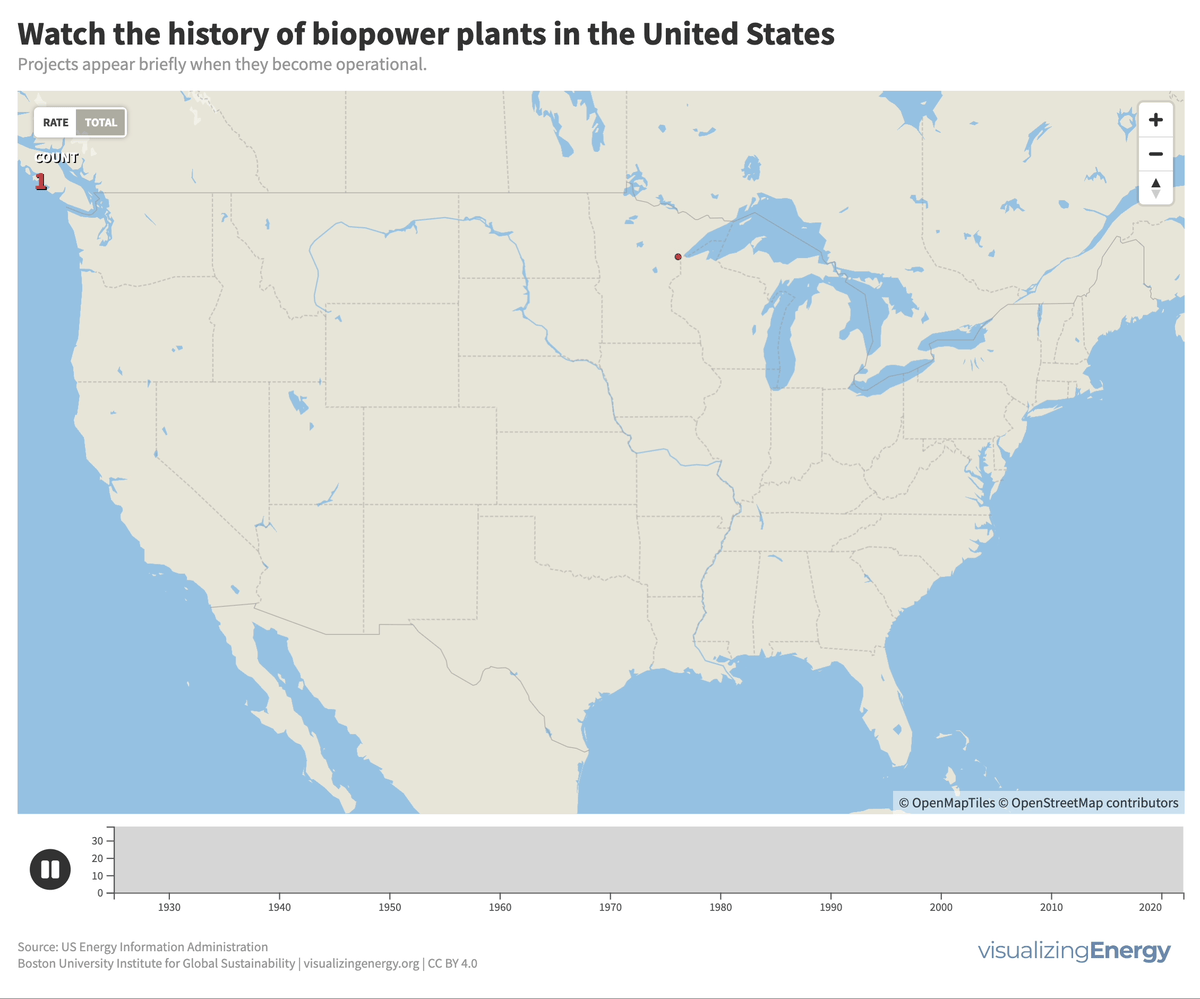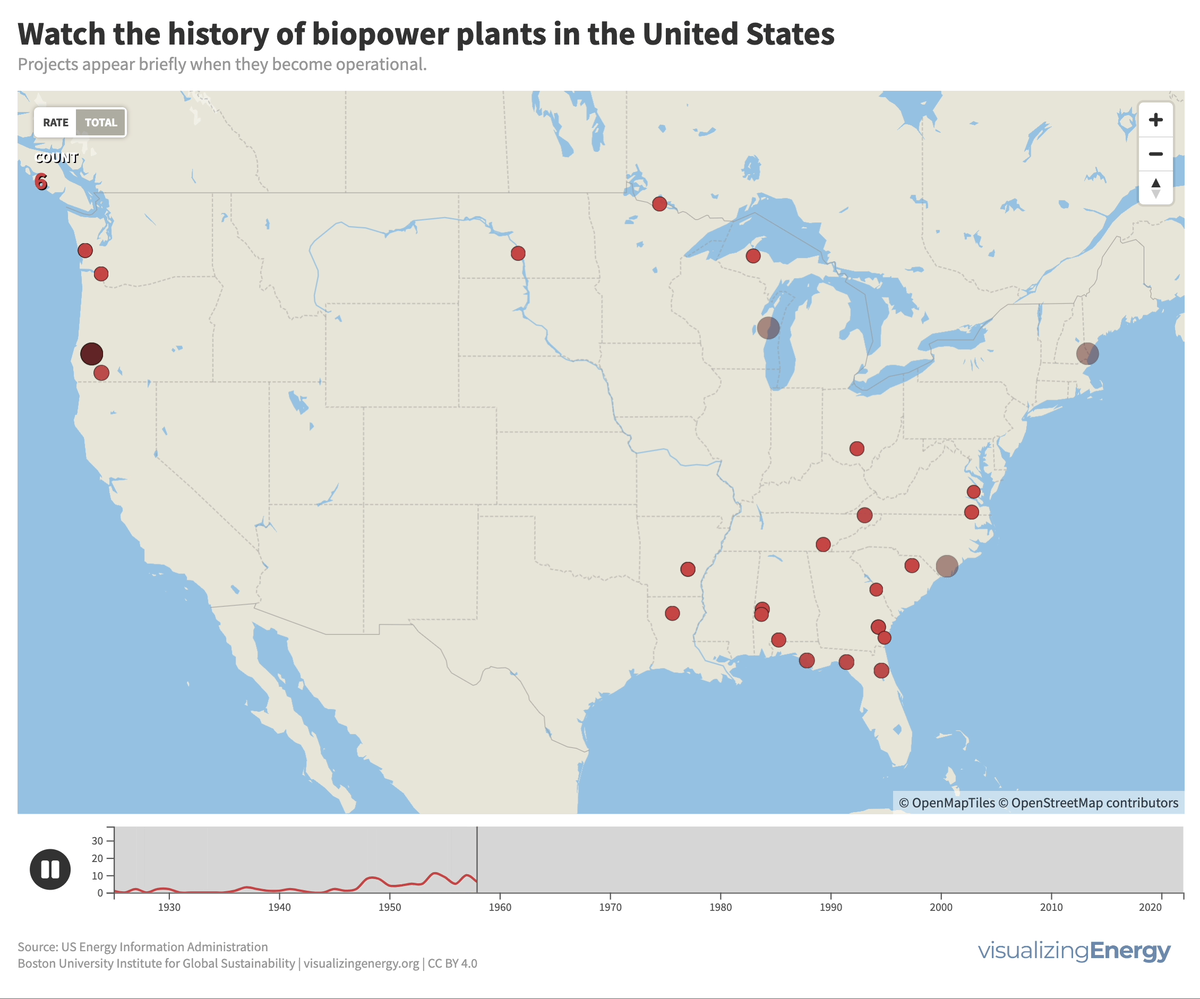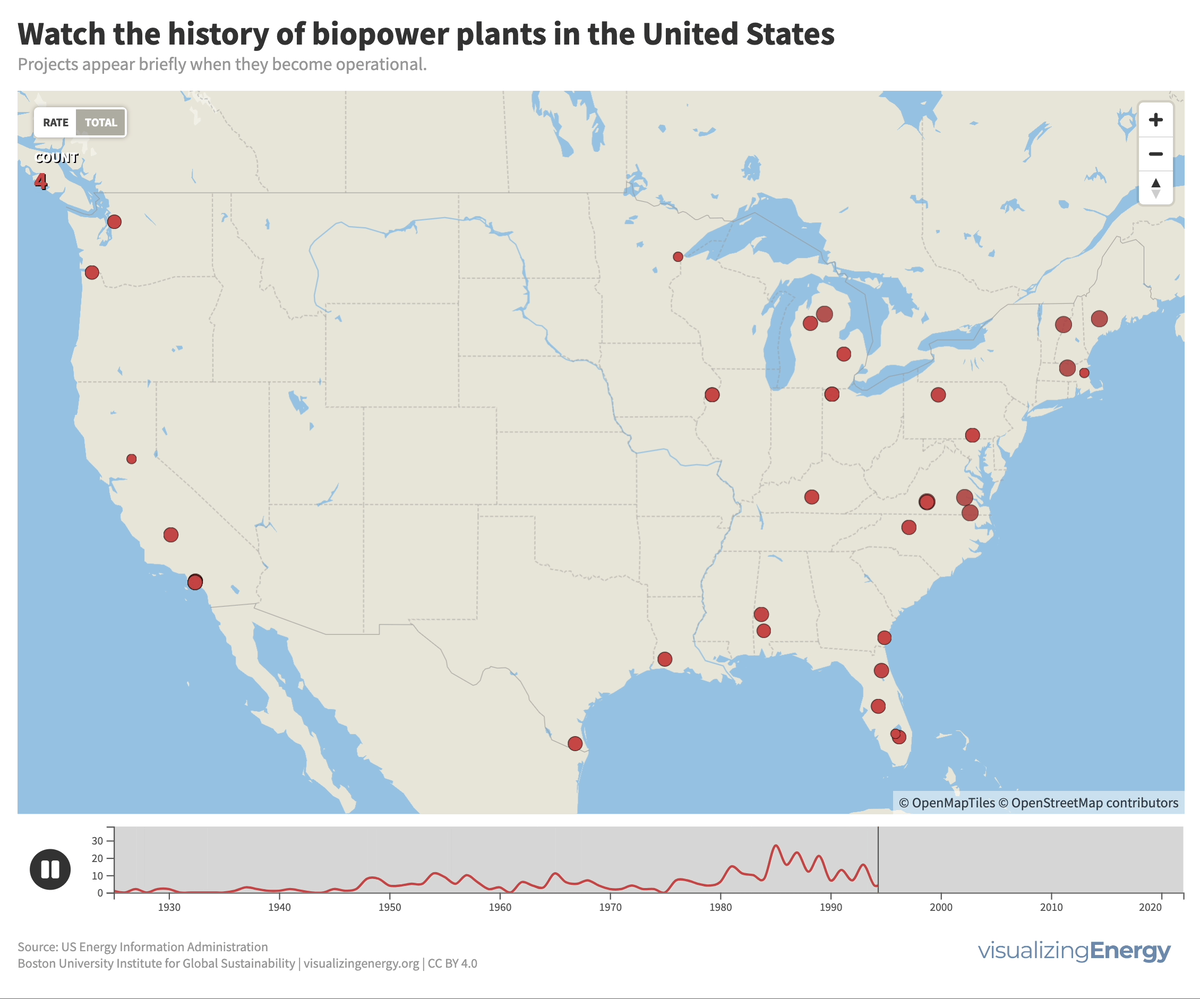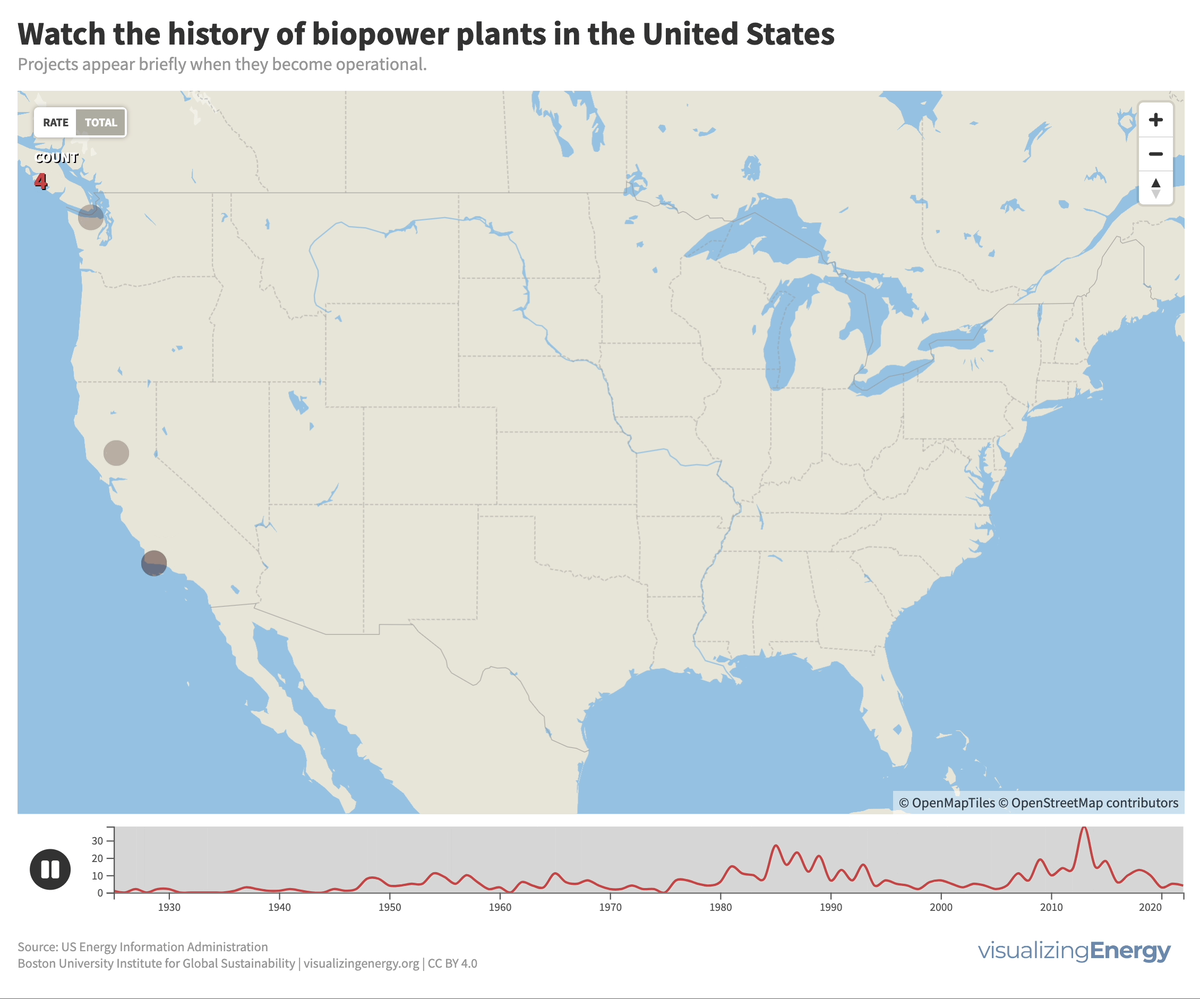
Biomass generates electricity, or biopower, from sources like wood, agricultural residues, and urban waste. In the US, it accounts for 1.2% of electricity.
