Global black carbon emissions, 1750-2022
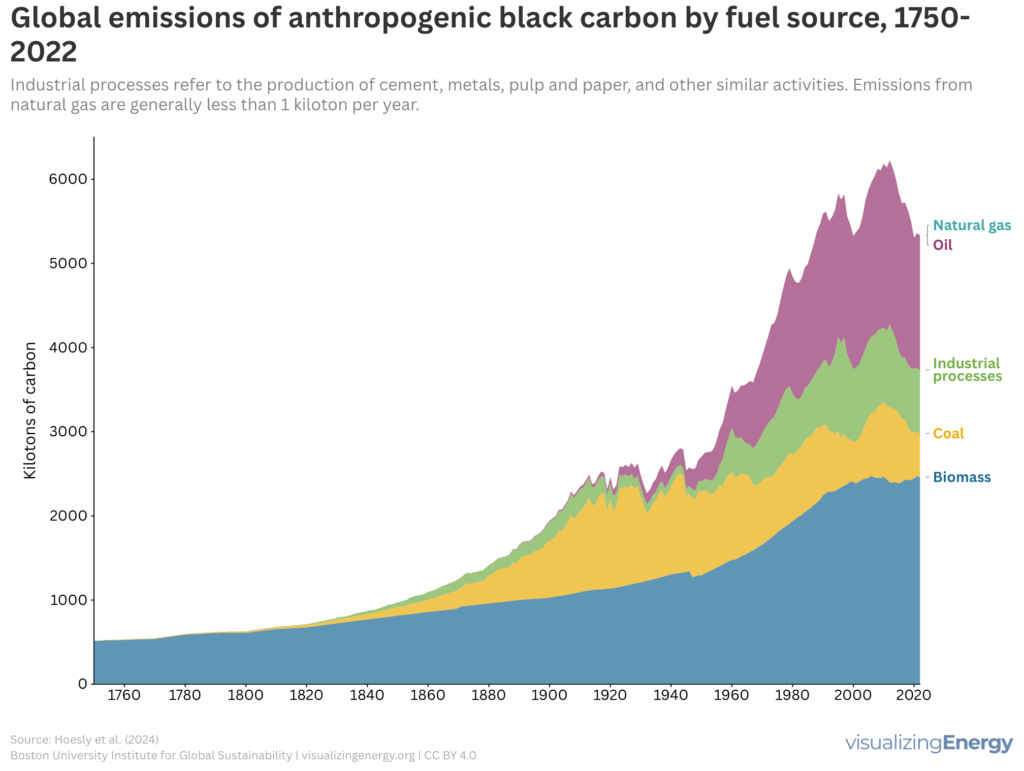
Anthropogenic black carbon, or soot, arises from incomplete combustion of organic materials, significantly impacting climate change and public health. It causes global warming, degrades air quality, and leads to various health issues. Major contributors include residential fuel usage and transportation emissions. Reducing black carbon relies on cleaner fuel access and improved combustion technologies.
Oil and chemical releases into United States waters
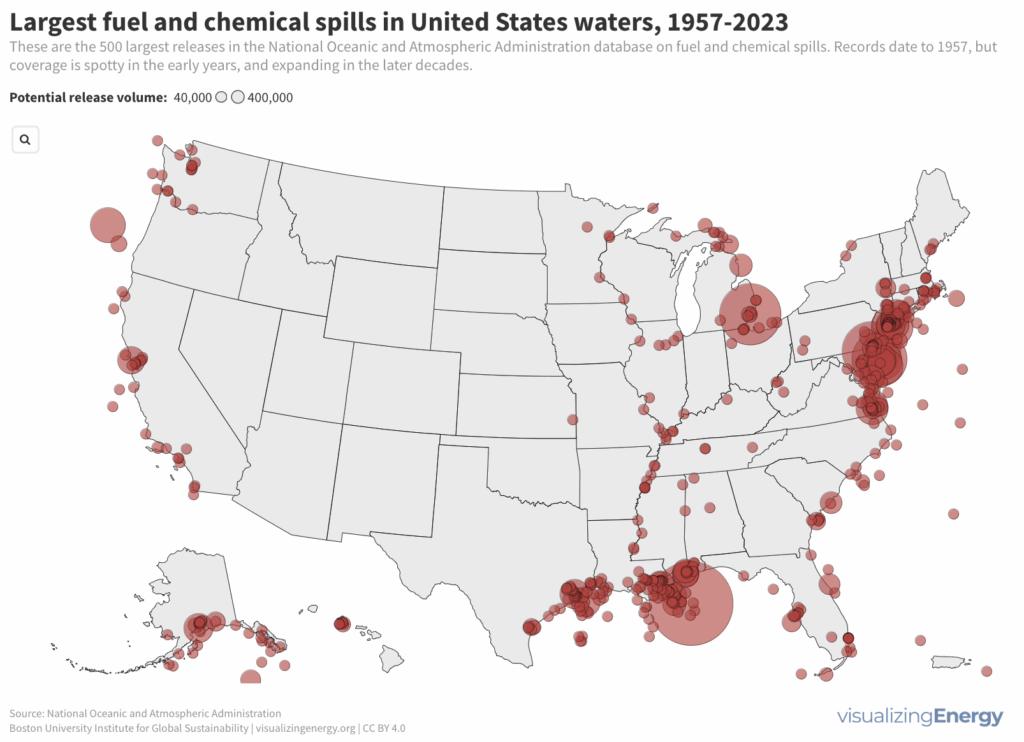
Crude oil and natural gas are refined into numerous fuel types and petrochemicals, contributing to over 6000 consumer products. However, extraction and processing lead to significant accidents, with approximately 4600 incidents reported since 1957, primarily affecting rivers and coastal areas due to industrial activities and transportation routes, highlighting environmental hazards.