Where do people lack access to electricity?
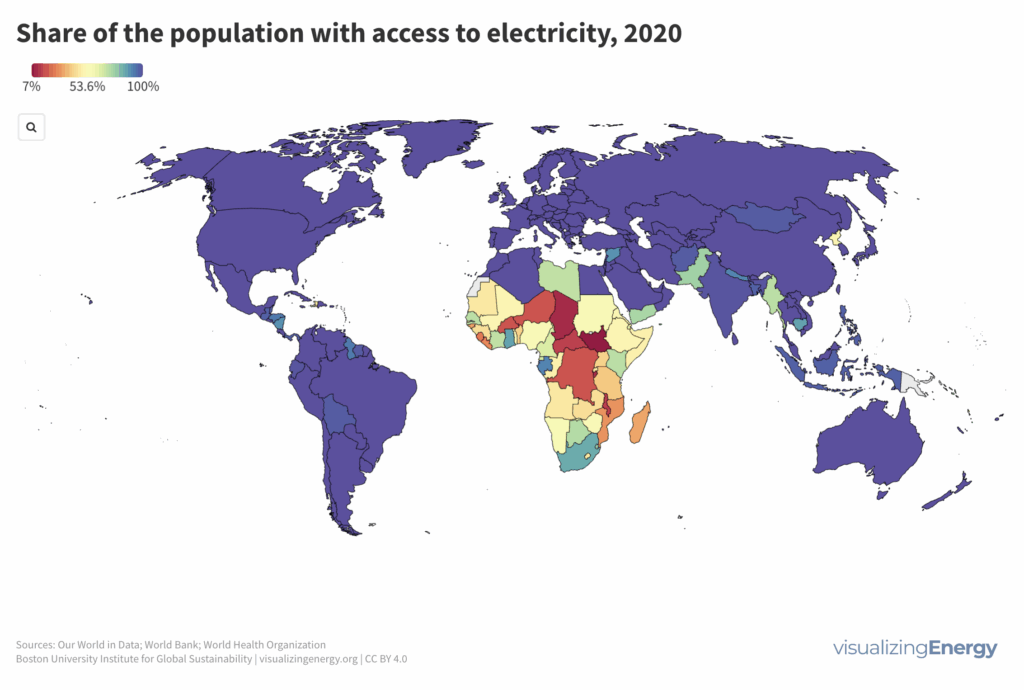
The United Nations’ 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) include SDG7, which aims to ensure affordable and sustainable energy for all. The share of global population with access to electricity has increased to 90% in 2022, yet around 800 million people are still without access, mostly in sub-Saharan Africa. Various factors influence access to electricity, impacting income and well-being.
Watch the history of coal power plants in the United States