What fuels have the lowest CO2 emissions?
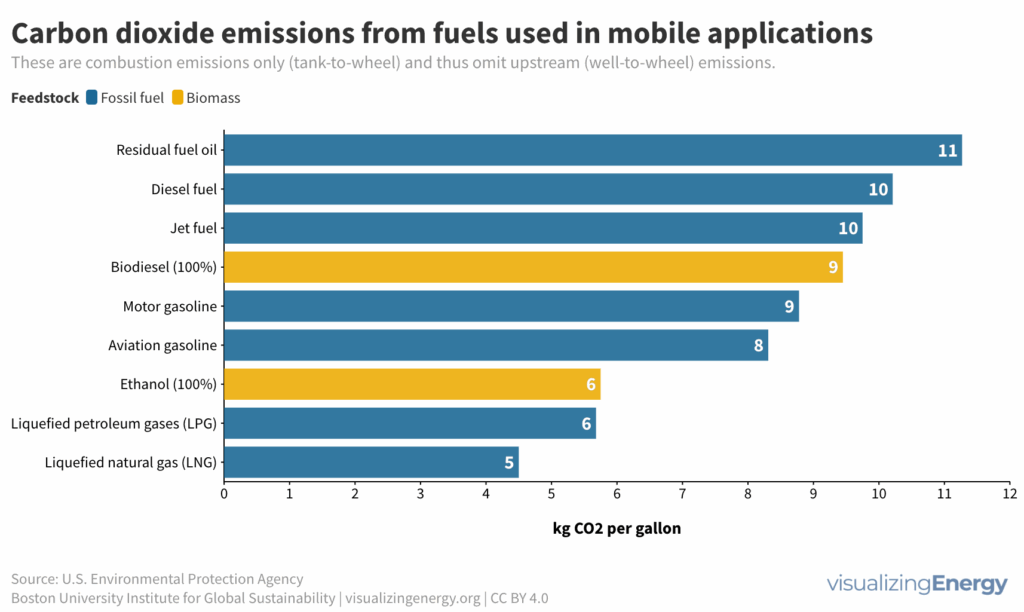
There are two main sources of greenhouse gas emissions: stationary (e.g., power plants, refineries) and mobile (e.g., cars, trucks). Transportation contributes 24% of energy-related CO2 emissions, with fossil fuels dominating. LNG in maritime transport shows potential for reduced CO2 emissions, but methane leakages must be addressed. Coal has the highest CO2 emissions factor among widely used fuels.
Where in the United States is the net carbon benefit of direct air capture the greatest?