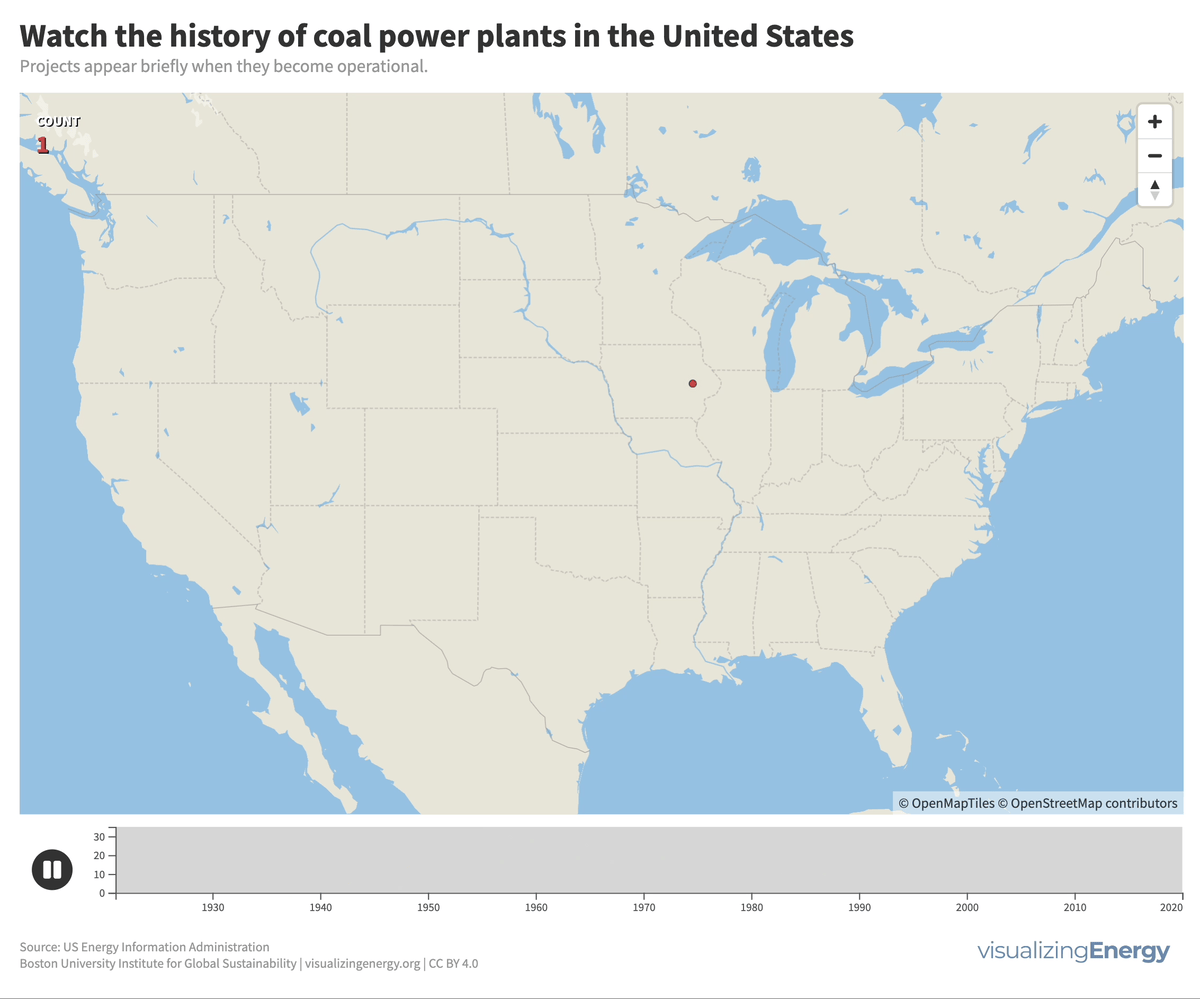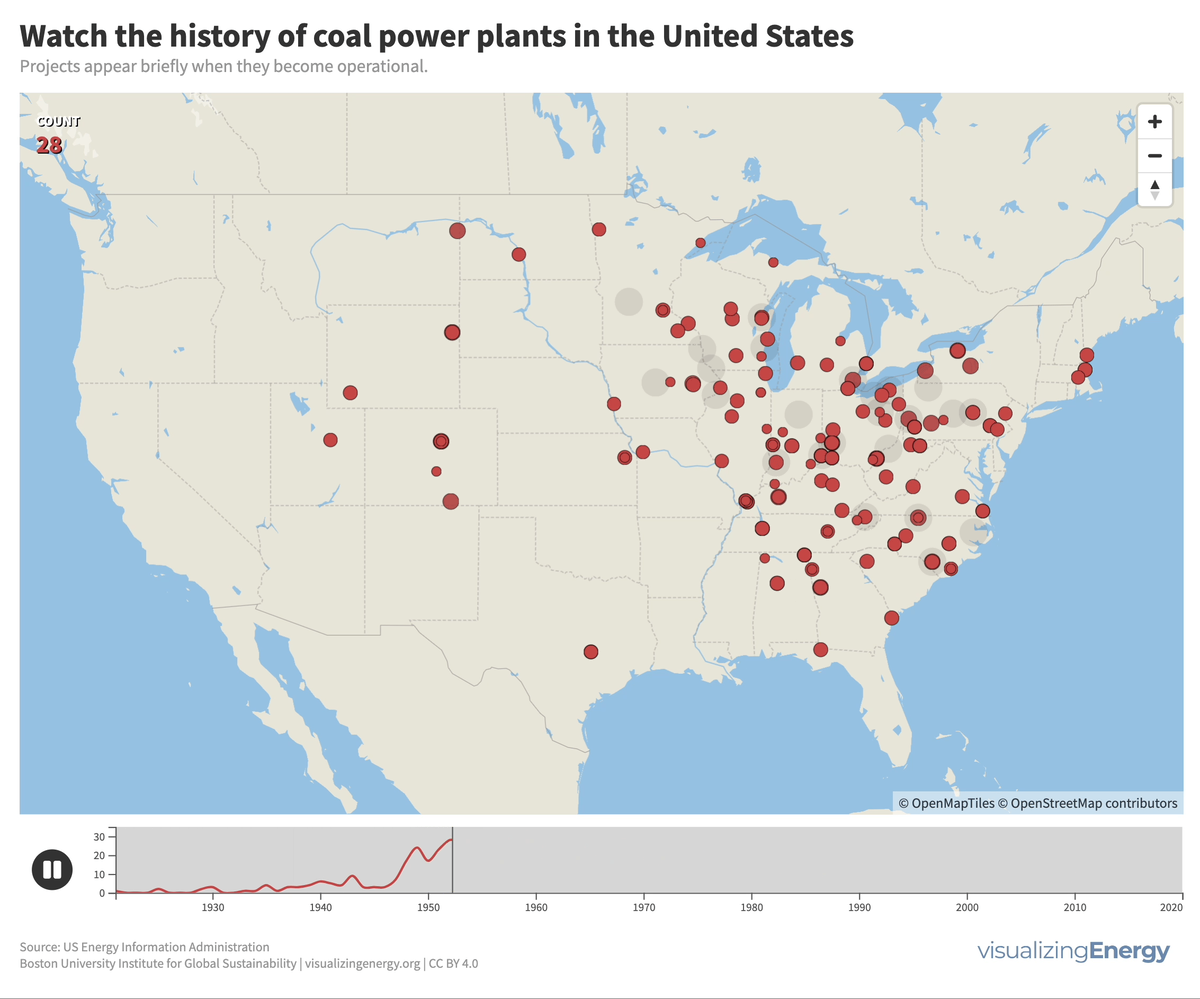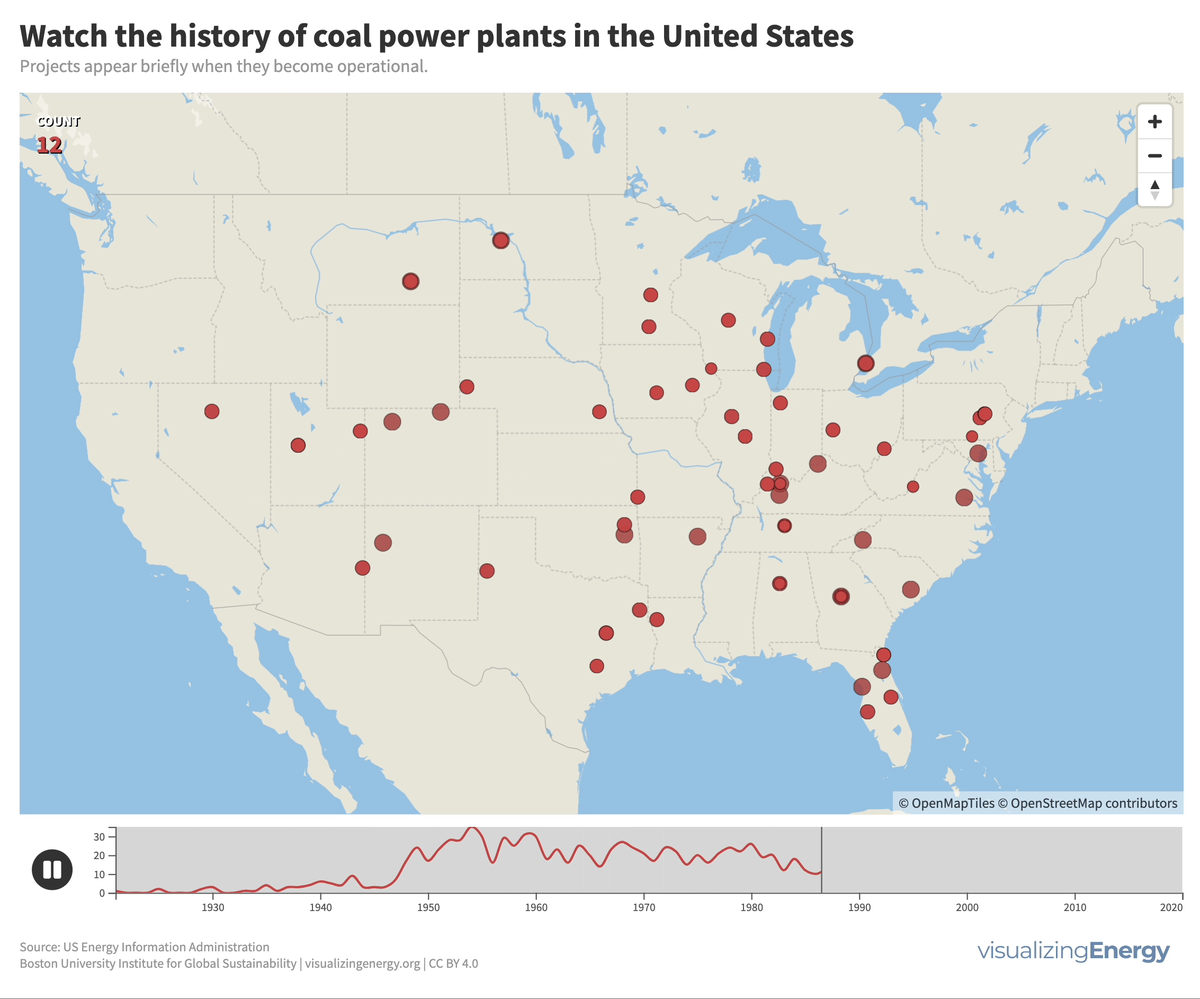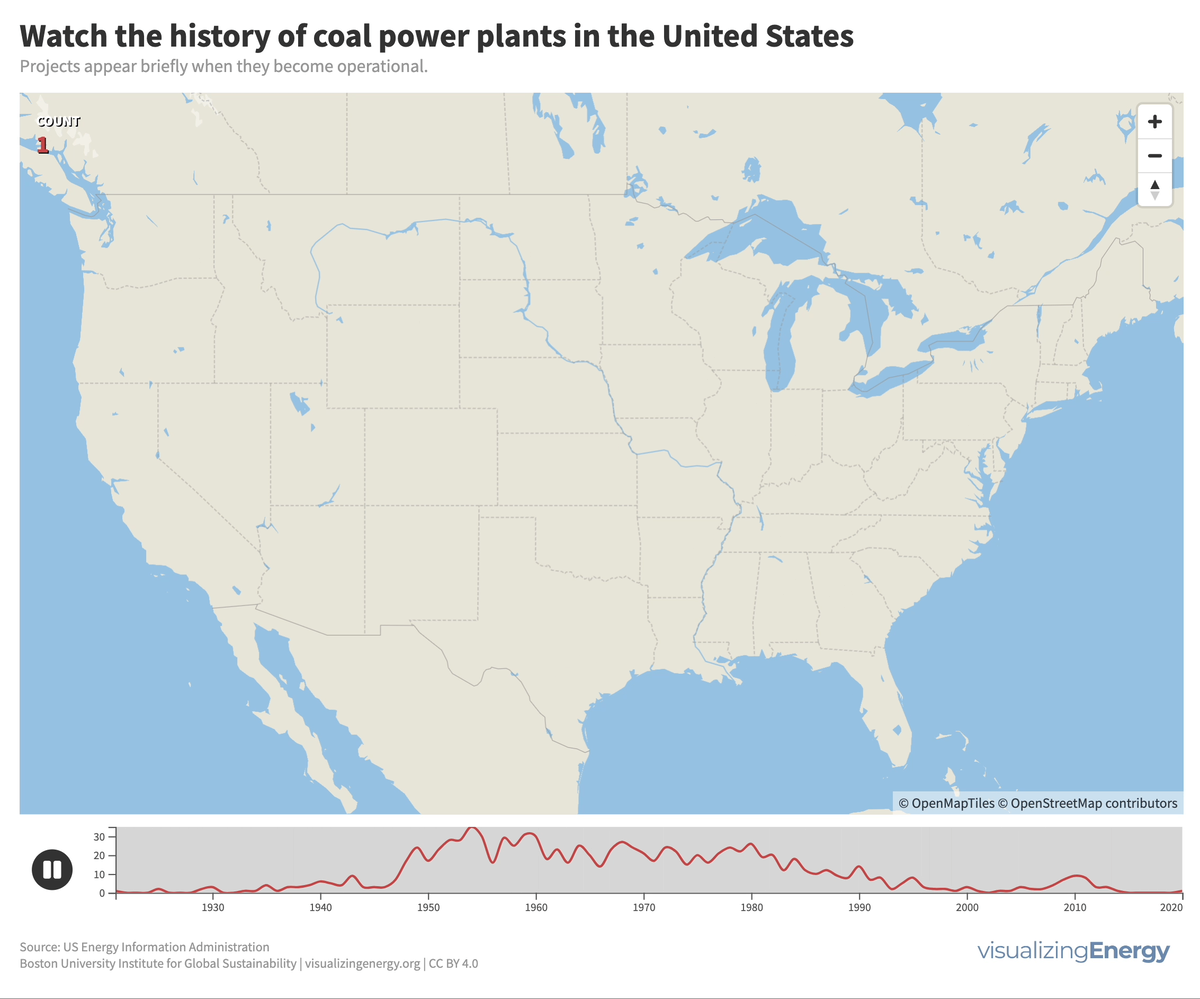
Coal played a significant role in the US, generating half of the nation’s electricity in 1920 and maintaining that share for decades. However, aging coal plants are being retired due to competition from efficient natural gas and renewable energy sources, as well as state climate policies. This shift reflects growing concerns about cost and carbon emissions.
Watch the history of geothermal power in the United States
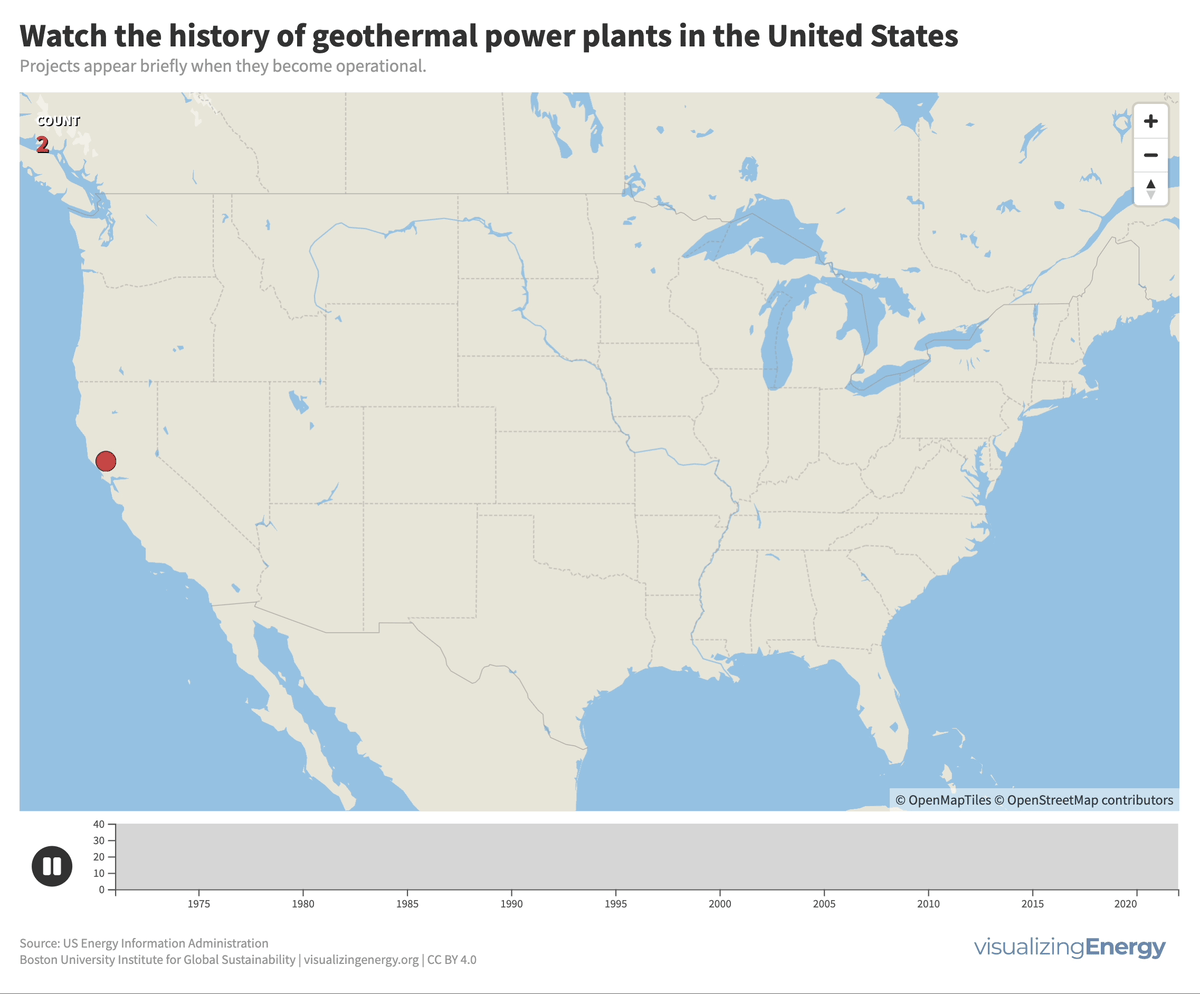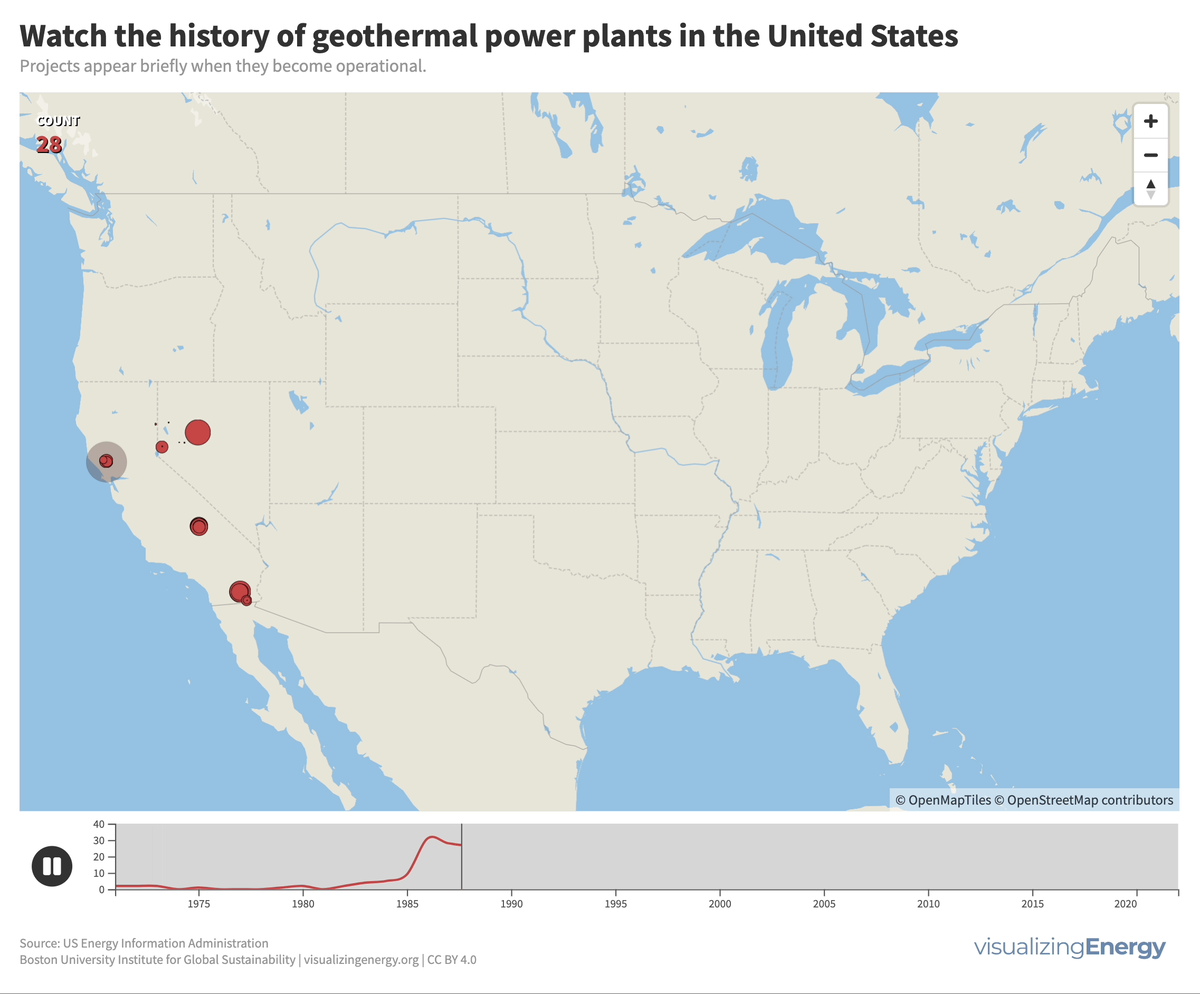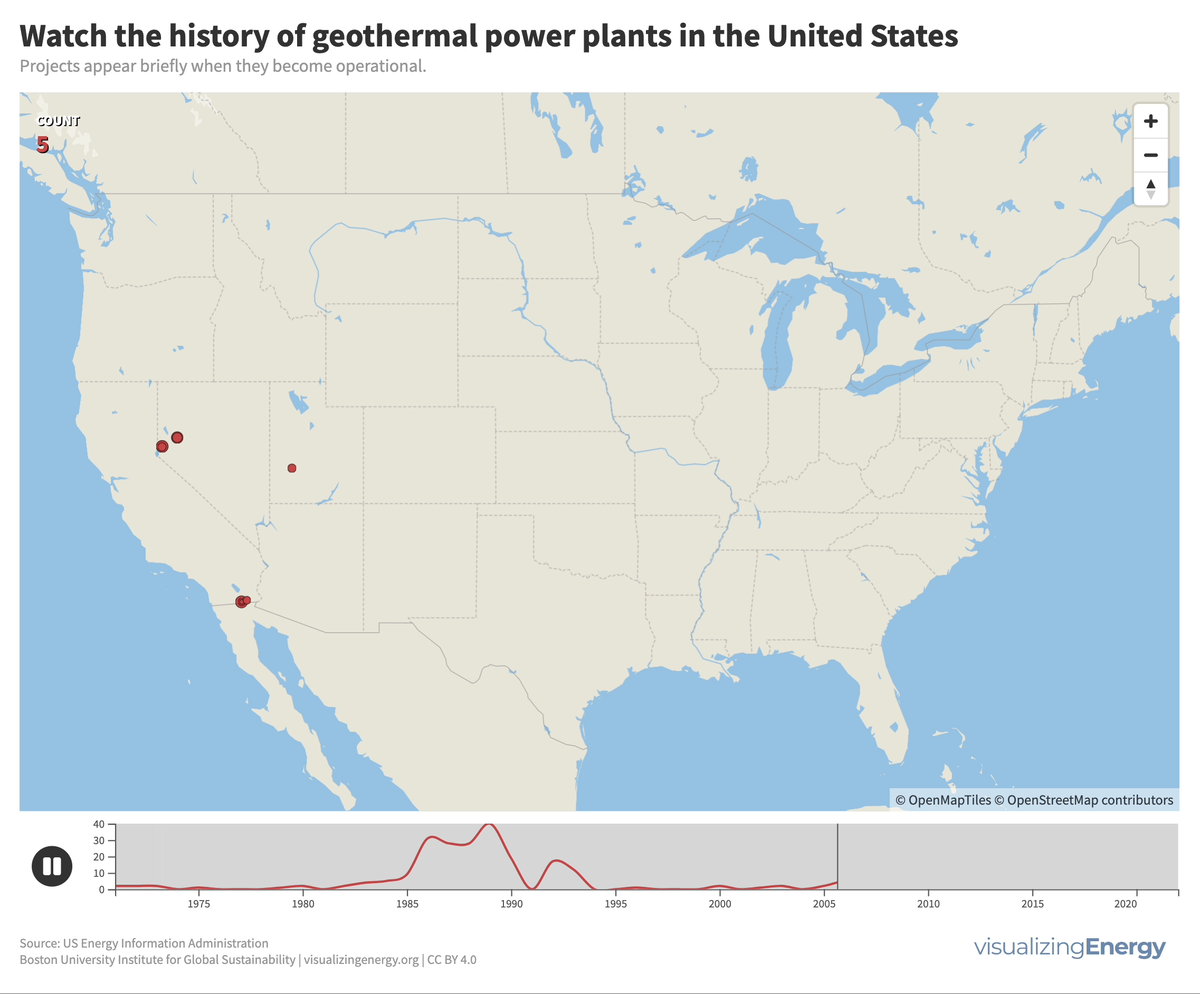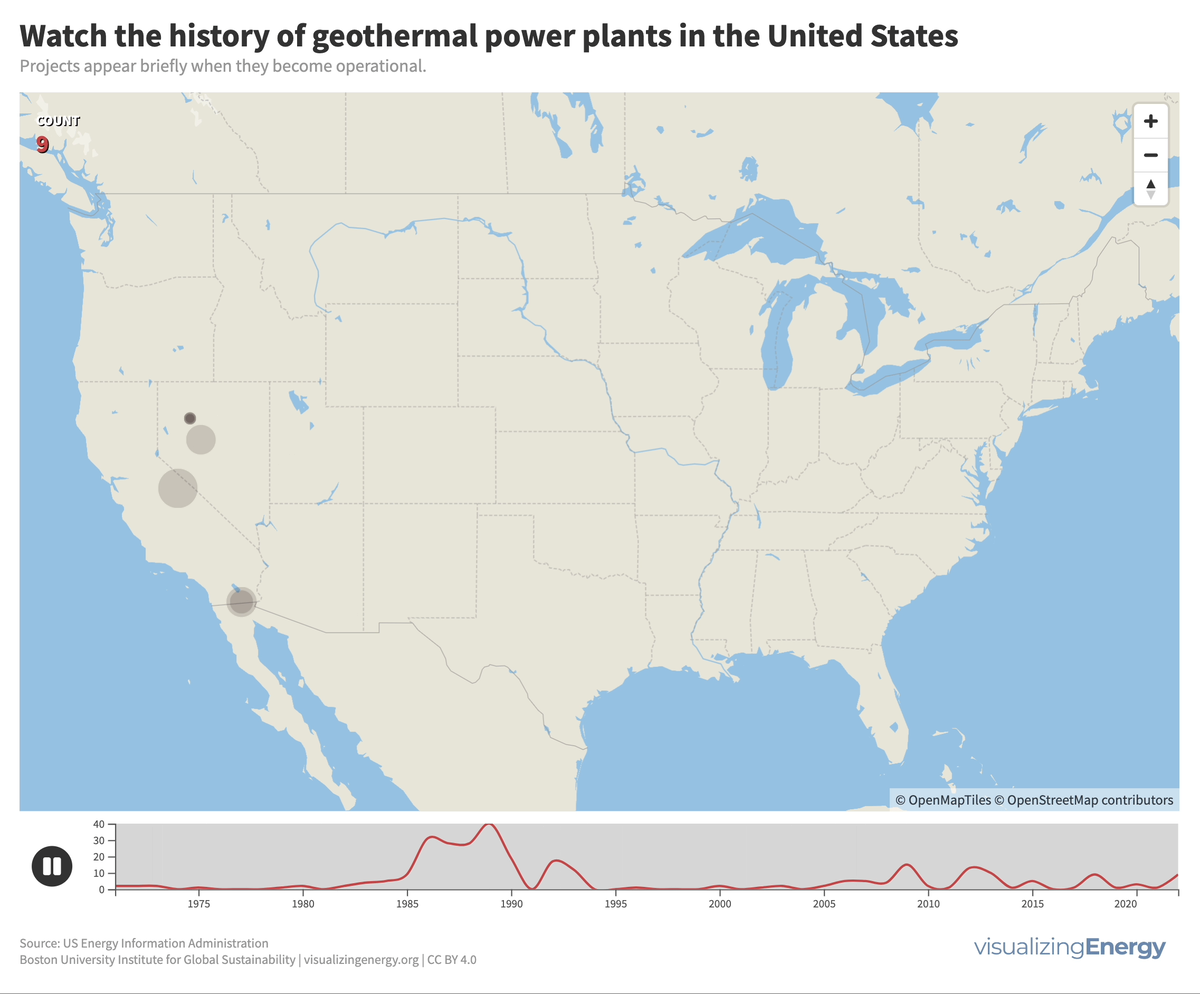
In the United States, geothermal power plants are predominantly located in six western states due to significant tectonic activity. In 2022, California housed 72% of this capacity, generating 6% of its electricity from geothermal power. The Geysers project in northern California is the world’s largest geothermal array.