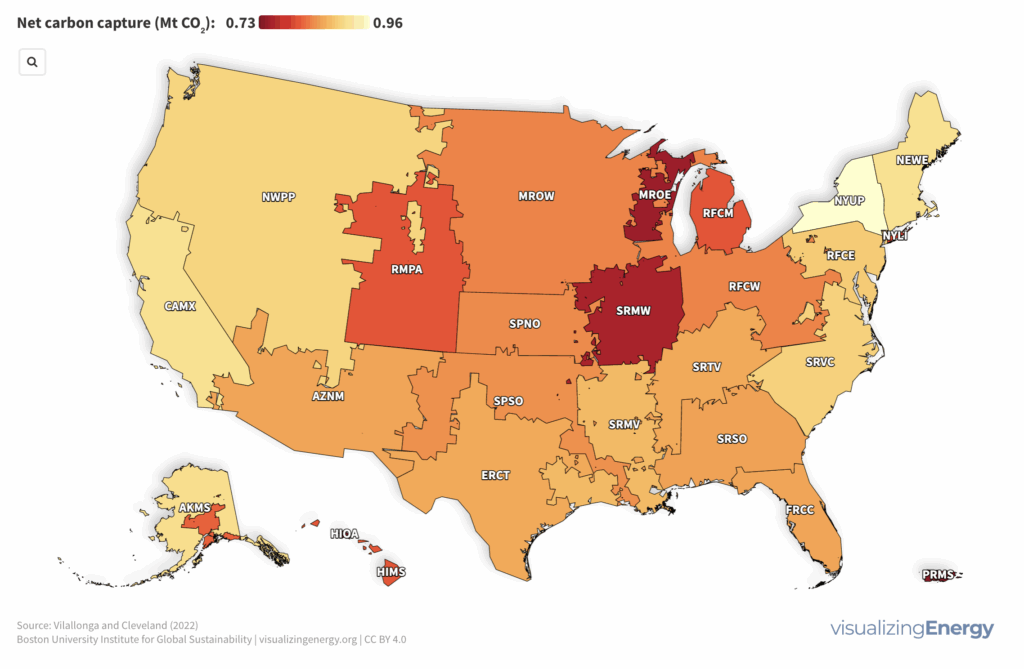
Direct Air Capture and Storage (DACCS) systems, which remove CO2 from the atmosphere, offer a significant carbon benefit depending on the energy mix of the regional grid. The greatest carbon benefit is achieved when DAC processes utilize zero-carbon sources like renewables and nuclear power. The ongoing decarbonization of the grid in most regions of the United States supports the effectiveness of DAC and electrification technologies.
Coal mine superemitters of methane
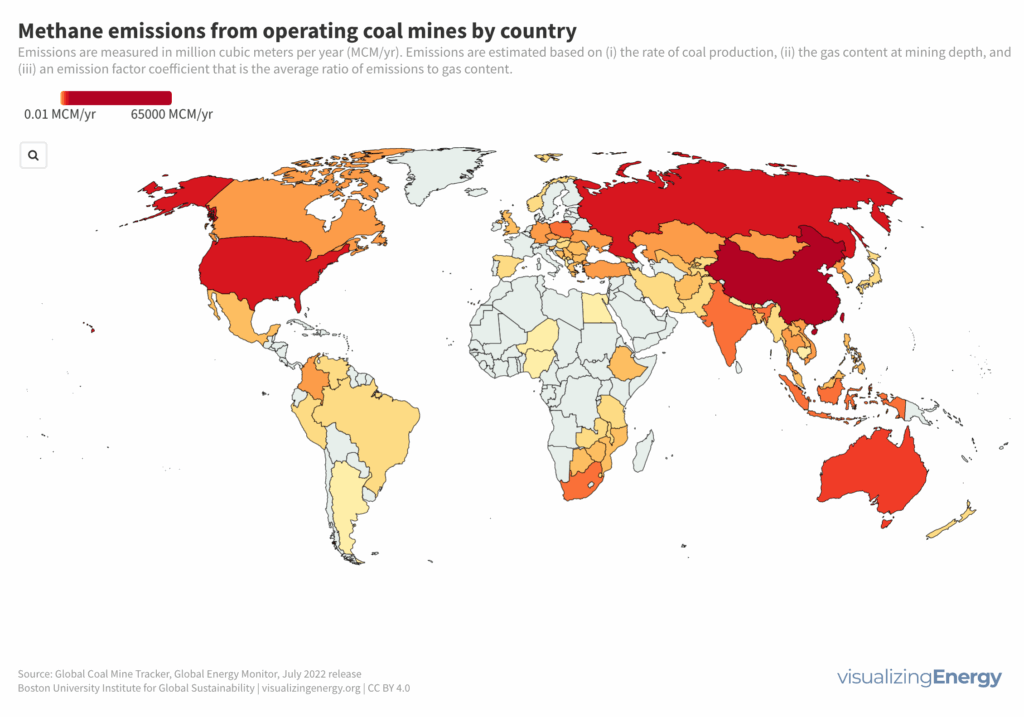
Methane emissions from coal mines are a significant concern for greenhouse gas reduction. Certain mines, known as “superemitters,” contribute a large proportion of global methane emissions. Factors like mine depth and coal rank affect methane content. While reducing coal use in electricity generation is important, mitigating methane emissions from mines needs greater attention.
Explore Boston’s Energy, Climate, and Equity Initiatives

Is Boston on track to be carbon-neutral by 2050?
Boston strives for carbon neutrality by 2050, but faces hurdles with its reliance on fossil fuels. Buildings contribute most to emissions, driven by electricity and natural gas. Decarbonizing the grid and eliminating natural gas are vital for success. While progress has been made, meeting targets remains uncertain. Priorities include electrifying buildings, local energy planning, coastal resilience, and climate justice.