Watch the history of solar power in the United States
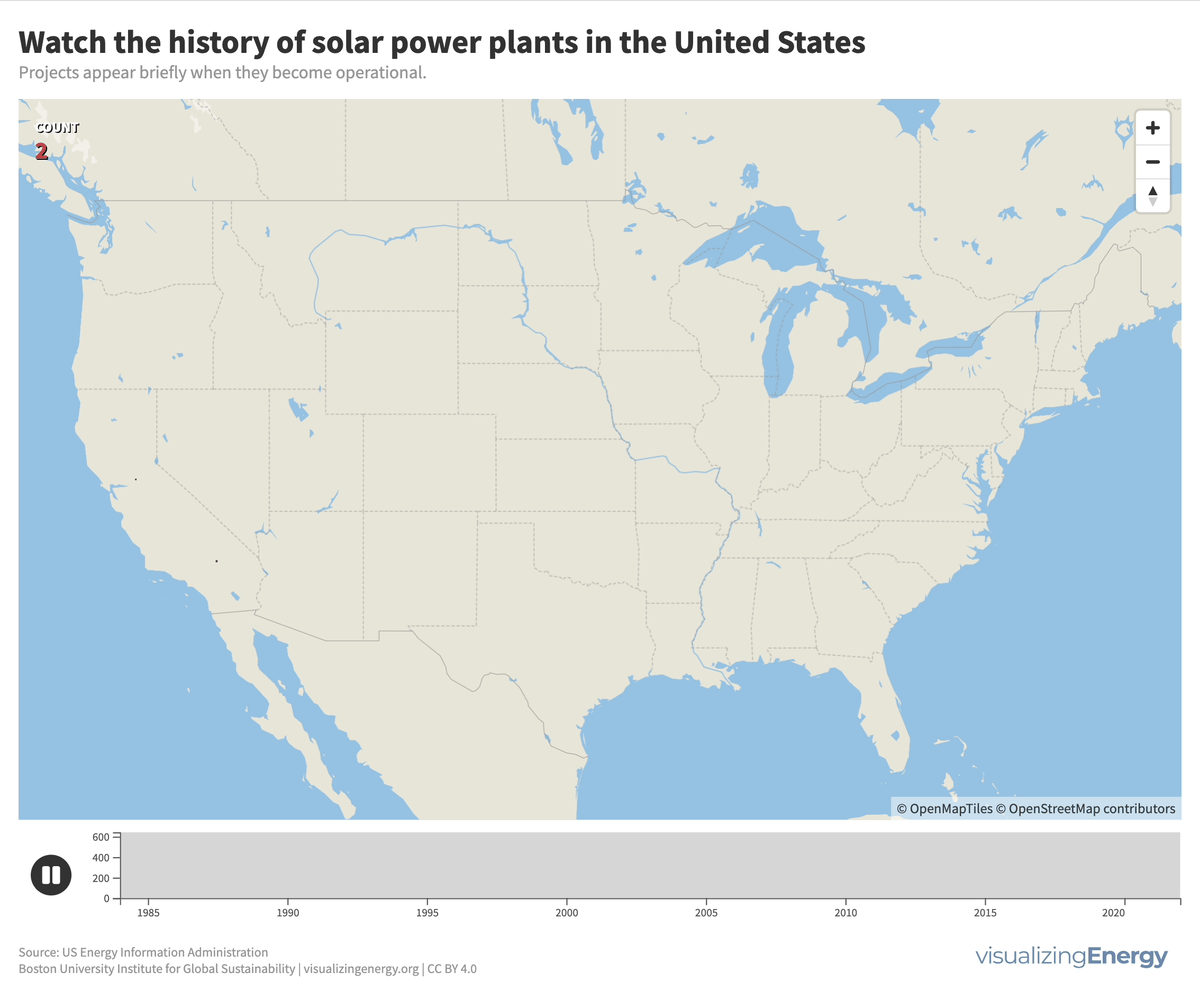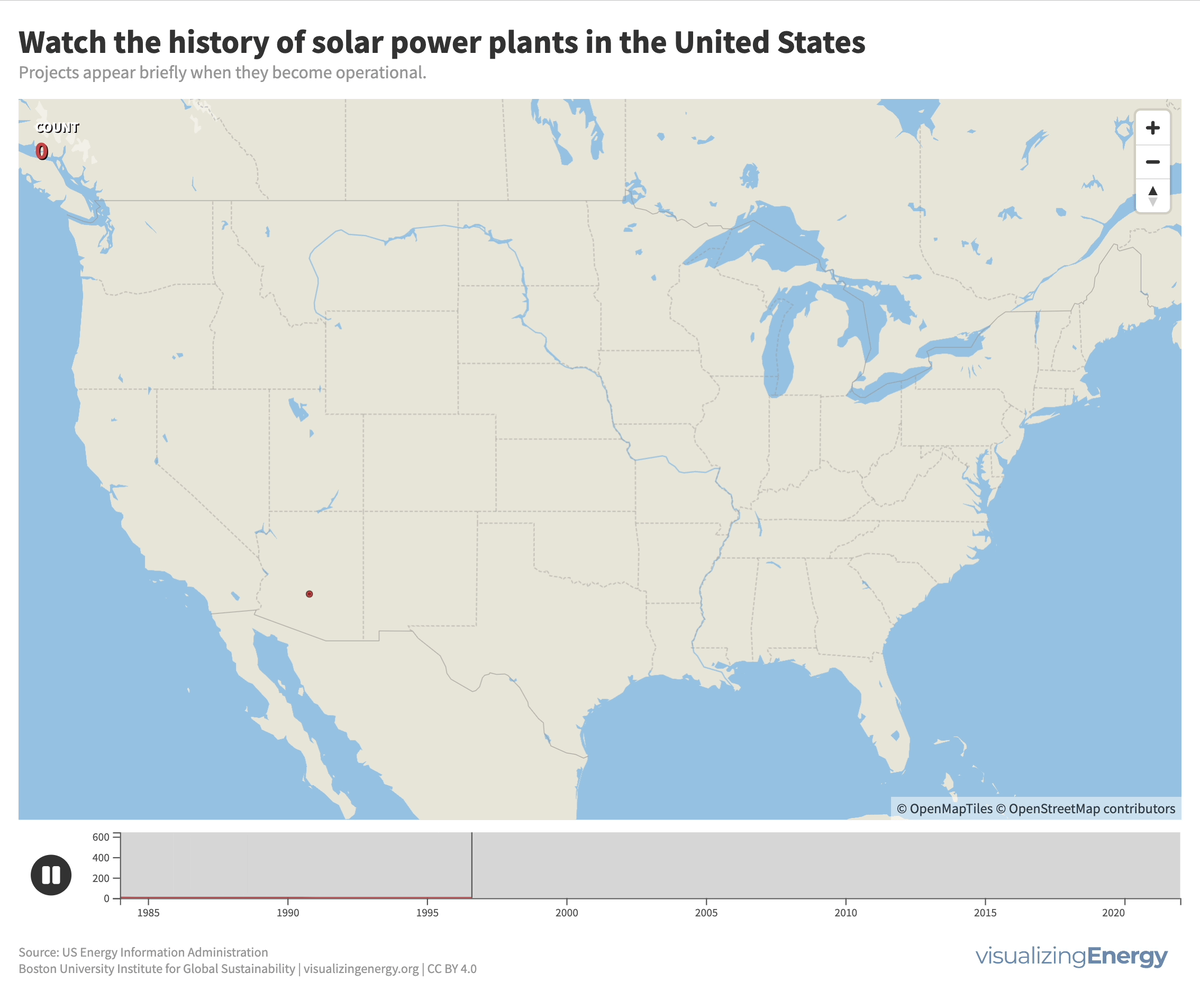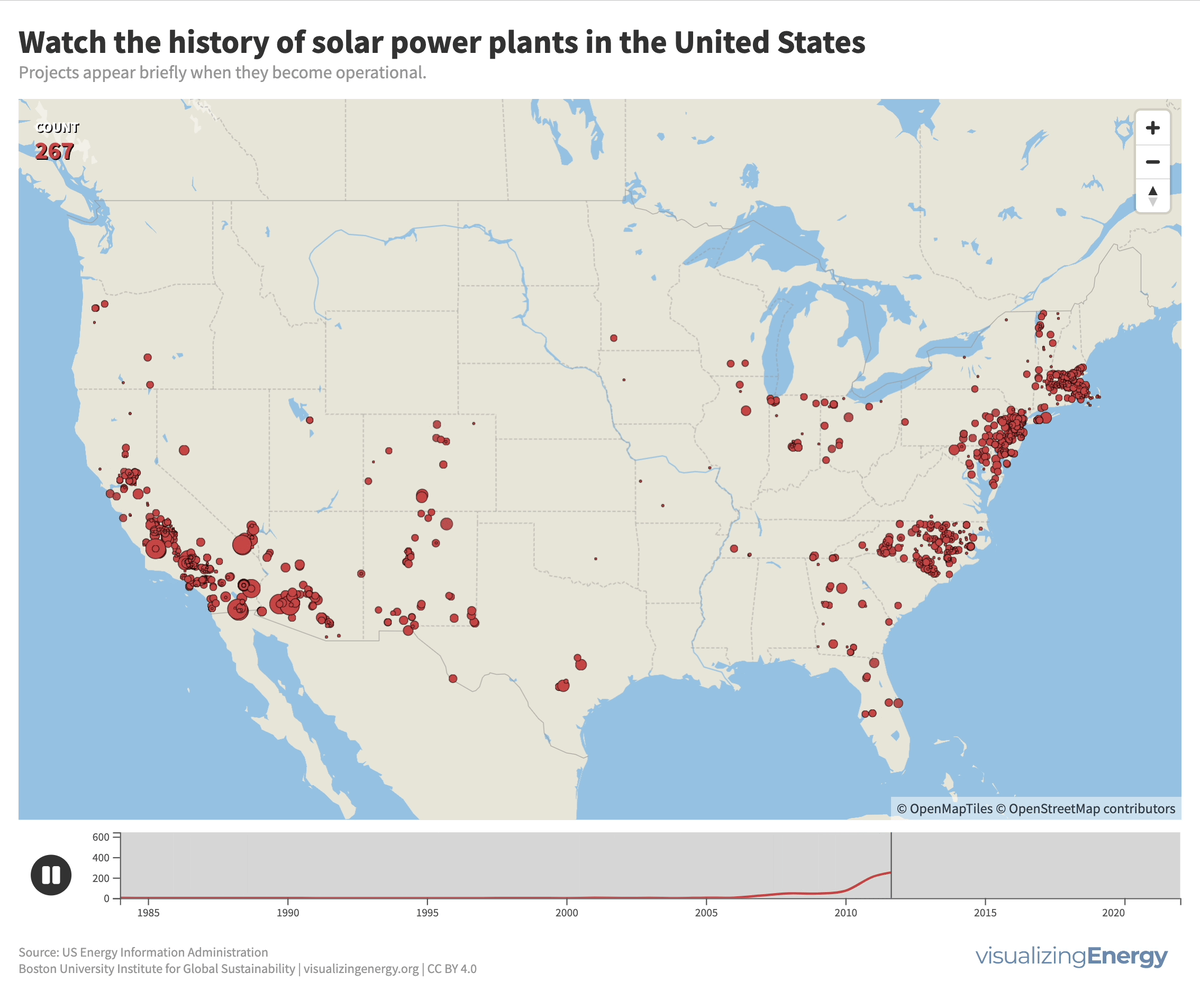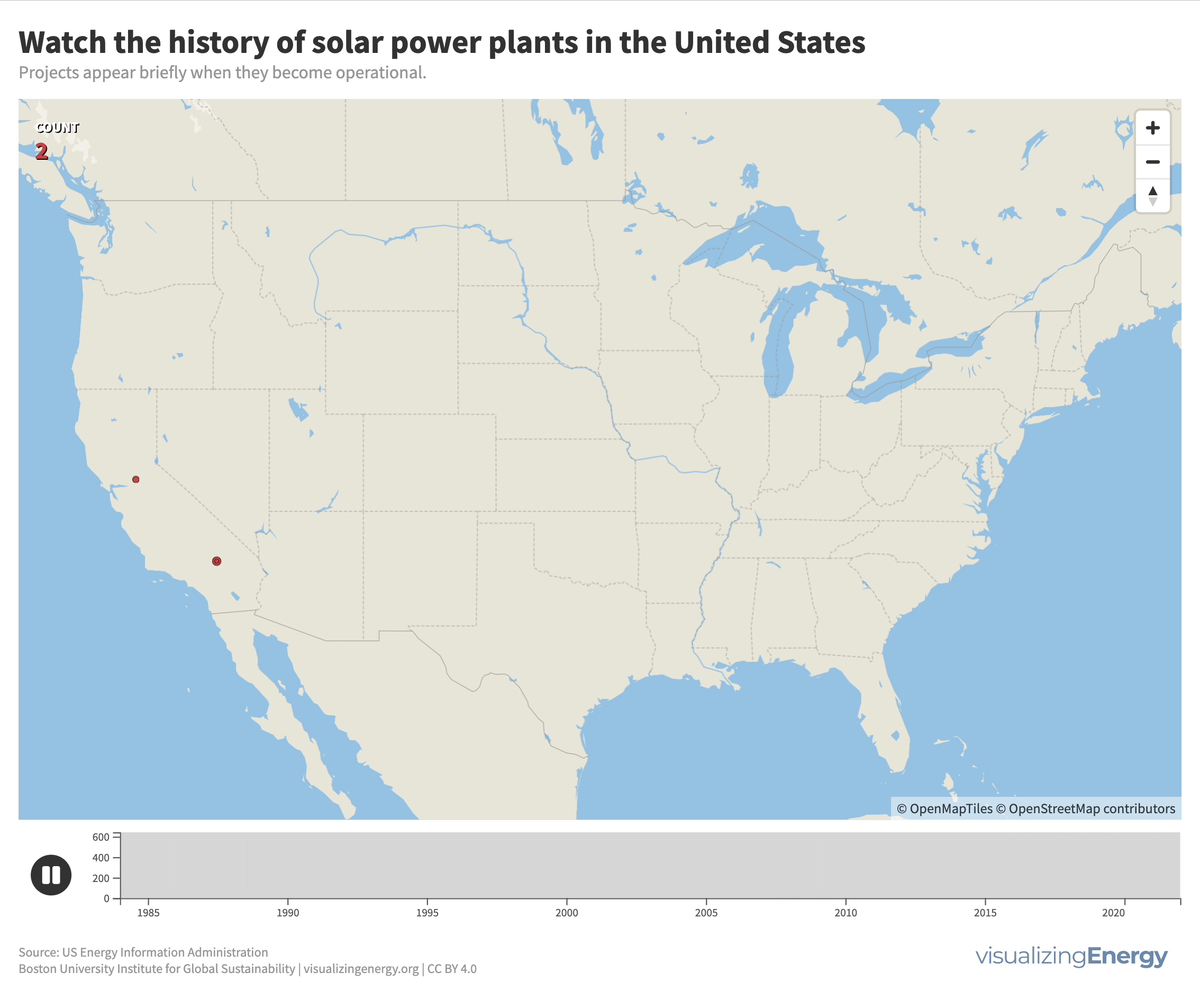
In 2022, the United States saw a significant rise in solar power generation, with 5730 utility-scale solar PV plants and 13 solar thermal plants producing 146 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity, equal to 3.4% of total utility-scale generation. This growth traces back to the 2000s, marked by falling solar system costs, enhanced efficiency, and government incentives like the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009.
Watch the history of oil power plants in the United States
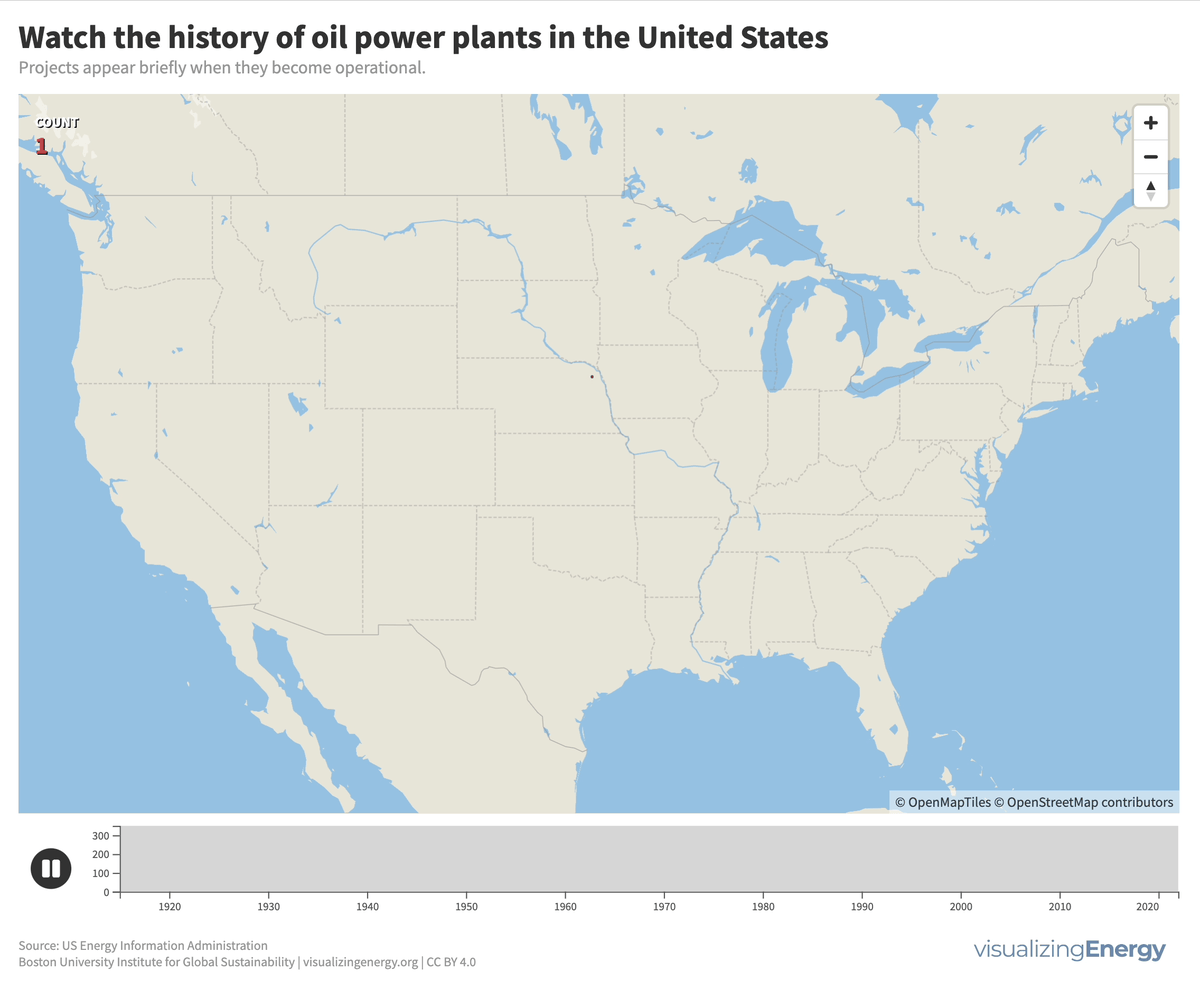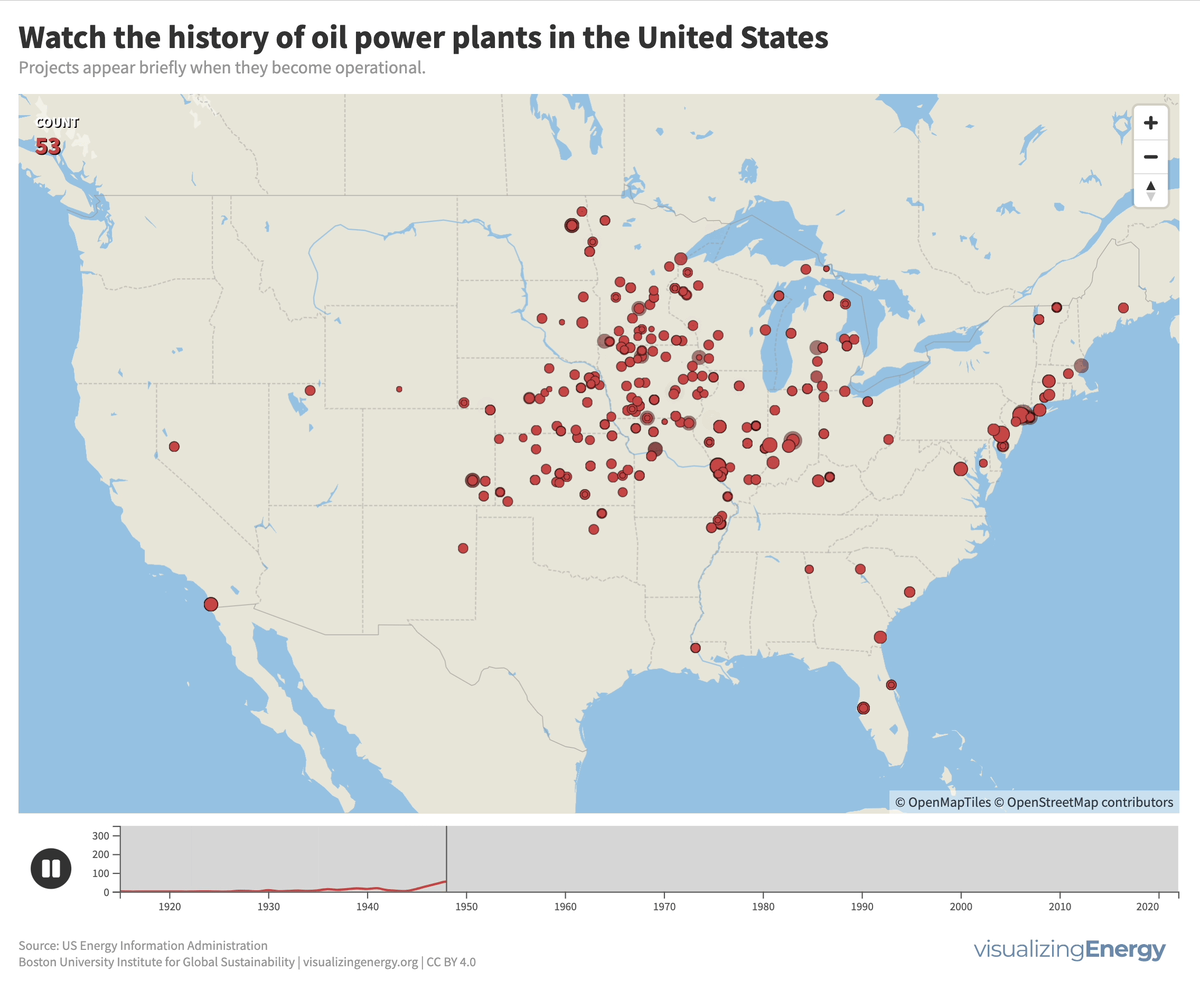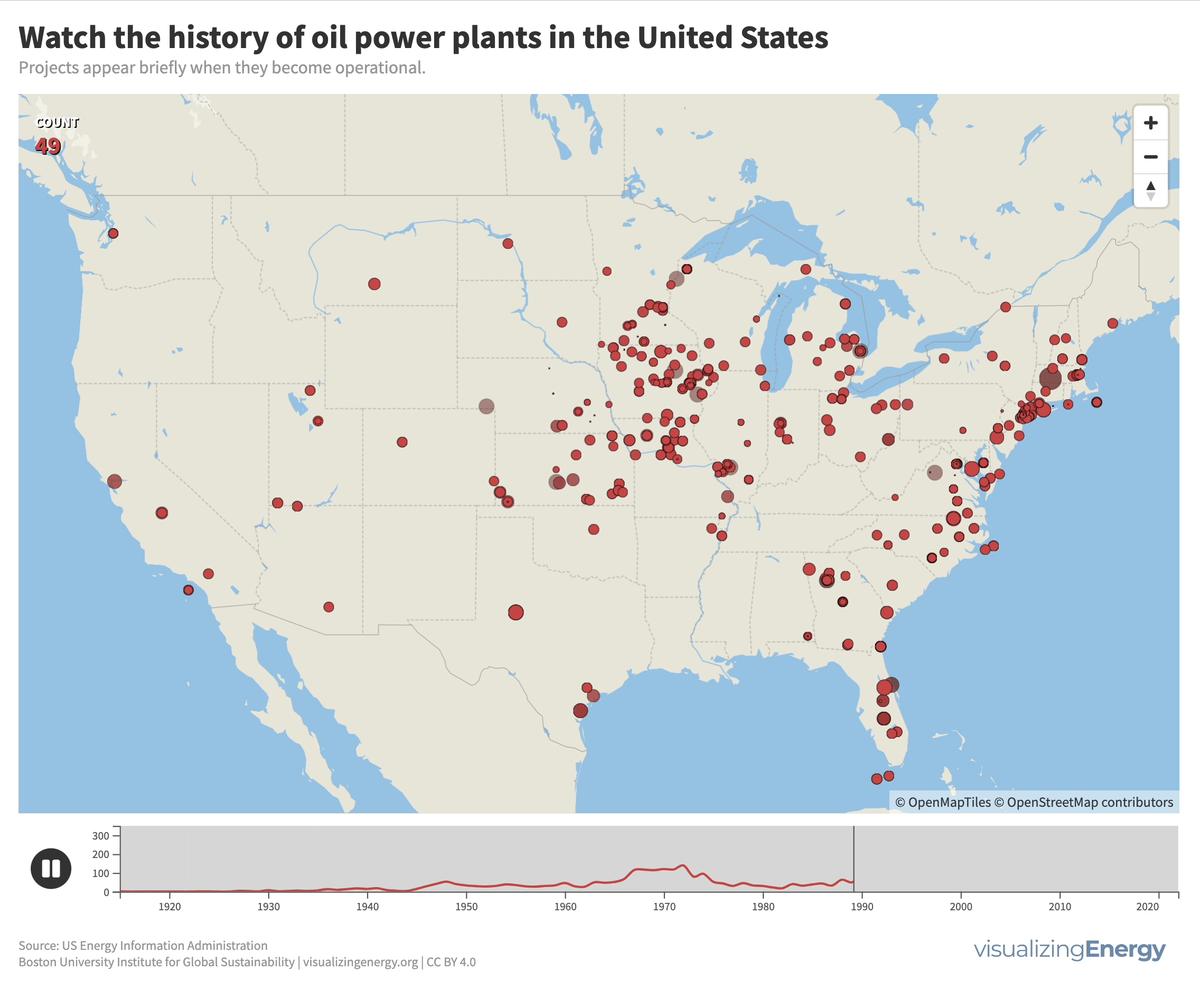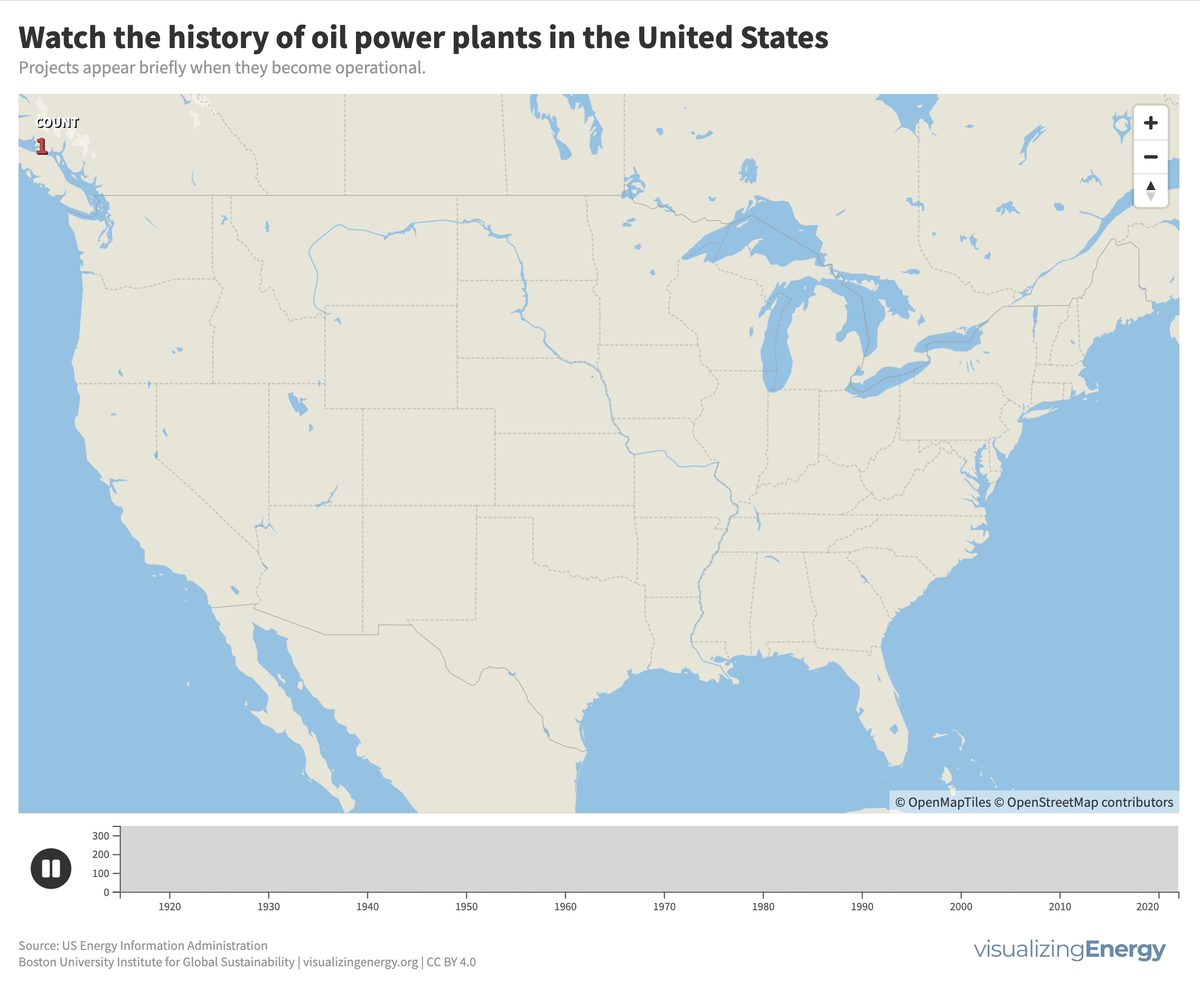
In 2022, the US had about 4,000 petroleum-burning generators, providing only 0.6% of the nation’s electricity due to lower efficiency and higher costs than alternatives. These smaller generators are mainly used for peak power and emergency backup, with policies since 1978 discouraging their use to reduce oil dependence for national security.
World electricity generation since 1900
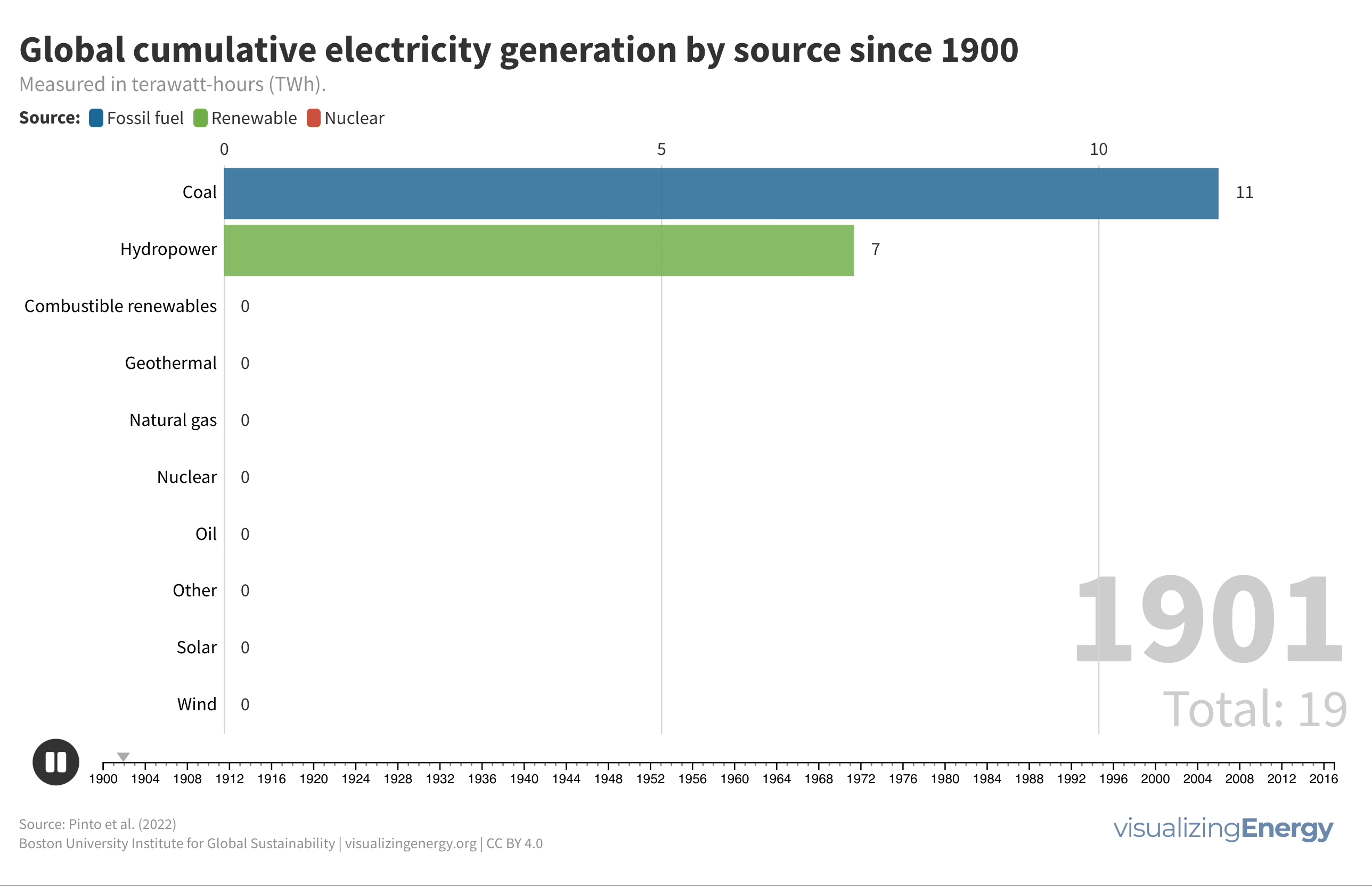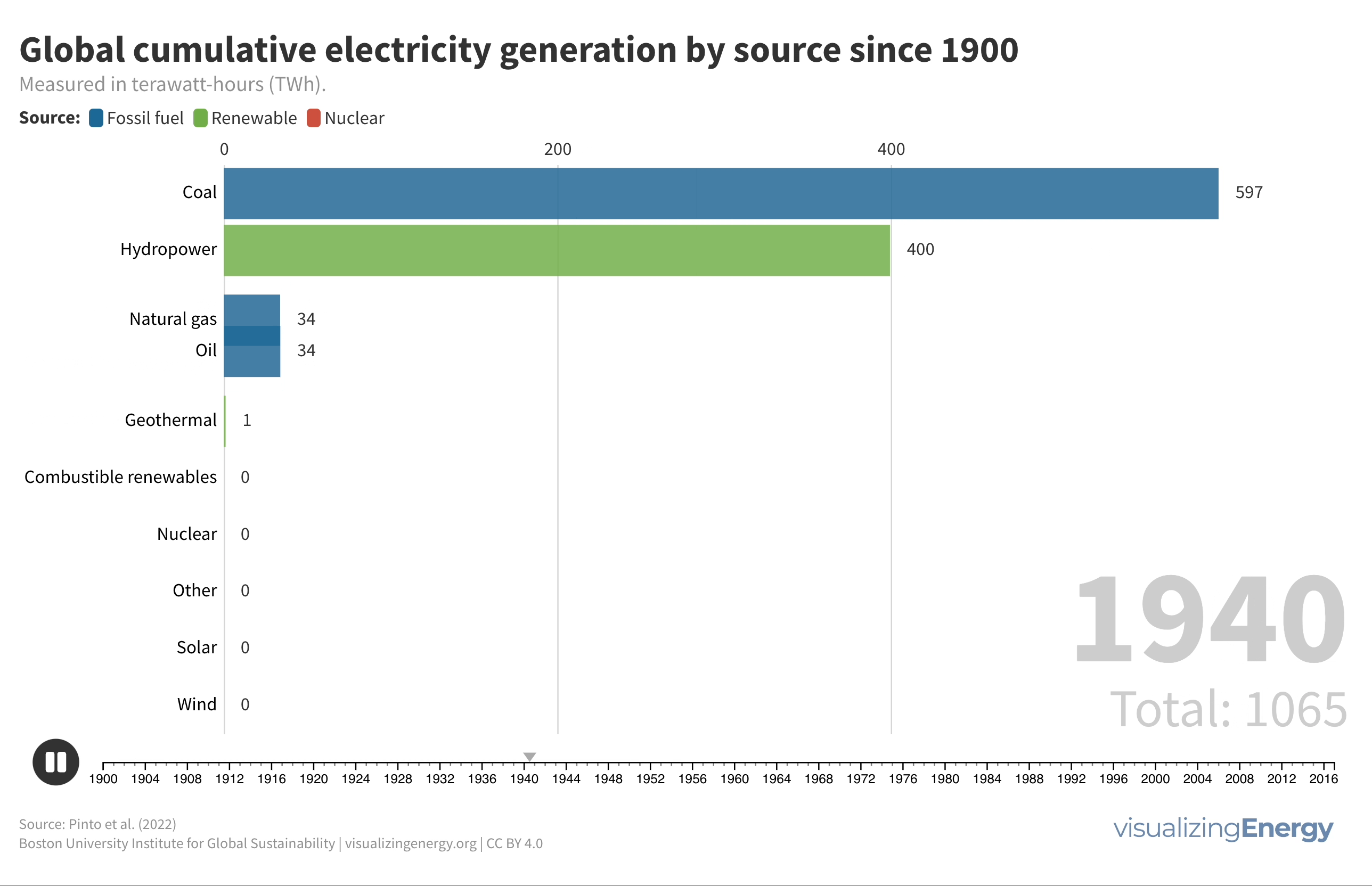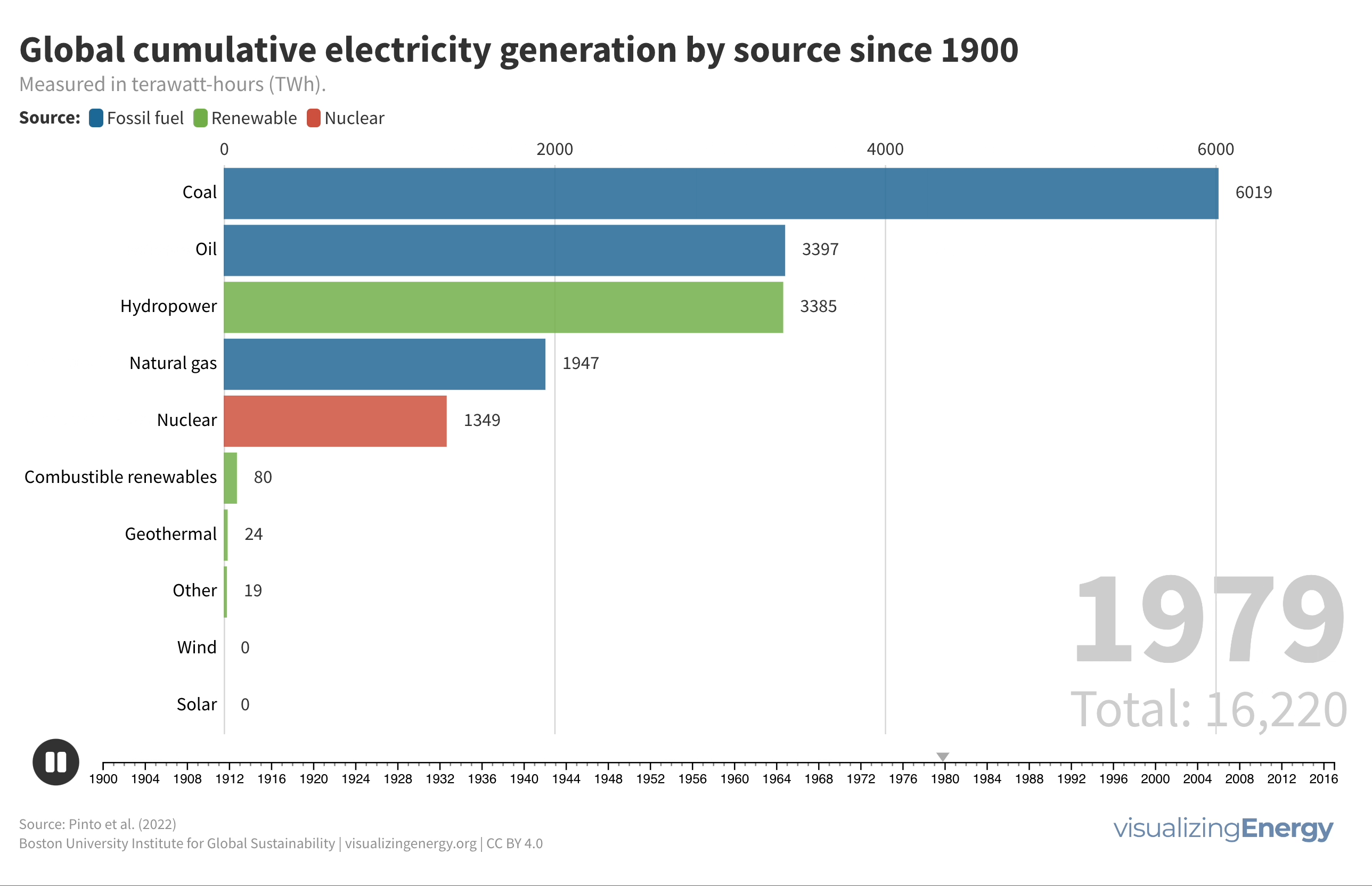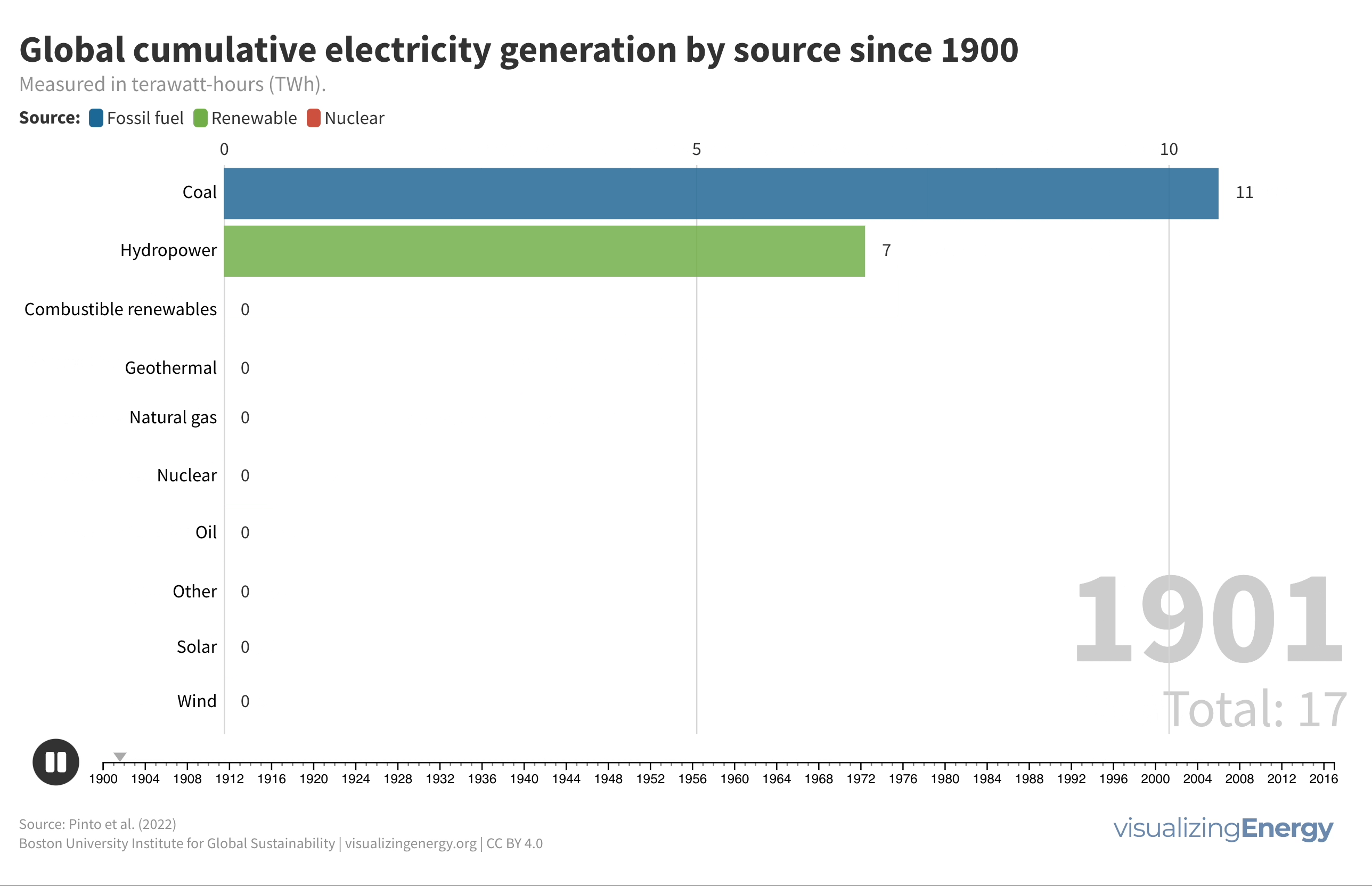
From 1900 to 2022, global electricity generation grew remarkably from 66.4 TWh to 29,165 TWh. Fossil fuels maintained a stable share of around 60% throughout this period, while renewables like wind and solar saw rapid growth from the 2000s. The 1960s saw a rise in oil power plants, but energy price shocks in the 1970s shifted focus to natural gas and nuclear generation, with significant investments in gas power plants from the 2000s onward.
Power plant efficiency since 1900
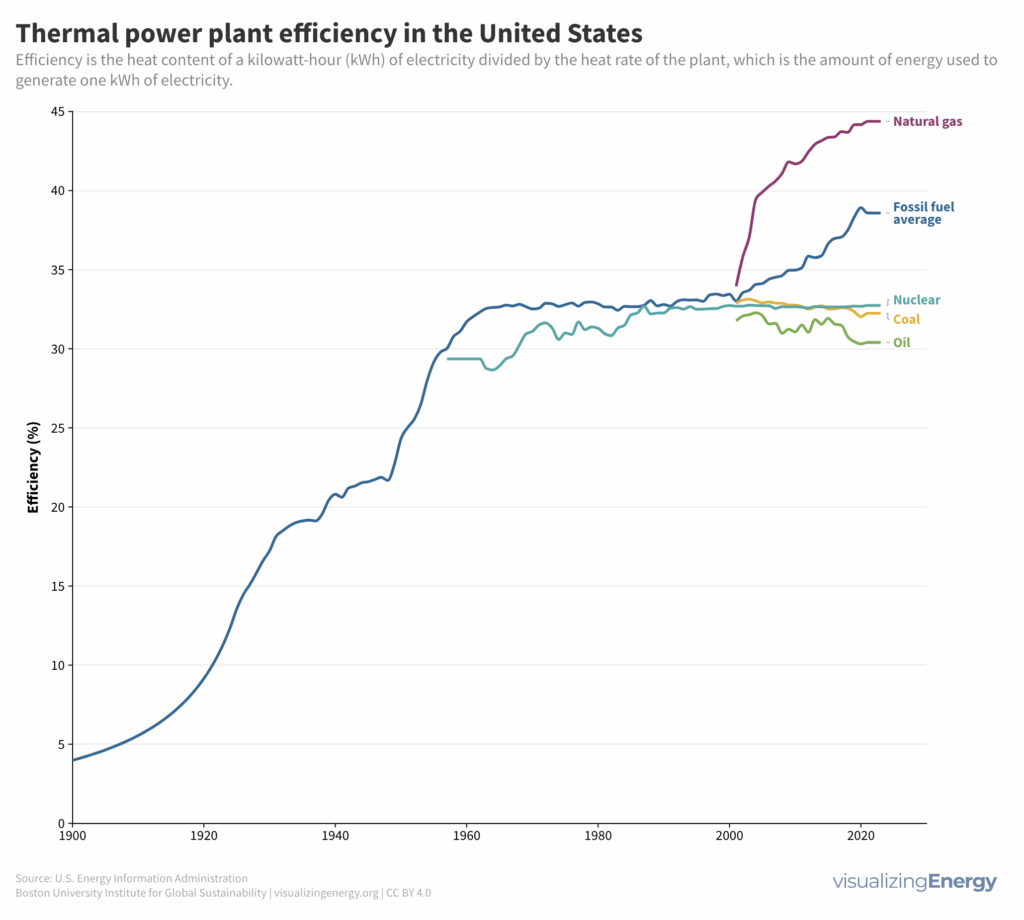
The efficiency of a thermal power plant is the ratio of the electricity output to the energy input, taking into account the heat losses. Over the years, the average efficiency of thermal power plants using fossil fuels in the United States has significantly increased, from 4% in 1900 to 43% in 2023. This improvement is attributed to reducing heat loss in the three main energy conversion processes: fuel combustion, steam generation, and electricity generation.
Explore world solar power capacity added in 2020
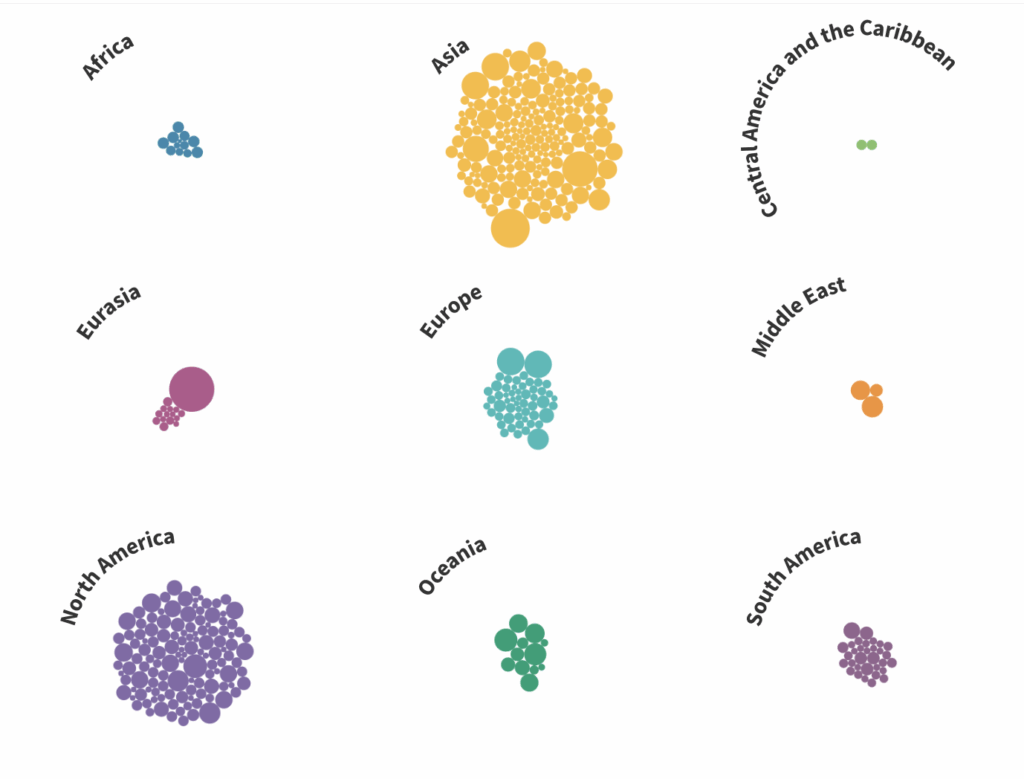

In 2020, 437 new solar electricity projects worldwide added a total capacity of 38,941 MW. The largest project was the 1348 MW Karapınar YEKA-1 solar farm in Turkey. Asia, North America, and Europe were the main contributors to solar capacity, with China leading with 23% of the global additions.
